Forest Biodiversity: Why It Matters for Nature and Humanity
- August 16, 2024
- 0 comment
Forest biodiversity encompasses the vast array of living organisms found in forest ecosystems, ranging from towering trees and lush understory plants to diverse animal species, fungi, and microorganisms. These forests, which cover approximately 31% of the Earth’s land surface, are home to more than 80% of terrestrial biodiversity. The importance of forest biodiversity extends beyond its sheer variety; it underpins the health and resilience of ecosystems, providing essential services that benefit both nature and humanity.

The Role of Forest Biodiversity
Ecosystem Services
Forest biodiversity is a cornerstone of ecosystem services that are vital to human survival and well-being. These services are categorized into four main types:
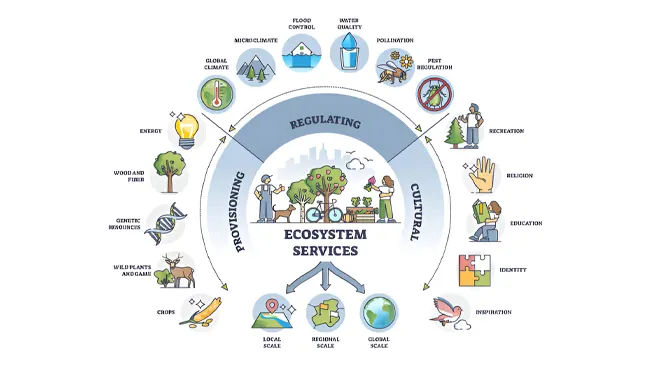
- Provisioning Services: Forests supply resources such as timber, fuelwood, food, and medicinal plants. The variety of species ensures the sustainability and availability of these resources.
- Regulating Services: Biodiverse forests contribute significantly to climate regulation, water purification, disease control, and pollination. For instance, diverse plant species enhance carbon sequestration, playing a vital role in mitigating climate change.
- Cultural Services: Forests offer cultural, spiritual, and recreational value. The rich biodiversity enhances aesthetic and recreational experiences, contributing to tourism and mental health.
- Supporting Services: These include essential processes like nutrient cycling, soil formation, and primary production. Biodiversity is crucial for the stability and functioning of these foundational ecosystem processes.
Conservation and Sustainable Management of Forest Biodiversity
Protecting forest biodiversity requires a comprehensive approach that combines conservation and sustainable management practices. This involves protecting existing forests, restoring degraded areas, and promoting sustainable land-use practices.

Protected Areas and Restoration Efforts
Establishing protected areas is a key strategy for conserving forest biodiversity. Protected areas provide safe havens for species and help maintain ecological processes. Restoration efforts, such as reforestation and afforestation, aim to recover degraded landscapes and enhance biodiversity.
Sustainable Forest Management
Sustainable forest management involves balancing the extraction of forest resources with the conservation of biodiversity. This includes practices such as selective logging, agroforestry, and community-based management, which help maintain ecosystem health and resilience.
Community Involvement and Education
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for the success of biodiversity initiatives. Community involvement fosters a sense of stewardship and ensures that conservation strategies are culturally and socially appropriate. Education and awareness-raising activities can also promote the value of forest biodiversity and encourage sustainable behaviors.
Global Initiatives and Policies
International cooperation is crucial for addressing the global challenges facing forest biodiversity. Several international agreements and initiatives aim to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable forest management.

Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
The CBD is a global agreement that aims to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable use, and ensure the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. The CBD provides a framework for countries to develop and implement national biodiversity strategies and action plans.
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
The UNFCCC addresses climate change and its impacts on biodiversity. Initiatives such as REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) aim to reduce emissions from deforestation while promoting conservation and sustainable management.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The SDGs, adopted by the United Nations, include goals related to biodiversity and sustainable forest management. Goal 15 focuses on life on land and aims to protect, restore, and promote the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems.
Ecological Balance and Resilience
Biodiverse forests are more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances such as climate change, disease outbreaks, and invasive species. The presence of diverse species helps maintain ecological balance and enables ecosystems to recover from disturbances more effectively. For example, a variety of tree species provides habitat for numerous animal species, supporting complex food webs and maintaining ecological equilibrium.
Biodiversity and Climate Change Mitigation
Forests play a critical role in combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing carbon in biomass and soil. Biodiverse forests are particularly effective at carbon sequestration due to their higher productivity and stable ecosystem functions. Diverse plant communities can better adapt to changing climate conditions, ensuring the continued provision of carbon sequestration services.

Biodiversity and Human Health
Forest biodiversity has a direct impact on human health. Forests are a source of many medicinal plants, and biodiversity facilitates the discovery of new medicines. Additionally, biodiverse forests enhance air and water quality, which are essential for human health. The psychological benefits of biodiverse natural environments, such as reduced stress and improved mental well-being, are also significant.

Threats to Forest Biodiversity
Despite its importance, forest biodiversity faces numerous threats from human activities, including deforestation, habitat fragmentation, pollution, and climate change. These threats can lead to species loss and ecosystem degradation, with significant consequences for the environment and human society.

Deforestation and Habitat Loss
Deforestation, driven by agriculture, logging, and urbanization, is the primary threat to forest biodiversity. Habitat loss results in declining species populations and disrupts ecological processes. Fragmentation of forests also isolates species, reducing genetic diversity and increasing vulnerability to extinction.
Pollution and Climate Change
Pollution from industrial activities and agriculture can harm forest ecosystems by contaminating soil and water. Climate change poses additional threats by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to shifts in species distributions and ecosystem dynamics.
Invasive Species
Invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, leading to a decline in biodiversity. They can disrupt food webs and ecological processes, further threatening the health and resilience of forest ecosystems.
Conclusion
Forest biodiversity is fundamental to the health of our planet and the well-being of human societies. It supports essential ecosystem services such as clean air and water, soil fertility, and pollination, which are vital for human survival and agricultural productivity. Biodiverse forests also play a significant role in climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon dioxide and stabilizing climate patterns. Furthermore, forests with rich biodiversity contribute to human health by providing medicinal resources, enhancing mental well-being, and sustaining livelihoods. The complex interplay of species within these ecosystems fosters resilience, allowing forests to adapt to environmental changes and recover from disturbances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is forest biodiversity?
Forest biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms found within forest ecosystems, including trees, plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the ecological interactions among them. - Why is forest biodiversity important for humans?
Forest biodiversity provides essential ecosystem services such as clean air and water, food and medicine, climate regulation, and recreational opportunities, all of which directly benefit human well-being. - How does forest biodiversity contribute to climate change mitigation?
Biodiverse forests are more effective at carbon sequestration, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change. - What are the main threats to forest biodiversity?
The main threats include deforestation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species, all of which can lead to species loss and ecosystem degradation. - How can we protect forest biodiversity?
Protecting forest biodiversity involves establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable forest management practices, restoring degraded landscapes, and engaging local communities in conservation efforts. - What role do forests play in supporting biodiversity?
Forests provide habitats for a wide range of species, support complex food webs, and maintain ecological processes, making them critical for sustaining biodiversity. - How does forest biodiversity affect ecosystem resilience?
Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances, allowing them to maintain balance and recover more effectively from events like natural disasters and disease outbreaks. - What are some examples of ecosystem services provided by forests?
Ecosystem services provided by forests include provisioning services (e.g., timber and food), regulating services (e.g., climate and water regulation), cultural services (e.g., recreation and spiritual value), and supporting services (e.g., nutrient cycling and soil formation). - How does forest biodiversity benefit human health?
Forest biodiversity supports human health by providing medicinal resources, enhancing air and water quality, and offering recreational and psychological benefits that improve mental well-being. - What global initiatives support forest biodiversity conservation?
Global initiatives include the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), all of which aim to promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable forest management.
We hope this article has deepened your understanding of why forest biodiversity is crucial for both nature and humanity. Do you have experiences or insights into the significance of forest biodiversity or strategies for its conservation? Share your thoughts and join the conversation below. Your contributions can help others appreciate the value of biodiversity and encourage action to protect these vital ecosystems. Don’t forget to share this article with others interested in preserving our planet’s biodiversity!

Evan Bennett
Forestry AuthorEvan Bennett brings over a decade of expertise in forestry wildlife management to the forefront, specializing in habitat conservation, biodiversity, and human-wildlife interaction. Evan's work ensures harmonious coexistence between wildlife and human communities through effective and sustainable practices. Continuously engaging in research and workshops, Evan stays at the cutting edge of wildlife management advancements. As a trusted advisor and contributor to leading environmental journals, Evan is dedicated to preserving the natural world for future generations.






Leave your comment