How Does Hydroponics Work: A Beginner’s Guide to Soil-Free Gardening
- January 26, 2024
- 0 comment
In recent years, hydroponics has emerged as a groundbreaking method in gardening and agriculture. Unlike traditional soil-based gardening, hydroponics allows for plant cultivation in a soil-free environment, where nutrients are delivered directly to plant roots via a water-based solution. This innovative approach to gardening is gaining popularity for its efficiency, space-saving qualities, and sustainability.
Hydroponics, a revolutionary approach to cultivation, allows for plant growth in a soil-free environment by utilizing nutrient-rich water solutions. This innovative technique optimizes plant nutrition and growth, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional agriculture. Ideal for urban settings and limited spaces, hydroponics is gaining popularity for its efficient use of resources and potential to yield crops year-round, irrespective of climatic conditions.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, where nutrients are delivered directly to plant roots through a water-based solution. This technique allows plants to grow faster and more efficiently, as they can access nutrients and oxygen more easily than in traditional soil. Ideal for space-constrained environments, hydroponics is versatile, sustainable, and can be set up indoors or outdoors.

It’s particularly popular for cultivating herbs, leafy greens, and small fruits, offering a soil-free alternative that reduces water usage and eliminates the need for chemical pesticides, fostering a cleaner and more controlled growth environment.
The Science Behind Hydroponics
At its core, hydroponics operates on a simple principle: providing plants with exactly what they need, when they need it. In the absence of soil, plants draw their nutrients from a solution, which is carefully monitored and adjusted for pH and nutrient levels. This direct feeding to roots increases growth efficiency and can lead to faster growth rates compared to soil gardening.
Hydroponics is based on the efficient principle of directly supplying plants with the precise nutrients and water they require at the right times. Without soil, plant roots absorb these essentials from a controlled solution, where pH and nutrient concentrations are meticulously regulated. This method ensures optimal nutrient uptake, resulting in increased growth efficiency and potentially faster growth rates than traditional soil-based gardening.
Several Types of Hydroponics
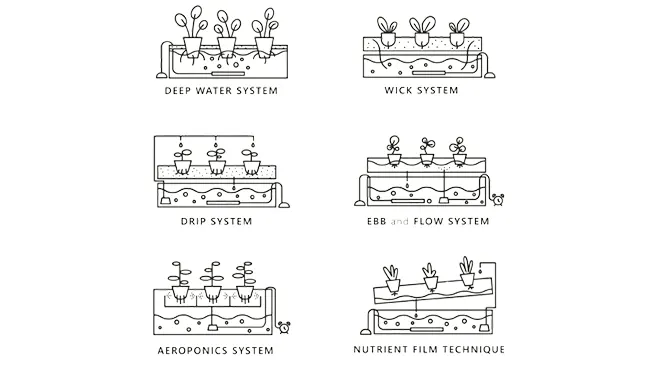
| Type of Hydroponics | Description |
|---|---|
| Wick System | Simplest type, uses wicks to draw nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant roots. |
| Deep Water Culture (DWC) | Plants are suspended in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water. |
| Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) | A constant flow of nutrient solution runs over the roots, usually on a slight tilt to allow for runoff. |
| Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) | Plants are flooded with nutrient solution at intervals and then drained back to the reservoir. |
| Aeroponics | Roots are suspended in air and misted with nutrient solution. |
| Drip System | Slow drip of nutrient solution is delivered to each plant, commonly used in large-scale operations. |
Benefits of Hydroponic Gardening
Hydroponics presents multiple benefits over conventional gardening methods, most notably in its efficient water usage and nutrient recycling, making it a more sustainable choice. Its ability to facilitate high-density planting is particularly advantageous in urban settings where space is at a premium.
Versatile in nature, hydroponic systems can be installed indoors, outdoors, or in greenhouses, allowing for continuous cultivation throughout the year, irrespective of external weather conditions. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponic systems significantly diminishes the prevalence of pests and diseases, thereby reducing the dependency on pesticides, contributing to a more environmentally friendly and healthier crop production.
Pros
- Water Efficiency: Uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil gardening, as water in hydroponic systems is recirculated.
- Faster Plant Growth: Plants often grow faster in hydroponic systems due to the efficient delivery of nutrients to roots.
- Year-Round Growing: Allows for indoor cultivation, independent of external weather conditions.
- Space-Saving: Ideal for urban settings or places with limited space, as it doesn’t require large plots of land.
- Reduced Pests and Diseases: With no soil, there’s a lower risk of soil-borne pests and diseases.
- No Weeding Required: Eliminates the labor-intensive task of weeding.
- Control Over Variables: Offers greater control over nutrient balance, pH levels, and growth conditions.
Cons
- Initial Setup Cost: The initial investment for equipment and setup can be higher than traditional gardening.
- Technical Knowledge Required: Successful hydroponic gardening requires some understanding of the system’s mechanics and plant nutrition.
- Electricity Dependence: Most systems rely on electricity for lighting, pumps, and timers, which could be a problem during power outages.
- Water and Electricity Risks: The combination of water and electricity requires careful management to avoid hazards.
- System Failure Risk: Plants can die quickly if the hydroponic system fails (e.g., pump failure), as they depend entirely on the system for nutrients and water.
- Limited Crop Variety: Not all plants are suitable for hydroponic systems; generally, it’s more suited for leafy greens and herbs.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Systems require regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal plant growth conditions.
Getting Started with Hydroponics
Initiating a hydroponic garden involves assembling a few fundamental components. Firstly, a suitable growing medium is needed to support plant roots; common options include Rockwool or clay pellets, which offer stability and proper air-water balance. Next, a nutrient solution, rich in essential minerals, is required to feed the plants. This solution is stored in a water reservoir. To transport the nutrient solution to the plants, a delivery system such as a pump (for active systems) or a wick (for passive systems) is used.
Additionally, adequate lighting is crucial for plant growth, which can be provided by natural sunlight or artificial grow lights, depending on the location of the setup. For those new to hydroponics, starting with simpler systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC) or a Wick system is advisable. These systems are less complex and provide a good foundation for understanding hydroponic principles before moving on to more intricate setups.
Steps to setup hydroponic system
- Choose a Hydroponic System: Decide on the type of hydroponic system you want to use, such as Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or Ebb and Flow. Each has its own setup and maintenance requirements.
- Gather Supplies: Obtain necessary supplies including a growing container, water reservoir, air pump (for oxygenating the water), growing medium (like Rockwool or clay pebbles), and hydroponic nutrients.
- Set Up the Growing Container: Place your growing medium in the container. If using a system like DWC, ensure the roots will be able to reach the nutrient solution.
- Prepare the Nutrient Solution: Mix water with hydroponic nutrients following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Adjust the pH of the solution to the appropriate level, usually between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Plant Your Seeds or Seedlings: Plant your seeds or seedlings in the growing medium. Ensure they are secure and have adequate space for growth.
- Install Lighting: If growing indoors, set up grow lights above your plants. Ensure they receive enough light daily, typically 14-16 hours for most plants.
- Monitor and Maintain: Regularly check the pH and nutrient levels in your solution, adjusting as needed. Also, monitor plant growth and watch for any signs of distress.
- Harvest: Once your plants have matured, harvest your crops. Most leafy greens and herbs will be ready to harvest in a few weeks.
Managing a Hydroponic Garden
Managing a hydroponic garden involves meticulous monitoring and adjustment of key factors to ensure optimal plant growth. This includes regularly checking and balancing the nutrient solution’s pH and concentration, ensuring adequate lighting, and maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels.

Additionally, it’s crucial to monitor for signs of plant stress or disease and to promptly address any issues with the system’s equipment, such as pumps or lights, to prevent disruptions in plant growth. Effective management results in a thriving hydroponic garden with healthy, high-yielding plants.
Key steps to ensure effective maintenance
- Monitor Nutrient Solutions: Regularly check and adjust the nutrient concentration (EC or PPM) and pH levels of your solution to ensure they are within the ideal range for your plants.
- Change Water Regularly: Replace the nutrient solution in your system every 2-3 weeks to prevent the buildup of salts and harmful pathogens.
- Clean and Sterilize: Regularly clean all components of your system, including reservoirs, pumps, and growing trays, to prevent algae growth and disease. Use non-toxic cleaners and rinse thoroughly.
- Inspect Plant Health: Keep an eye out for signs of nutrient deficiencies, pests, or diseases. Early detection and treatment are key to maintaining healthy plants.
- Control Environmental Factors: If your system is indoors, manage lighting, temperature, and humidity to create an optimal growing environment for your plants.
- Prune and Train Plants: Regularly prune dead or overgrown foliage to promote better air circulation and light exposure to all parts of the plant.
- System Checks: Regularly inspect your system for leaks, clogs, or equipment malfunctions. Ensure pumps, timers, and aerators are functioning correctly.
- Record Keeping: Keep a log of nutrient levels, pH adjustments, and any issues or changes you make. This can help in troubleshooting and improving your system over time.
Hydroponics in Different Environments
Hydroponics is highly adaptable, functioning effectively in various environments ranging from small urban apartments to large commercial greenhouses. Its versatility allows for indoor setups where space is limited, offering a solution for city dwellers to grow their produce.

In commercial settings, hydroponic systems enable large-scale production, optimizing space and yield. Moreover, hydroponics can be utilized in challenging climates, such as arid regions or areas with poor soil quality, demonstrating its potential as a sustainable solution for diverse agricultural needs.
Future of Hydroponics
The prospects for hydroponics are highly promising, especially in the context of advancing technologies and sustainability. Innovations in LED lighting are continuously improving energy efficiency and plant growth conditions. Automated systems are being developed to precisely manage nutrient delivery, optimizing plant health and yield with minimal human intervention.

These technological advancements, coupled with sustainable practices, position hydroponics as a key player in addressing global challenges like climate change and increasing population. As traditional agricultural methods face limitations due to environmental changes and land scarcity, hydroponics offers a viable alternative for producing food efficiently and sustainably, making it an increasingly important tool in the quest for future food security.
Conclusion
Hydroponics represents a significant advancement in modern agriculture, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional soil-based farming. By utilizing a soil-free, water-based system enriched with essential nutrients, hydroponics allows for precise control over plant growth conditions, leading to higher yields, faster growth rates, and efficient use of resources. Its ability to conserve water, reduce the need for pesticides, and enable year-round cultivation in varied environments makes it particularly appealing in urban areas and regions with challenging climates.
As global concerns like climate change and food security intensify, hydroponics stands out as a promising solution, harnessing technological innovation to meet the agricultural demands of a growing population while minimizing environmental impact. This method not only embodies a step forward in agricultural productivity but also offers a pathway towards more sustainable and resilient food production systems worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is hydroponics? Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent.
- How does hydroponics work? In hydroponics, plants are grown in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution, which allows plant roots to absorb essential minerals directly from the solution.
- What are the benefits of hydroponics over traditional soil gardening? Benefits include water efficiency, faster plant growth, year-round cultivation, space efficiency, reduced pests and diseases, and no need for weeding.
- Can any plant be grown hydroponically? While many plants can be grown hydroponically, leafy greens and herbs are the most successful. Some larger plants or root vegetables may not be as suitable.
- What equipment do I need to start a hydroponic garden? Basic equipment includes a growing medium, nutrient solution, water reservoir, system for delivering nutrients (like a pump or wick), and lighting.
- Is hydroponic food as nutritious as soil-grown food? Yes, hydroponically grown food can be just as nutritious, if not more so, as the nutrient levels can be precisely controlled.
- Does hydroponic gardening save water? Yes, hydroponics can save up to 90% of water compared to traditional soil gardening, due to the recirculation of water in the system.
- How do I maintain a hydroponic system? Regular maintenance includes monitoring and adjusting nutrient solutions, ensuring proper lighting, and maintaining the right temperature and humidity.
- Can hydroponics be organic? Yes, hydroponics can be organic if organic nutrient solutions are used and if the overall system follows organic growing principles.
- Is hydroponic gardening expensive? The initial setup can be costly, but ongoing costs may be lower compared to soil gardening due to reduced water and pesticide use.

Kristine Moore
Forestry AuthorI'm Kristine Moore, a seasoned garden landscaping professional with over 30 years of experience. My extensive career has been dedicated to transforming outdoor spaces into stunning, sustainable landscapes. With a deep understanding of horticulture, design principles, and environmental stewardship, I have become a respected figure in the field, known for creating harmonious, visually appealing, and eco-friendly gardens. My commitment to excellence and continuous learning in landscaping trends and techniques has solidified my reputation as an expert in garden design and implementation.













Leave your comment