Eastern Cottonwood Poplar Lumber
- July 31, 2023
- 0 comment
Eastern Cottonwood Poplar lumber, derived from the Populus deltoides tree, boasts its origin as a native domestic hardwood in North America. Renowned for its distinctive rapid growth rate, Eastern Cottonwood thrives in wetland regions and alongside riverbanks, making it a common sight in such environments. Its prevalence and fast growth contribute to its popularity as a source of lumber for various applications.
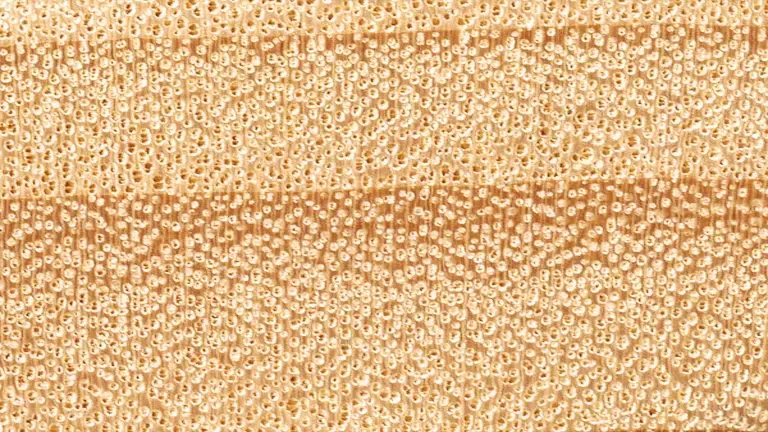
The lumber derived from Eastern Cottonwood Poplar is favored for its relatively lightweight characteristics, making it easy to handle and work with. Its pliability and straightforward workability lend themselves well to woodworking projects, allowing craftsmen to shape, cut, plane, and sand the wood with ease.
These favorable attributes make it a preferred choice for various indoor projects, including furniture, cabinetry, millwork, and plywood, as well as for crafting boxes, pallets, and crates due to its affordability and availability. In addition to its practical applications, Eastern Cottonwood Poplar also holds ecological significance due to its role in sustainable forestry practices. With its rapid growth and capacity for regeneration, it stands as an environmentally responsible option for lumber sourcing.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Name(s) | Eastern Cottonwood, Cottonwood |
| Scientific Name | Populus deltoides |
| Distribution | North America |
| Tree Size | 80-100 feet tall, 3-5 feet trunk diameter |
| Avg. Dried Weight | 24 lbs/ft^3 (385 kg/m^3) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.39 |
| Janka Hardness | 430 lbf (1,910 N) |
| Modulus of Rupture | 7,300 lbf/in^2 (50.3 MPa) |
| Elastic Modulus | 1,070,000 lbf/in^2 (7.38 GPa) |
| Crushing Strength | 3,500 lbf/in^2 (24.1 MPa) |
| Shrinkage | Radial: 4.0%, Tangential: 7.6%, Volumetric: 11.8% |
Color/Appearance:
The heartwood of Eastern Cottonwood is usually a pale brown to light gray, while the sapwood tends to be slightly lighter in color. The wood can display subtle streaks or variations in tone, resulting in a pleasing appearance when finished.
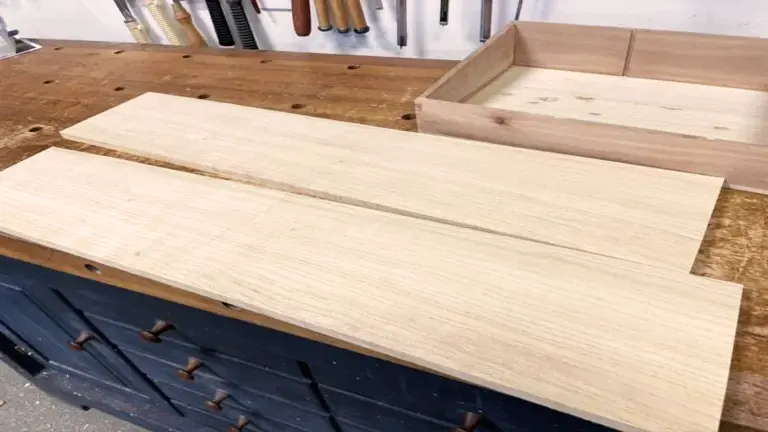



Grain/Texture:
The grain of Cottonwood is typically straight, with a fine to medium texture. It has a low natural luster, and the surface takes finishes well, offering a smooth and attractive appearance.
Rot Resistance:
Eastern Cottonwood is not naturally durable and is susceptible to decay and insect attack. As such, it is best suited for indoor or protected applications.
Workability:
This wood is easy to work with both hand and machine tools. It cuts, planes, and sands smoothly, making it a popular choice for various woodworking projects. However, care should be taken when nailing or screwing, as it can be prone to splitting.
Odor:
Eastern Cottonwood may have a faint, somewhat unpleasant odor when freshly cut, which tends to dissipate as the wood dries.
Allergies/Toxicity:
While there have been no significant reports of allergic reactions to Eastern Cottonwood, as with any wood, it’s advisable to take basic precautions like using dust masks and proper ventilation when working with it.
Pricing/Availability:
Eastern Cottonwood is generally more affordable compared to many other hardwoods, making it an economical choice for projects. Its availability can vary depending on the region and local demand.
Sustainability:
Eastern Cottonwood is relatively fast-growing and readily regenerates, making it a sustainable choice for responsible forestry practices.
Common Uses:
Eastern Cottonwood Poplar lumber finds applications in various indoor projects, including cabinetry, furniture, millwork, and plywood. It is also used for boxes, pallets, and crates due to its lightweight and low cost.

FAQs:
- Is Eastern Cottonwood a suitable wood for outdoor use?
No, Eastern Cottonwood is not naturally resistant to decay or insects, making it unsuitable for outdoor applications without proper protective treatments. - How does Eastern Cottonwood compare to other hardwoods in terms of hardness?
Eastern Cottonwood is relatively soft compared to many other hardwoods, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications that require high resistance to wear and denting. - Can Eastern Cottonwood be stained or finished easily?
Yes, Eastern Cottonwood accepts stains and finishes well, producing a smooth and attractive surface when properly prepared and treated. - Is Eastern Cottonwood a good choice for carving or intricate detailing?
Yes, its ease of workability and fine texture make Eastern Cottonwood suitable for carving and delicate woodworking projects. - How does Eastern Cottonwood lumber differ from Western Cottonwood?
While they share similar characteristics, Eastern Cottonwood (Populus deltoides) is typically considered slightly denser and harder than Western Cottonwood (Populus trichocarpa). However, the differences are generally subtle and may not significantly impact most woodworking applications.








Leave your comment