Joshua Tree
- January 16, 2024
- 1 comment
The Joshua Tree, scientifically known as Yucca brevifolia, stands as a resilient emblem of the North American deserts, particularly gracing the landscapes of the Mojave and Sonoran Deserts. With its unmistakable silhouette, this iconic tree boasts tall, slender trunks crowned by a collection of spiky, palm-like leaves arranged in a distinctive rosette pattern. Flourishing in the harsh conditions of arid environments, Joshua Trees showcase a remarkable adaptability to extreme temperatures, from scorching hot summers to chilly winters.
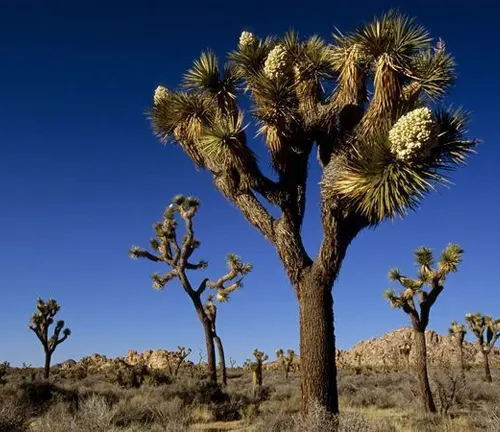

What Kind of Tree is Joshua Tree?
Known for their unique reproductive strategy, these trees rely on the yucca moth for pollination, ensuring the continuation of their species. Beyond their ecological importance, Joshua Trees hold cultural significance, with indigenous communities historically utilizing various parts of the tree for practical and spiritual purposes. The trees have become symbolic of resilience and endurance in modern culture, featuring prominently in art, literature, and media. As guardians of the desert, Joshua Trees play a vital role in supporting biodiversity and conserving soil. Joshua Tree National Park, established in their honor, provides a sanctuary for enthusiasts to marvel at the beauty and adaptability of these intriguing desert giants.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Yucca brevifolia |
| Common Name | Joshua Tree |
| Family | Asparagaceae |
| Genus | Yucca |
| Native Habitat | Mojave Desert, Sonoran Desert |
| Geographic Range | California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Mexico |
| Climate Preferences | Hot summers, cold winters |
| Height | Up to 40 feet |
| Leaves | Spiky, palm-like rosette arrangement |
| Branching | Distinctive “yucca” shape with arms |
| Reproductive Strategy | Relies on yucca moth for pollination |
| Life Span | Several hundred years |
| Cultural Significance | Historically used by indigenous communities, modern symbol of resilience |
| Conservation Status | Not currently endangered, faces threats from climate change and habitat loss |
| Role in Ecosystem | Provides habitat and sustenance for wildlife, soil conservation |
Exploring the Enigmatic Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia)
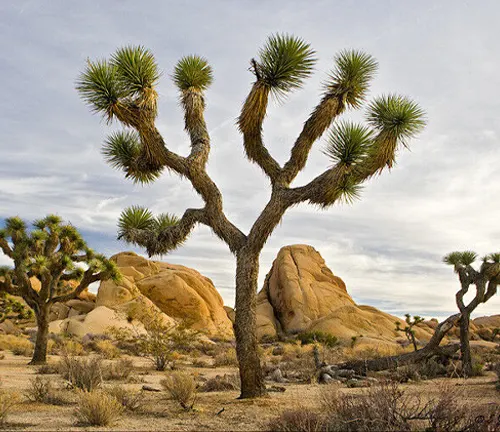

Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia), an iconic species of the desert, stands tall and proud amidst the arid landscapes of North America. In this article, we delve into the unique characteristics, ecological significance, and cultural importance of these resilient trees that have captured the imaginations of many.
The Joshua Tree, scientifically known as Yucca brevifolia, is a distinctive member of the agave family. With its spiky leaves and towering presence, it thrives in the harsh environments of the Mojave Desert and parts of the Sonoran Desert.
Despite the challenging conditions, Joshua Trees play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the desert ecosystem. Their presence provides habitat and sustenance for various wildlife, showcasing the resilience of life in arid regions.
Origin and Distribution
Native Habitats
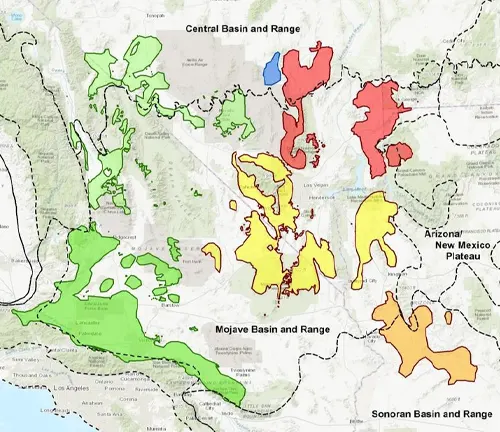
Joshua Trees are native to specific regions, primarily the Mojave Desert in California, Nevada, Utah, and Arizona, as well as the Sonoran Desert in Arizona and Mexico. Their ability to adapt to diverse conditions contributes to their widespread distribution.
Geographic Distribution and Climate Preferences
These trees prefer elevations between 2,000 and 6,000 feet and thrive in areas with hot summers and cold winters. Their unique distribution pattern is a testament to their adaptability to a range of climates.
Physical Characteristics
Description of Joshua Tree’s Appearance
Characterized by their tall, slender trunks and spiky leaves, Joshua Trees can reach heights of up to 40 feet. The leaves, arranged in a rosette pattern, create a striking silhouette against the desert sky.
Notable Features and Adaptations
One of the most distinctive features is their “yucca” shape, with branching arms extending in various directions. These arms, unique to mature trees, add to their aesthetic appeal and aid in reproduction.
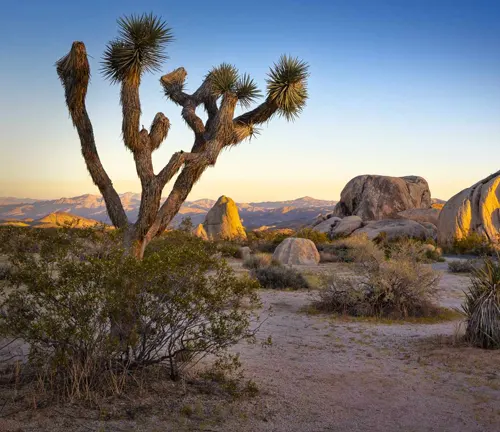

Life Cycle
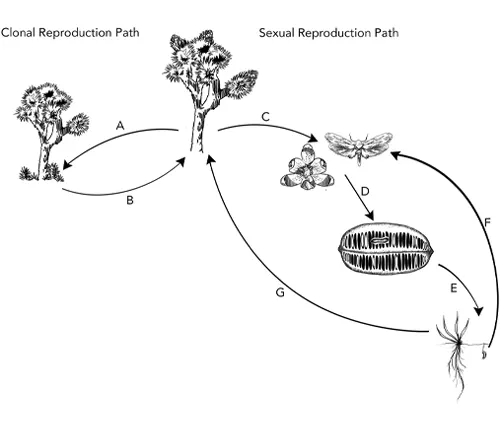
Reproduction and Pollination Mechanisms
Joshua Trees have a fascinating reproductive strategy involving the yucca moth. The moth pollinates the flowers, and as the tree matures, it produces seeds within its fruit capsules, ensuring the continuation of its species.
Growth Stages and Longevity
From seed germination to the establishment of a mature tree, the life cycle of Joshua Trees spans several decades. Some individuals can live for hundreds of years, adding a layer of mystique to these desert giants.
Ecological Role
Impact on the Ecosystem
Beyond their aesthetic value, Joshua Trees contribute significantly to the desert ecosystem. They provide shelter for birds, reptiles, and insects, creating microhabitats that support biodiversity.
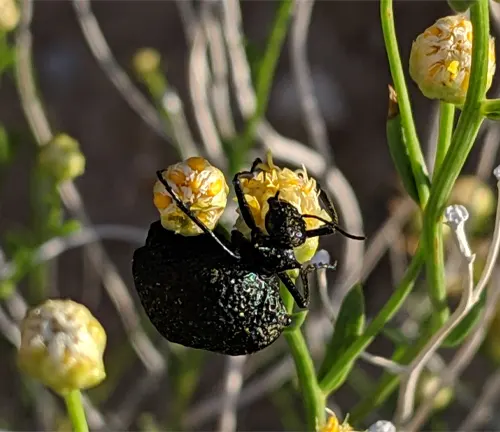
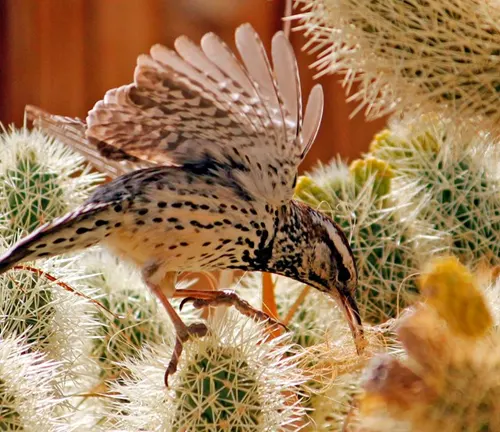


Interactions with Flora and Fauna
Joshua Trees are integral to the survival of various species, and their branches serve as nesting sites for birds. Their fruits are a source of food for several animals, emphasizing their interconnectedness with the desert ecosystem.
Cultural Significance
Historical Importance to Indigenous Communities
For centuries, indigenous communities in the region have held the Joshua Tree in high regard. The tree’s fibrous leaves were used for weaving, and its presence in the landscape held cultural and spiritual significance.
Modern-Day Cultural Symbolism
In contemporary culture, Joshua Trees have become symbolic of resilience and adaptation. Their images often grace artworks, and their association with the desert has made them an emblem of endurance.

Threats and Conservation
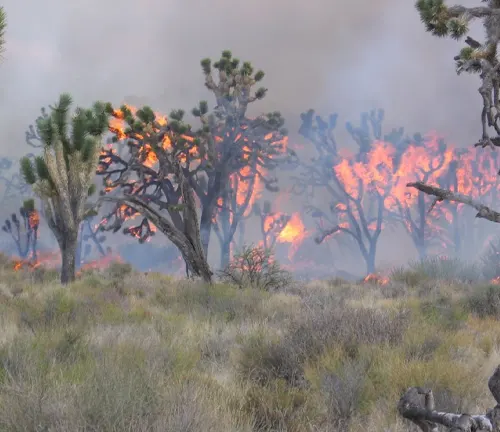
Natural Threats to Joshua Trees
Despite their adaptability, Joshua Trees face challenges such as climate change, wildfires, and diseases. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies.

Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Various organizations and initiatives are working towards preserving Joshua Trees. However, conservation efforts are not without challenges, including land use conflicts and limited resources.
Joshua Tree National Park
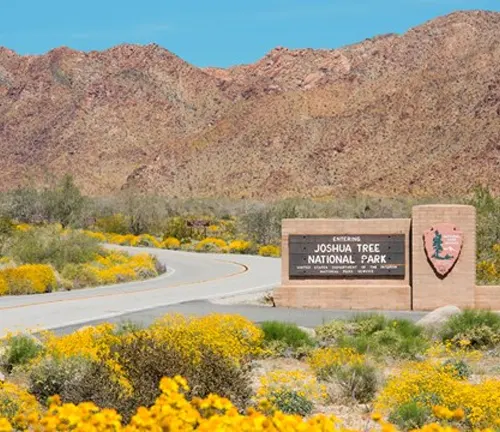

Overview of the National Park
Joshua Tree National Park, established in 1994, is a haven for enthusiasts and researchers alike. The park showcases the beauty of the Mojave Desert and the unique flora and fauna that call it home.
Attractions and Activities for Visitors
Visitors can explore the park’s hiking trails, rock formations, and stargazing opportunities. Joshua Tree National Park offers a chance to witness the beauty of these trees in their natural habitat.
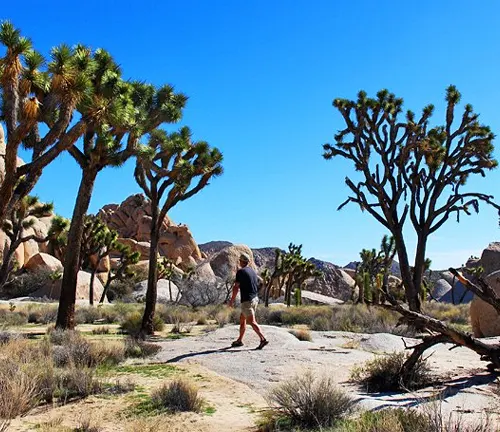

Joshua Tree in Popular Culture
Depictions in Art, Literature, and Media
The mystique surrounding Joshua Trees has inspired artists, writers, and filmmakers. From paintings to novels, these trees have left an indelible mark on the creative landscape.

Impact on Tourism and Awareness
The allure of Joshua Trees has contributed to the popularity of the desert regions they inhabit. Tourism centered around these unique trees has grown, bringing attention to the need for responsible exploration.
Unique Features
Joshua Tree as a Symbol of Resilience
In the face of harsh conditions, Joshua Trees stand tall, symbolizing resilience. Scientists study their ability to thrive in extreme environments, seeking insights that may have broader ecological implications.
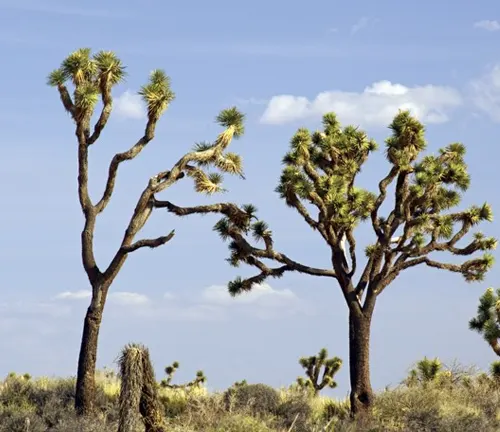

Scientific Studies and Discoveries
Researchers continue to make discoveries related to Joshua Trees, uncovering new aspects of their biology and ecology. These studies contribute to our understanding of the intricate relationships within desert ecosystems.
Growing Joshua Trees
Tips for Cultivating Joshua Trees
For enthusiasts interested in growing Joshua Trees, understanding their specific needs is crucial. Proper soil, watering, and sunlight conditions are key factors for successful cultivation.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Growing Joshua Trees may pose challenges, such as susceptibility to certain pests and diseases. However, with proper care and attention, these challenges can be effectively addressed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Joshua Trees endangered?
Joshua Trees are not currently classified as endangered, but they face threats from climate change, wildfires, and habitat loss. Conservation efforts are underway to ensure their continued survival. - Can Joshua Trees survive extreme temperatures?
Yes, Joshua Trees are adapted to thrive in the extreme temperatures of the desert. They can withstand both hot summers and cold winters. - Do Joshua Trees have any medicinal uses?
Historically, indigenous communities used various parts of the Joshua Tree for medicinal purposes, such as treating wounds and ailments. However, modern uses are limited, and caution should be exercised. - How do Joshua Trees reproduce?
Joshua Trees reproduce through a unique pollination process involving the yucca moth. The moth transfers pollen between flowers, leading to the production of seeds within the tree’s fruit capsules. - Can Joshua Trees be grown outside of their natural habitat?
Yes, Joshua Trees can be cultivated in gardens and landscapes, but they require specific conditions such as well-draining soil and sufficient sunlight. Care should be taken to mimic their native environment. - Do Joshua Trees bloom every year?
Joshua Trees do not bloom every year. They typically flower in the spring, and the frequency of blooming may vary based on environmental conditions and the tree’s age. - Are there any pests or diseases that affect Joshua Trees?
Joshua Trees can be susceptible to pests like scale insects and diseases like leaf spot. Regular monitoring and proper care can help prevent and address these issues. - What is the lifespan of a Joshua Tree?
Joshua Trees have a long lifespan, with some individuals living for several hundred years. The exact lifespan can vary based on environmental conditions and other factors. - Are Joshua Trees the only vegetation in the Mojave Desert?
While Joshua Trees are a prominent feature of the Mojave Desert, they coexist with a variety of other plant species, including cacti, shrubs, and grasses. - Do Joshua Trees have economic value?
While not a major economic resource, Joshua Trees do contribute to local economies through tourism. The attraction of Joshua Tree National Park and surrounding areas draws visitors interested in experiencing the unique desert landscape. - Are there any specific regulations for visiting Joshua Tree National Park?
Yes, visitors to Joshua Tree National Park are subject to park regulations. These include guidelines for camping, hiking, and the preservation of the natural environment. Visitors are encouraged to follow Leave No Trace principles. - Are Joshua Trees only found in the United States?
Joshua Trees are primarily found in the United States, specifically in the Mojave and Sonoran Deserts. While their natural habitat extends into Mexico, the majority of Joshua Trees are concentrated in the U.S. - How do Joshua Trees contribute to soil conservation?
Joshua Trees play a role in soil conservation by preventing erosion. Their extensive root systems help stabilize soil, especially in areas prone to desert winds. - What role do Joshua Trees play in climate resilience?
Joshua Trees demonstrate resilience in arid climates, making them valuable indicators of environmental health. Studying their adaptations can provide insights into climate change impacts on ecosystems. - Are there any known hybrid species of Joshua Trees?
As of current knowledge, there are no documented hybrid species of Joshua Trees. Yucca brevifolia remains a distinct and unique species within the Yucca genus.














please add a survival mechanism. great page for kids to look at and do assignments.
nancy clark
June 22, 2024 2:16 pm