Kitti’s Hog-Nosed Bat
- March 22, 2024
- 0 comment
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, also known as the bumblebee bat, is a remarkable mammal renowned for its diminutive size and distinctive appearance. Holding the title of the world’s smallest bat and one of the tiniest mammals, this fascinating creature inhabits limestone caves in select regions of Thailand and Myanmar. Its small size, with a wingspan of just a few inches and a weight of mere grams, belies its remarkable adaptations. Notably, it possesses a hog-like snout that aids in echolocation and prey detection in its dark cave habitats.
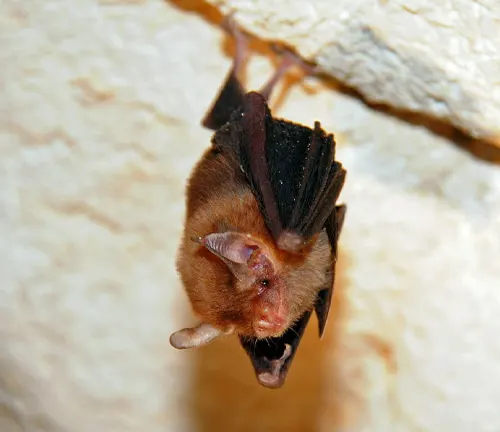

Despite its minute stature, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling insect populations. However, it faces significant threats to its survival, primarily due to habitat loss, disturbance in cave ecosystems, and human encroachment. Conservation efforts are crucial for safeguarding this unique species and ensuring its continued existence in the wild.
Kitti’s Hog-nosed bat Characteristics
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Craseonycteris thonglongyai |
| Common Name | Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, Bumblebee Bat |
| Family | Craseonycteridae |
| Order | Chiroptera |
| Wingspan | Few inches |
| Weight | Few grams |
| Snout | Hog-like, aids in echolocation |
| Fur Color | Brown to gray |
| Habitat | Limestone caves in Thailand and Myanmar |
| Diet | Primarily feeds on small insects such as mosquitoes, beetles, and moths |
| Behavior | Forms tight clusters in dark cave roosts to conserve body heat |
| Reproduction | Low fecundity, typically gives birth to a single offspring each year |
| Conservation Status | Endangered |
| Threats | Habitat loss, disturbance in cave ecosystems, human encroachment |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat restoration, community-based conservation programs, enforcement of wildlife protection laws |
| Importance in Ecosystem | Controls insect populations, contributes to ecosystem health |
Unveiling the Mysteries of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat
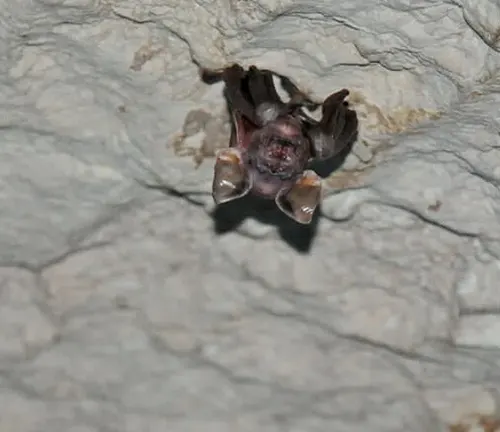

Kitti’s hog-nosed bat, scientifically known as Craseonycteris thonglongyai, is an enigmatic mammal that holds the record for being the world’s smallest bat and one of the smallest mammals. Also referred to as the bumblebee bat due to its diminutive size, this unique creature possesses several intriguing characteristics that set it apart from other bat species.
Taxonomy and Classification
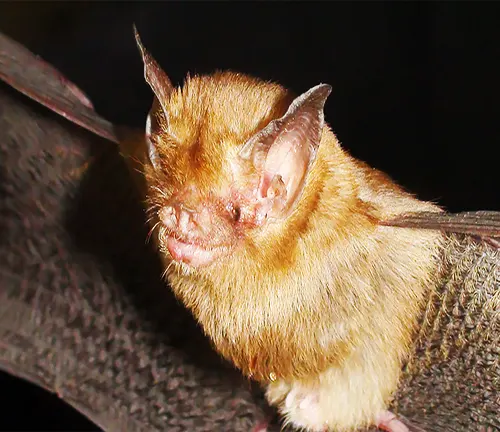
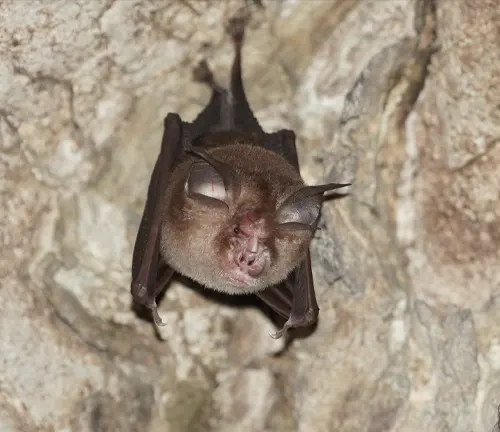


Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, scientifically known as Craseonycteris thonglongyai, belongs to the family Craseonycteridae and the order Chiroptera. Within the animal kingdom, it represents a unique lineage of microbats distinguished by its small size and specialized features. The species name “thonglongyai” honors the Thai zoologist who first discovered and described this diminutive bat species. Despite its tiny stature, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat stands as a testament to the vast diversity and evolutionary adaptations present within the bat family.
Physical Characteristics
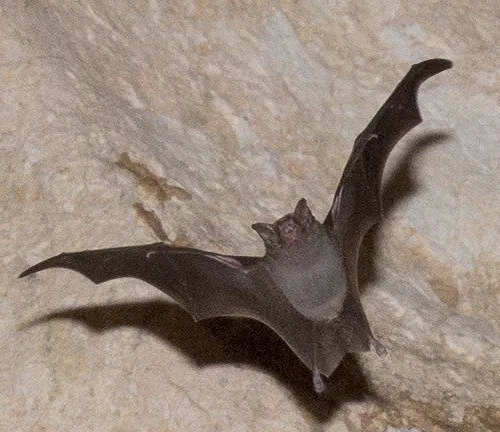
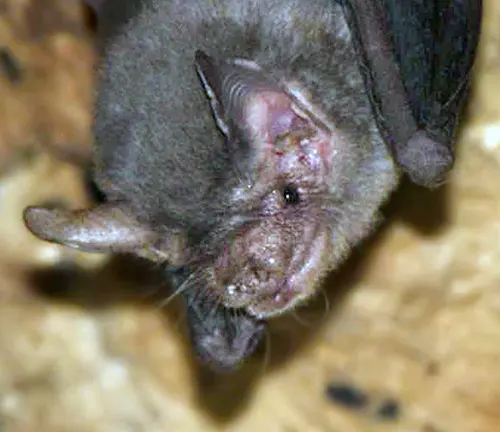


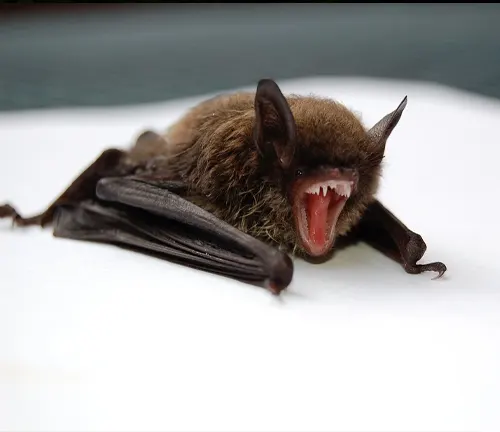
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, commonly known as the bumblebee bat, exhibits several distinct physical traits that set it apart from other bat species. Despite its diminutive size, this fascinating mammal possesses remarkable adaptations for survival in its cave-dwelling habitat. One of the most notable features of the Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat is its hog-like snout, which gives it its characteristic appearance and serves a crucial function in echolocation and prey detection.
This unique snout aids the bat in emitting high-frequency sound waves and interpreting the echoes that bounce back, allowing it to navigate through dark caves and locate prey with precision. Additionally, the fur of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat varies in coloration, ranging from brown to gray, providing camouflage in its natural environment. Despite its small size, this bat species plays a vital role in ecosystem dynamics, contributing to insect control and maintaining ecological balance within its habitat.
Habitat and Distribution
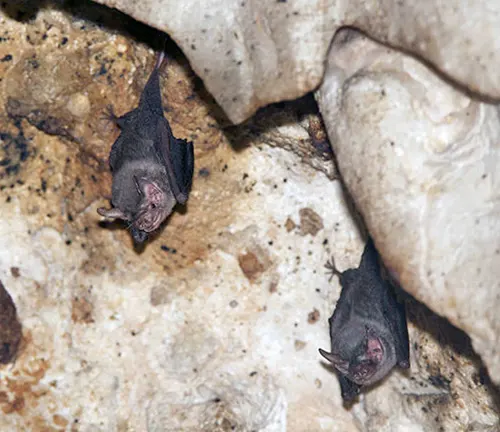

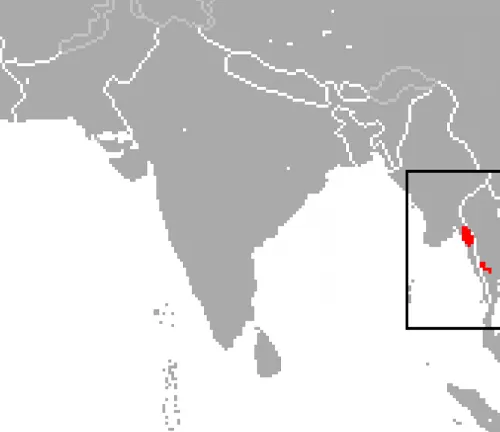
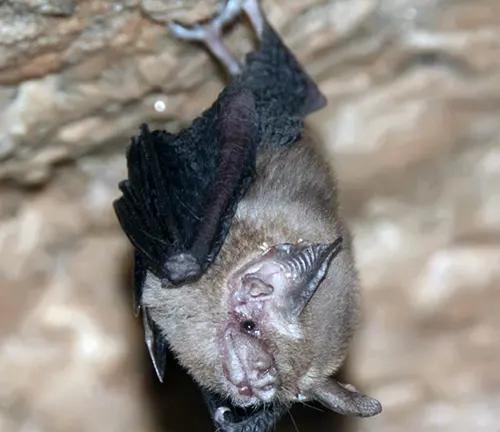
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat primarily inhabits limestone caves located in specific regions of Thailand and Myanmar. These caves provide the bat with suitable roosting sites, offering protection from predators and stable microclimatic conditions essential for its survival. Within these cave systems, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat tends to occupy the darkest and most remote sections, where it forms tight clusters with other individuals to conserve body heat and maintain optimal conditions for roosting.
The bat’s preference for limestone caves with stable environmental conditions reflects its specialized habitat requirements. In terms of distribution, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat is endemic to a limited geographical range, primarily found in the limestone karst regions of central and western Thailand, as well as parts of Myanmar. Despite its restricted distribution, efforts to study and conserve this unique bat species are essential for its long-term survival.
Feeding Habits
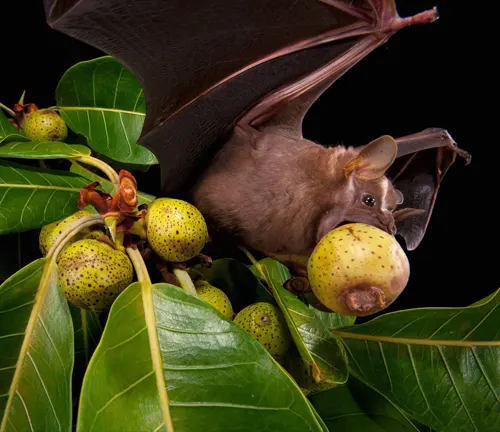
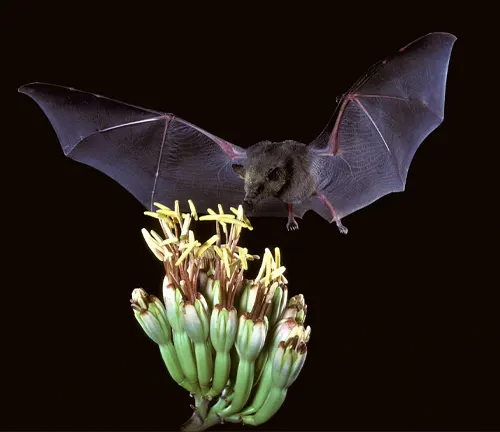


Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat has specialized feeding habits that contribute to its survival in its natural habitat. As an insectivorous mammal, it primarily preys on small insects such as mosquitoes, beetles, and moths. Despite its diminutive size, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat possesses remarkable echolocation abilities, which enable it to detect and locate prey with precision, even in complete darkness. Using echolocation, the bat emits high-frequency sound waves and listens for the echoes that bounce back from surrounding objects, including potential prey.
Once a target is detected, the bat swoops in to capture its prey using its agile flight and sharp claws. The consumption of insects not only fulfills the bat’s nutritional requirements but also plays a crucial role in controlling insect populations within its ecosystem. By regulating insect numbers, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat contributes to ecological balance and helps maintain the health of its habitat.
Unique Behaviors
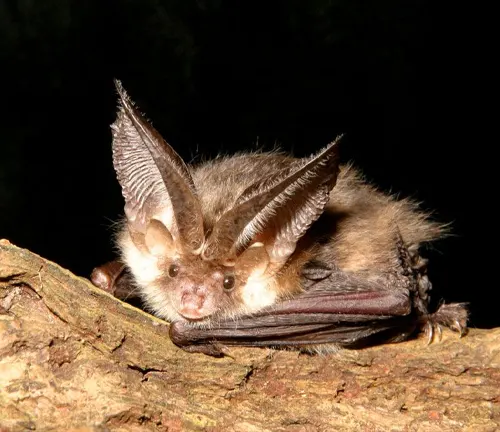
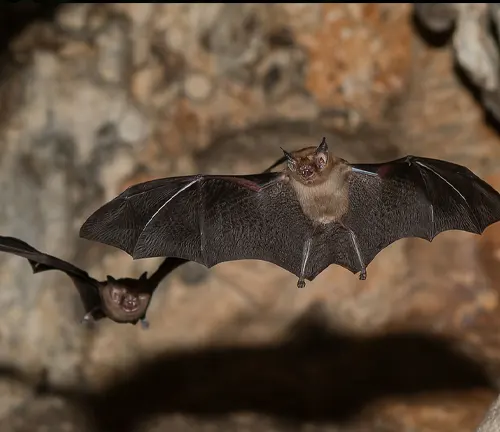


Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat exhibits several unique behaviors that distinguish it from other bat species. One of the most fascinating behaviors is its roosting habits within cave environments. Unlike many other bats that roost in more accessible areas of caves, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat tends to inhabit the darkest and most remote sections. Here, it forms tight clusters with other individuals, huddling closely together to conserve body heat and maintain optimal conditions for survival.
This behavior not only helps the bats regulate their body temperature but also provides protection from predators and disturbances. Additionally, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat demonstrates remarkable agility and maneuverability during flight, allowing it to navigate through narrow cave passages and dense vegetation with ease. Despite its small size, this bat species plays a vital role in maintaining ecosystem health through its feeding habits and interactions with its environment. Understanding and protecting the unique behaviors of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat are crucial for its conservation and long-term survival.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
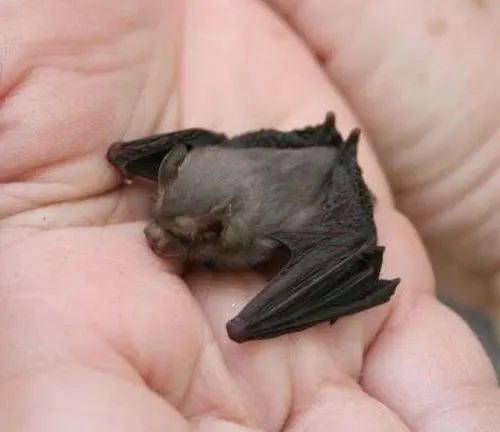


Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat follows a distinctive reproductive and life cycle adapted to its cave-dwelling lifestyle. Like many other bat species, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat exhibits low fecundity, with females typically giving birth to a single offspring each year. The reproductive cycle of these bats begins with mating, which typically occurs during specific times of the year when environmental conditions are favorable.
After mating, female bats undergo a gestation period lasting several months, during which they carry their developing offspring. Once the gestation period is complete, females give birth to a single pup, which they nurse and care for in the safety of the cave roost.
Maternal care plays a crucial role in the survival of young Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats, as mothers provide warmth, protection, and nourishment to their offspring during the early stages of life. As the young bats grow and develop, they gradually become more independent, learning to fly and forage for food alongside their mothers. Over time, young bats reach maturity and become capable of reproducing, thus continuing the cycle of life within the Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat population.
The life cycle of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat is intricately linked to its cave habitat and the availability of resources within its environment. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting both cave ecosystems and bat populations are essential for ensuring the continued survival of this unique species for future generations to admire and study.
Conservation Status
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat faces significant conservation challenges due to various threats to its habitat and population. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat as endangered, reflecting its vulnerable status in the wild. One of the primary threats to the conservation of this bat species is habitat loss, resulting from factors such as deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urban development. Destruction of limestone cave habitats, which serve as crucial roosting sites for Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, further exacerbates this threat.
Additionally, disturbance in cave ecosystems poses a significant risk to the survival of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat populations. Human activities such as cave exploration, tourism, and unregulated development can disrupt bat roosts, disturb breeding colonies, and lead to declines in bat populations. Furthermore, illegal wildlife trade poses a threat to Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, as these tiny bats are sometimes captured and sold for their perceived rarity or novelty.
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat and its habitat are essential for ensuring the species’ long-term survival. These efforts may include habitat restoration projects, establishment of protected areas, and enforcement of regulations to prevent illegal trade and habitat destruction. Public awareness and education programs can also play a crucial role in fostering appreciation for the importance of bats in ecosystems and encouraging conservation action to safeguard their future.
Threats to Survival
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat faces numerous threats to its survival, primarily stemming from human activities and habitat degradation. One of the most pressing threats is habitat loss, resulting from deforestation, agricultural expansion, and urban development. Destruction of limestone cave habitats, which serve as critical roosting sites for Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, directly impacts bat populations by reducing available roosting space and disrupting natural behaviors.
Additionally, disturbance in cave ecosystems poses a significant risk to the survival of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat populations. Human activities such as cave exploration, tourism, and unregulated development can disturb bat roosts, disrupt breeding colonies, and lead to declines in bat populations. Furthermore, illegal wildlife trade poses a threat to Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, as these tiny bats are sometimes captured and sold for their perceived rarity or novelty.
Climate change also poses emerging threats to Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, as alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt ecosystems and affect the availability of suitable habitat and food sources. These changes may exacerbate existing threats and pose additional challenges to the survival of this endangered bat species.
Efforts to mitigate these threats and conserve Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat are essential for ensuring the species’ long-term survival. Conservation initiatives may include habitat restoration, establishment of protected areas, enforcement of regulations to prevent habitat destruction and illegal trade, and public awareness campaigns to promote appreciation for bats and their ecological importance.
Efforts for Conservation
Efforts for the conservation of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat are underway to mitigate the threats it faces and ensure its long-term survival. Conservation organizations, governmental agencies, and local communities are collaborating to implement various strategies aimed at protecting both the bat species and its habitat. These efforts include habitat restoration projects focused on preserving and restoring limestone cave ecosystems, where Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat roosts.
Additionally, the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves helps safeguard critical habitats from further degradation and human encroachment. Furthermore, enforcement of regulations to prevent illegal wildlife trade and habitat destruction is essential for combating threats to the bat’s survival. Community-based conservation programs engage local stakeholders in conservation efforts, fostering stewardship of natural resources and promoting coexistence between humans and bats.
Importance in Ecosystem
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat plays a crucial role in ecosystem dynamics and contributes to maintaining ecological balance. As an insectivorous mammal, it helps regulate insect populations by consuming large quantities of insects, including mosquitoes, beetles, and moths. By controlling insect numbers, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat helps prevent the proliferation of pest species and reduces agricultural damage caused by insect pests.
Additionally, the bat’s foraging behavior contributes to nutrient cycling and ecosystem health, as guano (bat feces) serves as a valuable source of nutrients for plants and other organisms. Furthermore, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat serves as a pollinator for some plant species, facilitating plant reproduction and biodiversity within its habitat. Overall, the presence of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat contributes to the resilience and functioning of ecosystems, highlighting its ecological importance.
Interaction with Humans
The interaction between Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat and humans is limited, primarily due to the bat’s preference for remote cave habitats. However, human activities such as cave exploration, tourism, and urban development can indirectly impact bat populations and their habitats. Disturbance in cave ecosystems, caused by human presence and activities, can disrupt bat roosts, disturb breeding colonies, and lead to declines in bat populations.
Additionally, misconceptions and fear surrounding bats may contribute to negative attitudes and perceptions towards Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat and other bat species. Educating the public about the importance of bats in ecosystems and the need for their conservation is essential for fostering positive attitudes and promoting coexistence between humans and bats.
Myths and Misconceptions
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, like many other bat species, is surrounded by myths and misconceptions that can lead to its persecution and misunderstanding. One common myth is that bats are aggressive and carry diseases such as rabies, leading to fear and avoidance of these animals. In reality, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat is a shy and non-aggressive species that poses minimal risk to humans when left undisturbed.
Additionally, bats play valuable roles in ecosystems as pollinators, seed dispersers, and insect controllers, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem health. Dispelling myths and misconceptions about bats through education and awareness campaigns is essential for promoting their conservation and fostering appreciation for these unique mammals.
Future Research Directions
Future research on Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat should focus on addressing knowledge gaps related to its ecology, behavior, and conservation. Understanding the habitat requirements, population dynamics, and distribution patterns of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and management plans. Research on the impact of human activities, such as habitat destruction and disturbance, on bat populations can inform conservation efforts and mitigate threats to bat survival.
Furthermore, studies on the interaction between Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat and other species within its ecosystem can provide insights into its ecological role and importance. Additionally, monitoring the effects of climate change on bat populations and their habitats is crucial for predicting future conservation challenges and implementing adaptive management strategies. Overall, continued research efforts are essential for advancing our understanding of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat and promoting its conservation for future generations.
Different Species
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, scientifically known as Craseonycteris thonglongyai, is the only species within its genus, Craseonycteris, and the family Craseonycteridae. As such, there are no different species of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat?
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat, also known as the bumblebee bat, holds the title of the world’s smallest bat and one of the smallest mammals. Its scientific name is Craseonycteris thonglongyai. - Where is Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat Found?
These tiny bats are predominantly found in limestone caves in select regions of Thailand and Myanmar. - What Does Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat Eat?
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats primarily feed on small insects such as mosquitoes, beetles, and moths. - How Does Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat Navigate in the Dark?
Despite their small size, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats possess remarkable echolocation abilities, using high-frequency sound waves to navigate and locate prey in their dark cave habitats. - Are Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats Endangered?
Yes, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats are classified as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) due to threats like habitat loss and disturbance. - What Threats Do Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats Face?
Major threats to the survival of Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats include habitat destruction, disturbance in cave ecosystems, and illegal wildlife trade. - How Can I Help Conserve Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats?
You can contribute to conservation efforts by supporting habitat restoration projects, raising awareness about the importance of protecting their habitats, and advocating for stronger wildlife protection laws. - What Makes Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bat Unique?
Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats stand out for their tiny size, hog-like snout, and impressive echolocation abilities, making them a fascinating subject of study for researchers. - Do Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats Hibernate?
While they undergo periods of torpor during colder months, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats are not true hibernators. - Can Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats Be Kept as Pets?
No, Kitti’s Hog-nosed Bats are wild animals and are protected by law. It is illegal to keep them as pets.














Leave your comment