5 Shocking Secrets About Deforestation and Global Warming
- September 24, 2024
- 0 comment
As the world grapples with the escalating crisis of global warming, one culprit lurks in the shadows, often underestimated: deforestation. This destructive practice not only robs us of our precious forests but also plays a significant and shocking role in accelerating climate change.
What is Deforestation?
Deforestation refers to the widespread and deliberate removal of forest cover. This process typically occurs when forested areas are cleared for agricultural expansion, urban development, logging, or mining. Trees are either cut down or burned, transforming forested lands into non-forest use. The implications of deforestation extend beyond mere loss of trees; it significantly impacts the biodiversity, climate, and ecosystems services that forests provide. Forests are crucial for carbon storage, absorbing a substantial amount of the world’s carbon dioxide emissions. Thus, when they are removed, not only is this carbon storage capacity lost, but the carbon stored in trees is released back into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming.

Globally, deforestation is driven by several economic and social factors. In regions like the Amazon, the expansion of agricultural lands, especially for commodities like soy and beef, is a primary driver. In Indonesia, large-scale palm oil production leads to significant forest loss. Deforestation not only results in the decline of habitat for countless species, contributing to biodiversity loss, but it also affects local communities, particularly indigenous groups whose livelihoods depend on forests. Moreover, the alteration of landscapes due to deforestation affects local climates and reduces the availability of clean air and water, further demonstrating the profound and far-reaching consequences of this environmental issue.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, creating what is known as the greenhouse effect. This effect is natural and necessary for life on Earth as it keeps the planet warm enough to sustain life. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, and deforestation, have intensified this effect, leading to higher temperatures.

The consequences of global warming are wide-ranging and severe. They include more frequent and severe weather events like hurricanes, floods, and droughts; rising sea levels due to melting polar ice caps and glaciers, which threaten coastal communities; and disruptions to ecosystems and biodiversity, such as shifts in animal migration patterns and plant blooming times. Additionally, global warming impacts human health, agriculture, water supplies, and even economic stability, making it a critical issue of our time that requires concerted global action to manage and mitigate.
How is Global Warming Linked to Deforestation?
Global warming and deforestation are closely connected through critical environmental mechanisms. Forests, acting as carbon sinks, absorb substantial amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, when these forests are removed, this capability diminishes, and the stored carbon is released, elevating greenhouse gas levels and intensifying global warming. Additionally, forests help regulate local and global climates through evapotranspiration, which affects humidity and atmospheric temperatures. The loss of trees disrupts this balance, potentially increasing temperatures further.

Secondary impacts of deforestation also aggravate global warming. Soil erosion, triggered by deforestation, degrades land and alters the Earth’s albedo, reducing its ability to reflect sunlight and thereby heating the local environment. Moreover, the reduction in water vapor released into the atmosphere from deforested areas decreases cloud formation and can reduce rainfall, impacting climate patterns. These interconnected effects emphasize the dual role of deforestation in heightening global warming, highlighting the urgent need for effective forest management and conservation strategies.
Here are 5 Shocking Secrets Link About Deforestation and Global Warming
1. Carbon Storage Capacity of Forests
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change through their ability to sequester carbon dioxide, a principal greenhouse gas. Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in their wood, leaves, and soil, effectively acting as carbon sinks. It’s estimated that tropical forests alone can store about 229 billion tons of carbon in their biomass.

However, when forests are cleared or burned, not only is this carbon storage capacity lost, but the stored carbon is also released back into the atmosphere, contributing to increased CO2 levels and global warming. The impact is particularly severe in primary forests, which are mature and have developed complex ecosystems, compared to secondary forests, which are generally younger and have less accumulated biomass and biodiversity.
2. Albedo Effect Changes Due to Deforestation
The albedo effect refers to the reflectivity of the Earth’s surface; ice, for example, has a high albedo compared to other surface types and reflects more sunlight back into space. Forests generally have a lower albedo, meaning they absorb more heat, which helps in moderating the planet’s temperature.
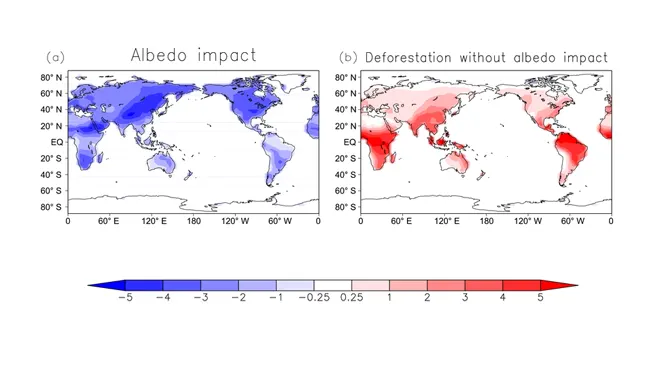
When forests are removed, the land surface often becomes lighter, such as when replaced by agriculture or urban areas, thus increasing the albedo and reflecting more sunlight back into the atmosphere. This change can alter local climate conditions, often leading to higher surface temperatures. Studies have shown that in regions like the Amazon, deforestation has led to measurable increases in local temperatures due to these changes in albedo.
3. Impact on Water Vapor and Cloud Formation
Forests significantly influence the water cycle through the process of Evapotranspiration where water is transferred from the land to the atmosphere by evaporation and by transpiration from plants. This process not only helps in maintaining local and regional humidity levels but also contributes to cloud formation, which can cool the Earth’s surface by reflecting sunlight away.
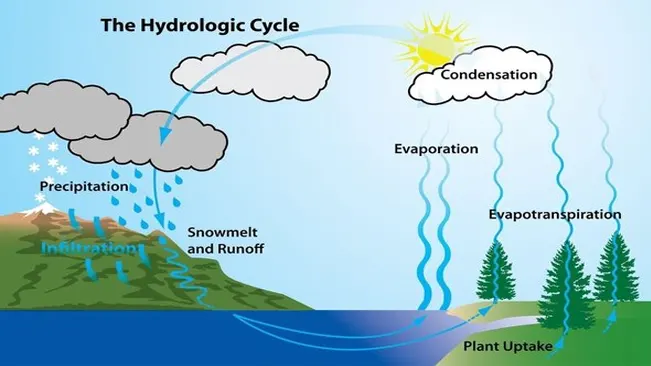
Deforestation disrupts these processes, reducing atmospheric moisture and cloud cover, which can lead to a drier climate and enhanced warming. Research indicates that in areas like Southeast Asia, extensive deforestation has resulted in decreased cloud cover and altered rainfall patterns, exacerbating the effects of global warming.
4. Loss of Biodiversity and Its Climate Implications
Forests are rich ecosystems that support a diverse range of species, and their biodiversity is crucial for ecological stability and climate resilience. The loss of forests due to deforestation leads to a significant reduction in biodiversity, as species lose their habitats and are pushed towards extinction.

This loss of biodiversity not only affects ecological balance but also reduces the resilience of ecosystems to climate changes. Studies have shown that diverse ecosystems can better withstand and adapt to climate variations, whereas areas with reduced biodiversity are less adaptable and more susceptible to the impacts of global warming.
5. Socioeconomic Practices That Exacerbate Deforestation and Global Warming
The expansion of agricultural land, along with logging and mining, are primary drivers of deforestation globally. These practices are often fueled by global economic demands for commodities such as palm oil, soy, beef, and timber. The removal of forests for such activities not only reduces carbon storage and biodiversity but also contributes directly to increased greenhouse gas emissions.

Moreover, these socioeconomic practices often lead to unsustainable land use, further intensifying their environmental impact. The interconnections of local actions and global climate effects underscore the need for sustainable practices and policies to mitigate deforestation and its contributions to global warming.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between deforestation and global warming is significant and impactful. The destruction of forests leads to the release of stored carbon, amplifying the greenhouse effect and disrupting essential natural processes like the albedo effect and water vapor production. Additionally, the loss of biodiversity compromises the ecological stability necessary to combat climate change. Socioeconomic activities such as agriculture, logging, and mining drive deforestation, posing challenges to environmental sustainability. To mitigate these effects, a global commitment to sustainable land management and conservation is crucial. By addressing these interconnected issues, we can help lessen global warming and preserve our planet for future generations.
FAQs
- What is deforestation?
Deforestation refers to the large-scale removal or thinning of forest vegetation, primarily due to human activities such as logging, agriculture, and urban development. - How does deforestation contribute to global warming?
Deforestation contributes to global warming by releasing significant amounts of stored carbon dioxide when trees are cut down and burned. This increases greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect and raising Earth’s temperature. - What is the albedo effect and how is it related to deforestation?
The albedo effect describes how surfaces reflect sunlight. Forested areas have a low albedo, absorbing more heat. When trees are removed, the land surface often becomes lighter, reflecting more sunlight and heat, which can contribute to local and global temperature increases. - How does deforestation affect biodiversity and climate change?
Deforestation leads to loss of habitat, which is critical for many species, thereby reducing biodiversity. This loss affects ecological balance and reduces the resilience of natural systems to climate change, as diverse ecosystems are better at adapting to environmental changes. - What socioeconomic practices exacerbate deforestation?
Key practices include agricultural expansion, logging, and mining, driven by global demand for commodities like timber, palm oil, and minerals. These activities directly lead to forest degradation and contribute to increased carbon emissions. - Can reforestation help combat global warming?
Yes, reforestation can significantly mitigate global warming. Planting trees helps absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, restoring the balance of greenhouse gases and aiding in climate regulation. - What are some effective strategies to prevent deforestation?
Effective strategies include enforcing strict forestry laws, promoting sustainable land use practices, supporting Eco-friendly businesses, and raising awareness about the impacts of deforestation. - How can individuals contribute to reducing deforestation?
Individuals can help by consuming products that are certified as sustainable, supporting conservation efforts, reducing meat consumption, and advocating for policies that protect forests.

Joel Cunningham
Forestry AuthorI'm Joel Cunningham, an expert in pruning and weed management with over a decade of experience. My skills are rooted in formal training and extensive practice, focusing on advanced pruning techniques and efficient weed control. I'm known for my quality work, precision, and deep understanding of plant health and soil dynamics. My contributions extend to educational initiatives where I share sustainable practices and advice, establishing myself as a reliable and authoritative figure in the gardening community.













Leave your comment