7 Key Benefits of Sustainable Forest Management
- August 6, 2024
- 0 comment
Sustainable forest management (SFM) has emerged as a vital strategy for maintaining the health and productivity of the world’s forests. As deforestation, climate change, and biodiversity loss continue to intensify, the need for sustainable forest management practices becomes increasingly urgent.
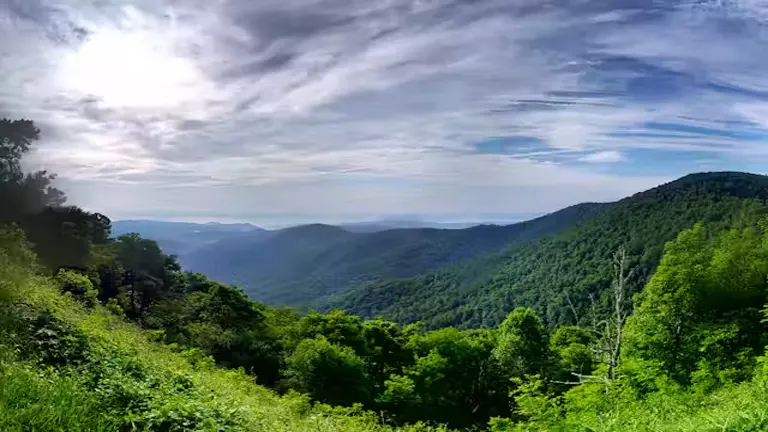

SFM addresses these pressing issues by balancing ecological, economic, and social needs. By implementing sustainable practices, we can ensure the longevity and vitality of forests, benefiting both the environment and local communities. Consequently, the importance of managing forests sustainably cannot be overstated in our efforts to combat these global challenges.
Understanding Sustainable Forest Management
Sustainable forest management involves the careful stewardship and utilization of forests and forest lands to maintain their biodiversity, productivity, regeneration capacity, and overall vitality. It ensures that forests can continue to fulfill their ecological, economic, and social roles at local, national, and global levels both now and in the future. This approach strikes a balance between environmental preservation and economic and societal needs. By integrating these diverse aspects, sustainable forest management promotes the long-term health and resilience of forest ecosystems. This holistic method is essential for addressing the multifaceted challenges faced by our forests today.
7 Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Forest Management
1. Biodiversity Conservation
Forests house a substantial portion of the world’s terrestrial species, making biodiversity conservation one of the primary benefits of sustainable forest management. By adopting practices that protect habitats and ecosystems, SFM helps preserve the genetic diversity of both flora and fauna.
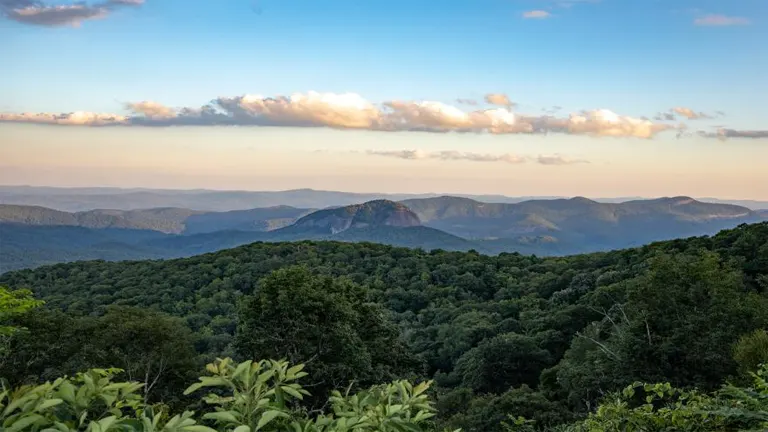

This conservation effort, in turn, supports essential ecosystem services such as pollination, pest control, and nutrient cycling. These services are crucial for the health of natural environments and are equally important for human agriculture. Ultimately, sustainable forest management ensures that biodiversity continues to thrive, providing invaluable benefits to ecosystems and human societies alike.
2. Climate Regulation
One of the most critical environmental benefits of sustainable forest management is its role in climate regulation. Forests function as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in biomass and soil. Sustainable practices ensure that forests continue to sequester carbon effectively, thereby mitigating the impacts of climate change.
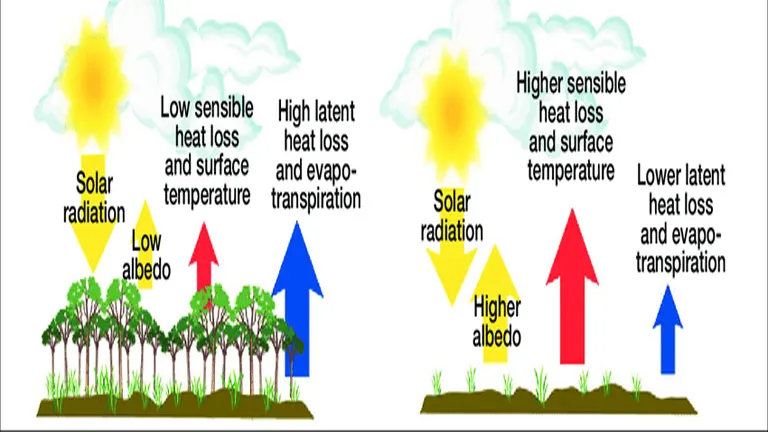
Additionally, SFM minimizes carbon release through activities such as controlled logging and reforestation. These practices are essential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a healthier climate.
3. Soil Preservation
Sustainable forest management plays a crucial role in preserving soil quality and preventing erosion. Forests protect the soil with their intricate root systems, anchoring it and preventing erosion caused by rain.
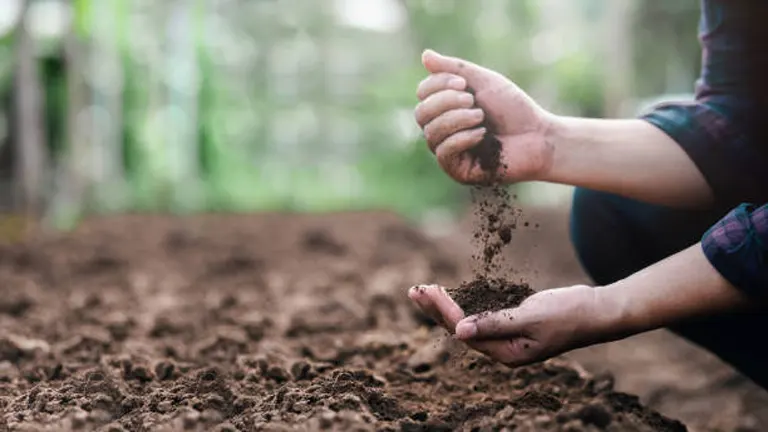

Sustainable practices such as selective logging and maintaining ground cover help retain soil structure and fertility. These measures are vital for the health of forest ecosystems and agricultural productivity. By safeguarding the soil, sustainable forest management ensures the long-term viability of both natural landscapes and human agricultural endeavors.
4. Sustainable Timber Production
Forests provide timber, a valuable resource for construction, furniture, and paper industries. Sustainable forest management ensures that timber production is maintained at a level that does not compromise the forest’s ability to regenerate.
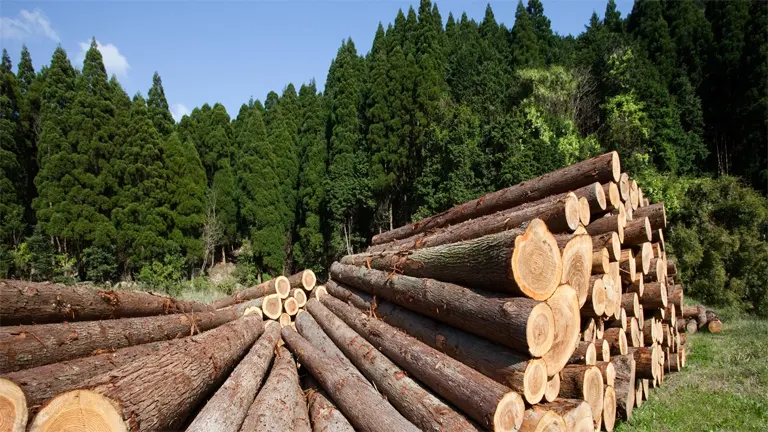

This approach not only supports long-term economic stability but also guarantees that future generations will have access to forest resources. Certification schemes like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) promote sustainable practices by ensuring that timber comes from responsibly managed forests.
5. Ecotourism and Recreation
Sustainable forest management opens up opportunities for ecotourism and recreational activities, which can provide significant economic benefits. Well-managed forests attract tourists who are interested in experiencing nature, wildlife, and cultural heritage.
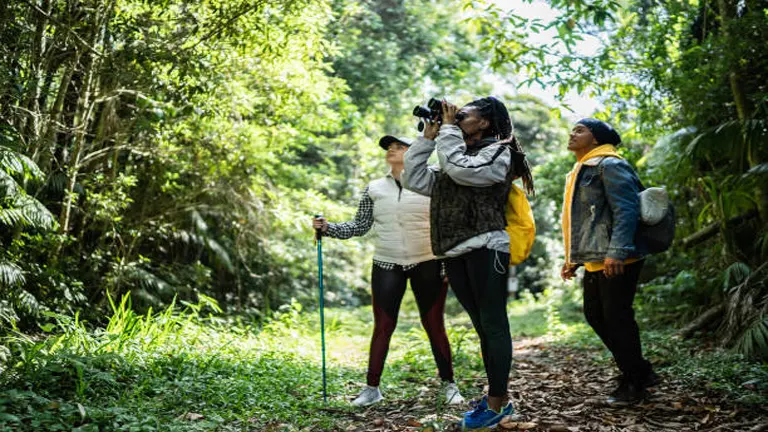

This influx of visitors can boost local economies through spending on lodging, food, and guided tours. Moreover, promoting ecotourism raises awareness about the importance of conservation. It also supports funding for further sustainable management efforts, creating a positive cycle of economic growth and environmental stewardship.
6. Supporting Indigenous Communities
Many indigenous communities around the world rely on forests for their livelihoods, culture, and traditions. Sustainable forest management practices respect the rights and knowledge of these communities, ensuring they can continue to use forest resources sustainably.
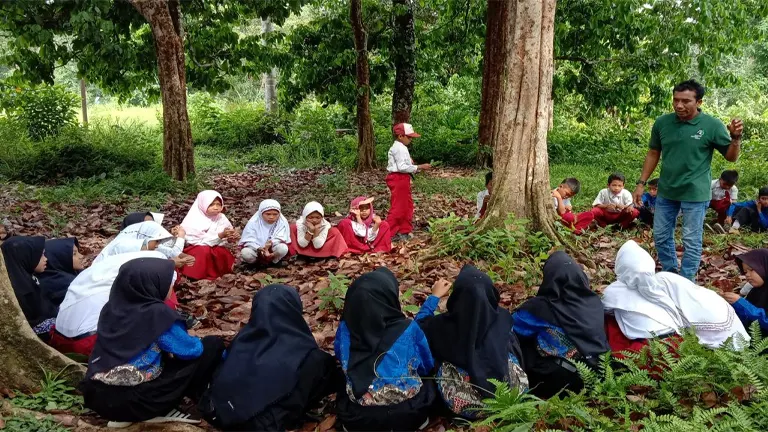

By involving indigenous people in decision-making processes and recognizing their land rights, SFM helps improve their quality of life and preserve their cultural heritage. This inclusive approach not only supports the well-being of indigenous populations but also enriches the broader goals of conservation and sustainable resource use.
7. Enhancing Community Livelihoods
Beyond indigenous communities, sustainable forest management also supports the livelihoods of local communities by creating jobs in forestry, conservation, and tourism. These employment opportunities can improve living standards and provide economic stability.
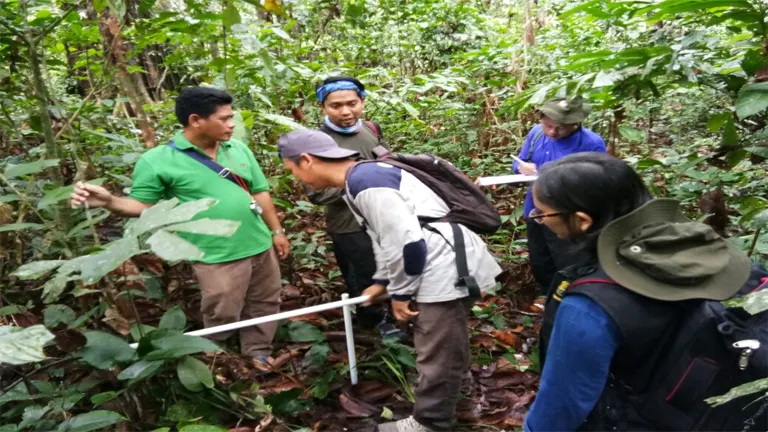

Additionally, SFM practices often involve the development of local infrastructure and services, such as roads, schools, and healthcare facilities. This development enhances the overall quality of life for community members. By fostering economic growth and improving living conditions, sustainable forest management contributes to the well-being and resilience of local communities.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Forest Management
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing sustainable forest management is not without challenges. These can include lack of funding, insufficient political will, and conflicts over land use. Additionally, balancing the immediate economic needs of communities with long-term sustainability goals can be difficult. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts from governments, NGOs, and the private sector.
Strategies for Promoting Sustainable Forest Management
Promoting sustainable forest management involves a range of strategies, including policy development, education, and community engagement. Governments can create and enforce regulations that support SFM, while educational programs can raise awareness about the benefits and practices of sustainable management. Engaging local communities and stakeholders in the planning and implementation of SFM initiatives ensures that these efforts are culturally appropriate and widely accepted.
Global Initiatives and Policies
Several global initiatives and policies support sustainable forest management. The United Nations’ REDD+ program (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) incentivizes developing countries to manage their forests sustainably. Similarly, international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Paris Agreement highlight the importance of conserving forests and promoting sustainable practices.
Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Forest Management
Examining case studies of successful sustainable forest management can provide valuable insights and lessons. For instance, Costa Rica’s payment for ecosystem services (PES) program has been instrumental in reducing deforestation and promoting reforestation. By financially compensating landowners for maintaining forest cover, the program has enhanced biodiversity and contributed to climate change mitigation.
The Future of Sustainable Forest Management
The future of sustainable forest management lies in continued innovation and collaboration. Advances in technology, such as remote sensing and GIS (Geographic Information Systems), offer new tools for monitoring forest health and implementing sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and communities will be crucial in overcoming challenges and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the world’s forests.
Conclusion
Sustainable forest management plays a crucial role in preserving the ecological, economic, and social functions of our forests. It ensures the maintenance of biodiversity, the regulation of climate, and the support of local communities. By offering a holistic approach to forest conservation, SFM addresses these multiple facets effectively. Overcoming challenges and promoting sustainable practices through sound policies, educational initiatives, and collaborative efforts is essential. Such comprehensive efforts will ensure that our forests continue to thrive and provide their invaluable benefits for generations to come.
FAQs
- What is sustainable forest management?
Involves practices that maintain the health and productivity of forests while meeting ecological, economic, and social needs. - Why is biodiversity conservation important in sustainable forest management?
Biodiversity conservation ensures the survival of various species and ecosystems, supporting essential services like pollination and pest control. - How does sustainable forest management help in climate regulation?
Sustainable practices enhance forests’ ability to sequester carbon, reducing greenhouse gases and mitigating climate change. - What are the economic benefits of sustainable forest management?
Economic benefits include sustainable timber production, job creation, and opportunities in ecotourism and recreation. - How does sustainable forest management support indigenous communities?
It respects their rights and knowledge, involving them in decision-making and improving their livelihoods and cultural preservation. - What are some challenges in implementing sustainable forest management?
Challenges include funding shortages, political resistance, and balancing immediate economic needs with long-term sustainability goals. - How does sustainable forest management contribute to soil preservation?
Practices help maintain soil structure and fertility by minimizing soil erosion. Techniques such as selective logging and maintaining ground cover protect the soil from being washed away, ensuring its health for future forest growth and agricultural use. - What role does ecotourism play in sustainable forest management?
Ecotourism provides significant economic benefits by attracting visitors interested in nature and wildlife. This influx of tourists generates income for local communities through spending on lodging, food, and tours. Additionally, ecotourism promotes conservation awareness and funds further sustainable management efforts. - Can sustainable forest management help combat climate change?
Yes, Its crucial in combating climate change. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Sustainable practices ensure that forests continue to sequester carbon effectively, reducing greenhouse gases and mitigating climate change impacts. - What are some global initiatives that support sustainable forest management?
Global initiatives like the United Nations’ REDD+ program and international agreements such as the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Paris Agreement support sustainable forest management. These initiatives provide frameworks and incentives for countries to adopt and implement sustainable practices, aiming to reduce deforestation and promote forest conservation worldwide.

James Wilson
Forestry AuthorJames Wilson has over 15 years of experience in forestry economics, specializing in sustainable practices, investment opportunities, and financial management. He has contributed to notable publications like "Forestry Today" and "EcoFinance Journal" and is known for providing practical and insightful advice. With a degree in Environmental Economics, James stays updated through continuous learning and active participation in industry discussions. Outside work, he enjoys hiking and nature photography, bringing a well-rounded perspective to his professional role.








Leave your comment