Great Tit Bird
- December 7, 2023
- 0 comment
The Great Tit, scientifically known as Parus major, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Paridae family within the order Passeriformes. This charming bird is widely recognized for its distinctive and colorful plumage, making it a popular subject for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
Physical Appearance
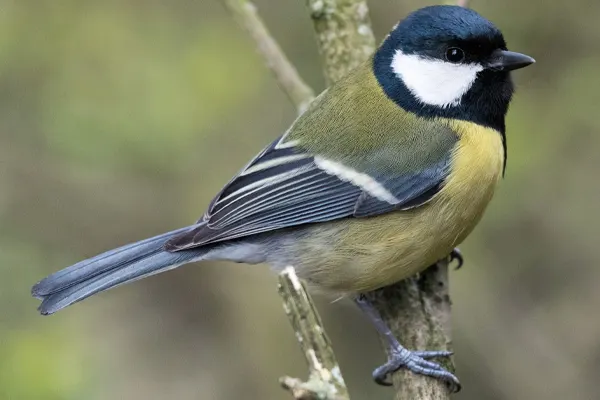

Great Tit
- Lifespan: 5-years
- Habitat: Coniferous forests
- Diet: Insects, Seeds, Fruits, and even small vertebrates.
- Size: 14 cm
- Weight: 16 g
- Wingspan: 20 to 25 cm
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Population Trend: Stable populations, localized declines due to habitat loss and climate change.
Measuring approximately 14 centimeters in length, the Great Tit boasts a compact yet robust build. Its plumage is characterized by a striking combination of yellow, black, white, and greenish hues, contributing to its vibrant appearance. The species displays sexual dimorphism, with males often exhibiting bolder and more intense colors than females.
Species Type
The Paridae family, the Great Tit is part of a diverse group of small to medium-sized birds commonly referred to as tits. These birds are known for their acrobatic movements, vibrant plumage, and distinctive calls. The Great Tit, with its colorful appearance and adaptable nature, is a prominent representative of this avian family.
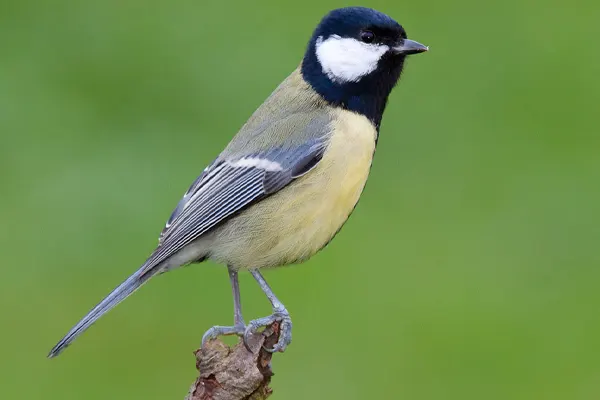

Feather Coloration
The feather coloration of the Great Tit (Parus major) is characterized by a striking and vibrant combination of hues, contributing to its distinctive and appealing appearance. The plumage of the Great Tit exhibits sexual dimorphism, meaning there are visual differences between males and females.
In general, both male and female Great Tits have a mix of yellow, black, white, and greenish tones in their plumage. The crown of the head is often black, creating a bold contrast with the white cheeks. A yellow breast and belly further enhance the bird’s colorful and eye-catching appearance. The wings and tail typically feature a blend of greenish and blueish hues.
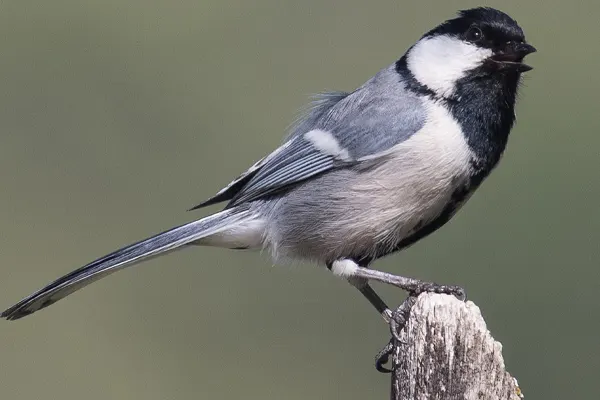
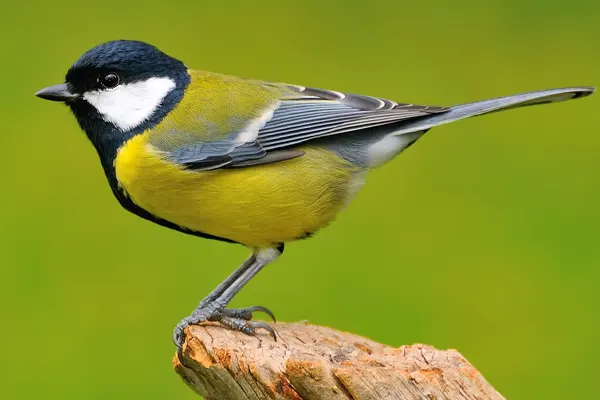


Males tend to have more intense and vivid colors compared to females. This enhanced coloration in males is often associated with attracting mates during the breeding season. The distinct color patterns not only contribute to the Great Tit’s aesthetic appeal but also play a role in species recognition and communication among individuals.
Flight Characteristics
The Great Tit is known for its exceptional agility in the air. With swift and coordinated wing movements, these birds navigate through dense vegetation and complex environments. Their ability to make quick turns and sudden maneuvers enables them to efficiently capture insects mid-flight.
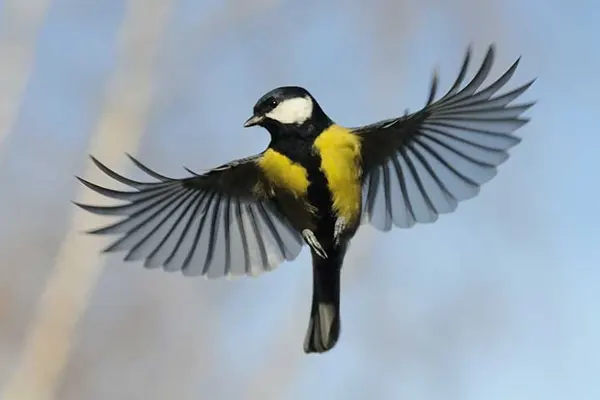

Despite their small size, Great Tits demonstrate strong and direct flight. Their wings, characterized by a pointed shape, provide the necessary lift and thrust for rapid and purposeful movement. This flight strength is crucial for covering expansive territories in search of food and suitable nesting sites.
Migration Patterns


The Great Tit (Parus major) is generally considered a non-migratory bird, meaning that it does not undertake long-distance seasonal migrations like some other bird species. Instead, Great Tits are known for their sedentary behavior, remaining in or near their breeding territories throughout the year.
However, within this general pattern of non-migration, there are some variations and localized movements observed in Great Tit populations. These movements are typically driven by factors such as food availability, environmental conditions, and territorial considerations.
Habitat & Distribution
Habitat of the Great Tit
- Woodlands and Forests: Great Tits are commonly found in deciduous and mixed woodlands, where they utilize trees for nesting sites. They demonstrate a preference for areas with mature trees, providing suitable nesting cavities and abundant insect prey.
- Urban and Suburban Areas: Notably adaptable, Great Tits have successfully adapted to urban and suburban environments. Gardens, parks, and residential areas with trees and shrubbery offer nesting sites and a variety of food sources, including insects, seeds, and scraps.
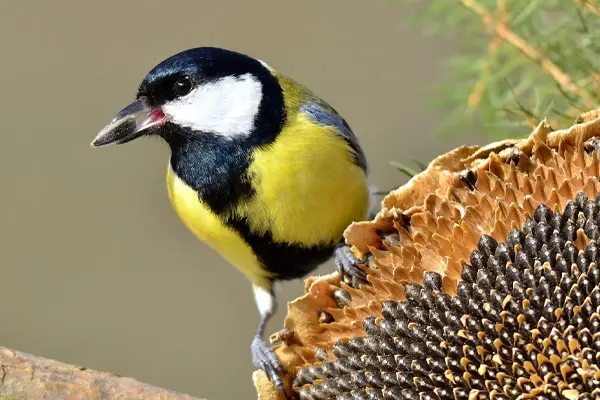
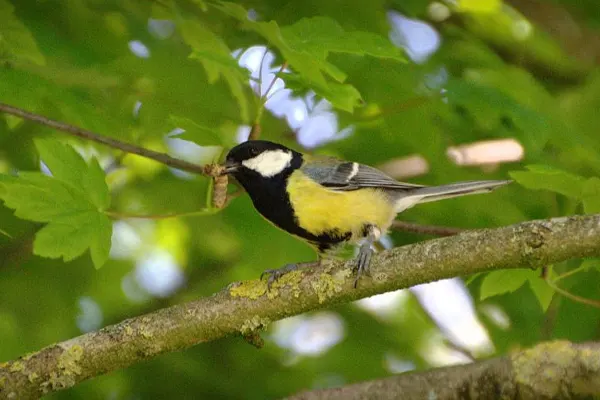


Distribution of the Great Tit
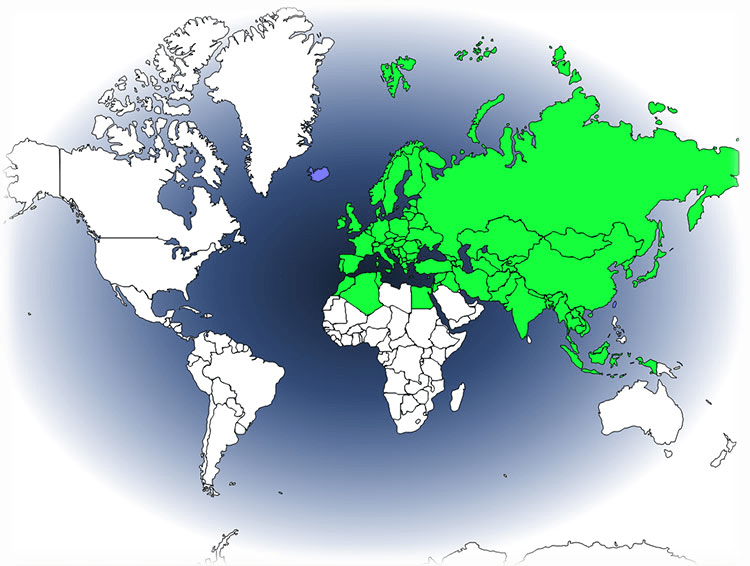
- Europe and Asia: The Great Tit has a vast distribution across Europe and Asia. Its range extends from the British Isles in the west to Japan in the east. The species is found across a variety of climatic zones, from temperate forests to subtropical regions.
- Northern Africa: In addition to its Eurasian distribution, the Great Tit is also present in northern parts of Africa. Countries in North Africa, such as Morocco and Algeria, host populations of these birds.
Behavioral Traits
The Great Tit (Parus major) is not only distinguished by its vibrant plumage and melodious songs but also by a fascinating array of behavioral traits. From complex social interactions to intricate breeding rituals, the behavioral characteristics of Great Tits contribute to their adaptability and success as a species. Let’s delve into the intriguing behavioral traits that define these charming birds
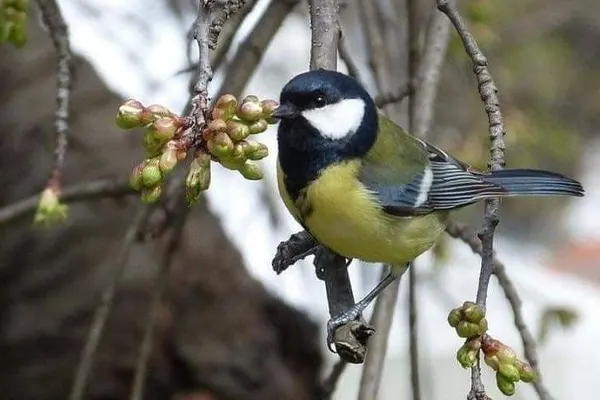

- Territorial Behavior: Great Tits are known for their territorial nature, especially during the breeding season. Males vigorously defend their chosen territories, engaging in vocalizations and physical displays to deter potential competitors.
- Social Structure: Great Tits exhibit social behaviors within their communities. They form loose flocks, particularly during the non-breeding season, foraging together for food resources. These flocks contribute to increased efficiency in finding food and navigating their environment.
- Interaction with Humans: Great Tits readily interact with humans in urban and suburban environments. They often visit bird feeders, becoming accustomed to human presence. This interaction provides opportunities for birdwatchers and researchers to observe their behaviors up close.
- Adaptation to Urban Environments: Great Tits demonstrate a remarkable ability to adapt to urban settings. They readily utilize nest boxes, explore gardens, and take advantage of supplementary food sources provided by humans, showcasing their adaptability to human-altered landscapes.
Role in Ecosystem
The Great Tit (Parus major) plays a vital and multifaceted role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As an omnivorous bird with diverse foraging habits and active involvement in the food web, the Great Tit contributes significantly to the ecological balance of its environment.
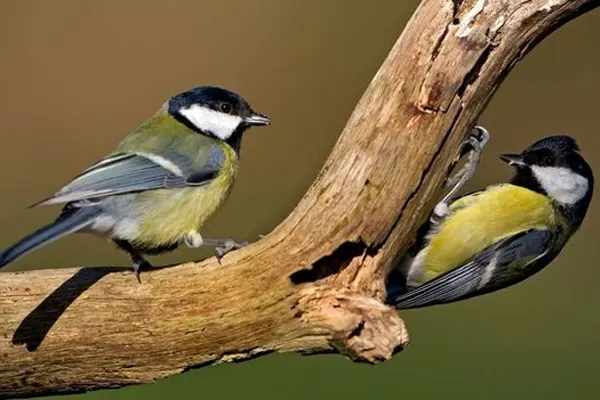

- Insect Control: Great Tits are voracious insectivores, with a diet that includes a wide variety of insects and their larvae. By actively foraging for caterpillars, beetles, and other insects, they help control insect populations, particularly those that can be detrimental to plants and crops.
- Seed Dispersal: As part of their omnivorous diet, Great Tits consume seeds and fruits. In the process, they unintentionally contribute to seed dispersal. The seeds ingested by Great Tits can be deposited in different locations through droppings, aiding in plant regeneration and diversity.
- Balancing Herbivorous Insect Populations: By preying on herbivorous insects, such as caterpillars, Great Tits indirectly contribute to maintaining a balance in plant-eating insect populations. This helps prevent overgrazing on vegetation and supports overall plant health.
- Pollination Assistance: While not primary pollinators, Great Tits may contribute to pollination processes. Their visits to flowers for nectar or insects may inadvertently transfer pollen, assisting in the reproduction of certain plant species.
- Ecosystem Indicator: Changes in the abundance or behavior of Great Tit populations can serve as indicators of broader ecological shifts. Monitoring their populations can provide insights into the overall health of ecosystems and potential environmental changes.
Dietary Habits
The dietary habits of the Great Tit (Parus major) are diverse and adaptable, reflecting its status as an omnivorous bird. This species displays a wide range of feeding behaviors and consumes various food items depending on seasonal availability and environmental conditions.
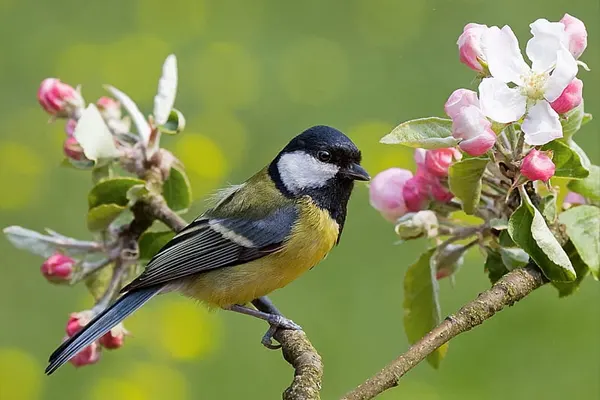
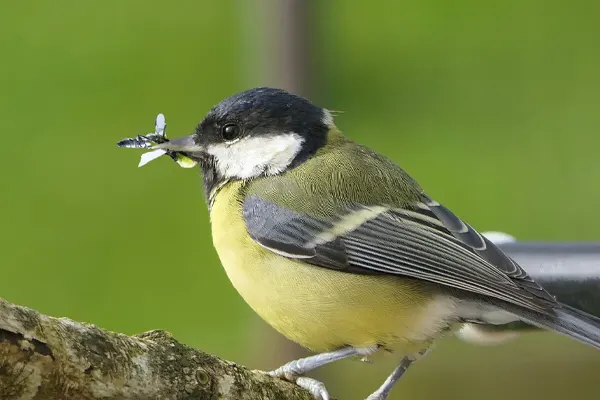


Nectar and Sap Feeding: While not specialized nectar feeders, Great Tits may occasionally feed on flower nectar and tree sap. This behavior is observed more opportunistically and may contribute to their overall dietary diversity.
Insectivorous Diet: Great Tits are primarily insectivores, with insects forming a significant part of their diet. They actively forage for a variety of insects, including caterpillars, beetles, spiders, and ants. This insect-rich diet is especially crucial during the breeding season when growing nestlings require a high protein intake.
Interesting Facts
Great Tits are accomplished singers with a repertoire of melodious songs. Their vocalizations include a variety of calls and trills, often used for communication, attracting mates, and establishing territory.
Unlike some bird species, Great Tits readily adapt to urban and suburban environments. They are commonly found in gardens, parks, and even visit bird feeders, showcasing their ability to coexist with human-altered landscapes.
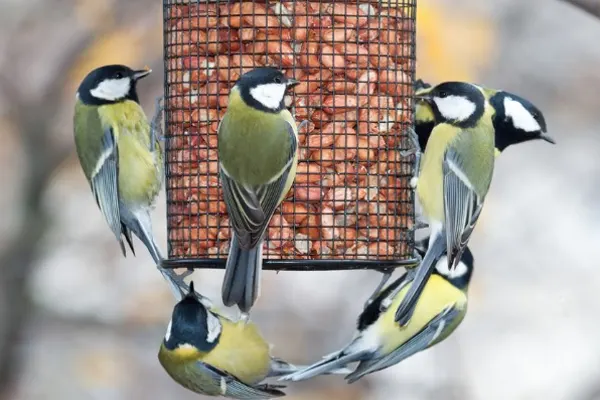

- Clever Problem-Solvers: Research has revealed the cognitive abilities of Great Tits, including problem-solving skills. They have been observed learning to access food in novel feeders and adapting their behavior to changing conditions.
- Social Foraging: Great Tits engage in social foraging during the non-breeding season. Forming loose flocks, they work together to locate food sources more efficiently, demonstrating a cooperative aspect of their behavior.
- Winter Survival Techniques: To survive harsh winter conditions, Great Tits employ tactics such as fluffing up their feathers to create insulating layers, seeking shelter in tree cavities, and utilizing supplementary food sources provided by humans.
Nesting Habits
The nesting habits of the Great Tit (Parus major) are intricate and well-adapted to its varied environments. These small birds exhibit careful planning and construction when it comes to creating a secure and comfortable nesting space for their offspring.
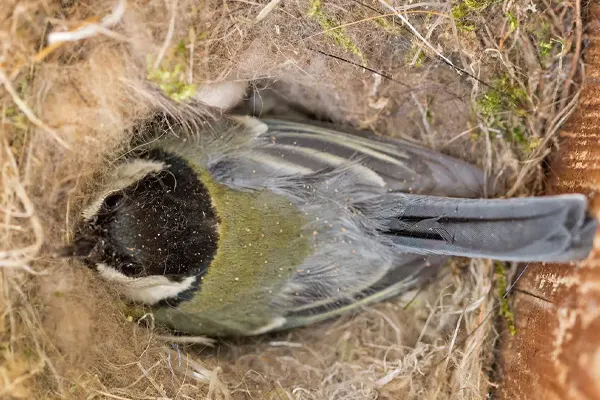
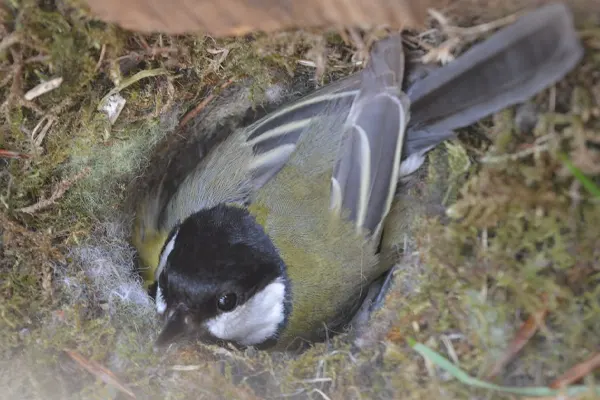


Great Tits are cavity-nesting birds, meaning they prefer nesting in enclosed spaces. Natural sites include tree hollows, crevices in rocks, and old woodpecker holes. However, they readily adapt to using artificial nesting sites, such as nest boxes provided by humans.
Nest building is primarily the responsibility of the female Great Tit. The construction process involves collecting a variety of materials, including moss, leaves, feathers, fur, and even fine twigs. These materials are meticulously arranged to create a cup-shaped nest.
Melodious Song & Vocalizations
The Great Tit (Parus major) is renowned for its melodious songs and a diverse range of vocalizations that play a crucial role in communication, mate attraction, and territorial defense. These vocalizations exhibit complexity and variation, allowing Great Tits to convey different messages to their conspecifics.
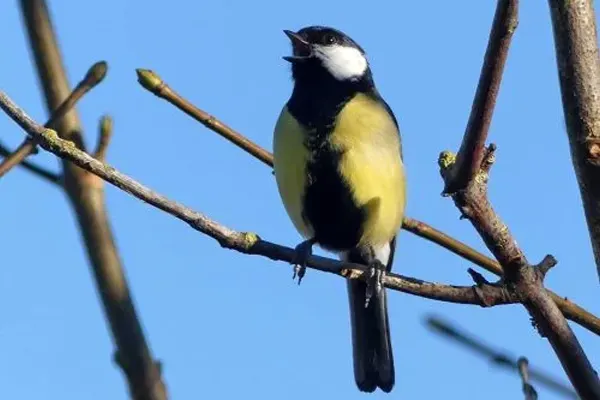

- Rich Repertoire: Great Tits have a rich repertoire of songs, with males typically producing more varied and complex vocalizations than females. The songs are characterized by clear and melodious notes.
- Territorial Songs: Male Great Tits use songs to establish and defend their territories during the breeding season. These songs serve as audible markers, indicating the boundaries of their territory and deterring rival males.
- Communication with Mates: Great Tits use contact calls to communicate with their mates, especially during the breeding season. These calls help maintain proximity between mates and coordinate activities such as nest-building and feeding.
Ecological Significance
The Great Tit (Parus major) holds significant ecological importance in various ecosystems, playing a multifaceted role that extends beyond its charming appearance and melodious songs. As an omnivorous bird with adaptable behaviors, the Great Tit contributes to the ecological balance in several ways

- Balancing Herbivorous Insect Populations: By preying on herbivorous insects like caterpillars, Great Tits indirectly contribute to balancing plant-eating insect populations. This helps prevent overgrazing on vegetation and supports overall plant health.
- Pollination Assistance: While not specialized pollinators, Great Tits may assist in pollination processes. Their visits to flowers for nectar or insects may result in inadvertent pollen transfer, contributing to the reproduction of certain plant species.
- Nutrient Cycling: Through their feeding habits, Great Tits contribute to nutrient cycling. The consumption of insects and other invertebrates enriches the soil and surrounding vegetation, playing a role in nutrient turnover within ecosystems.
Conservation Status
Conserving natural habitats, including woodlands and forests, is crucial for the Great Tit. Preservation of diverse ecosystems ensures the availability of suitable nesting sites and natural food sources.
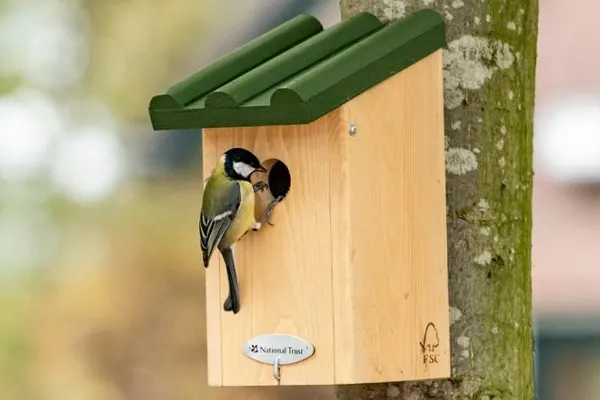


The use of nest boxes, along with natural nesting sites, has contributed to successful breeding for Great Tits. This adaptability in choosing nesting locations supports their reproductive success.
Research and Ongoing Studies
Research on the Great Tit (Parus major) is extensive and covers various aspects of its behavior, ecology, and adaptation to changing environments. Ongoing studies contribute valuable insights into avian biology, population dynamics, and the impact of environmental factors on bird species.
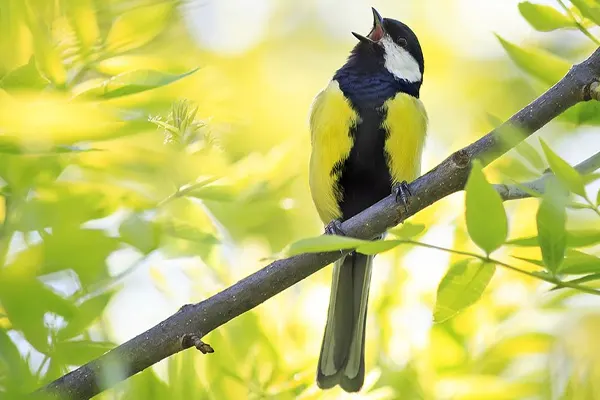

- Behavioral Ecology: Ongoing research explores the behavioral ecology of Great Tits, including aspects such as foraging behavior, social interactions, mate selection, and territoriality. Studies may investigate how these behaviors contribute to their reproductive success and overall fitness.
- Impact on Ecosystems: Research explores the ecological role of Great Tits in different ecosystems. This includes their impact on insect populations, seed dispersal, and interactions with other bird species. Understanding their ecological functions contributes to broader conservation strategies.
Educational and Ecotourism Opportunities of Great Tit
The Great Tit (Parus major) offers unique educational and ecotourism opportunities, drawing enthusiasts, birdwatchers, and nature lovers. These opportunities provide a chance to learn about avian ecology, biodiversity, and the importance of conservation.
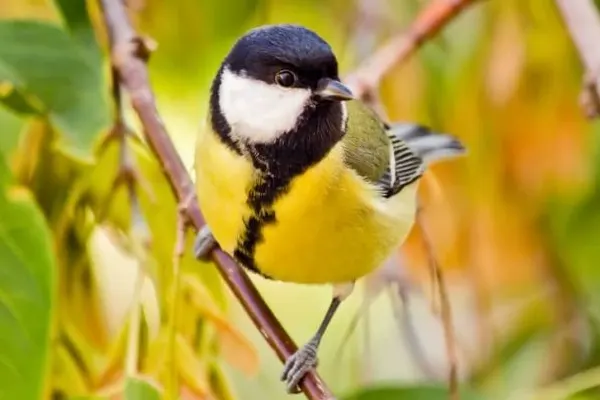

- Educational Nature Walks: Guided nature walks with knowledgeable naturalists offer participants the chance to observe Great Tits in their natural habitat. Interpretive discussions can cover topics such as foraging behavior, vocalizations, and nesting habits.
- Educational Displays and Exhibits: Nature centers and wildlife reserves can feature educational displays and exhibits showcasing the life cycle, behavior, and ecological significance of Great Tits. Interactive exhibits enhance the learning experience for visitors of all ages.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries and Reserves: Establishing or promoting wildlife sanctuaries and reserves that support Great Tit populations provides ecotourism opportunities. Visitors can enjoy observing these birds in their natural habitats while supporting conservation efforts.
- Photography Expeditions: Photography expeditions centered around the Great Tit attract photographers interested in capturing the beauty of these birds. Professional guides can lead groups to prime locations for photography.
Conclusion
The Great Tit’s vocalizations, from territorial songs to chick-feeding calls, serve as a vibrant language that communicates within the avian community. As an indicator of environmental health, its presence in diverse habitats reflects the overall well-being of ecosystems.
The Great Tit (Parus major) stands as a remarkable and adaptable species, weaving its significance into the intricate fabric of ecosystems across Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa. From its melodious songs to its diverse behaviors and ecological roles, the Great Tit has captured the fascination of birdwatchers, researchers, and nature enthusiasts alike.
As a generalist species, the Great Tit navigates various environments, showcasing its resilience and ability to adapt to changing landscapes, including urban areas. Its nesting habits, marked by meticulous construction and strategic site selection, reflect a commitment to ensuring the survival of future generations.














Leave your comment