Sweet Cherry Tree
- September 22, 2023
- 0 comment

- Common Name: Sweet Cherry Tree
- Botanical Name: Prunus avium
- Family: Rosaceae
- Plant Type: Deciduous fruit tree
Lumber
While Sweet Cherry trees are primarily grown for their delicious fruits, the wood from these trees is also valuable. Sweet Cherry wood, known for its rich reddish-brown color and fine grain, is highly prized in the woodworking industry for making furniture and cabinetry. It is a dense and durable wood that polishes to a beautiful finish.

Mature Size and Growth Rate
Sweet Cherry trees typically reach a height of 20 to 30 feet (6 to 9 meters) and have a similar spread. They have a moderate growth rate, and it takes several years for them to reach maturity and start producing abundant fruit.
Soil Type
Sweet Cherry trees flourish in soil that drains well and contains ample organic matter. This type of soil ensures proper water distribution and nutrient availability.

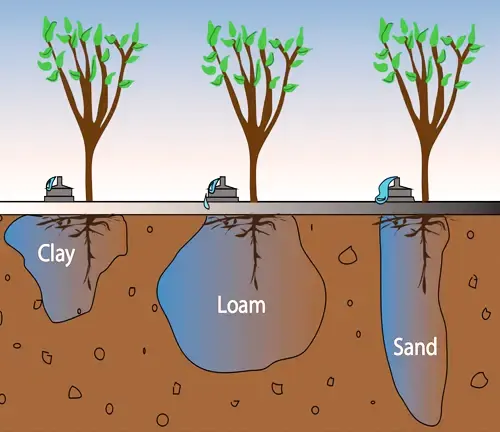
Soil Preferences
Sweet Cherry trees have a preference for soil that is slightly acidic to neutral, with an ideal pH range between 6.0 and 7.5. Maintaining this pH range supports optimal nutrient uptake and overall tree health.
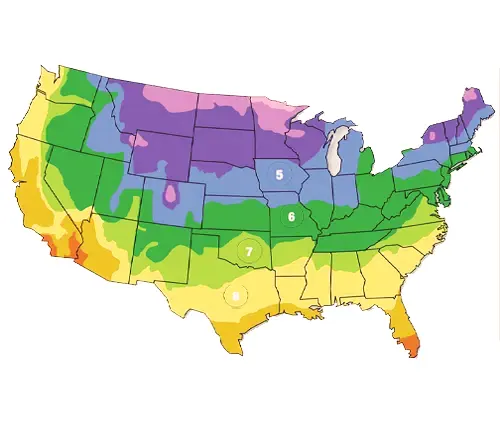
Hardiness Zone
Sweet Cherry trees are hardy in USDA Zones 5 to 8, although specific varieties may have different cold tolerances.
Sun Preference
These trees require full sun to produce the best fruit yields. They should receive at least 6 to 8 hours of sunlight per day.
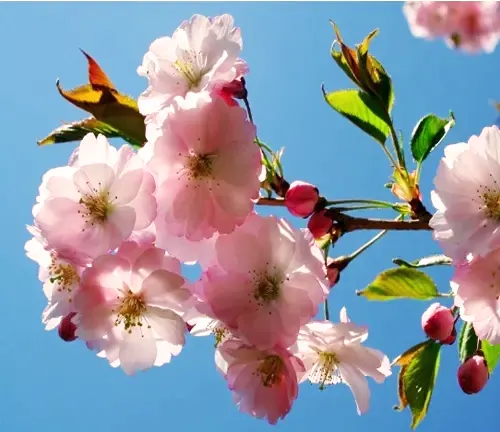

Attributes and Characteristics
Sweet Cherry trees are prized for their delectable red to dark-purple cherries, which ripen in late spring to early summer. They also boast clusters of white or pinkish spring flowers and glossy green leaves that transform into vibrant hues of orange and red in the fall, making them both fruitful and visually appealing.
Wildlife Value
Sweet Cherry trees attract various wildlife, including birds and insects. Birds are particularly fond of the ripe fruit, and bees and other pollinators are attracted to the flowers during the blooming season.
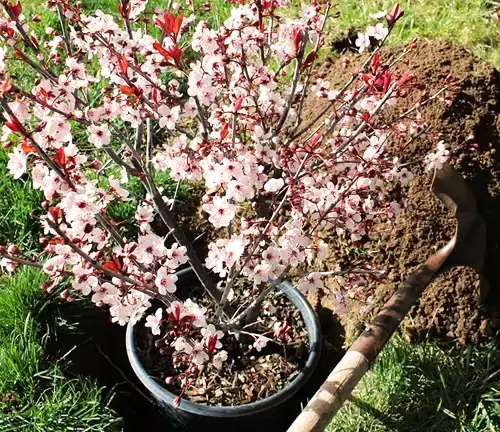

Care
Proper care includes regular pruning to maintain shape and encourage fruit production, adequate watering, and protection from common pests and diseases.
Benefits
Sweet Cherry trees offer a dual advantage. Their foremost benefit lies in the production of delectable, fresh fruit that finds its way into various culinary delights, from fresh snacking to the creation of mouthwatering baked goods and preserves. Beyond their edible bounty, these trees also lend an aesthetic touch to landscapes, gracing them with exquisite spring blossoms and a spectacular display of autumn foliage.
Invasive
Sweet Cherry trees are not considered invasive. They are cultivated for their fruit and wood and do not typically spread aggressively in natural ecosystems.
Lifespan
With proper care, Sweet Cherry trees can live for several decades, often reaching 20 to 40 years or more.
Disadvantages
Sweet Cherry trees, while offering delicious rewards, come with their set of challenges. They are susceptible to a range of pests and diseases, including troublesome invaders like aphids, brown rot, and the cherry fruit fly, necessitating vigilant and proactive management. Additionally, their tendency to reach substantial sizes may pose space constraints, rendering them less suitable for compact gardens or confined outdoor areas.
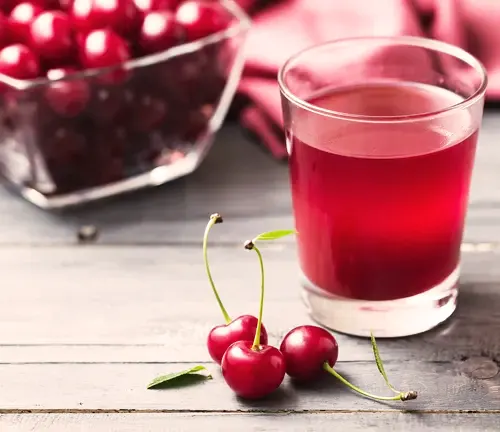

Edible or Not
Yes, the fruit of the Sweet Cherry tree is edible and is widely enjoyed for its sweet and juicy flavor.
Habitat Requirements
Sweet Cherry trees are native to Europe and western Asia but have been cultivated in many parts of the world. They thrive in temperate regions with distinct seasons and require cold winter temperatures for adequate fruit development.
Name of Origin
The common sweet cherry, Prunus avium, is believed to have originated in Europe and western Asia.
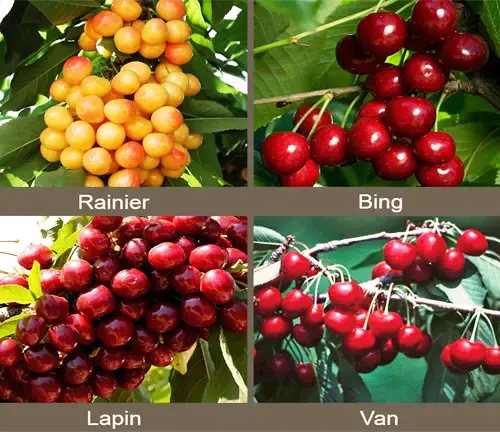

Varieties
There are numerous varieties of sweet cherries, each with its unique flavor profile and growing characteristics. Some popular varieties include Bing, Rainier, Stella, and Lapins.
Pruning
Pruning is essential for shaping the tree, removing dead or diseased branches, and promoting fruit production. It is typically done during the dormant winter months.
Propagating
Sweet Cherry trees can be propagated through various methods, including grafting and rooting hardwood cuttings.

Common Pests & Diseases
Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and cherry fruit fly. Diseases that can affect sweet cherry trees include brown rot, bacterial canker, and powdery mildew.
Fun Facts
- Sweet Cherry trees belong to the same family as almonds, apricots, and peaches, collectively known as the Rosaceae family.
- The cherry blossom is a symbol of renewal and the ephemeral nature of life in Japanese culture. It is celebrated during the annual Cherry Blossom Festival, or Hanami.
- Sweet cherries are not only delicious but also nutritious, containing vitamins, antioxidants, and dietary fiber.
Discover the difference today and explore our range of Forestry Services – don’t miss out on the opportunity to elevate your experience!
FAQs
- When is the best time to plant a Sweet Cherry tree?
It’s best to plant Sweet Cherry trees in late winter to early spring, while they are still dormant. - How do I protect my cherry tree from pests and diseases?
Regular inspections, proper pruning, and the use of organic or chemical treatments as needed can help protect your tree from common pests and diseases. - Can I grow Sweet Cherry trees in containers?
While it’s possible to grow dwarf or patio varieties in containers, standard Sweet Cherry trees are better suited for open-ground planting due to their size. - How long does it take for a Sweet Cherry tree to start bearing fruit?
It typically takes 3 to 5 years for a Sweet Cherry tree to start producing significant fruit yields, with full production reached after 7 to 10 years.
In conclusion, the Sweet Cherry tree, with its delectable fruit and ornamental charm, stands as a prized addition to gardens and orchards. While it offers a bounty of culinary delights and enhances the visual appeal of landscapes, it does demand careful attention to combat potential pests and diseases and consideration of its space requirements. With proper care, these trees can grace your surroundings with both beauty and flavor, making them a delightful addition to any horticultural endeavor.



Leave your comment