Sustainable Forestry Hacks: Insider Techniques to Try
- August 8, 2024
- 0 comment
Sustainable forestry is more than just a practice—it’s a commitment to preserving the health and diversity of forest ecosystems for future generations. “Sustainable Forestry Hacks: Insider Techniques to Try” explores innovative and practical methods that professionals use to manage forests responsibly. This overview delves into a range of techniques, from precision tree planting and selective logging to advanced monitoring systems that track forest health in real-time.

By adopting these insider tips, forestry practitioners can enhance their efforts in promoting biodiversity, preventing soil erosion, and managing wildlife habitats. The focus is on actionable, easy-to-implement strategies that not only boost productivity but also ensure that forests remain resilient and vibrant. Whether you’re a seasoned forester or a newcomer to the field, these hacks offer valuable insights to improve sustainable forestry practices and contribute to the overall health of our planet’s vital green spaces.
List of Sustainable Forestry Hacks To Try
- Precision Tree Planting
- Selective Logging Practices
- Advanced Monitoring Systems
- Biodiversity Enhancement
- Soil Erosion Prevention
- Wildlife Habitat Management
- Forest Health and Disease Management
- Community Involvement and Education
- Technological Innovations in Forestry
Precision Tree Planting

Importance of Species Selection
Choosing the right species for planting is crucial in sustainable forestry. Different tree species thrive in various soil types, climates, and elevations. Selecting species that are native to the area helps maintain the ecological balance and supports local wildlife. Additionally, planting a diverse range of species can enhance biodiversity and improve forest resilience against pests and diseases.
Optimal Planting Techniques
Optimal planting techniques ensure that trees grow healthily and efficiently. This includes proper spacing to avoid overcrowding, ensuring sufficient sunlight, and preventing competition for nutrients. Planting during the right season, usually in the early spring or late fall, allows seedlings to establish roots before extreme weather conditions. Additionally, using biodegradable tree guards can protect young trees from herbivores.
Tools and Technologies for Precise Planting

Modern tools and technologies have revolutionized tree planting. GPS-guided planting machines ensure accurate spacing and placement of seedlings. Drones equipped with seed dispersal systems can cover large areas quickly and efficiently. Furthermore, data analytics can help foresters decide the best locations for planting based on soil quality, moisture levels, and other environmental factors.
Selective Logging Practices

Definition and Benefits
Selective logging involves harvesting specific trees while preserving the overall structure and function of the forest. This method reduces environmental impact compared to clear-cutting and helps maintain biodiversity. It allows younger trees to grow and promotes a healthier, more resilient forest ecosystem.
Techniques for Minimal Environmental Impact
Minimizing environmental impact during selective logging requires careful planning and execution. Techniques include using low-impact machinery to avoid soil compaction and erosion, planning skid trails to reduce damage, and ensuring that harvested areas regenerate naturally. Additionally, leaving some deadwood and fallen trees can provide habitats for wildlife and contribute to nutrient cycling.
Advanced Monitoring Systems
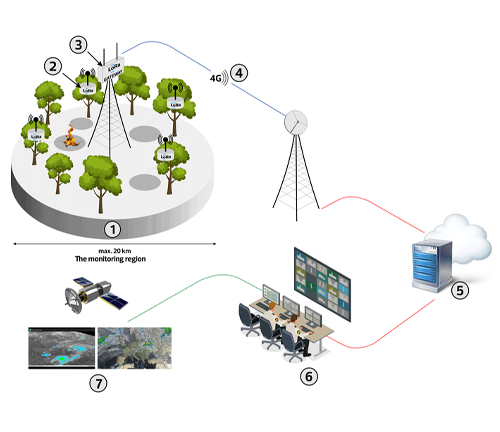
Types of Monitoring Systems
Advanced monitoring systems, such as drones, satellite imagery, and ground sensors, have become essential in sustainable forestry. Drones can capture high-resolution images and videos, providing real-time data on forest health and growth patterns. Satellite imagery offers large-scale monitoring capabilities, helping track changes in forest cover over time. Ground sensors measure soil moisture, temperature, and other critical factors affecting tree health.
How They Improve Forest Health Tracking
These technologies enable precise and continuous monitoring of forest health. By identifying signs of disease, pest infestations, or environmental stress early, foresters can take proactive measures to mitigate damage. Additionally, data collected from these systems helps in making informed decisions on forest management practices, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the ecosystem.
Implementation and Cost Considerations
Implementing advanced monitoring systems requires an initial investment in equipment and training. However, the long-term benefits, such as improved forest health, increased productivity, and reduced environmental impact, outweigh the costs. Collaboration with research institutions and leveraging government grants can also help offset expenses.
Biodiversity Enhancement

Techniques for Promoting Diverse Plant and Animal Life
Promoting biodiversity is essential for a resilient and healthy forest. Techniques include planting a variety of tree species, maintaining natural underbrush, and preserving wetland areas. Creating microhabitats, such as leaving standing dead trees and fallen logs, supports a wide range of organisms. Additionally, managing forest edges to provide diverse habitats can attract various wildlife species.
Importance of Mixed-Species Planting
Mixed-species planting enhances forest resilience by reducing the risk of disease and pest outbreaks. Different species have varying resistance levels, so a diverse forest is less likely to be entirely affected by a single threat. This diversity also supports a wider range of wildlife, contributing to a balanced and thriving ecosystem.
Creating and Maintaining Habitat Corridors

Habitat corridors connect isolated patches of forest, allowing wildlife to move freely and safely. These corridors are crucial for species that require large territories or migrate seasonally. Establishing and maintaining these pathways involves preserving existing natural areas, restoring degraded habitats, and implementing landscape-level planning to ensure connectivity.
Soil Erosion Prevention

Erosion Control Methods
Preventing soil erosion is vital for maintaining forest health. Techniques such as terracing, contour plowing, and mulching help stabilize the soil. Planting cover crops or ground cover vegetation protects the soil from erosion caused by wind and water. Additionally, using erosion control mats and retaining walls in vulnerable areas can prevent soil displacement.
Importance of Ground Cover
Ground cover plays a significant role in preventing erosion by reducing the impact of raindrops on the soil and providing a barrier against wind. It also helps retain moisture, improve soil structure, and increase organic matter content. Maintaining a healthy ground cover layer is essential for sustainable forest management.
Role of Water Management in Erosion Prevention
Effective water management practices, such as constructing swales and check dams, help control runoff and prevent erosion. These structures slow down water flow, allowing it to seep into the ground rather than washing away soil. Proper drainage systems and regular maintenance of waterways are also crucial in minimizing erosion risks.
Wildlife Habitat Management

Identifying Key Species and Their Needs
Understanding the needs of key species in the forest ecosystem is essential for effective wildlife habitat management. This involves identifying critical habitats, food sources, and nesting sites. Conservation efforts should focus on protecting these essential elements and ensuring that the forest environment supports the life cycles of various species.
Creating and Maintaining Nesting Sites, Food Sources, and Shelter
Creating and maintaining nesting sites, food sources, and shelter involves actions such as preserving old-growth trees, installing nesting boxes, and maintaining diverse vegetation. These efforts provide essential resources for wildlife and contribute to a balanced ecosystem. Regular monitoring and adaptive management ensure that these habitats remain functional and beneficial.
Monitoring and Adapting Habitat Management Strategies
Continuous monitoring of wildlife populations and habitat conditions allows for adaptive management. By tracking changes and assessing the effectiveness of management practices, foresters can make informed adjustments. This dynamic approach ensures that habitat management remains relevant and effective in promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Forest Health and Disease Management

Early Detection Techniques for Pests and Diseases
Early detection of pests and diseases is crucial for preventing widespread damage. Techniques include regular visual inspections, installing pheromone traps, and using remote sensing technologies. Early identification allows for targeted interventions, reducing the need for extensive chemical treatments.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators or parasites of pests, offer an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. These methods help maintain a natural balance and reduce the impact of harmful pests. Additionally, promoting biodiversity and healthy ecosystems naturally regulates pest populations.
Best Practices for Maintaining Tree Health
Maintaining tree health involves regular pruning, ensuring adequate water and nutrient supply, and protecting trees from physical damage. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, such as combining biological control with cultural practices, enhances tree health and reduces the risk of disease outbreaks.
Community Involvement and Education

Engaging Local Communities in Sustainable Practices
Engaging local communities in sustainable forestry practices fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Initiatives such as community tree planting events, forest clean-ups, and educational workshops encourage active participation. Collaborative efforts between foresters and communities lead to more effective and sustainable forest management.
Educational Programs and Workshops
Educational programs and workshops provide valuable knowledge and skills to community members. Topics can include tree planting techniques, wildlife conservation, and sustainable resource use. These programs empower individuals to contribute to forest sustainability and promote environmental stewardship.
Benefits of Community Involvement in Forest Management
Community involvement in forest management offers numerous benefits, including increased awareness, enhanced forest protection, and stronger social ties. Communities that actively participate in forest management are more likely to support conservation efforts and sustainable practices, leading to healthier and more resilient forests.
Technological Innovations in Forestry

Emerging Technologies and Their Applications
Emerging technologies, such as remote sensing, GIS, and AI, are transforming sustainable forestry. Remote sensing provides detailed data on forest conditions, while GIS helps in mapping and planning. AI can analyze large datasets to predict trends and optimize management practices. These technologies enhance decision-making and improve forest sustainability.
Benefits and Challenges of New Technologies
The benefits of new technologies include increased efficiency, improved data accuracy, and better forest health monitoring. However, challenges such as high initial costs, the need for specialized training, and potential technical issues must be addressed. Balancing these benefits and challenges is key to successful implementation.
Future Trends in Sustainable Forestry Technology
Future trends in sustainable forestry technology include the integration of IoT devices for real-time monitoring, the use of blockchain for transparent supply chains, and advancements in drone technology. These innovations will continue to enhance sustainable forestry practices, making forest management more efficient and effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are Sustainable Forestry Hacks?
Sustainable forestry hacks are practical, innovative techniques used by forestry professionals to manage forests in a way that maintains their health, biodiversity, and productivity for future generations. These methods aim to balance ecological integrity with economic viability. - Why are species selection and optimal planting techniques important in sustainable forestry?
Species selection and optimal planting techniques are crucial because they ensure that the right trees are planted in suitable locations, promoting healthy growth and biodiversity. Proper species selection helps maintain the ecological balance, supports local wildlife, and enhances forest resilience against diseases and pests. - What is selective logging, and how does it benefit the environment?
Selective logging involves carefully choosing which trees to harvest while preserving the overall structure and health of the forest. This method reduces environmental impact compared to clear-cutting, helps maintain biodiversity, and supports sustainable timber production. - How do advanced monitoring systems improve forest health tracking?
Advanced monitoring systems, such as drones, satellite imagery, and ground sensors, provide real-time data on forest conditions. These technologies enable precise monitoring of forest health, early detection of issues, and informed decision-making for effective forest management. - What techniques are used to enhance biodiversity in forests?
Techniques to enhance biodiversity include mixed-species planting, maintaining natural underbrush, preserving wetland areas, and creating habitat corridors. These methods promote diverse plant and animal life, contributing to a balanced and resilient forest ecosystem. - How can soil erosion be prevented in forestry practices?
Soil erosion can be prevented using methods such as terracing, mulching, planting ground cover vegetation, and constructing swales or check dams. These techniques stabilize the soil, reduce runoff, and protect the forest floor from erosion. - What are some effective wildlife habitat management strategies?
Effective wildlife habitat management strategies include identifying key species and their needs, creating and maintaining nesting sites, food sources, and shelter, and continuously monitoring and adapting habitat management practices to support diverse wildlife populations. - How can early detection of pests and diseases be achieved in forests?
Early detection of pests and diseases can be achieved through regular visual inspections, installing pheromone traps, using remote sensing technologies, and promoting biological control methods. Early identification allows for targeted interventions to prevent widespread damage. - Why is community involvement important in sustainable forestry?
Community involvement is important because it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards forest conservation. Engaging local communities through educational programs, workshops, and collaborative projects leads to more effective and sustainable forest management. - What are some emerging technologies in sustainable forestry?
Emerging technologies in sustainable forestry include remote sensing, GIS, AI, and IoT devices for real-time monitoring. These technologies enhance data accuracy, improve forest health tracking, and support efficient decision-making in forest management. - What are the benefits and challenges of implementing new technologies in forestry?
The benefits of new technologies include increased efficiency, improved data accuracy, and enhanced forest health monitoring. However, challenges such as high initial costs, the need for specialized training, and potential technical issues must be addressed for successful implementation. - What are the future trends in sustainable forestry technology?
Future trends in sustainable forestry technology include the integration of IoT devices, blockchain for transparent supply chains, and advancements in drone technology. These innovations will continue to enhance sustainable forestry practices, making forest management more efficient and effective.

Gilbert Griffin
Forestry AuthorGilbert Griffin is a forest management expert specializing in sustainable practices, forest health, conservation, and land management. With extensive knowledge in pest control, disease management, and habitat restoration, Gilbert develops strategies to preserve forest ecosystems and biodiversity. Passionate about the natural world, Gilbert adapts to changes in forest management and stays updated through continuous learning. Gilbert also provides seasonal advice to optimize forest care throughout the year.


Leave your comment