African Helmeted Turtle
- April 2, 2024
- 0 comment
The African Helmeted Turtle, scientifically known as Pelomedusa subrufa, is a captivating reptile native to various regions across sub-Saharan Africa. This species is characterized by its unique physical features, including a domed shell that ranges in color from shades of brown to olive green. With streamlined bodies and webbed feet, these turtles are well-adapted to both aquatic and terrestrial environments. They primarily inhabit freshwater habitats such as rivers, ponds, and marshes, where they play vital roles in the ecosystem. African Helmeted Turtles are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and carrion.
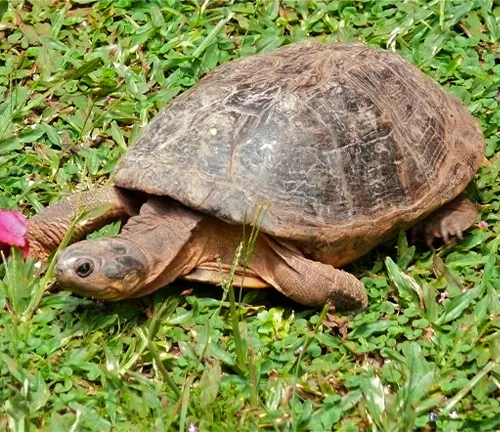

During the breeding season, males engage in courtship displays to attract females, and females lay eggs in nests dug into sandy soil. Despite facing threats from habitat loss, pollution, and the pet trade, conservation efforts aim to protect these turtles and their natural habitats. African Helmeted Turtles are also popular choices in the pet trade due to their small size and hardy nature, although responsible ownership is essential to ensure their welfare. Understanding and appreciating the African Helmeted Turtle’s significance can contribute to their conservation and preservation for future generations to enjoy.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pelomedusa subrufa |
| Common Names | African Helmeted Turtle, Marsh Terrapin |
| Habitat | Freshwater habitats including rivers, ponds, marshes |
| Geographic Range | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| Size | Adults typically range from 15 to 25 centimeters |
| Shell Structure | Domed shell with varying shades of brown or green |
| Diet | Omnivorous, feeding on aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and carrion |
| Reproduction | Females lay eggs in nests dug into sandy soil |
| Lifespan | Can live for several decades |
| Conservation Status | Not currently classified as endangered |
| Threats | Habitat loss, pollution, pet trade |
| Conservation Efforts | Protection of natural habitats, mitigation of human impacts |
| Adaptations | Ability to retract head into shell, basking behavior |
| Ecological Role | Regulates insect populations, prey for predators |
| Importance in Pet Trade | Popular due to small size and hardy nature |
| Legal Regulations | Varies by region, may require permits for ownership |
African Helmeted Turtle: A Fascinating Reptile of the African Landscape
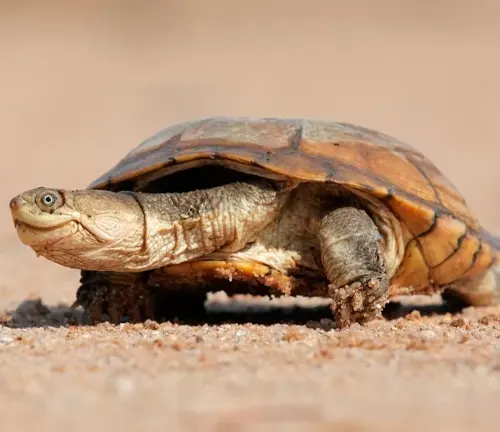

The African Helmeted Turtle, scientifically known as Pelomedusa subrufa, is a captivating reptile species found in various parts of Africa. Characterized by its distinctive appearance and interesting behaviors, this turtle species holds a unique place in the ecosystem and human culture alike.
Habitat and Distribution
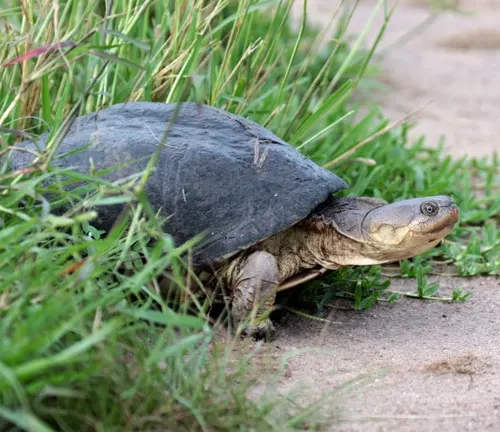

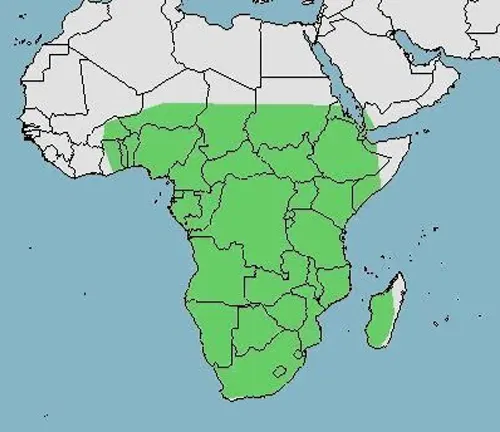
The African Helmeted Turtle, scientifically known as Pelomedusa subrufa, inhabits a variety of freshwater environments throughout sub-Saharan Africa. These turtles can be found in rivers, ponds, marshes, and other aquatic habitats across the continent. Their distribution spans countries such as South Africa, Botswana, Namibia, Zimbabwe, and many others within the region. African Helmeted Turtles are well-adapted to both aquatic and terrestrial habitats, utilizing both water and land areas for feeding, basking, and nesting. Their ability to thrive in diverse environments contributes to their widespread distribution across Africa.
Physical Features
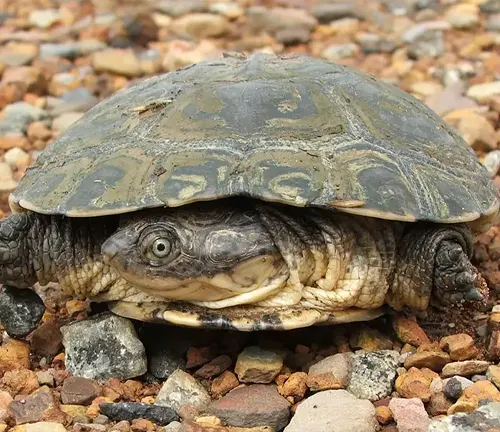
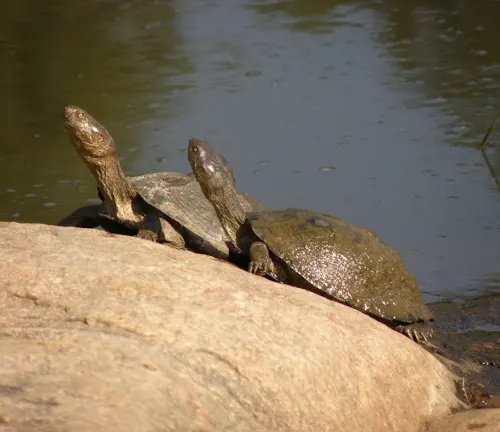


The African Helmeted Turtle, scientifically known as Pelomedusa subrufa, boasts distinct physical characteristics. Its most notable feature is its domed shell, varying in hues from brown to olive green. This shell serves as protection against predators and environmental hazards. Additionally, African Helmeted Turtles possess streamlined bodies and webbed feet, facilitating efficient movement both in water and on land. These adaptations contribute to their survival in a range of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa, from rivers and ponds to marshes and wetlands.
Diet and Feeding Habits
African Helmeted Turtles are omnivorous creatures, meaning they consume a diverse array of food items. Their diet typically includes aquatic plants, insects, small fish, and carrion. These turtles exhibit opportunistic feeding behavior, scavenging for food in their environment. Their ability to adapt their diet to available resources contributes to their survival in various habitats. African Helmeted Turtles play a crucial role in ecosystem dynamics by regulating populations of prey species and contributing to nutrient cycling through their feeding habits.
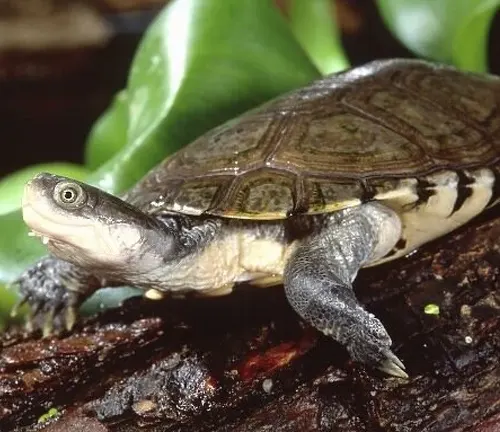

Reproduction and Lifecycle
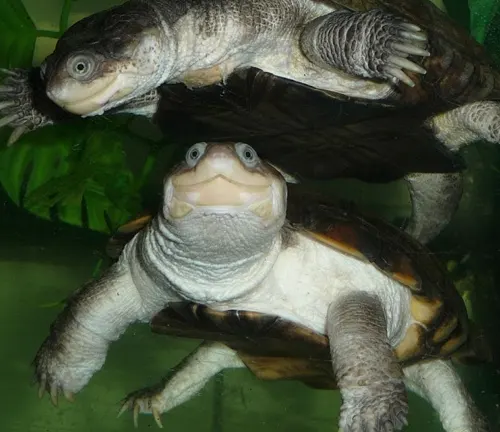

The reproduction and lifecycle of African Helmeted Turtles are fascinating aspects of their biology. During the breeding season, typically in warmer months, male turtles engage in elaborate courtship displays to attract females. Once a female selects a mate, she lays her eggs in nests dug into sandy soil, often near water bodies. The number of eggs laid can vary but generally ranges from a few to several dozen, depending on factors such as the female’s size and age. After the eggs are laid, the female covers them with soil and leaves them to incubate.
Behavioral Adaptations
African Helmeted Turtles showcase several remarkable behavioral adaptations that aid in their survival in diverse environments. One of their primary adaptations is the ability to retract their heads into their shells when threatened, providing crucial protection from predators. This behavior serves as a defense mechanism, allowing them to avoid potential harm.
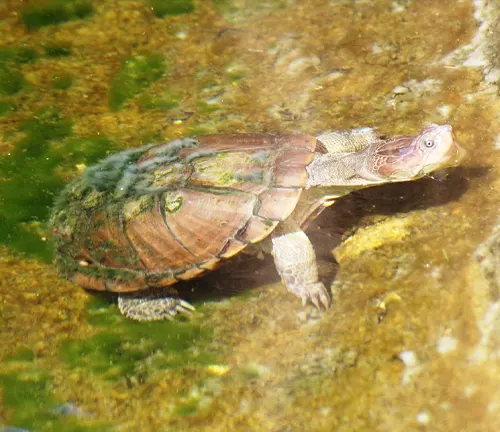

Additionally, African Helmeted Turtles exhibit basking behavior, where they soak up sunlight to regulate their body temperature. Basking helps them maintain optimal physiological functions and energy levels. By spending time in the sun, these turtles can thermoregulate effectively, ensuring they remain active and healthy.
Furthermore, African Helmeted Turtles display an instinctual understanding of their surroundings, allowing them to navigate various habitats with ease. Whether traversing through water or on land, these turtles demonstrate agility and adaptability, utilizing their streamlined bodies and webbed feet for efficient locomotion.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of African Helmeted Turtles is of concern due to various threats they face in their natural habitats. While not currently classified as endangered, these turtles are susceptible to habitat loss, pollution, and the pet trade. Efforts to conserve African Helmeted Turtles include habitat protection, conservation education, and regulations on the pet trade to ensure sustainable populations in the wild.
Interactions with Humans
African Helmeted Turtles have significant interactions with humans, particularly in the pet trade. Due to their small size and hardy nature, they are popular choices as pets. However, irresponsible ownership, such as improper care and release into the wild, can have detrimental effects on both captive and wild populations. Conservation efforts aim to promote responsible pet ownership and minimize negative interactions between turtles and humans.
Common Misconceptions
One common misconception about African Helmeted Turtles is that they can survive solely on land. In reality, these turtles require access to water for hydration, feeding, and thermoregulation. Additionally, some may mistakenly believe that these turtles pose a threat to humans, but they are generally harmless and shy away from confrontation.
Role in the Ecosystem
African Helmeted Turtles play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems as both predators and prey. They help regulate populations of aquatic organisms, such as insects and small fish, contributing to ecosystem balance. Additionally, their presence as prey species supports the food web, providing sustenance for larger predators. By maintaining healthy populations, African Helmeted Turtles contribute to the overall biodiversity and stability of their habitats.
Conservation Tips
To support the conservation of African Helmeted Turtles, individuals can take several actions. These include avoiding the purchase of wild-caught specimens, supporting habitat conservation efforts, and educating others about the importance of protecting these turtles and their habitats. Responsible pet ownership, including providing proper care and not releasing captive turtles into the wild, is also essential for their conservation.
Different Species
Pelomedusa galeata
Also known as the Helmeted Turtle, this species is native to southern Africa, including countries like South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique. It is closely related to Pelomedusa subrufa and shares similar habitat preferences.
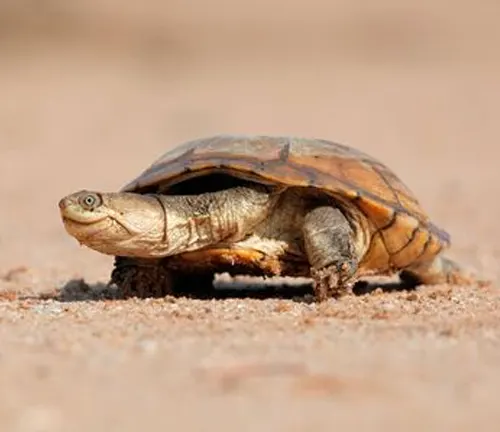
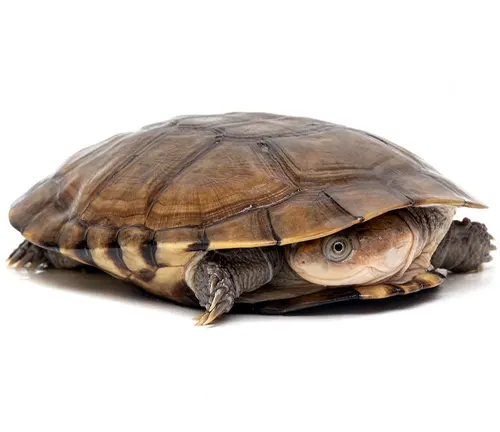


Pelomedusa olivacea
Found in parts of eastern and southern Africa, Pelomedusa olivacea is distinguished by its olive-colored shell and slightly different distribution compared to other Pelomedusa species.
Pelomedusa schweiggeri
This species, commonly known as Schweigger’s African Helmeted Turtle, is native to parts of West Africa, including countries like Ghana, Ivory Coast, and Nigeria. It exhibits similar characteristics to other African Helmeted Turtles but may have slight variations in coloration and size.
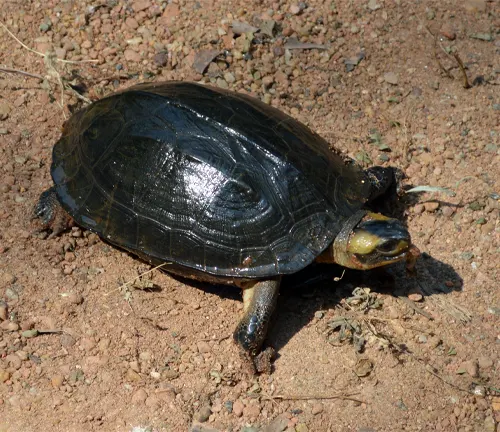
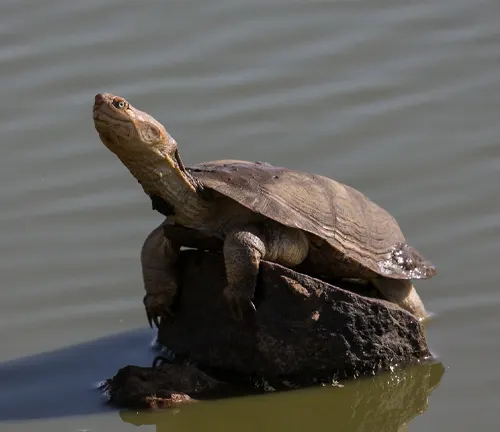


Pelomedusa neumanni
Neumann’s African Helmeted Turtle is found in central and eastern Africa, including regions of Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania. It is named after German herpetologist Neumann and is known for its distinct shell pattern.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- Are African Helmeted Turtles suitable as pets?
African Helmeted Turtles can make suitable pets for experienced reptile keepers who can provide the appropriate care and habitat requirements. However, they may not be suitable for beginners due to their specific needs. - How long do African Helmeted Turtles live?
African Helmeted Turtles have a relatively long lifespan and can live for several decades in captivity, often reaching 20 to 30 years or more with proper care. - What is the ideal habitat setup for captive African Helmeted Turtles?
The ideal habitat setup for captive African Helmeted Turtles includes a spacious enclosure with both water and land areas, a basking spot with a heat lamp, UVB lighting, clean water for swimming, and a substrate suitable for burrowing. - Can African Helmeted Turtles hibernate?
Yes, African Helmeted Turtles may hibernate in response to seasonal changes in temperature and daylight hours. However, hibernation is not necessary for their health and well-being in captivity. - What are the legal regulations regarding the ownership of African Helmeted Turtles?
Legal regulations regarding the ownership of African Helmeted Turtles vary by country and region. In some areas, permits may be required for ownership, and there may be restrictions on importing or exporting them. - Do African Helmeted Turtles require special dietary supplements?
African Helmeted Turtles may benefit from occasional dietary supplements, particularly calcium and vitamin D3, to support shell and bone health. However, a balanced diet consisting of varied foods can often meet their nutritional needs. - How can I tell the gender of my African Helmeted Turtle?
Determining the gender of African Helmeted Turtles can be challenging, especially in younger individuals. However, males typically have longer and thicker tails, while females may have shorter and thinner tails. - What diseases or health issues are common in African Helmeted Turtles?
Common health issues in African Helmeted Turtles include shell rot, respiratory infections, parasites, and metabolic bone disease. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper husbandry practices can help prevent these issues. - How often should I clean my African Helmeted Turtle’s enclosure?
Enclosures should be spot-cleaned daily to remove waste, and water should be changed regularly to maintain cleanliness. A thorough cleaning of the entire enclosure should be done weekly or as needed. - Can African Helmeted Turtles be housed with other turtle species?
African Helmeted Turtles can often be housed with other turtle species that have similar habitat requirements and temperaments. However, careful monitoring is essential to prevent aggression or territorial disputes. - What temperature range is suitable for African Helmeted Turtles?
The ideal temperature range for African Helmeted Turtles is typically between 75 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit (24 to 29 degrees Celsius), with a basking spot reaching temperatures of 90 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit (32 to 35 degrees Celsius). - Do African Helmeted Turtles require UVB lighting?
Yes, African Helmeted Turtles require UVB lighting to help them metabolize calcium and maintain proper bone health. UVB bulbs should be provided in their enclosure for 10 to 12 hours a day. - What type of substrate is best for African Helmeted Turtle enclosures?
Suitable substrates for African Helmeted Turtle enclosures include fine sand, gravel, or a mix of soil and coconut coir. The substrate should allow for burrowing and be easy to clean. - Can African Helmeted Turtles be handled safely?
African Helmeted Turtles can be handled safely but should be handled with care and gentleness to avoid stress or injury. It’s essential to support their body properly and avoid excessive handling. - What enrichment activities are recommended for African Helmeted Turtles?
Enrichment activities for African Helmeted Turtles include providing hiding spots, objects to explore and climb on, live plants, and varied food items to stimulate natural behaviors and mental stimulation.














Leave your comment