Honeycrisp Apple Tree
- October 3, 2023
- 0 comment
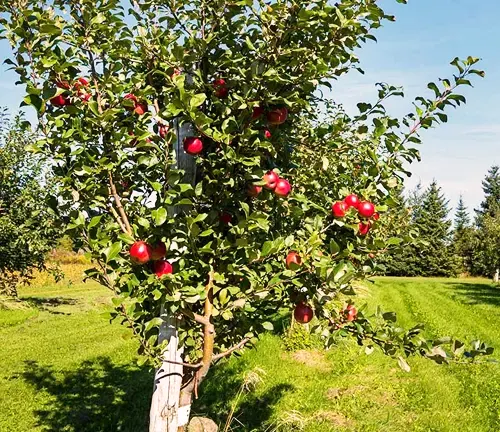

The Honeycrisp Apple Tree, scientifically known as Malus domestica ‘Honeycrisp’, stands out as a paragon of orchard excellence, tracing its roots to the innovative breeding program at the University of Minnesota in the 1960s. This tree has become a cornerstone in modern orchards, not only for its ornamental beauty but, more significantly, for the remarkable qualities of its fruit. The Honeycrisp apple, with its distinctive blend of sweetness and crispness, has garnered widespread acclaim, making it a preferred choice for those who appreciate the artistry of apple cultivation.
Characterized by a deciduous canopy that adorns orchards with vibrant red and green foliage, the Honeycrisp Apple Tree is not just a bearer of fruit but also a visual delight. Its moderate growth rate and relatively compact size make it an accessible option for orchardists of varying scales, from commercial operations to backyard gardens. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the Honeycrisp tree is known for its adaptability to different climates, making it suitable for a range of geographical locations.
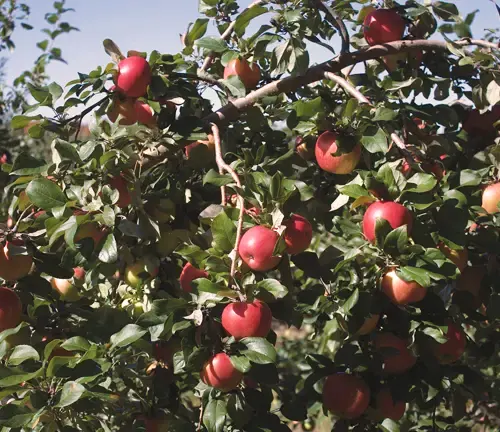

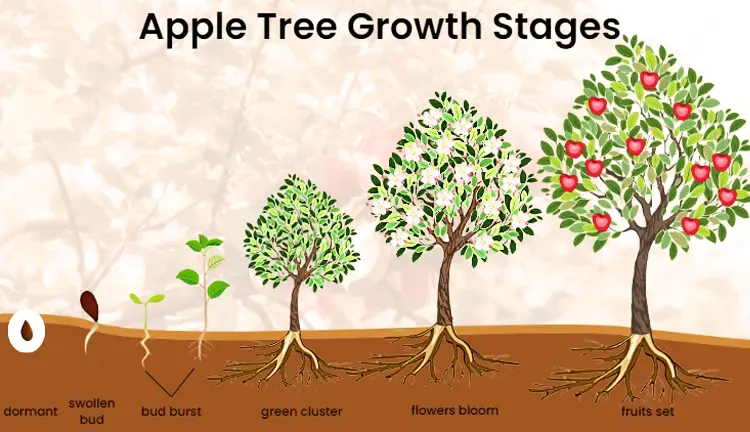
As the seasons unfold, the Honeycrisp apple tree transforms through a captivating journey. In spring, the tree bursts into life with elegant pink and white blossoms, creating a picturesque scene in orchards. This heralds the beginning of a meticulous process of pollination, crucial for the development of the large, round Honeycrisp apples. Come late summer or early fall, orchardists are rewarded with a bountiful harvest of apples that are as visually striking as they are delicious.

| Characteristic | Description |
| Scientific Name | Malus domestica ‘Honeycrisp’ |
| Size at Maturity | Medium-sized tree, typically reaching 15 to 20 feet in height |
| Growth Rate | Moderate growth rate |
| Bloom Time | Spring, produces pink and white blossoms |
| Fruit Season | Late summer to early fall |
| Canopy Shape | Rounded, spreading canopy. |
| Pollination | Self-sterile, requires cross-pollination with another apple tree for optimal fruit set. |
| Soil Requirements | Flourishes in well-drained soil conditions. |
| Sunlight Requirements | Thrives in full sunlight, ensuring robust fruit production. |
| Harvesting Time | Timing varies by region but generally occurs in late summer to early fall. |
A Brief History
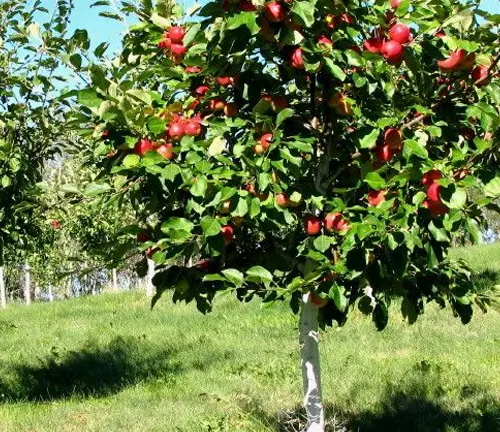

In the orchards of the world, one apple tree stands out not only for its delectable fruit but also for its fascinating history—the Honeycrisp apple tree. This cultivar, a product of human ingenuity and a bit of serendipity, was developed at the University of Minnesota in the 1960s. Its journey from a humble seedling to a globally renowned apple variety is a testament to the intersection of science and nature.
Color/Appearance
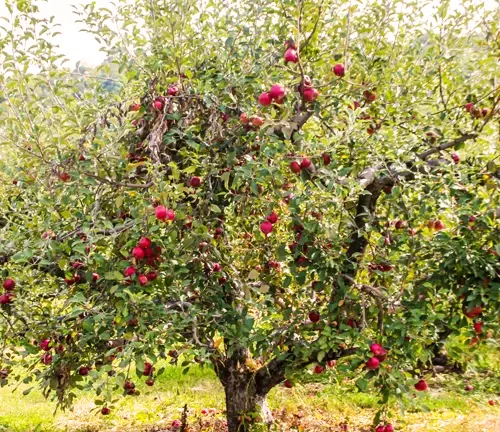
The Honeycrisp apple, with its distinctive red and yellow hues, is a visual feast. Its skin is marked by a vibrant crimson blush over a yellow-green background, creating an enticing contrast that makes it instantly recognizable. The luscious appearance of a ripe Honeycrisp is a prelude to the burst of flavor awaiting those who bite into its crisp, juicy flesh.
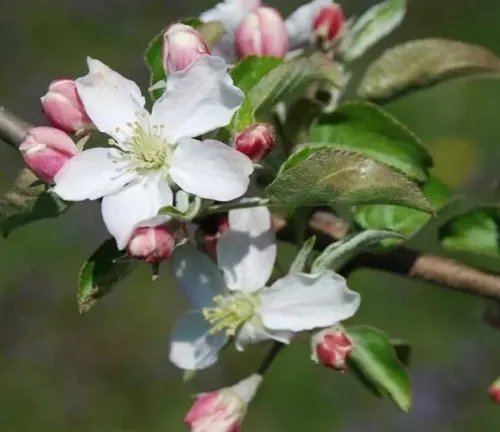

Life Cycle
The life cycle of the Honeycrisp apple tree is a fascinating journey through the seasons. In spring, delicate blossoms grace its branches, enticing pollinators to orchestrate the dance of fertilization. As summer arrives, the apples begin to take shape, growing and maturing under the warm sun. Come autumn, the tree offers its bounty, and the crisp apples are ready for harvest, embodying the culmination of a year-long cycle of growth and development.
Adaptability and Resilience
One of the remarkable qualities of the Honeycrisp apple tree is its adaptability and resilience. Thriving in a variety of climates, from the chilly northern regions to milder southern zones, this tree has proven its ability to withstand diverse environmental conditions. Its resilience against common apple tree diseases adds to its appeal for orchardists and home gardeners alike.
Ecological Importance
Beyond its commercial value, the Honeycrisp apple tree is vital to the ecosystem. The blossoms provide nectar for pollinators, supporting the health of bee populations. Additionally, fallen apples contribute to soil fertility as they decompose, creating a sustainable cycle that benefits both the tree and the environment.
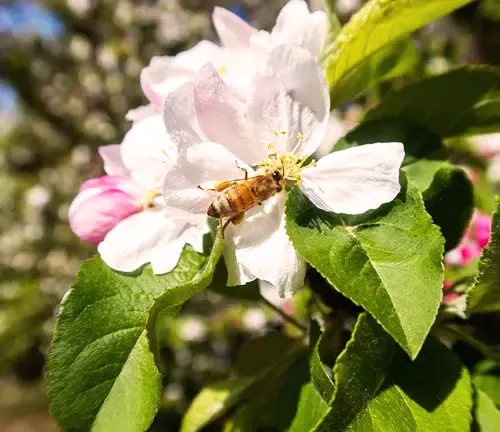

Culinary Applications
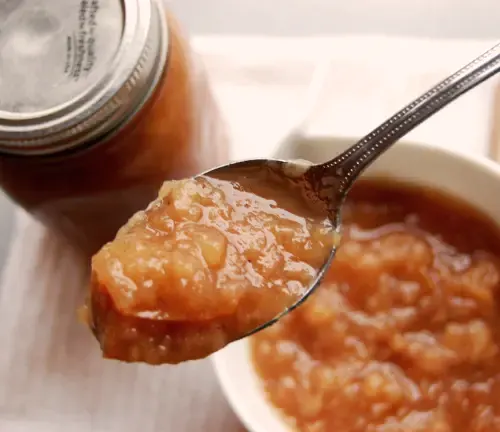

Renowned for its crisp texture and sweet-tart flavor, the Honeycrisp apple is a favorite in kitchens around the world. Whether enjoyed fresh, sliced into salads, or transformed into pies and sauces, its versatility makes it a culinary delight. The apple’s natural sweetness enhances both sweet and savory dishes, earning it a cherished place in the hearts of chefs and home cooks alike.

Wood Products and Applications
While the primary attraction of the Honeycrisp apple tree lies in its fruit, its wood is not to be overlooked. Prized for its fine grain and durability, Honeycrisp wood has found applications in crafting furniture, utensils, and decorative items. The versatility of the tree extends beyond the kitchen, adding a touch of rustic elegance to various wood products.


Cultivation and Care

Cultivating a thriving Honeycrisp apple tree requires a delicate balance of attention and care. From selecting the right planting location to providing adequate nutrients and water, each step in the cultivation process contributes to the tree’s overall health and fruitfulness. Pruning, pest management, and disease prevention are crucial aspects of ensuring a bountiful harvest.
Benefits
The benefits of the Honeycrisp apple tree are as diverse as its uses. For growers, it offers a reliable and economically valuable crop. For consumers, its crisp, juicy apples provide a delicious and nutritious snack. From an ecological perspective, the tree contributes to biodiversity and sustainable agriculture. The Honeycrisp apple tree, with its rich history and myriad benefits, stands as a testament to the harmonious relationship between humanity and the natural world.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why is the Honeycrisp apple tree called “Honeycrisp”?
The Honeycrisp apple tree got its name from its crisp, juicy texture and its sweet, honey-like flavor. The “honey” in the name reflects the apple’s natural sweetness, while “crisp” highlights its signature crunchy bite. - What makes the Honeycrisp apple tree’s wood special for woodworking?
Honeycrisp apple wood is prized for its fine grain and durability, making it an excellent choice for woodworking projects. Its unique appearance and strength make it ideal for crafting furniture, cutting boards, and even decorative items. Its distinctive reddish-brown color and tight grain pattern set it apart from other hardwoods. - Can Honeycrisp apple trees be grown organically?
While it can be challenging, it is possible to grow Honeycrisp apple trees organically. Organic cultivation methods involve using natural pest control, avoiding synthetic chemicals, and prioritizing soil health. These practices help maintain the tree’s natural resilience and produce organic Honeycrisp apples. - Are there any unique regional variations in the flavor of Honeycrisp apples?
Yes, there can be subtle flavor variations in Honeycrisp apples depending on the region in which they are grown. Factors such as soil composition, climate, and local growing practices can influence the apple’s flavor profile. Some connoisseurs argue that Honeycrisp apples from certain regions may have slightly different taste nuances. - What are some innovative culinary uses for Honeycrisp apples beyond traditional recipes?
Honeycrisp apples are known for their versatility in the kitchen. Beyond classic apple pies and salads, creative cooks have used them in innovative ways. Some ideas include using thinly sliced Honeycrisp apples in sushi rolls, incorporating them into homemade jams, or even experimenting with apple-based cocktails, where their natural sweetness and crispness add a unique twist to beverages.














Leave your comment