American Hazelnut Tree
Overview
Appearance
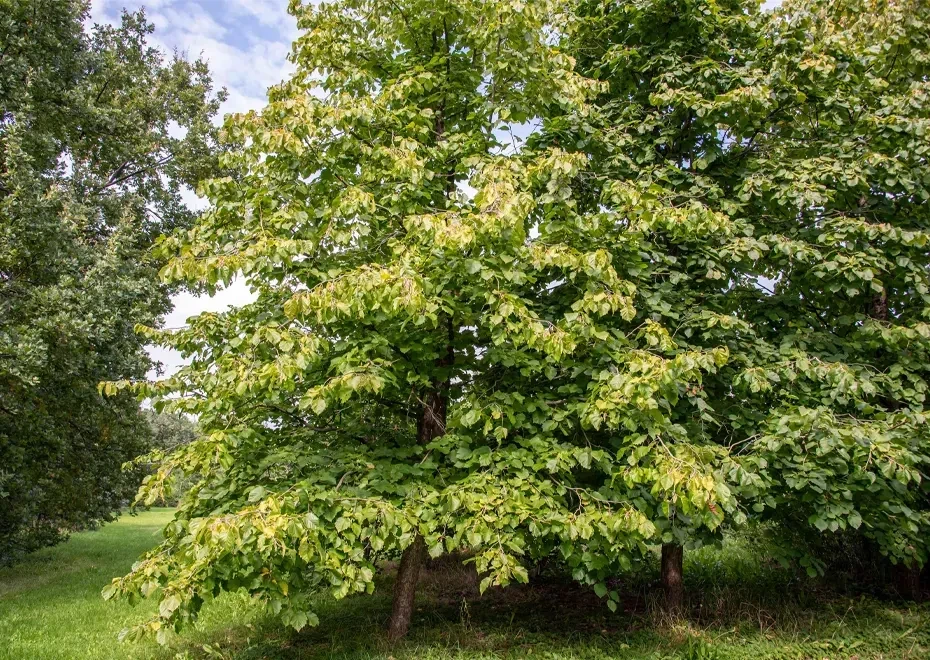
The American hazelnut also known as (Corylus Americana) is a deciduous shrub native to eastern North America. It grows up to 12 to 20 feet in height with an irregular, rounded shape and arching branches. The leaves are broadly oval and dark green.
Flowers
In late winter or early spring, the tree produces small, yellowish-brown, and inconspicuous flowers. These flowers are wind-pollinated, and the tree is self-incompatible, requiring pollen from another individual to produce nuts.
Nuts
The American hazelnut tree produces edible nuts that are small, round, and covered by a husk or bract. Inside the husk, there is a hard shell protecting the kernel or nutmeat. The nuts are ready for harvest in late summer or early fall.
Wildlife Value
The nuts of the American hazelnut are a valuable food source for various wildlife, including squirrels, chipmunks, deer, and various bird species, contributing to local ecosystems by providing food and habitat.
Cultural Uses
Native Americans and early European settlers utilized American hazelnuts as a food source. They can be eaten raw, roasted, or used as an ingredient in various dishes and confections.
Horticultural Uses
American hazelnut trees are also planted as ornamental shrubs for their attractive appearance, especially during the fall when the leaves turn yellow and orange.
Hazelnut Industry
While not as widely cultivated as the European hazelnut, there is a growing interest in breeding and developing improved American hazelnut varieties for potential commercial production. Efforts aim to establish a domestic hazelnut industry in North America.
Wood Products from American Hazelnut Tree
Small Crafts and Artistic Items
The wood of the American Hazelnut Tree can be used to create small crafts and artistic items, such as walking sticks, wooden spoons, and carved sculptures. Its fine grain and attractive color make it suitable for decorative pieces.
Wood Turning Projects
American Hazelnut wood is favored by woodturners due to its ease of working and smooth finish. It can be used to craft bowls, vases, candle holders, and other turned wooden items.
Furniture Components
The American Hazelnut wood can be used as components in furniture making, such as chair legs, table accents, and decorative inlays. Its unique color and texture can add character to furniture pieces.
Smoking and Grilling Chips
The wood of the American Hazelnut Tree is sometimes used as smoking or grilling chips to add a mild, nutty flavor to food, particularly in barbecuing and smoking meat.
Tool Handles
American Hazelnut wood can be fashioned into tool handles, such as hammers, chisels, and gardening tools. Its strength and durability make it suitable for this purpose.
Firewood
The wood from American Hazelnut Tree can also be used as firewood, providing a steady and long-lasting burn. It's considered a good option for campfires and home heating.
Benefits of American Hazelnut Tree
Edible Nuts
The American Hazelnut Tree produces edible nuts that are not only enjoyed by humans but also serve as a valuable food source for various wildlife, including birds, squirrels, and deer.
Ecosystem Support
These trees play a vital role in supporting local ecosystems. They provide food and habitat for wildlife, contributing to biodiversity and ecological balance.
Soil Erosion Control
The dense root system of American Hazelnut Trees helps in controlling soil erosion. Their presence along stream banks and in wooded areas can prevent soil erosion and stabilize slopes.
Ornamental Value
American Hazelnut Trees are often planted as ornamental shrubs due to their attractive appearance. Their rounded shape, arching branches, and changing leaf colors during fall make them visually appealing in landscaping.
Sustainable Agriculture
With ongoing interest in developing a domestic hazelnut industry, the American Hazelnut Tree presents a potential crop for sustainable agriculture. Its nuts are a nutritious and renewable food source.
Wood Products
The wood of the American Hazelnut Tree can be utilized for various woodcrafts, including small artistic items, wood turning projects, furniture components, tool handles, and smoking chips.
Carbon Sequestration
Like other trees, American Hazelnut Trees help in carbon sequestration, capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus mitigating the effects of climate change.
Cons of Using American Hazelnut Tree
Small Nut Size
Compared to some commercial hazelnut varieties, the nuts produced by the American Hazelnut Tree are relatively small. This can be a drawback for those seeking larger nuts for culinary purposes or commercial production.
Limited Commercial Cultivars
As of my last update in September 2021, there were no widely recognized distinct commercial cultivars of the American Hazelnut Tree. This may limit its use in large-scale commercial production compared to other hazelnut species with established commercial varieties.
Nut Yield
The American Hazelnut Tree may have lower nut yields compared to some other hazelnut species or cultivars. This could be a consideration for those seeking high nut production for commercial purposes.
Long Maturation Time
American Hazelnut Trees can take several years to start producing nuts. This long maturation time may discourage those seeking a quicker return on investment for nut production.
Nut Predators
While the nuts of the American Hazelnut Tree are valuable food sources for wildlife, they can also attract nut predators like squirrels, chipmunks, and birds, potentially leading to reduced nut yields.
Hybridization
The American Hazelnut Tree can hybridize with other hazelnut species, leading to some variation in characteristics and nut quality in wild populations. This can be a concern for maintaining the purity of the species in certain regions.
Tips for Planting and Maintaining American Hazelnut Tree
Choose the Right Location
Plant the American Hazelnut Tree in a location that receives full to partial sunlight. Ensure the soil is well-draining and moderately fertile. Avoid areas prone to waterlogging or excessive drought.
Planting
Plant young saplings in the spring or fall. Dig a hole that is twice the size of the root ball and backfill with soil mixed with organic compost. Water the tree thoroughly after planting.
Spacing
Allow enough spacing between multiple trees to ensure good air circulation and prevent overcrowding as the tree grows. Spacing requirements may vary depending on the expected size of the mature tree.
Watering
During the first year, water the young tree regularly to establish its root system. Once established, the American Hazelnut Tree is relatively drought-tolerant, but it's best to water during prolonged dry spells.
Mulching
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil structure. Keep the mulch away from the tree trunk to prevent rot.
Pruning
Prune the tree during its dormant season to remove any dead, damaged, or diseased branches. This helps promote healthy growth and shape the tree's structure.
Fertilization
American Hazelnut Trees generally do not require heavy fertilization. However, if the soil is deficient in nutrients, you can apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring or as recommended by a soil test.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor the tree regularly for signs of pests or diseases. Common issues include aphids, caterpillars, and fungal diseases. Address problems promptly using appropriate measures.
Harvesting Nuts
Once the tree starts producing nuts, harvest them in late summer or early fall when the husks have turned brown and the nuts have fully matured. Store the nuts in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion
Valuable Native Tree
The American Hazelnut Tree (Corylus americana) is a valuable native tree in eastern North America. It offers numerous benefits, such as producing edible nuts enjoyed by both wildlife and humans, providing food and habitat for various animals, and contributing to the stability of ecosystems.
Potential for Cultivation
While not as widely cultivated as the European hazelnut, the American Hazelnut Tree holds promise as a potential crop for sustainable agriculture and the development of a domestic hazelnut industry.
Ornamental and Woodcraft Uses
American Hazelnut Trees are also appreciated for their ornamental value, with attractive appearances and seasonal leaf color changes. Additionally, the wood of these trees is utilized in various woodcraft projects, including small artistic items, furniture components, and tool handles.
Care and Conservation
Proper care, such as choosing the right location, providing adequate water, pruning, and managing pests and diseases, is essential for the health and longevity of American Hazelnut Trees. Conservation efforts are also important to preserve the genetic diversity of this native species.
Environmental Contribution
As with other trees, the American Hazelnut Tree plays a role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Future Prospects
With ongoing research and horticultural advancements, there may be emerging cultivars and improved varieties of the American Hazelnut Tree that further enhance its potential for commercial cultivation and other uses.
FAQs:
1. What is the American Hazelnut Tree?
The American Hazelnut Tree (Corylus americana) is a deciduous shrub native to eastern North America. It produces edible nuts and is valued for its contributions to local ecosystems and potential commercial applications.
2. Are the nuts of the American Hazelnut Tree edible?
Yes, the nuts produced by the American Hazelnut Tree are edible. They are enjoyed by various wildlife, such as birds and mammals, and can also be consumed by humans. Native Americans and early European settlers used them as a food source.
3. Can I grow American Hazelnut Trees in my garden?
American Hazelnut Trees can be grown in gardens if the climate and soil conditions are suitable. They prefer well-draining soil and full to partial sunlight. Before planting, consider the tree's space requirements and whether it is compatible with your garden's size.
4. What are the benefits of planting American Hazelnut Trees?
Planting American Hazelnut Trees offers several benefits, including providing a valuable food source for wildlife, contributing to ecosystem support, preventing soil erosion, adding ornamental value to landscaping, and potential woodcraft and commercial uses.
5. Do American Hazelnut Trees require special care?
Young American Hazelnut Trees may require regular watering to establish their root systems. Once established, they are relatively drought-tolerant. Proper pruning, mulching, and pest management are also essential for their health and longevity.
6. Can I grow American Hazelnut Trees for commercial nut production?
While the American Hazelnut Tree holds potential for commercial nut production, as of my last update in September 2021, there were no widely recognized distinct commercial cultivars. However, ongoing research and breeding efforts may lead to improved varieties suitable for commercial use in the future.
7. Are there any pests or diseases that affect American Hazelnut Trees?
American Hazelnut Trees can be susceptible to various pests, including aphids and caterpillars. They may also be vulnerable to certain fungal diseases. Regular monitoring and appropriate pest and disease management practices can help maintain tree health.
8. How do I harvest and store nuts from American Hazelnut Trees?
Harvest nuts from the American Hazelnut Tree in late summer or early fall when the husks have turned brown, and the nuts are fully matured. Store the nuts in a cool, dry place to keep them fresh.