Northern Catalpa
- February 19, 2025
- 0 comment
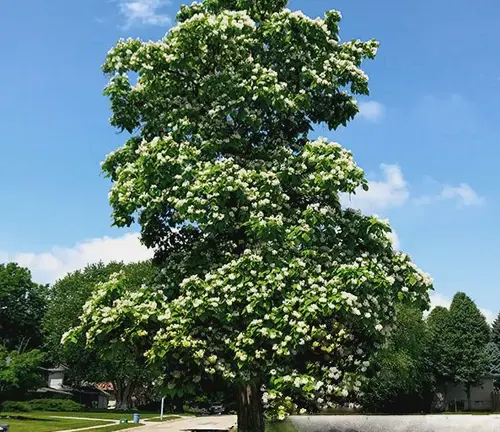
The Northern Catalpa, scientifically known as Catalpa speciosa, is a deciduous tree native to the central United States. Renowned for its striking appearance, this tree is characterized by large, heart-shaped leaves that provide ample shade during the warmer months. One of its most distinctive features is the showy display of orchid-like flowers that bloom in late spring to early summer, forming dense clusters of white blossoms with purple and yellow markings.
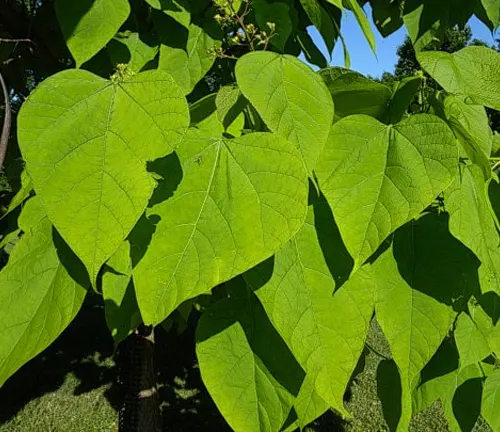
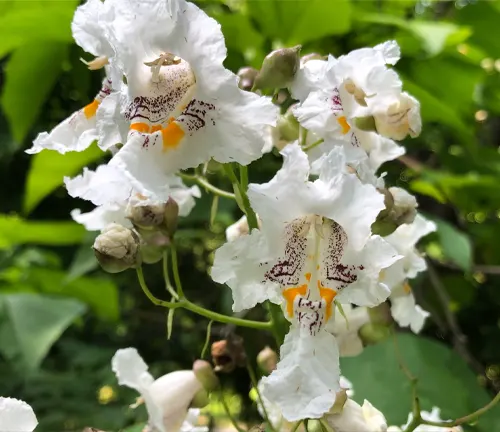


The Northern Catalpa is also recognized for its long, slender seed pods, which can reach lengths of up to 18 inches. These pods persist through the winter months, adding an interesting aesthetic to the tree’s silhouette. With a fast growth rate, the Northern Catalpa is often favored for landscaping purposes, providing quick coverage and an appealing visual impact.
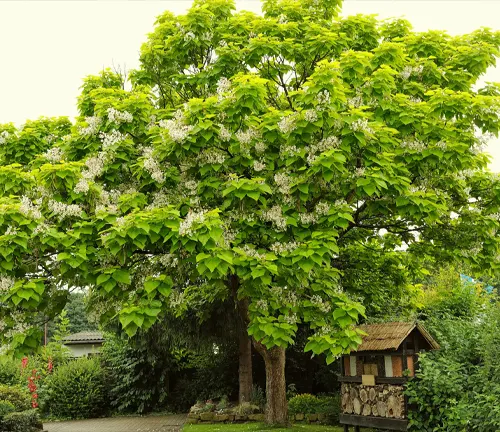

Its tolerance to a variety of soil types and resilience in urban environments make it a popular choice for city streets and parks. Beyond its ornamental value, the wood of the Northern Catalpa has been historically used for fence posts and railroad ties due to its durability. Overall, the Northern Catalpa stands out as a distinctive and adaptable tree, appreciated for both its aesthetic appeal and practical uses.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Catalpa speciosa |
| Common Name | Northern Catalpa |
| Type | Deciduous Tree |
| Native Range | Central United States |
| Foliage | Large, heart-shaped leaves |
| Flowering Season | Late spring to early summer |
| Flower Color | White with purple and yellow markings |
| Seed Pods | Long, slender pods, up to 18 inches in length |
| Growth Rate | Fast |
| Landscape Use | Landscaping, shade tree |
| Soil Tolerance | Adaptable to various soil types |
| Urban Tolerance | Resilient in urban environments |
| Uses | Ornamental, shade, wood for fence posts and ties |
| Wood Durability | Durable, historically used for fence posts and ties |
Brief Overview of the Tree
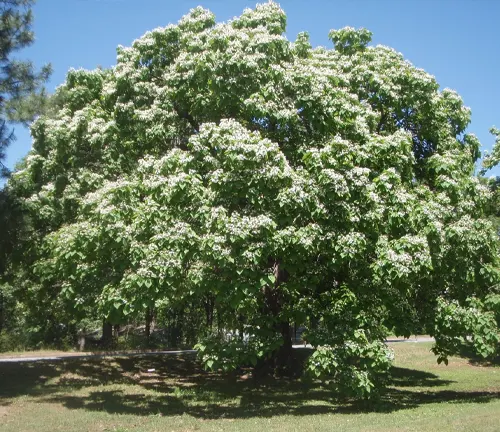

The Northern Catalpa, scientifically known as Catalpa speciosa, stands as a testament to the beauty and resilience of nature. Originating from the central United States, this deciduous tree has captured the hearts of nature enthusiasts and landscapers alike.
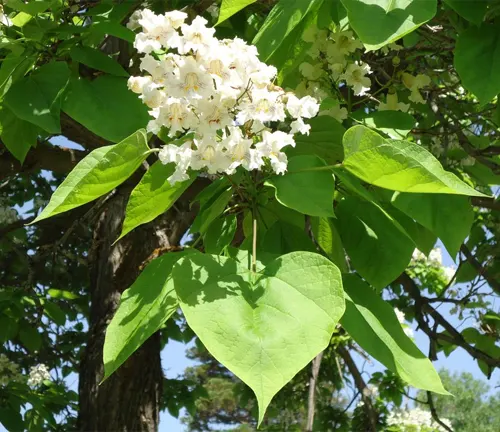

Attributes and Characteristics
With its large, heart-shaped leaves and orchid-like flowers, the Northern Catalpa presents a distinctive aesthetic. Fast-growing and boasting a spreading canopy, it offers not only visual appeal but also practical benefits for landscaping.
Natural Setting
Adaptable to diverse environments, the Northern Catalpa can be found gracing riverbanks and open woods. Its natural setting reflects its ability to thrive in various habitats across the central United States.
Soil Type
A true survivor, the Northern Catalpa demonstrates adaptability to an array of soil types, showcasing its resilience in sandy, loamy, and clayey soils.
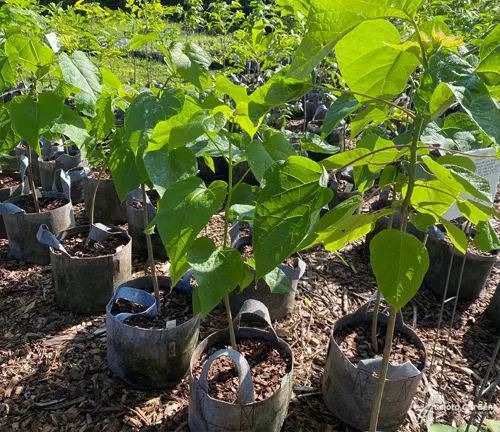

Soil Preferences
While it tolerates different soil compositions, the Northern Catalpa flourishes best in well-drained soils, ensuring optimal growth and vitality.
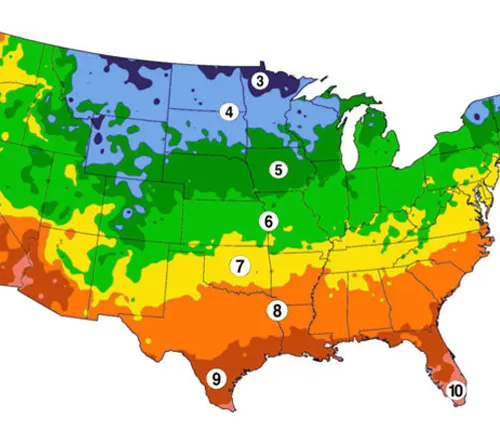
Hardiness Zone
Suited for a range of climates, this hardy tree typically thrives in USDA zones 4 to 8, making it a versatile choice for diverse landscapes.
Sun Preference
Preferring the spotlight, the Northern Catalpa revels in full sun, showcasing its best growth and flowering potential under direct sunlight.
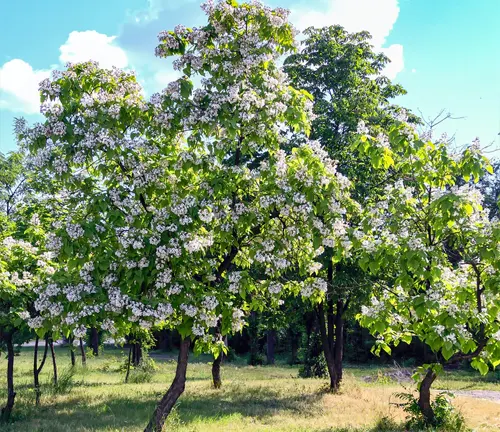
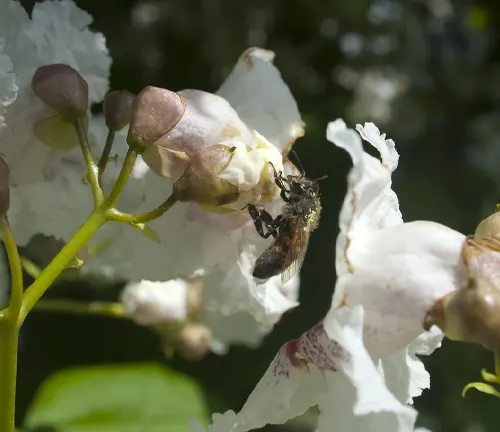


Wildlife Value
Beyond its aesthetic charm, the Northern Catalpa plays a crucial role in supporting wildlife. Bees and butterflies are frequent visitors, highlighting its importance in local ecosystems.
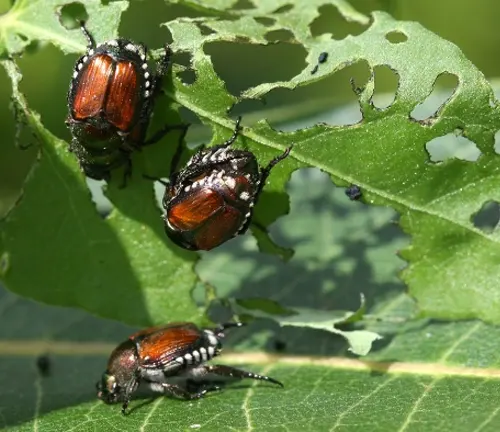
Common Pests & Diseases
While generally robust, the Northern Catalpa is not immune to challenges. Keep an eye out for potential threats such as catalpa sphinx moths and fungal issues, addressing them promptly to maintain the tree’s health.

Care and Maintaining Northern Catalpa
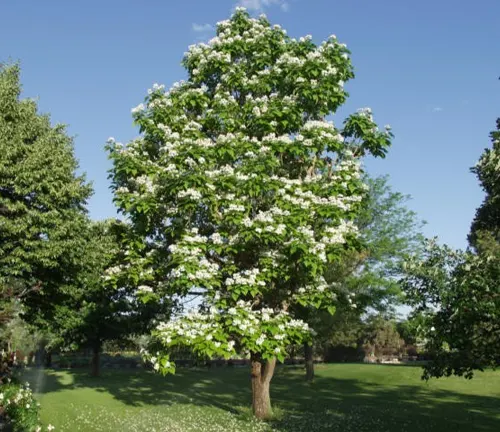

To encourage a well-shaped and healthy tree, regular pruning is recommended. Adequate watering, especially during dry spells, contributes to the overall well-being of the Northern Catalpa.
Health
Vigilance is key to maintaining the health of this tree. Regular monitoring, prompt action against pests, and proper care foster a thriving and resilient Northern Catalpa.
Safety
To ensure safety, plant the Northern Catalpa a safe distance from structures, considering its expansive root system. Regular inspections for weak or dead branches enhance the safety of the tree in urban settings.
Wood Products
The durable wood of the Northern Catalpa has found historical applications in the construction industry, particularly in the making of fence posts and railroad ties.

Edible or Not
While not a common choice for human consumption, some sources suggest that the young leaves of the Northern Catalpa are edible and can be used in salads.
Benefits
Beyond its ornamental value, the Northern Catalpa offers shade, contributes to biodiversity, and has historical significance in various industries, showcasing its multifaceted benefits.
Enhancing the Quality of Life
By providing aesthetic appeal, shade, and habitat support for wildlife, the Northern Catalpa enhances the quality of life in the areas it graces.

Contribution to the Environment
This tree plays a vital role in the environment, supporting pollinators, producing oxygen, and contributing to carbon sequestration, underscoring its positive impact on the ecosystem.
Disadvantages
While an asset in many ways, the Northern Catalpa’s expansive root system can pose challenges near structures. Occasional susceptibility to pests and diseases necessitates careful monitoring.

Longevity
With proper care, the Northern Catalpa can live for several decades, offering enduring beauty and benefits to the environment and those who appreciate its presence.
Fun Facts
Adding a touch of whimsy to its profile, the Northern Catalpa’s large leaves, unique flowers, and persistent seed pods make it a fascinating and memorable feature in any landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Northern Catalpa? The Northern Catalpa (Catalpa speciosa) is a deciduous tree native to the central United States, known for its distinctive features, including large heart-shaped leaves, orchid-like flowers, and long seed pods.
2. Where is the Northern Catalpa typically found? The tree is native to the central United States and is commonly found in a variety of habitats, including riverbanks and open woods.
3. What are the key characteristics of the Northern Catalpa? The tree is characterized by large, heart-shaped leaves, showy orchid-like flowers in late spring, and long seed pods. It has a fast growth rate and a spreading canopy.
4. Is the Northern Catalpa suitable for landscaping? Yes, the Northern Catalpa is often chosen for landscaping projects due to its aesthetic appeal, fast growth, and ability to provide ample shade.
5. What types of soil does the Northern Catalpa prefer? The Northern Catalpa is adaptable to various soil types, including sandy, loamy, and clayey soils. However, it thrives best in well-drained soils.
6. In which hardiness zones does the Northern Catalpa thrive? The tree is generally hardy in USDA zones 4 to 8, making it suitable for a range of climates.
7. Does the Northern Catalpa attract wildlife? Yes, the tree attracts wildlife such as bees and butterflies, contributing to local ecosystems by supporting pollinators.
8. What are common pests and diseases affecting the Northern Catalpa? While generally hardy, the tree may face challenges such as catalpa sphinx moths and certain fungal issues. Regular monitoring is essential for maintaining its health.
9. How do you care for a Northern Catalpa tree? Care involves regular pruning for shape, adequate watering, and monitoring for pests and diseases. Proper spacing from structures is also important to avoid root-related issues.
10. Is the wood of the Northern Catalpa used for any specific purposes? Yes, the durable wood of the Northern Catalpa has historical applications in the construction industry, particularly for making fence posts and railroad ties.
11. Are there any edible parts of the Northern Catalpa? While not commonly consumed, some sources suggest that the young leaves of the Northern Catalpa are edible and can be used in salads.
12. What benefits does the Northern Catalpa offer? Beyond its ornamental value, the tree provides shade, contributes to biodiversity, and has historical significance in various industries.
13. How does the Northern Catalpa contribute to the environment? The tree supports pollinators, produces oxygen, and contributes to carbon sequestration, making it environmentally valuable.
14. Are there any disadvantages to planting the Northern Catalpa? The tree’s expansive root system can pose challenges near structures, and occasional susceptibility to pests and diseases requires careful monitoring.
15. How long does the Northern Catalpa tree typically live? With proper care, the Northern Catalpa can live for several decades, offering enduring beauty and benefits to the environment.














Leave your comment