Why Are Bees Important? Examining Their Critical Role in Biodiversity and Crop Pollination
- February 5, 2024
- 0 comment
Bees have fascinated people for thousands of years not just for their hardworking nature and the honey they produce but also for their essential role in the environment. These small creatures are more vital than their size implies. As pollinators, they play a crucial role in helping plants reproduce, which supports biodiversity and sustains many other life forms. Without bees, many plants wouldn’t thrive, impacting food security and ecosystems globally. Their importance goes beyond the hive, making bees a key part of our natural world.

This relationship between bees and plants is crucial for our ecosystems and has a direct impact on agriculture. Bees pollinate many of the crops we rely on, from fruits and vegetables to nuts, making them essential to food production and our overall food security. Beyond honey, bees are central to maintaining ecological balance, supporting biodiversity, and boosting the agricultural economy. Without their pollination efforts, both the natural world and our food supply would face serious challenges.
Introduction to Bees and Their Ecosystem Services
Bees, with their incredible variety, are vital to our planet’s biodiversity. As nature’s expert pollinators, their visits from flower to flower are essential for the reproduction of most flowering plants. This pollination process does more than help plants thrive; it supports a wide range of animals that depend on the fruits and seeds these plants produce. By transferring pollen, bees ensure successful fertilization, which in turn sustains a rich, diverse ecosystem. This natural cycle highlights the immense role bees play in maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity.

The services bees provide go beyond the wild they’re essential to human agriculture, making them crucial to our food systems. Bees pollinate many crops like fruits, vegetables, and nuts, and some of these are almost entirely dependent on bee pollination. This interdependence between bees, plants, and people supports both natural ecosystems and agricultural productivity. But with bee populations declining, our food variety and security are at risk. Protecting bees is not only about preserving nature’s balance; it’s also about sustaining the agricultural practices we rely on for survival. Conservation efforts to protect these vital pollinators have become a global priority.
The Science of Pollination
Pollination is a key process in plant reproduction, involving the transfer of pollen from a flower’s male anther to its female stigma, which leads to seed and fruit production. Bees, with their unique body structures and foraging habits, are some of the best pollinators in nature. As they search for nectar and pollen, they carry pollen on their bodies, enabling cross-pollination between plants. This process promotes genetic diversity, boosts plant health, and supports the growth of many crops that depend heavily on bee pollination.
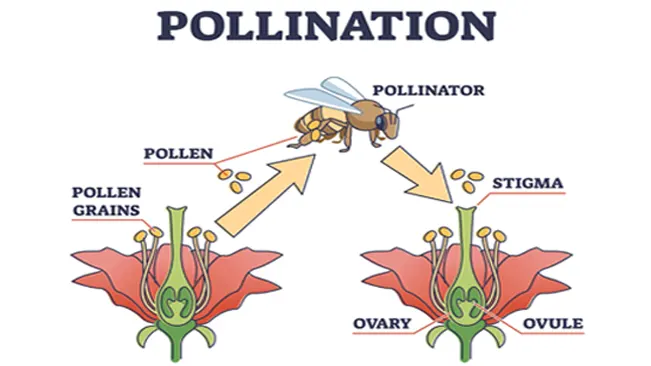
Bees are especially important for certain crops, like almonds, blueberries, and cherries, which rely almost entirely on bee pollination for fruit production. This partnership between bees and plants is essential not only for ecological balance but also for agriculture and food security. Bees play an irreplaceable role in our ecosystems, making it crucial to protect and preserve them to ensure the ongoing health of our planet.
Bees and Agriculture
The relationship between bees and agriculture is essential for both the environment and the economy. Through their pollination, bees improve crop quality and significantly boost yields. This natural process where bees transfer pollen between flowers is crucial for plant reproduction and supports much of the human food supply.

The economic value of bees reaches billions, proving their critical role in agriculture. Beyond promoting ecological diversity, bees drive agricultural productivity and economic growth. Their work sustains food crops, supports farmers’ livelihoods, and keeps ecosystems in balance, making bee conservation essential for food security and global stability.
Threats to Bee Populations
Although bees play a crucial role in biodiversity and agriculture, they face many environmental threats that endanger their survival. The widespread use of pesticides in modern farming disrupts bees’ natural behaviors and harms their health. Additionally, habitat loss from urban and agricultural expansion reduces the availability of diverse flowers and nesting sites essential for bee survival. Climate change further adds to these challenges, with changing weather and flowering patterns disrupting bee pollination activities.
Addressing these threats requires urgent conservation efforts. Protecting bees involves sustainable farming, restoring habitats, and implementing policies to counter climate impacts, ensuring these vital pollinators continue to thrive for future generations.
Conservation Efforts
Protecting bees involves a range of actions, from global campaigns to simple steps in our own gardens, showing that everyone can help preserve these essential pollinators. By working together, we can ensure that bees continue supporting our ecosystems and agriculture. Here are some practical ways to make a difference:
- Plant bee-friendly flowers like marigolds and sunflowers on balconies, terraces, or in gardens to provide bees with vital resources.
- Buy honey and hive products from local beekeepers to support those directly involved in bee conservation.
- Educate children about the importance of bees to build early awareness and support for beekeeping.
- Set up a small pollinator-friendly area to offer a safe space for bees to thrive.
- Preserve old meadows and plant nectar-rich flowers to maintain diverse habitats for bee health.
- Mow grass only after flowers have bloomed, and use bee-safe pesticides at times when bees are less active.
These individual and community actions contribute to a larger movement to protect bee populations, helping them continue their vital roles in pollinating crops and supporting biodiversity.
Related Topics
- How to Start a Beehive: Essential Tips for Aspiring Beekeepers
- How Do Bees Pollinate? An Exploration of Ecological Dynamics
Conclusion
Bees are essential not just for honey but for sustaining global biodiversity and food production. Their pollination work supports countless plants, including many crops that are key to our diets. Protecting bees goes beyond saving a single species; it’s about preserving ecosystem health and ensuring food security. By pollinating plants, bees maintain ecological balance and keep our food sources stable, making their conservation crucial for both the environment and human survival.
FAQs
- What makes bees such effective pollinators compared to other insects?
Bees are designed for pollination. They have hairy bodies that trap pollen, and they visit flowers systematically, ensuring efficient transfer of pollen. Their feeding habits require them to move between many flowers, making them natural pollinators. - Can bees pollinate all types of plants?
While bees can pollinate many types of plants, they are particularly effective with certain crops and wildflowers. Some plants rely exclusively on bees for pollination, whereas others may be pollinated by wind, water, or different insects. - What percentage of our food crops depend on bee pollination?
It’s estimated that about one-third of the food crops we consume rely on bee pollination. This includes fruits, vegetables, and nuts that are integral to a healthy diet. - How do bees impact the economy?
Bees have a substantial economic impact through their pollination services, which are crucial for the agricultural industry. In the U.S. alone, the contribution of bees to crop pollination and production is valued at over $15 billion annually. - What are the main causes of bee population decline?
The decline in bee populations is attributed to various factors, including pesticide use, habitat loss, climate change, disease, and the spread of invasive species that compete for resources. - What is Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD)?
Colony Collapse Disorder is a phenomenon where the majority of worker bees in a colony disappear, leaving behind a queen, food, and a few nurse bees to care for the remaining immature bees. The exact cause is unknown, but it’s believed to be a combination of factors including pesticides, stress, and pathogens. - How can gardeners and homeowners help bees?
Individuals can help by planting bee-friendly gardens, avoiding pesticides, providing water sources, and leaving natural areas in their gardens for bees to nest and forage. - Are all bees honey producers?
Not all bees produce honey. Of the over 20,000 species of bees, only a fraction, primarily in the genus Apis, are honeybees and capable of producing honey in significant quantities. - What is the role of bees in biodiversity?
Bees contribute to biodiversity by pollinating plants, which leads to the production of fruits, seeds, and more plants, creating a diverse and resilient ecosystem. - Can technology replace the role of bees in pollination?
While there have been attempts to create artificial pollinators, none have matched the efficiency and effectiveness of bees. The natural pollination process by bees is complex and difficult to replicate, making their conservation crucial.

Charles Hayes
Forestry AuthorI'm Charles Hayes, I bring over 15 years of specialized expertise in landscaping and woodworking, blending artistic design with sustainable environmental stewardship. My career, fueled by a profound passion for the natural world, encompasses extensive education and hands-on experience in creating harmonious, eco-friendly outdoor spaces and responsibly managing forest resources. Recognized for my professional standing, I am committed to continuous learning and certification in cutting-edge practices. My expertise is not only reflected in my work but also in my contributions to community projects, educational workshops, and collaborations with industry leaders. As an authoritative voice in my field, I strive to share knowledge and promote environmentally conscious approaches, making me a trusted resource in landscaping and forestry.




Leave your comment