Colville National Forest
- January 18, 2024
- 0 comment
Discover the hidden beauty of the Colville National Forest, a spectacular natural treasure tucked away in the northeastern corner of Washington State. Spread across a vast expanse of over 1.1 million acres, this forest is a kaleidoscope of nature’s best offerings. Imagine towering trees that whisper stories of the ages, and landscapes that shift from gentle streams to majestic mountains.
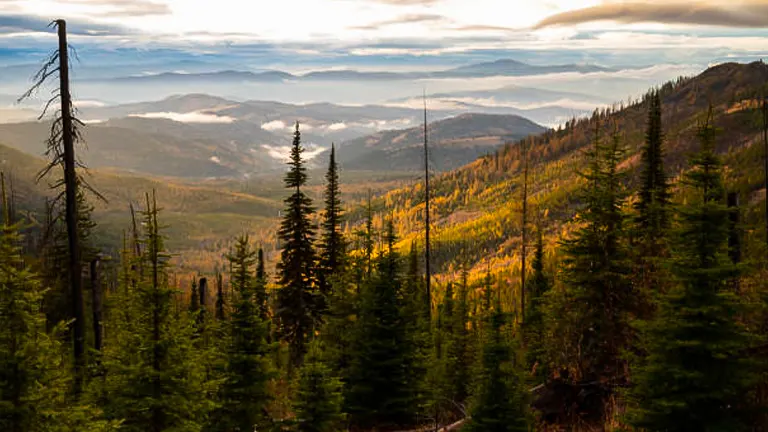

It’s a playground for adventurers and a sanctuary for wildlife, where each trail leads to a new discovery. Whether you’re a hiker, a wildlife enthusiast, or just someone seeking a moment of peace, the Colville National Forest is a destination that promises to capture your heart and ignite your imagination.
Characterizing Features
- Kettle River and Selkirk Mountain Ranges: The Colville National Forest is defined by the majestic Kettle River and Selkirk mountain ranges. These ranges offer not just a stunning backdrop but also a diverse range of recreational activities. The Kettle River Range, known for its rolling hills and scenic valleys, contrasts beautifully with the rugged and more alpine terrain of the Selkirk Range. This variety in topography makes the forest an appealing destination for hikers, climbers, and nature enthusiasts.
- Upper Columbia River: Flowing gracefully through the forest, the Upper Columbia River is a cornerstone of the region’s ecosystem. This river is not just a source of natural beauty, but it also provides vital habitats for numerous aquatic species. The river’s presence contributes significantly to the biodiversity of the area and offers recreational opportunities such as fishing, boating, and riverside camping.
- Columbia Mountains: Part of the forest’s unique geography includes the Columbia Mountains, which form the western foothills of the Rocky Mountains. This region is characterized by its diverse geology and distinct ecosystems. The Columbia Mountains within the Colville National Forest are a haven for geologists, ecologists, and those who simply appreciate the awe-inspiring power of nature’s creations.
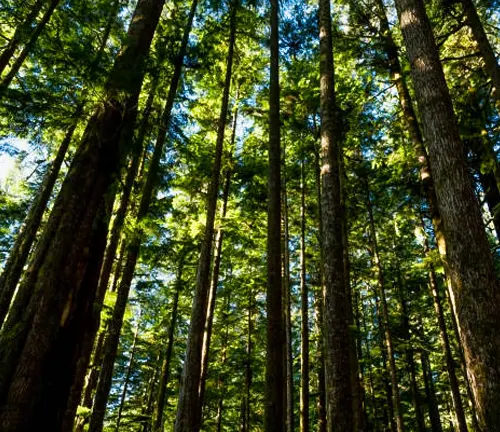
- Diverse Ecosystems and Landscapes: The Colville National Forest is a mosaic of ecosystems ranging from wetlands and river valleys to mountainous terrains. This diversity supports a wide array of flora and fauna, making it a hotspot for biodiversity. The forest’s landscapes change with elevation and orientation, offering varied experiences for visitors. From lush, dense forests in lower areas to alpine meadows in higher elevations, the forest showcases nature’s versatility.
- Historical and Cultural Significance: Beyond its natural beauty, the Colville National Forest is steeped in history and culture. From ancient times, when Native American tribes utilized these lands, through the era of European settlement and the establishment of the forest reserve in the early 20th century, the area has been a witness to a rich tapestry of human history. This historical depth adds an enriching layer to the visitor experience, offering a glimpse into the past and the evolution of land management practices.
- Recreational Hub: The forest serves as a premier destination for a variety of recreational activities. Its extensive network of trails, campgrounds, and waterways makes it a favorite among hikers, campers, anglers, and outdoor enthusiasts. The forest’s recreational offerings are designed to cater to both adventure seekers and those looking for a peaceful retreat in nature.
- Wildlife Sanctuary: Home to a diverse array of wildlife, the Colville National Forest is a sanctuary for species such as grizzly bears, wolves, and bald eagles. The forest’s habitats range from dense forests to open meadows and wetlands, each supporting different wildlife populations. This rich animal life not only contributes to the forest’s ecological diversity but also offers unique wildlife viewing opportunities for visitors.
Each of these features contributes to the Colville National Forest’s identity as a cherished natural area, offering a blend of ecological richness, recreational opportunities, and a window into America’s environmental history.
History
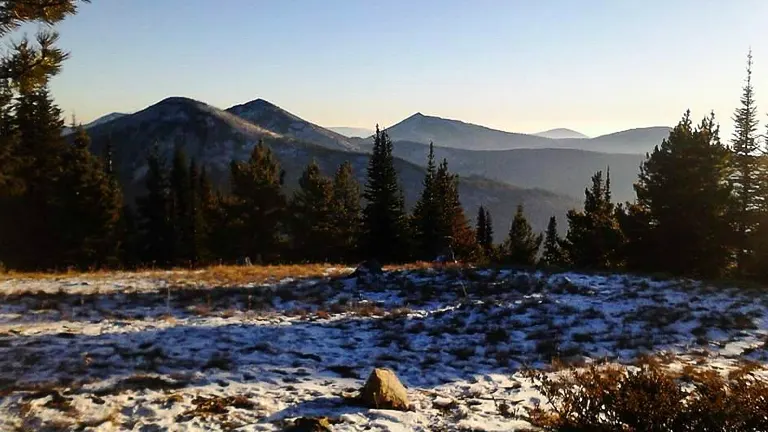

The Colville National Forest, located in northeastern Washington, was established on March 1, 1907, during President Theodore Roosevelt’s administration, as part of a nationwide effort to create forest reserves. Initially encompassing about 700,000 acres, the forest has since expanded to 1.5 million acres. It stretches from north of the Colville Indian Reservation to the Canadian Border, bordered by the Columbia River to the west and the Okanogan River to the east. The first Forest Supervisor, W.W. Cryder, managed the forest from its initial headquarters in Republic, Washington.
Throughout its history, the Colville National Forest has undergone significant changes, both in management and in land use. The forest’s boundaries and management objectives have been adjusted over time to meet evolving conservation and public use needs. Its landscape, shaped by natural forces like the Ice Age glaciers, has been a home to Native Americans, a site for fur trading, and affected by developments such as the construction of the Grand Coulee Dam in the 1930s, which led to the flooding of Kettle Falls and affected local salmon populations. Today, the Colville National Forest is a significant area for conservation, recreation, and natural resource management, reflecting a balance between environmental preservation and public enjoyment.
The Importance of Conservation and Recreation in Colville National Forest
The Colville National Forest holds significant value in both conservation and recreation. As a key conservation area, it plays a crucial role in preserving diverse ecosystems and wildlife habitats in northeastern Washington. Covering 1.5 million acres, the forest is home to a variety of species including grizzly bears, wolves, and bald eagles, and contributes to the ecological balance of the region. Its landscapes, ranging from mountainous terrains to river valleys, are not only important for wildlife but also act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate regulation.
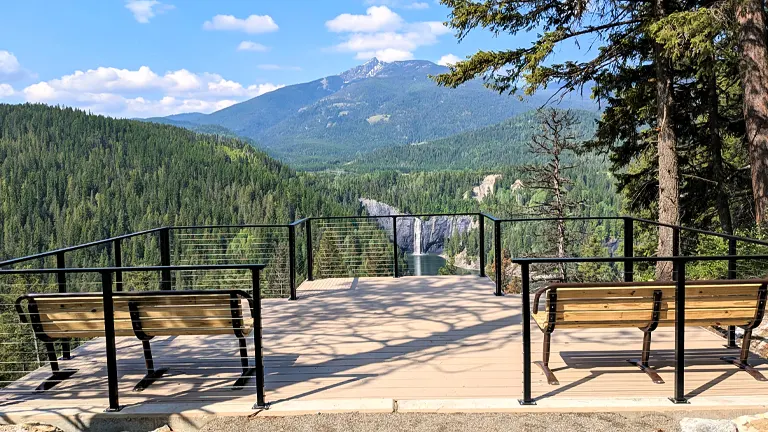

In terms of recreation, the Colville National Forest offers a wide array of activities that attract nature enthusiasts from all over. With over 486 miles of trails, it is a haven for hikers, bikers, and horseback riders. The forest’s rivers and lakes provide opportunities for fishing, boating, and swimming, while its diverse terrain makes it popular for camping and wildlife viewing. In winter, the forest transforms into a playground for snow sports like skiing and snowmobiling. This blend of recreational opportunities not only promotes outdoor lifestyles and public health but also plays a vital role in the local economy through tourism. Overall, the Colville National Forest is an invaluable asset, balancing the needs of conservation with the benefits of outdoor recreation.
Unique Location
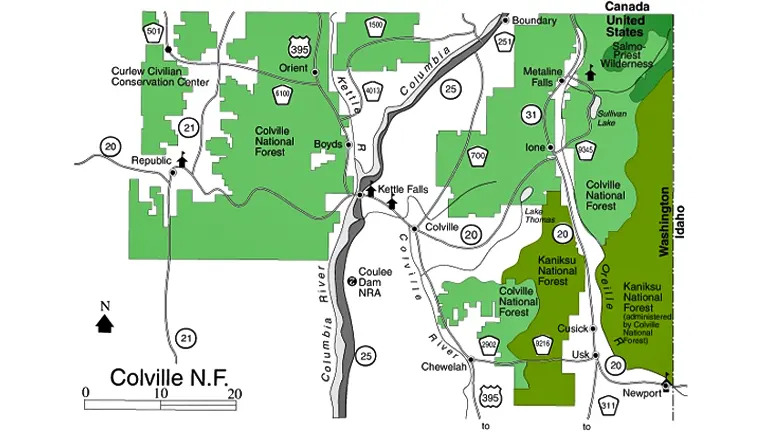
The Colville National Forest is uniquely located in northeastern Washington State, encompassing a diverse and strategic geographic area. Its location is characterized by the convergence of the Kettle River and Selkirk mountain ranges, part of the larger Columbia Mountains, which are the foothills of the Rocky Mountains. This positioning gives the forest a varied topography, from high mountain peaks to deep river valleys. It covers a total area of 1.5 million acres, extending from north of the Colville Indian Reservation to the Canadian border, and is flanked by the Columbia River to the west and the Okanogan River to the east. This distinctive setting not only provides a range of ecosystems, including old-growth forests and alpine meadows, but also makes the forest a corridor for wildlife and a catchment area for significant waterways. The Colville National Forest’s unique location contributes greatly to its ecological diversity, recreational opportunities, and its role in regional environmental health and water resource management.
Diverse Vegetation and Plant Species
- Old Growth Forests: The forest contains significant areas of old growth, including species like Western Red Cedar (Thuja plicata), Douglas Fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), and Western Hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla). These ancient ecosystems are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and serve as a habitat for many species.
- Huckleberries: Wild huckleberries (Vaccinium) are a staple in the forest. These berries not only provide food for wildlife but are also a popular foraging item for visitors.
- Ponderosa Pine: The Ponderosa Pine (Pinus ponderosa), known for its tall and straight trunk, thrives in the drier areas of the forest. It plays a key role in the forest ecology by providing habitat and food for wildlife.
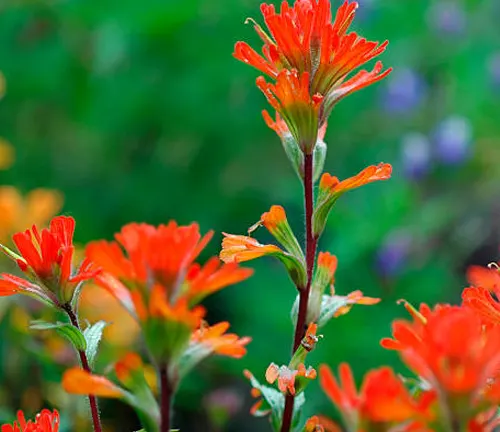
- Alpine Meadows: At higher elevations, the forest features alpine meadows with a variety of grasses and wildflowers, including lupines (Lupinus) and Indian Paintbrush (Castilleja). These meadows are not only visually stunning but also important for pollinators and other wildlife.
- Riparian Vegetation: Along rivers and lakes, the forest supports diverse riparian vegetation, including willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus). These plants are vital for stabilizing riverbanks and supporting aquatic ecosystems.


Fauna
- Grizzly Bears (Ursus arctos): Though rare, the forest is one of the few places in Washington where grizzly bears are found, making it an important habitat for this threatened species.
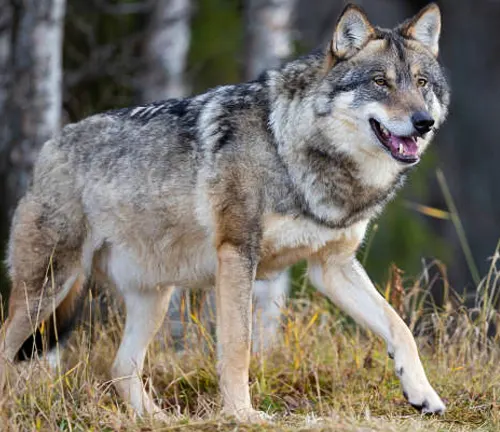
- Gray Wolves (Canis lupus): The forest provides a refuge for gray wolves, a species that plays a crucial role in the ecological balance by controlling prey populations and enhancing biodiversity.
- Bald Eagles (Haliaeetus leucocephalus): The majestic bald eagle, a symbol of American wildlife, is frequently seen along the waterways of the forest, where it nests and hunts.
- Canada Lynx (Lynx canadensis): This elusive cat inhabits the forest, particularly in areas with dense undergrowth, making the forest important for its conservation.
- Mountain Goats (Oreamnos americanus): Inhabiting the rocky and mountainous areas of the forest, mountain goats are a spectacular sight and are adapted to life in challenging terrains.
- Elk (Cervus canadensis): Large herds of elk roam the forest, especially in meadows and clearings. They are a vital part of the forest’s ecosystem and a popular sight among wildlife watchers.
- Moose (Alces alces): The Colville Forest is home to the largest member of the deer family, the moose, which is commonly found in wetland areas and near streams.


Each of these vegetation types and animal species contributes to the rich tapestry of life in the Colville National Forest, making it a diverse and ecologically significant area.
Different Attractions in Colville National Forest
1. Salmo-Priest Wilderness
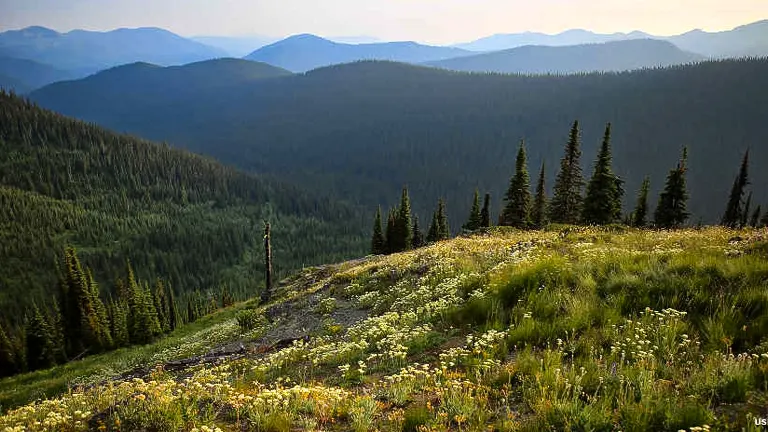

This remote wilderness area, located in the northernmost part of the forest, is a haven for those seeking solitude and unspoiled nature. The Salmo-Priest Wilderness is known for its rugged terrain, stunning old-growth forests, and the opportunity to see rare wildlife like the grizzly bear and Canada lynx. It’s a perfect destination for experienced hikers and backpackers who want to immerse themselves in a pristine natural environment.
2. Kettle River Range
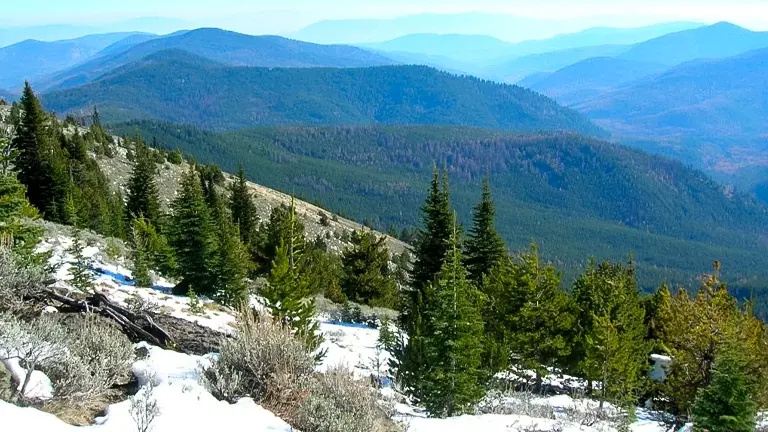

This range is a paradise for hikers and outdoor enthusiasts, offering stunning views and a variety of trails. The Kettle River Range is particularly famous for its beautiful vistas and diverse landscapes, ranging from forested valleys to alpine meadows. It’s an ideal spot for day hikes, photography, and wildlife observation.
3. Lake Roosevelt National Recreation Area
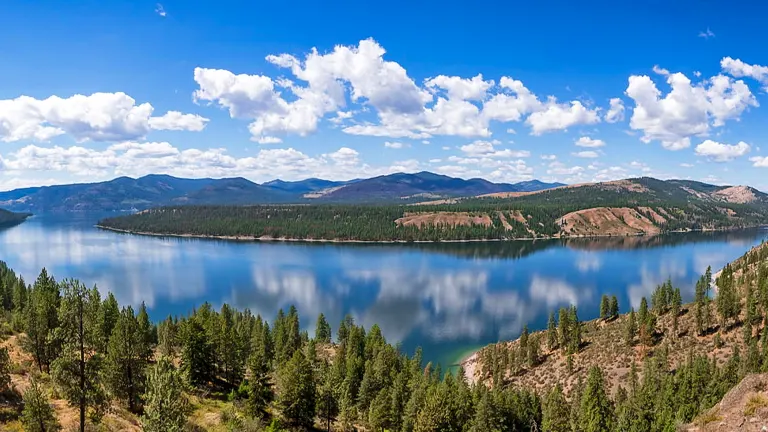

Adjacent to the Colville National Forest, this recreation area offers a plethora of activities such as boating, fishing, swimming, and camping. Lake Roosevelt, formed by the Grand Coulee Dam, spans 130 miles and provides a scenic backdrop for a range of water-based recreational activities. Its shores also offer picnicking spots and opportunities for bird watching.
4. Little Pend Oreille National Wildlife Refuge
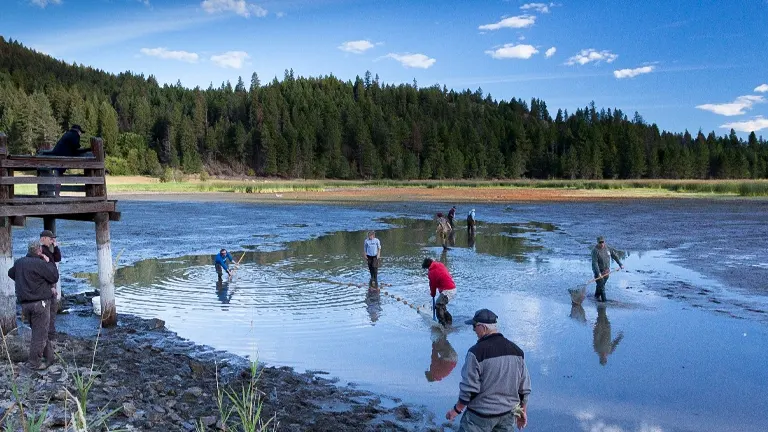

Bordering the forest, this wildlife refuge is a haven for birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts. It’s home to a diverse array of bird species, as well as other wildlife like deer and moose. The refuge’s varied habitats, including wetlands, forests, and meadows, make it an excellent spot for nature walks and photography.
5. Sherman Pass Scenic Byway
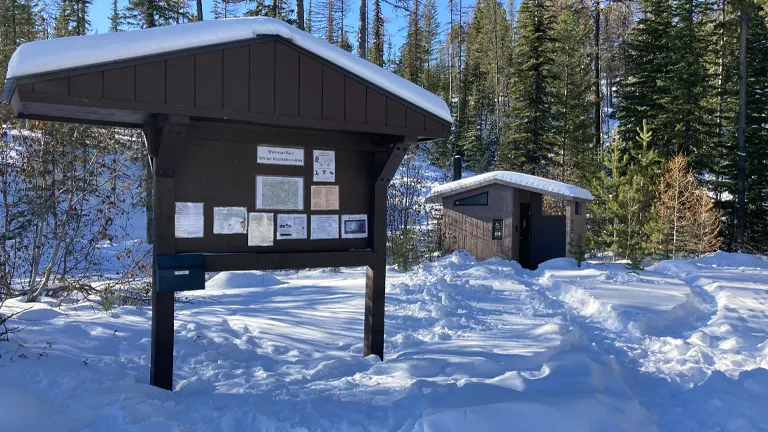

This byway, running through the forest, offers one of the most scenic drives in the region. It winds through mountainous terrain and provides breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape. Along the way, there are several viewpoints and picnic areas where travelers can stop to enjoy the scenery and learn about the forest’s ecology and history through interpretive signs.
6. Sullivan Lake
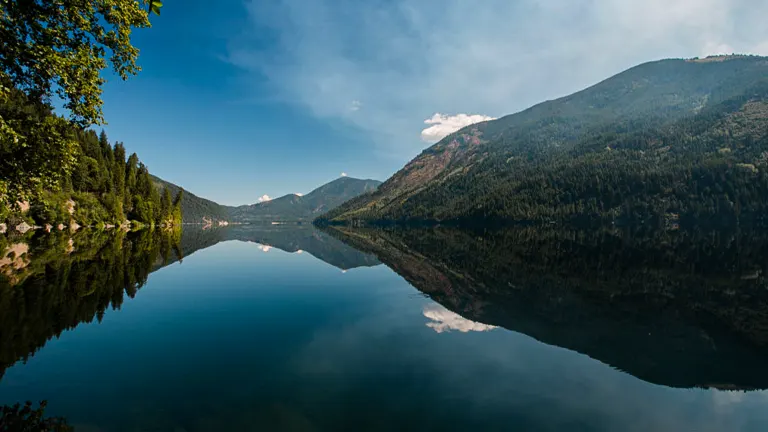

A picturesque lake nestled within the forest, Sullivan Lake is a popular destination for camping, fishing, and boating. The lake is surrounded by mountains and forests, offering a tranquil setting for relaxation and recreation. It also has well-maintained campgrounds, making it a great spot for family outings and weekend getaways.
Each of these attractions offers a unique way to experience the natural beauty and recreational opportunities of the Colville National Forest, making it a diverse and appealing destination for visitors of all interests.
Recreational Activities in Colville National Forest
1. Hiking and Backpacking
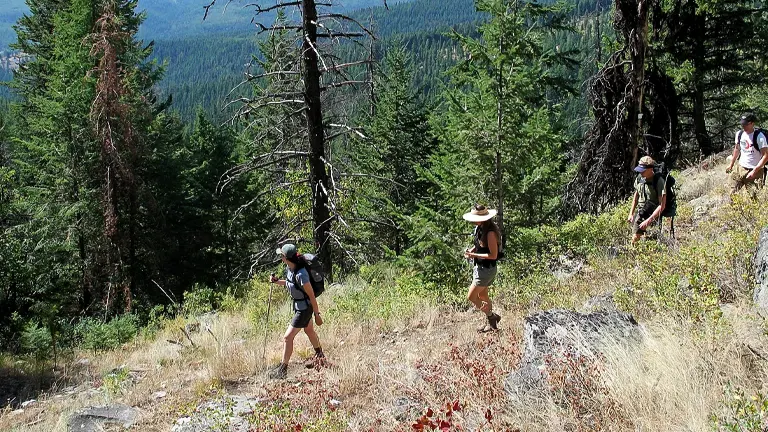

With over 486 miles of trails, Colville National Forest is a hiker’s paradise. These trails range from easy walks through serene forests to challenging treks in the mountainous terrain. Backpackers can immerse themselves in the wilderness, exploring the diverse landscapes, from lush valleys to alpine meadows.
2. Camping

The forest offers a wide range of camping experiences, from developed campgrounds with amenities to backcountry sites for a more rugged adventure. Campers can enjoy the tranquility of the forest, starry nights, and the chance to disconnect from the hustle of daily life.
3. Fishing and Boating

The numerous lakes and rivers within the Colville National Forest provide excellent opportunities for fishing and boating. Anglers can fish for various species, while boating enthusiasts can enjoy the scenic waterways, whether in a motorboat, kayak, or canoe.
4. Wildlife Viewing and Bird Watching
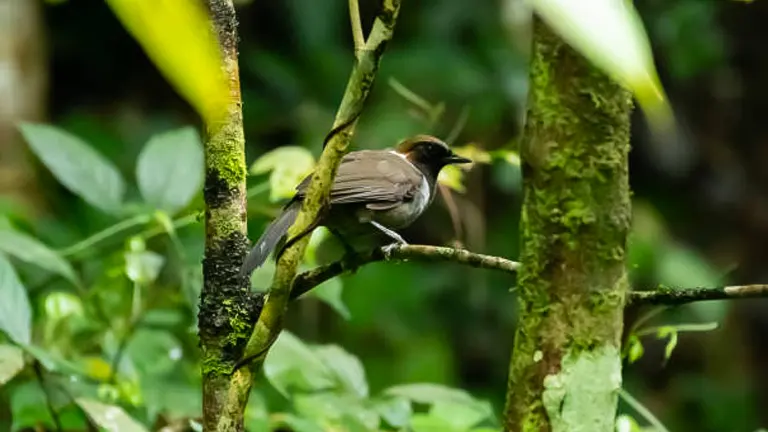

The forest’s diverse ecosystems are home to a wide array of wildlife, including deer, moose, and bears, as well as numerous bird species like bald eagles and ospreys. Nature lovers and birdwatchers can spend hours observing these creatures in their natural habitats.
5. Mountain Biking
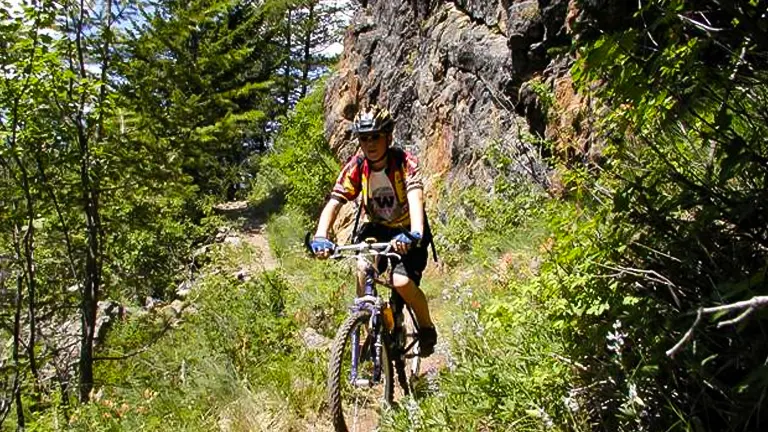

Mountain bikers can find a variety of trails suitable for different skill levels. The forest’s terrain offers everything from gentle rides through scenic landscapes to challenging mountain trails that test a rider’s skills.
6. Winter Sports
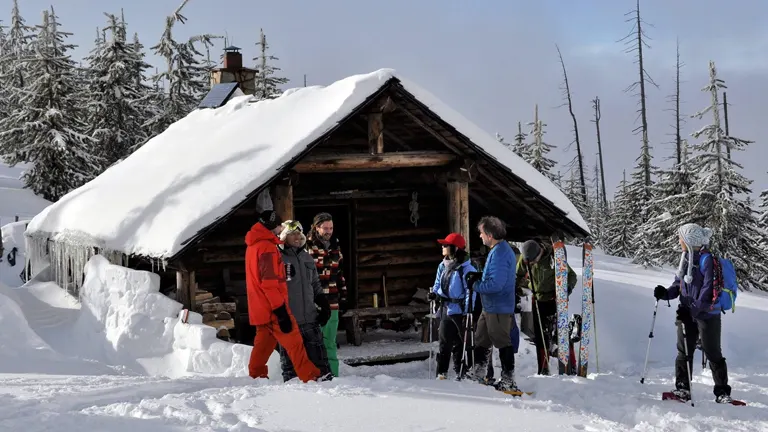

During the winter months, the forest transforms into a wonderland for snow sports. Activities like cross-country skiing, snowshoeing, and snowmobiling are popular, with the 49 Degrees North Ski Area providing downhill skiing and snowboarding opportunities.
7. Horseback Riding
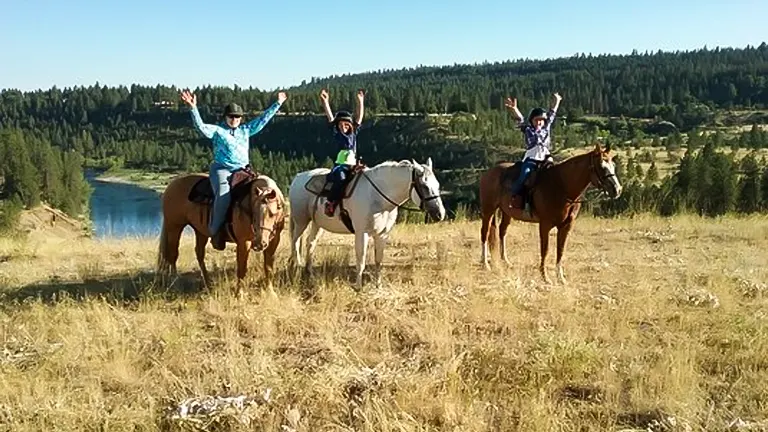

Equestrian enthusiasts can explore the Colville National Forest on horseback, enjoying the beauty of the forest from a unique perspective. Many trails and campgrounds are horse-friendly, offering a memorable experience for riders.
8. OHV (Off-Highway Vehicle) Riding
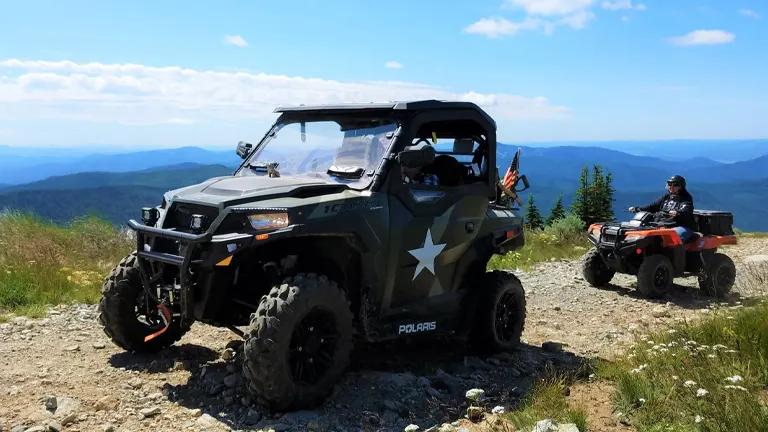

For those who enjoy off-road adventures, the forest offers designated trails for OHVs. These trails provide an exciting way to explore the more remote areas of the forest, though it’s essential to follow all regulations to protect the environment and ensure safety.
9. Picnicking
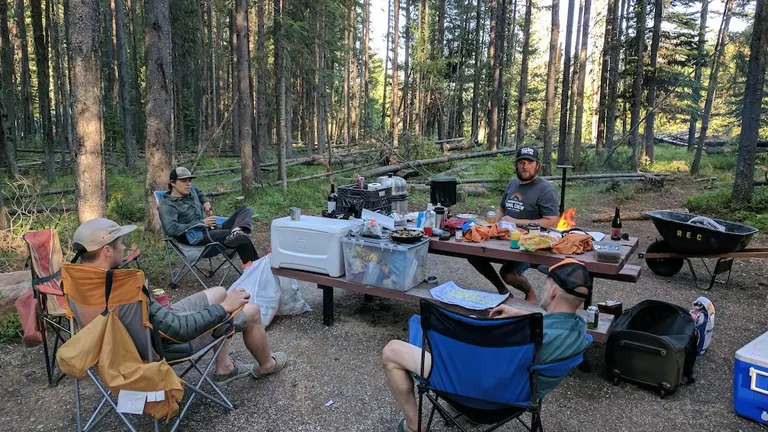

Scattered throughout the forest are numerous picnic areas, perfect for a family outing or a peaceful meal in nature. These spots offer a great way to relax and enjoy the forest’s beauty without the commitment of a longer hike or overnight stay.
10. Scenic Drives
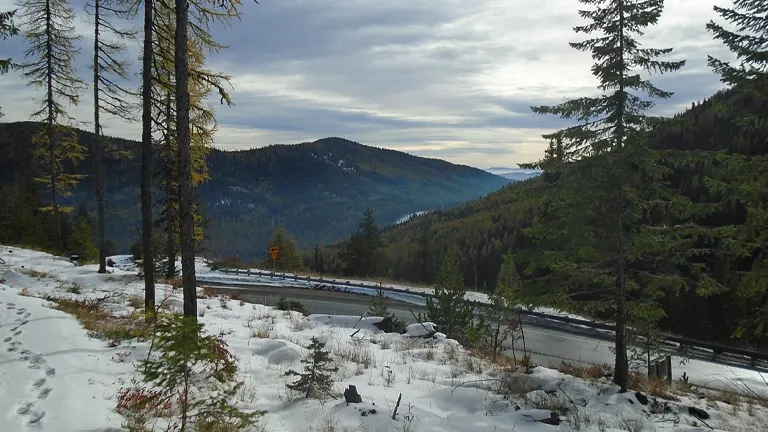

For those who prefer to take in the beauty of the forest from the comfort of their vehicle, there are several scenic drives, like the Sherman Pass Scenic Byway. These routes offer stunning views of the forest, mountains, and rivers, with plenty of stops for photo opportunities.
Each of these activities allows visitors to experience the Colville National Forest in their own way, whether they seek adventure, relaxation, or a bit of both. The forest’s diverse recreational offerings cater to all ages and interests, making it a cherished destination for outdoor enthusiasts.
Different Facilities and Amenities in Colville National Forest
- Developed Campgrounds: The Colville National Forest features numerous developed campgrounds equipped with essential amenities like picnic tables, fire rings, and restroom facilities. These campgrounds, such as those near Sullivan Lake and other scenic areas, provide comfortable and accessible options for families and individuals looking to enjoy the forest’s natural beauty overnight.
- Ranger Stations: The forest has several ranger stations, including those in Kettle Falls, Republic, and Newport. These stations serve as vital information hubs where visitors can learn about the forest, obtain maps, and receive guidance on outdoor activities and safety. The knowledgeable staff can also provide updates on trail conditions, fire restrictions, and wildlife activity.
- Picnic Areas: Scattered throughout the forest are designated picnic areas, ideal for day visitors. These areas often have tables and grills, allowing families and groups to enjoy a meal surrounded by nature. Some picnic spots are located near lakes or rivers, offering beautiful views and easy access to water activities.
- Trails for Various Activities: The forest boasts a network of multi-use trails suitable for hiking, mountain biking, horseback riding, and in some areas, off-highway vehicle (OHV) use. These trails are well-maintained and marked, catering to various skill levels and interests.
- Boat Launches and Fishing Access: Along the lakes and rivers within the forest, there are boat launches and designated fishing areas. These facilities provide anglers and boaters with easy access to the water, enhancing their recreational experience in the forest.
- Wildlife Viewing Areas: Specific areas in the forest are known for their wildlife viewing potential. These spots are often equipped with signage or viewing platforms, offering visitors a chance to observe animals like moose, bears, and eagles in their natural habitat.
- Interpretive Sites and Trails: The forest has several interpretive sites and trails where visitors can learn about the area’s ecology, history, and management. These educational resources provide a deeper understanding and appreciation of the forest environment.
- Winter Recreation Facilities: During the winter months, facilities such as the 49 Degrees North Ski Area come alive, offering skiing, snowboarding, and other snow sports. These areas are equipped with lifts, lodges, and rental services, catering to winter recreation enthusiasts.
- Backcountry Campsites: For those seeking a more rugged and remote experience, the forest offers backcountry campsites. These sites are typically more primitive, without the amenities of developed campgrounds, offering a true wilderness experience for backpackers and adventurers.
- Visitor Centers: Some areas of the forest have visitor centers, where guests can find educational exhibits, purchase souvenirs, and speak with staff for recommendations on activities and attractions. These centers are great starting points for first-time visitors to the Colville National Forest.
- These facilities and amenities enhance the visitor experience in the Colville National Forest, making it more accessible and enjoyable for people of all ages and interests. They play a key role in helping visitors safely and comfortably explore and appreciate the natural beauty and recreational opportunities the forest offers.
Tips and Advice for Visiting Colville National Forest
- Check Weather and Trail Conditions: Before heading out, it’s important to check the current weather conditions and trail statuses. The weather in the forest can change rapidly, especially in mountainous areas, so being prepared for varying conditions is crucial. Updated trail information can be obtained from the forest’s ranger stations or website, ensuring you know the status of trails, any closures, or special alerts.
- Respect Wildlife and Maintain Distance: The Colville National Forest is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including bears and moose. While wildlife encounters can be exciting, it’s essential to respect these animals by keeping a safe distance, not feeding them, and understanding how to react if you encounter them. This not only protects you but also helps in preserving the natural behavior of these wild animals.
- Practice Leave No Trace Principles: To help preserve the natural beauty and ecological integrity of the forest, visitors should follow Leave No Trace principles. This includes packing out all trash, staying on designated trails to avoid damaging sensitive habitats, and camping only in designated areas to minimize your impact on the environment.
- Prepare for Remote Areas: Much of the Colville National Forest is remote and without cell service. Visitors should prepare accordingly by bringing necessary supplies like water, food, a first-aid kit, and a map and compass or GPS. Letting someone know your plans and expected return time is also a good safety practice.
- Be Fire-Wise: Understanding and adhering to fire regulations is crucial, especially during dry months. Check for any fire restrictions before lighting campfires, and ensure all fires are completely extinguished before leaving. Using a portable stove can be a good alternative during high fire danger periods.
- Be Prepared for Various Activities: If you plan to engage in specific activities like fishing, boating, or hunting, ensure you have the appropriate licenses and are aware of the regulations. For activities such as hiking or mountain biking, having the right gear and understanding the trail difficulty levels is important for a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Respect Other Visitors and Share the Trails: The forest is a popular destination for various activities. Being courteous to other visitors, making noise to alert wildlife and others of your presence, and yielding appropriately on trails helps maintain a positive experience for everyone.
- Protect Water Sources: When camping or hiking, it’s important to protect water sources by camping at least 200 feet away from lakes and streams and using biodegradable soap. If you need to use water from the forest, be sure to treat it by boiling, using a water filter, or a chemical purifier.
- Be Aware of Hunting Seasons: If visiting during hunting seasons, be aware of hunters in the area. Wearing bright clothing and being noise-conscious can help in being visible and safe.
- Visit Ranger Stations for Information and Permits: Ranger stations are valuable resources for visitors. They provide up-to-date information, educational materials, and can issue necessary permits for certain activities like camping in designated wilderness areas.
- Following these tips and advice can greatly enhance your experience in the Colville National Forest, ensuring a safe, enjoyable, and environmentally responsible visit.
Recommendation
I strongly suggest exploring the Colville National Forest for a remarkable blend of natural beauty and historical richness. This forest is renowned for its varied ecosystems, notable landscapes, and abundant recreational opportunities, offering a unique and immersive experience. Delight in tranquil outdoor activities such as hiking and observing wildlife, while actively contributing to ongoing conservation efforts. The scenic trails, historical areas, and shared conservation projects make the Colville National Forest an essential destination for those seeking a perfect balance of nature and recreational exploration.
Conclusion
In summary, the Colville National Forest is a remarkable natural treasure. Encompassing a vast expanse of diverse landscapes, it offers an array of recreational activities, rich wildlife, and a profound sense of connection to nature. Its blend of ecological diversity and scenic beauty makes it an invaluable destination for both conservation and outdoor enjoyment, embodying the essence of the Pacific Northwest’s wilderness.
FAQs
- How has the Colville National Forest’s landscape been shaped by historical events?
The landscape of the Colville National Forest has been significantly shaped by Ice Age glaciers, which carved its major valleys and mountains. Additionally, human activities like the construction of the Grand Coulee Dam in the 1930s altered the region, flooding areas like Kettle Falls and impacting local salmon runs. - What are some rare plant species unique to Colville National Forest?
The forest is home to unique plant species like the Pacific yew tree, known for its medicinal properties, and the rare Calypso orchid, which thrives in the forest’s moist, shaded areas. - Can I find any historical artifacts or sites within the forest?
Yes, the forest contains historical sites, including remnants of early settlements and logging camps. However, it’s important to note that these artifacts are protected, and visitors should observe without disturbing them. - What’s the story behind the name ‘Colville’?
The forest is named after Fort Colville, a 19th-century fur trading post located near Kettle Falls. The fort itself was named after Andrew Colville, a London governor of the Hudson’s Bay Company. - Are there any specific conservation projects in the forest that visitors can learn about or participate in?
The Colville National Forest undertakes various conservation projects, such as habitat restoration and fire management. Visitors can learn about these efforts at ranger stations and sometimes participate in volunteer activities. - What is the significance of the Salmo-Priest Wilderness within the forest?
The Salmo-Priest Wilderness is significant for its pristine condition, representing one of the few remaining untouched wilderness areas in the region. It’s crucial for the conservation of species like the grizzly bear and the mountain caribou. - How does the forest change with the seasons, and what unique seasonal activities does it offer?
In spring and summer, the forest is a hub for hiking, camping, and wildlife watching. Fall brings stunning foliage and is popular for hunting. In winter, the landscape transforms for snow sports like skiing and snowshoeing. - Is there an area within the forest that is particularly known for its stunning views or photographic opportunities?
The Sherman Pass Scenic Byway is renowned for its breathtaking views and is a favorite among photographers, offering vistas of mountain ranges, forests, and valleys. The Kettle River Range also provides panoramic views and is especially picturesque during sunrise and sunset.
The Colville National Forest is more than just a forest; it’s a living museum, a playground for nature enthusiasts, and a sanctuary for wildlife. Whether you’re seeking adventure, tranquility, or a touch of history, the Colville National Forest welcomes you with open arms and endless trails.













Leave your comment