Moringa Tree
- December 27, 2023
- 0 comment
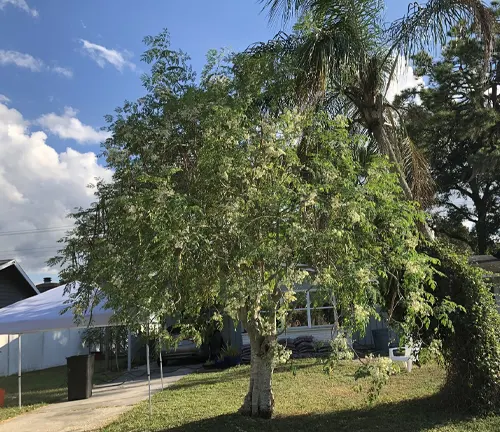
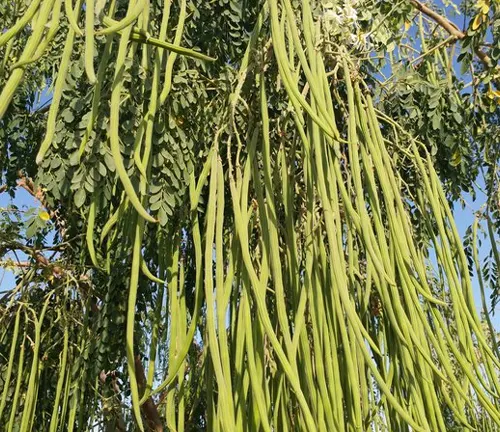
The Moringa tree, often referred to as the “drumstick tree” or “miracle tree,” is a versatile and hardy plant that has gained global recognition for its exceptional nutritional and medicinal properties. Native to parts of Africa and Asia, Moringa is characterized by its slender, elongated seed pods and vibrant green, compound leaves. One of its most remarkable features is its nutrient-rich profile, with leaves containing high levels of vitamins, minerals, and protein.


Moringa is celebrated for its potential to address malnutrition, as it provides a rich source of essential nutrients, including vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, and iron. Additionally, Moringa has been traditionally used in herbal medicine for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Beyond its nutritional and medicinal value, the Moringa tree is also prized for its ability to thrive in arid and drought-prone regions, making it a valuable resource for communities facing environmental challenges.
As awareness of its benefits continues to grow, the Moringa tree is increasingly cultivated and utilized worldwide, contributing to sustainable agriculture and holistic approaches to health and nutrition.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Moringa oleifera |
| Common Names | Drumstick tree, Miracle tree, Ben oil tree |
| Native Regions | Africa, Asia |
| Appearance | Slender, fast-growing tree with compound, green leaves |
| Seed Pods | Elongated, drumstick-shaped, containing seeds |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in vitamins (C, A), minerals (potassium, iron), protein |
| Medicinal Properties | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial |
| Adaptability | Thrives in arid and drought-prone regions |
| Cultivation | Grows well in a variety of soil types, requires minimal water |
| Sustainability | Valuable resource for sustainable agriculture |
| Traditional Uses | Addressing malnutrition, herbal medicine |
| Global Utilization | Increasingly cultivated and utilized worldwide |
Unveiling the Marvels of the Moringa Tree
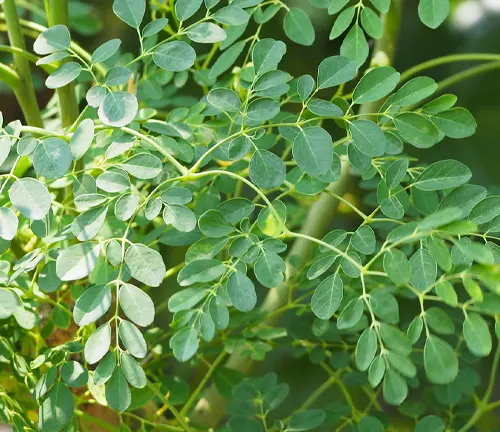

In the realm of botanical wonders, the Moringa tree (Moringa oleifera) stands as a beacon of natural elegance. With its slender frame and compound leaves, this fast-growing tree graces the landscapes of Africa and Asia, offering not just a picturesque silhouette but a wealth of botanical treasures.
The Graceful Presence of Moringa
The Moringa tree, often dubbed the “drumstick tree” or “miracle tree,” boasts woodland elegance that captivates onlookers. Its elongated seed pods, reminiscent of drumsticks, sway in the breeze, while the vibrant green leaves form a canopy that signifies life and vitality. Explore the aesthetic allure of the Moringa tree as we delve into its botanical charms.
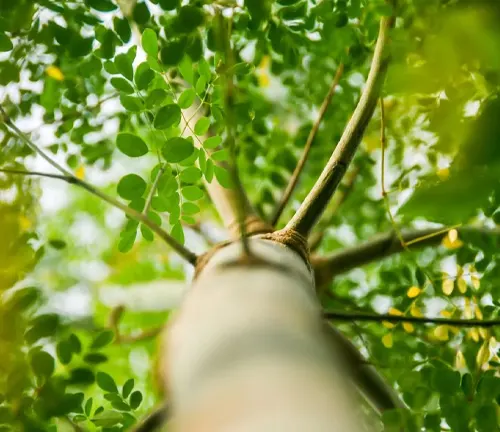


Moringa’s Role in Environmental Harmony
Beyond its visual appeal, the Moringa tree plays a vital role in ecological harmony. Thriving in arid and drought-prone regions, Moringa serves as a resilient guardian of the environment. Discover how this tree contributes to sustainable ecosystems and acts as a valuable resource in regions facing environmental challenges.
Nurturing the Miracle Tree
Unveiling the secrets of cultivating the Moringa tree, this section explores its adaptability to various soil types and its minimal water requirements. We delve into conservation efforts aimed at preserving this botanical marvel, ensuring its continued contribution to global biodiversity.
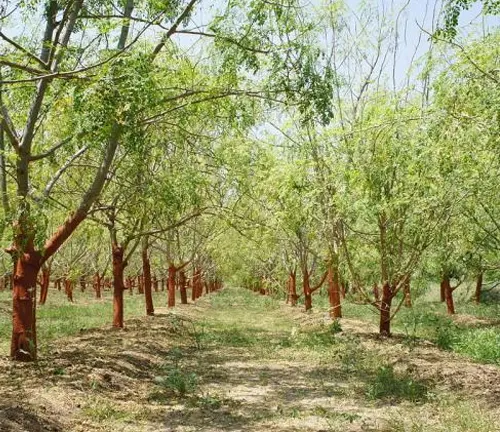


Moringa’s Underground Influence
Digging beneath the surface, we uncover the Moringa tree’s role in soil stabilization. Its extensive root system not only anchors the tree firmly but also helps prevent soil erosion. Learn how Moringa contributes to maintaining soil health and stability, making it an unsung hero in the fight against environmental degradation.
From Kitchen to Medicine Cabinet
Venturing into the practical realm, we explore the myriad ways in which the Moringa tree enriches human life. From its culinary uses, where its leaves and seed pods find a place in diverse cuisines, to its historical role in herbal medicine, discover the everyday applications that make Moringa a staple in many cultures.
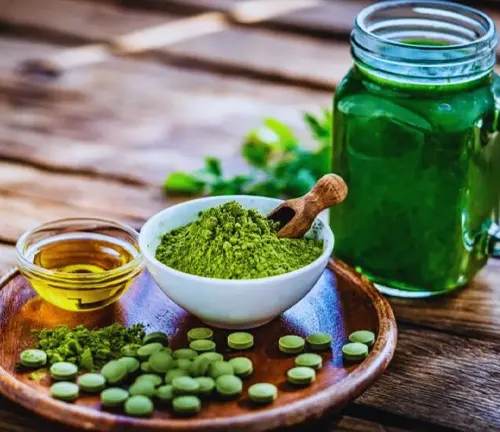

Nutritional and Medicinal Marvels of Moringa

Delving into the heart of the matter, this section unfolds the nutritional and medicinal benefits that have earned Moringa its “miracle tree” moniker. Packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and protein, Moringa leaves offer a potent solution to malnutrition. We also explore its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, highlighting the holistic health benefits this tree brings to the table.
The Intricacies of the Moringa Tree
The Moringa tree, scientifically known as Moringa oleifera, unveils a captivating biological tale that encompasses its growth, structure, and life cycle. This article embarks on a journey to unravel the intricacies of the Moringa tree’s biology, shedding light on what makes it a botanical marvel.
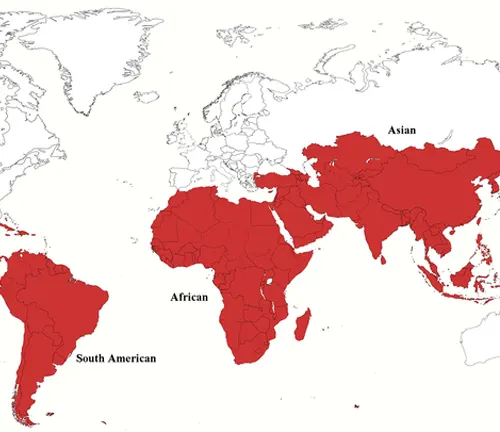
Tracing Moringa’s Roots Across Continents
Venturing into the geographical tapestry of the Moringa tree, this section maps out its natural habitat. From the sun-drenched landscapes of Africa to the lush regions of Asia, we explore the diverse environments where the Moringa tree thrives. Discover the unique ecosystems that have become home to this resilient and versatile plant.
Unveiling the Nutritional Riches of Moringa
Delving into the heart of the Moringa tree’s offerings, this article explores its various components, from leaves to seeds and roots. Uncover the nutritional riches that make Moringa a powerhouse of vitamins, minerals, and protein. Learn about the specific components that contribute to its reputation as a “miracle tree” and a nutritional treasure trove.
Navigating the Nuances of Moringa Consumption
In the pursuit of understanding the Moringa tree’s holistic impact, this section sheds light on potential side effects associated with its consumption. While Moringa is celebrated for its numerous health benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of any potential side effects. Navigate the nuances of Moringa consumption, exploring considerations for those incorporating it into their diet or healthcare routines.
Different Species
Moringa oleifera
This is the most widely cultivated and utilized species of the Moringa tree. Commonly known as the drumstick tree, it is valued for its nutritional and medicinal properties. The leaves, pods, seeds, and flowers of Moringa oleifera are all used for various purposes.
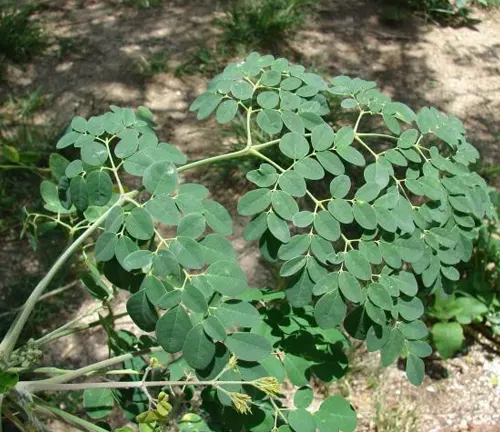


Moringa stenopetala
Also known as the African Moringa, this species is native to parts of East Africa, including Ethiopia and Kenya. Similar to Moringa oleifera, it is valued for its nutritional content, and its leaves and pods are used as food.
Moringa drouhardii
Found in southwestern Madagascar, Moringa drouhardii is a smaller, deciduous tree. It is adapted to arid conditions and has distinctive, bottle-shaped swollen trunks.


Moringa peregrina
Native to the southern parts of the Arabian Peninsula, including Yemen and Saudi Arabia, Moringa peregrina is well-adapted to arid environments. It has small, rounded leaflets and is known for its drought tolerance.
Moringa concanensis
Found in the Western Ghats region of India, Moringa concanensis is a lesser-known species with smaller leaves and pods. It is adapted to the specific climatic conditions of the region.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Moringa tree?
The Moringa tree, scientifically known as Moringa oleifera, is a fast-growing and drought-resistant tree native to parts of Africa and Asia. It is often referred to as the “drumstick tree” or “miracle tree.” - What are the key features of the Moringa tree?
The Moringa tree is characterized by its slender frame, compound leaves, and elongated seed pods. It is valued for its nutritional content and medicinal properties. - What are the nutritional benefits of Moringa?
Moringa is rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins (C, A), minerals (potassium, iron), and protein. Its leaves are often consumed for their nutritional value. - How is the Moringa tree used in traditional medicine?
Moringa has a history of use in traditional medicine, with reported anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Different parts of the tree, such as leaves, seeds, and roots, are used for various health purposes. - What environmental conditions does Moringa thrive in?
Moringa is known for its adaptability to diverse environments. It thrives in arid and drought-prone regions, making it a valuable resource for communities facing environmental challenges. - How is Moringa cultivated?
Moringa is relatively easy to cultivate and grows well in various soil types. It requires minimal water, making it suitable for regions with limited water availability. - What are the common uses of the Moringa tree?
The Moringa tree has versatile uses. Its leaves and seed pods are used in cooking, and it is employed in traditional medicine. Additionally, Moringa is increasingly utilized in the cosmetic and skincare industries. - Are there different species of the Moringa tree?
Yes, while Moringa oleifera is the most widely cultivated species, there are other species such as Moringa stenopetala, Moringa drouhardii, Moringa peregrina, and Moringa concanensis, each with unique characteristics. - What are the potential side effects of consuming Moringa?
While generally considered safe for consumption, excessive intake of Moringa supplements may lead to digestive issues. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before adding Moringa to your diet. - Is Moringa considered a sustainable resource?
Yes, Moringa is recognized for its sustainability. It is resilient, requires minimal resources for cultivation, and contributes to soil stabilization, making it a valuable asset in sustainable agriculture.














Leave your comment