How to Use GIS Tools in Forest Management
- August 29, 2024
- 2 comment
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized forest management by offering tools and techniques for spatial analysis, data management, and decision-making. In the past, forest management relied on manual surveys and simple maps, which were often outdated and lacked the detailed information needed for effective planning.
With GIS, forestry professionals can now access accurate, real-time data and sophisticated analytical tools that enable more informed decision-making, from monitoring forest health to planning sustainable harvests.
Key GIS Tools and Technologies Used in Forestry
GIS in forestry encompasses a range of tools and technologies designed to collect, analyze, and visualize spatial data. The primary tools include remote sensing technology, which uses satellite or aerial imagery to gather data on forest cover, health, and changes over time.

- Remote Sensing Technology: Covers the use of satellites and aerial imagery to collect data on forest conditions and changes over time.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software: Describes popular GIS software (e.g., ArcGIS, QGIS) used for data analysis and map creation.
- Global Positioning Systems (GPS): Explains the role of GPS in accurate location tracking and mapping within forest areas.
- Drone Technology Integration: Discusses how drones are used for detailed aerial surveys and data collection, offering high-resolution imagery.
GIS software, such as ArcGIS and QGIS, allows users to manipulate and analyze this data, creating detailed maps and models. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) provide precise location data, essential for mapping and navigation in forested areas. Drones are increasingly used to capture high-resolution images and videos, offering new perspectives and detailed data for forest management.
Data Collection and Management in GIS
Data is the backbone of any GIS system. In forestry, data collection can include satellite imagery, aerial surveys, and ground-based measurements. This data is then integrated into a GIS database, where it is organized, stored, and made accessible for analysis.

- Types of Data Used in Forest Management: Describes the different data types, such as spatial data, attribute data, and temporal data.
- Data Sources: Satellite Imagery, Aerial Surveys, and Ground Surveys: Explores the primary sources of data used in GIS, including remote sensing and on-the-ground data collection.
- Data Integration and Storage: Discusses the methods for integrating various data sources into a coherent GIS database and the importance of data storage solutions.
Proper data management is crucial to ensure accuracy, as errors can lead to incorrect conclusions and poor decision-making. Additionally, integrating data from multiple sources, such as combining satellite images with ground surveys, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the forest ecosystem.
Mapping and Analyzing Forest Ecosystems
One of the most significant applications of GIS in forestry is ecosystem mapping. Vegetation mapping, for instance, allows managers to classify and monitor different types of vegetation, assess forest health, and identify areas that may need intervention.
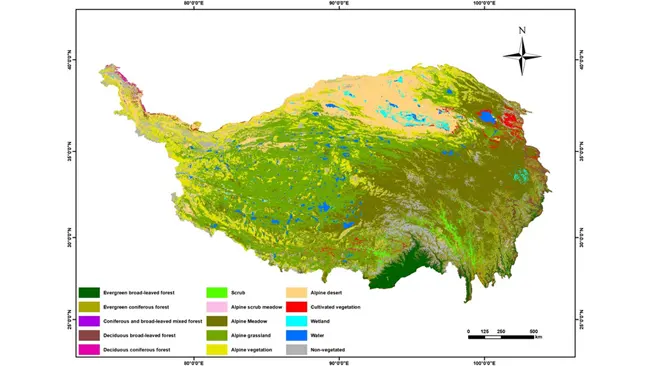
- Vegetation Mapping and Classification: Explains how GIS is used to classify and map different vegetation types, critical for managing forest health.
- Soil and Hydrology Mapping: Covers the mapping of soil types and water resources, essential for understanding forest ecosystems.
- Wildlife Habitat Mapping and Analysis: Details the use of GIS in identifying and analyzing wildlife habitats to support conservation efforts.
Soil and hydrology mapping helps in understanding the underlying environmental factors that affect forest growth and health. Wildlife habitat mapping is also crucial, as it helps in planning conservation efforts and ensuring that forest management practices do not adversely affect local biodiversity.
Forest Inventory and Monitoring
GIS plays a critical role in forest inventory and monitoring, providing tools for identifying tree species, estimating tree density, and assessing forest health.
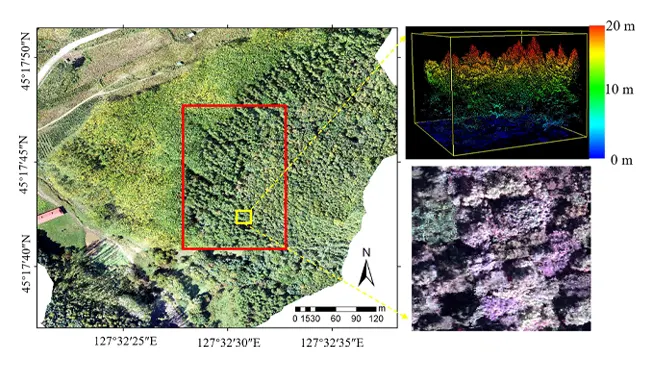
- Tree Species Identification and Distribution: Discusses how GIS helps in identifying tree species and understanding their distribution patterns.
- Forest Health Monitoring: Covers the tools and techniques used to monitor forest health, including the detection of diseases and pest infestations.
- Estimating Forest Biomass and Carbon Sequestration: Explains how GIS is used to estimate forest biomass and its role in carbon sequestration, important for climate change mitigation.
This data is vital for sustainable forest management, as it informs decisions on timber harvesting, reforestation, and conservation. Additionally, GIS tools can estimate forest biomass and carbon sequestration, which are important metrics in the context of climate change and carbon trading schemes.
Fire Management and Prevention with GIS
Fire management is a critical aspect of forest management, and GIS provides invaluable tools for predicting, monitoring, and mitigating forest fires. Predictive modeling uses historical data and environmental variables to assess fire risk and plan preventative measures.
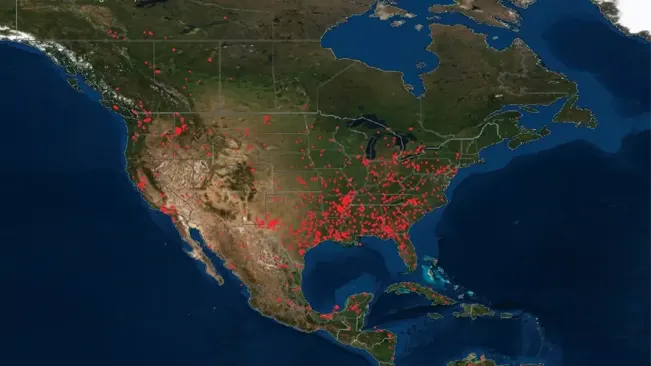
- Predictive Modeling for Fire Risk Assessment: Details the use of GIS for creating models that predict fire risk based on environmental conditions.
- Monitoring Active Fires: Discusses how GIS is used in real-time to monitor the spread of active forest fires and coordinate firefighting efforts.
- Post-Fire Recovery and Rehabilitation: Explains the role of GIS in assessing fire damage and planning the recovery of affected forest areas.
During active fires, GIS helps in tracking the fire’s spread, coordinating firefighting efforts, and protecting valuable resources. After a fire, GIS is used to assess damage and plan recovery efforts, ensuring that the forest can regenerate and that future fire risks are minimized.
Land Use Planning and Sustainable Forest Management
GIS is essential in land use planning, helping forest managers allocate land for various uses, such as timber production, conservation, and recreation. Zoning maps created with GIS can ensure that these activities are balanced and that forest resources are used sustainably.
- Zoning and Land Use Allocation: How GIS aids in the creation of zoning maps that allocate forest land for different uses, balancing conservation with commercial activities.
- Sustainable Timber Harvesting: The role of GIS in planning and monitoring timber harvests to ensure they are conducted sustainably, minimizing environmental impact.
- Conservation Planning and Protected Areas: GIS tools used in identifying and managing protected areas, ensuring that biodiversity and ecosystem services are preserved.
For example, GIS can help in planning sustainable timber harvesting by identifying areas that are suitable for logging while preserving critical habitats and preventing soil erosion.
GIS in Forest Conservation Efforts
Conservation is a key aspect of forest management, and GIS is a powerful tool for protecting biodiversity and managing conservation areas. By mapping species distribution and habitat types, GIS helps in identifying critical areas for conservation. Additionally, GIS can be used to monitor endangered species and track the success of habitat restoration projects, ensuring that conservation efforts are effective and adaptive to changing conditions.
Climate Change Impact Assessment Using GIS
As climate change continues to impact forests worldwide, GIS is increasingly used to monitor and assess these changes. GIS tools can track shifts in forest cover, identify areas vulnerable to climate change, and model the potential impacts of different climate scenarios. This information is vital for developing strategies to mitigate climate change’s effects on forests, such as planning for species migration or implementing forest management practices that enhance resilience.
GIS in Community-Based Forest Management
Community involvement is crucial for successful forest management, and GIS can facilitate participatory mapping and decision-making. By involving local communities in the mapping process, forest managers can ensure that their knowledge and needs are incorporated into management plans. GIS also supports indigenous land rights by providing tools for documenting and mapping traditional territories, ensuring that these areas are recognized and protected.
Conclusion
GIS has become an indispensable tool in forest management, providing the data and analysis needed for sustainable and effective decision-making. From mapping ecosystems to monitoring climate change impacts, GIS enables forest managers to address the complex challenges of modern forestry. As technology continues to evolve, the role of GIS in forest management will only grow, offering new opportunities for innovation and improving the stewardship of our planet’s forests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is GIS, and how is it used in forest management?
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is a technology that allows the collection, analysis, and visualization of spatial data. In forest management, GIS is used for mapping forest resources, monitoring forest health, planning sustainable land use, and supporting conservation efforts. - What are the key benefits of using GIS in forest management?
The key benefits of using GIS in forest management include improved decision-making through accurate data analysis, enhanced ability to monitor and manage forest resources, better planning for sustainable use, and more effective conservation strategies. - Which GIS tools are most commonly used in forestry?
Common GIS tools used in forestry include remote sensing technology, GIS software like ArcGIS and QGIS, GPS devices, and drones for aerial surveys. - How does GIS help in monitoring forest health?
GIS helps monitor forest health by enabling the analysis of satellite imagery and other data to detect changes in vegetation, identify areas affected by disease or pests, and assess the overall condition of the forest ecosystem. - Can GIS be used for fire management in forests?
Yes, GIS is widely used in fire management. It helps in predicting fire risk, monitoring active fires, coordinating firefighting efforts, and planning post-fire recovery. - How does GIS contribute to sustainable forest management?
GIS contributes to sustainable forest management by providing tools for land use planning, monitoring the impacts of logging, ensuring that resources are used responsibly, and supporting conservation initiatives. - What challenges are associated with using GIS in forest management?
Challenges include data accuracy and quality issues, high costs of technology and training, the complexity of integrating GIS with traditional knowledge, and the need for continuous system updates. - How is GIS used in community-based forest management?
GIS is used in community-based forest management by enabling participatory mapping, supporting the recognition of indigenous land rights, and facilitating community involvement in decision-making processes. - What role does GIS play in assessing the impact of climate change on forests?
GIS plays a crucial role in assessing climate change impacts by tracking changes in forest cover, modeling future scenarios, and helping to develop strategies for adaptation and mitigation - What is the future of GIS in forest management?
The future of GIS in forest management includes the integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning, improved remote sensing capabilities, and the development of global monitoring systems to enhance forest conservation and management efforts.

Jordan Blake
Forestry AuthorJordan Blake is a forestry expert with over 15 years of experience in arboriculture and community education. Passionate about sustainable forest management, Jordan regularly writes for Forestry.com and Tree Care Magazine. Holding certifications in tree health assessments and urban forestry management, Jordan conducts workshops to educate the public on sustainable practices. Jordan has a degree in Environmental Science and enjoys hiking and photography in their free time.













i have interested with book,it will help in my project
NIYOMUGABO Enock
October 9, 2024 9:24 amThanks for your interest! I’m glad to hear this post could be helpful for your project. Feel free to reach out if you have any specific questions or need more information!
Jordan Blake
October 11, 2024 12:18 am