Mastering Financial Management: Key Strategies for Successful Forestry Operations
- August 16, 2024
- 0 comment
Financial management aspects in forestry are crucial for maintaining healthy and productive forests while ensuring profitability and sustainability. Forestry operations face unique challenges, including fluctuating timber prices, environmental regulations, and unpredictable natural events. These challenges necessitate strategic financial management to navigate the complexities of the industry.

Financial management involves planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources to achieve the organization’s goals. In forestry, it encompasses everything from budgeting and cost control to revenue generation and risk management. Effective financial management ensures that forestry operations remain sustainable, profitable, and adaptable to changing circumstances.
Understanding Forestry Operations
Forestry operations encompass a wide range of activities aimed at managing forest resources for various purposes, including timber production, conservation, recreation, and ecosystem services. Understanding the different types of forestry operations and their key components is essential for effective financial management.

Types of Forestry Operations
- Commercial Forestry: Focused on timber production and sales, this type of operation involves activities such as planting, thinning, harvesting, and reforestation.
- Conservation Forestry: Aimed at preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem services, conservation forestry includes activities like habitat restoration, wildlife protection, and sustainable land management.
- Agroforestry: Combines agriculture and forestry practices to create integrated land-use systems, agroforestry enhances biodiversity and improves land productivity while providing additional income streams.
- Community Forestry: Involves local communities in forest management, community forestry emphasizes sustainable practices and equitable benefit-sharing among community members.
Importance of Financial Management in Forestry
Financial management plays a crucial role in ensuring the sustainability and success of forestry operations. It provides the framework for making informed decisions, optimizing resource allocation, and achieving long-term financial stability.
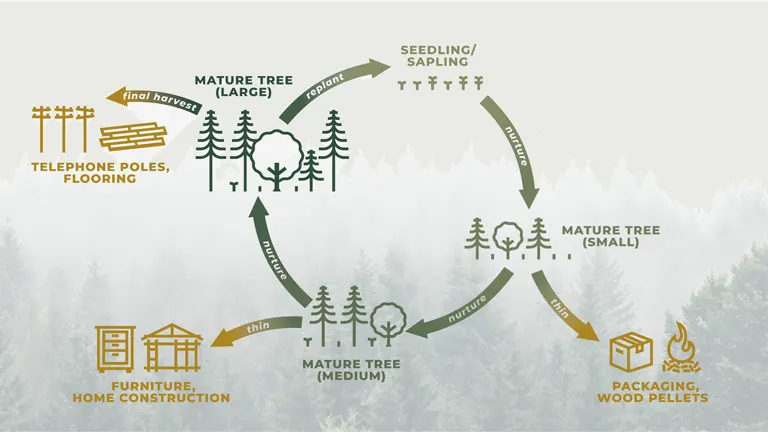
Role of Financial Management
- Resource Allocation: Financial management helps allocate resources effectively, ensuring that funds are directed toward high-priority activities and projects.
- Cost Control: By monitoring expenses and implementing cost-saving measures, financial management helps minimize waste and improve operational efficiency.
- Revenue Generation: Effective financial management identifies and maximizes revenue streams, ensuring a steady income to support ongoing operations.
- Risk Management: Financial management assesses potential risks and implements strategies to mitigate them, safeguarding the organization against financial losses.
- Sustainability: By balancing economic, environmental, and social goals, financial management promotes sustainable practices that benefit both the organization and the broader community.
Long-term Planning and Sustainability
Long-term planning is essential for ensuring the sustainability of forestry operations. Financial management provides the tools and insights needed to develop and implement strategic plans that account for future challenges and opportunities.
- Forecasting: Predicting future trends and developments in the forestry industry to make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment.
- Strategic Planning: Developing long-term plans that align with organizational goals and address potential risks and opportunities.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Implementing practices that promote environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability.
Effective financial management ensures that forestry operations remain resilient and adaptable in the face of changing circumstances, ultimately contributing to their long-term success and sustainability.
Budgeting for Forestry Operations
Creating a comprehensive budget is a critical component of financial management in forestry operations. It involves estimating revenues and expenses, setting financial targets, and monitoring performance to ensure that financial goals are achieved.

Creating a Comprehensive Budget
- Revenue Estimation: Forecasting income from various sources, such as timber sales, non-timber products, and ecosystem services.
- Expense Estimation: Identifying and estimating costs associated with forestry operations, including labor, equipment, materials, and administrative expenses.
- Financial Goals: Setting clear and achievable financial targets that align with organizational objectives.
- Budget Allocation: Distributing funds to different activities and projects based on priorities and expected returns.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly tracking financial performance and comparing it against the budget to identify deviations and make necessary adjustments.
Types of Costs in Forestry
- Direct Costs: Expenses directly related to forestry operations, such as labor, equipment, and materials.
- Indirect Costs: Overhead expenses that support forestry operations, including administrative costs, utilities, and insurance.
- Variable Costs: Costs that fluctuate with changes in production levels, such as fuel and transportation.
- Fixed Costs: Expenses that remain constant regardless of production levels, such as salaries and rent.
Monitoring and Adjusting Budgets
Effective financial management requires continuous monitoring of financial performance and making necessary adjustments to ensure that budgets remain relevant and aligned with organizational goals.
- Performance Analysis: Regularly analyzing financial performance to identify trends, deviations, and areas for improvement.
- Budget Adjustments: Making changes to the budget in response to changing circumstances, such as market fluctuations, regulatory changes, or unexpected expenses.
- Financial Reporting: Providing timely and accurate financial reports to stakeholders, ensuring transparency and accountability.
By creating and maintaining a comprehensive budget, forestry operations can optimize resource allocation, control costs, and achieve financial goals.
Revenue Streams in Forestry
Diversifying revenue streams is essential for ensuring the financial stability and sustainability of forestry operations. By tapping into various income sources, forestry operations can reduce their reliance on timber sales and mitigate financial risks.
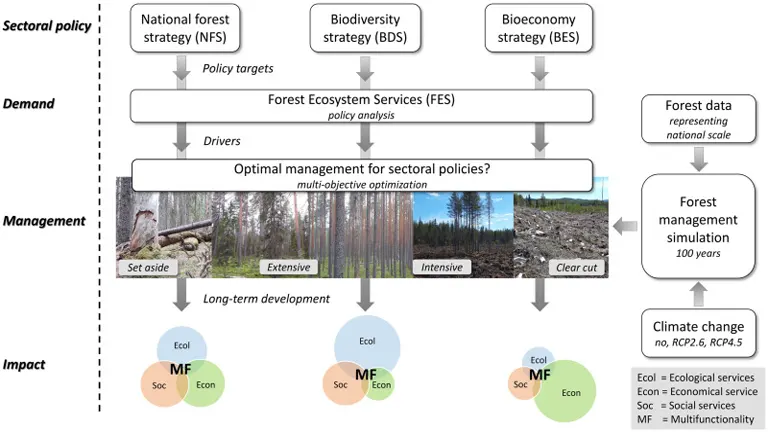
Timber Sales
Timber sales remain the primary source of revenue for most forestry operations. However, maximizing income from timber sales requires careful planning and management.
- Harvest Planning: Developing harvest plans that optimize timber yield while minimizing environmental impact.
- Market Analysis: Monitoring market trends and prices to make informed decisions about when and where to sell timber.
- Value-added Products: Exploring opportunities to produce value-added products, such as furniture, flooring, and paper, to increase revenue.
Non-timber Products
In addition to timber, forests provide a wide range of non-timber products that can generate additional income.
- Forest Fruits and Nuts: Harvesting and selling forest fruits and nuts, such as acorns, chestnuts, and berries.
- Medicinal Plants: Cultivating and selling medicinal plants, such as ginseng, echinacea, and goldenseal.
- Forest Crafts: Producing and selling crafts made from forest materials, such as baskets, carvings, and woven goods.
Ecosystem Services
Forests provide valuable ecosystem services that can be monetized to generate additional income.
- Carbon Credits: Participating in carbon credit programs that compensate forest owners for carbon sequestration and storage.
- Watershed Protection: Receiving payments for maintaining healthy watersheds that provide clean water to downstream communities.
- Recreation and Tourism: Developing recreational facilities and ecotourism activities that attract visitors and generate revenue.
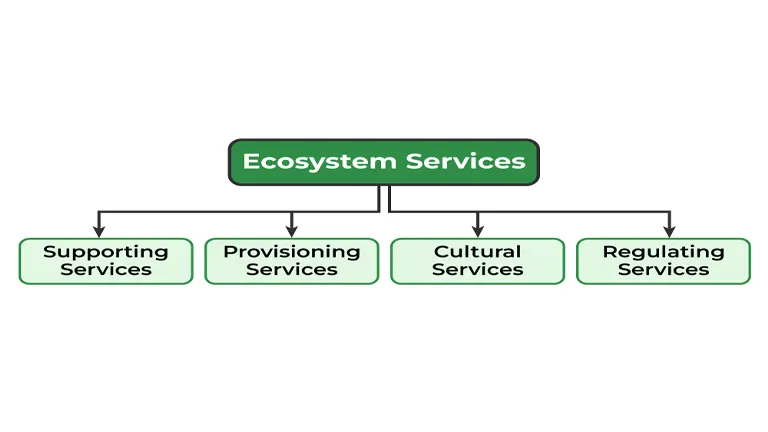
Diversification of Income
Diversifying income streams is essential for reducing financial risks and ensuring the sustainability of forestry operations.
- Agroforestry: Integrating agricultural and forestry practices to create diversified land-use systems that provide multiple income streams.
- Forest Certification: Obtaining certification for sustainable forest management practices, which can enhance market access and command premium prices.
- Community-based Enterprises: Involving local communities in forest management and income-generating activities, fostering social and economic development.
By diversifying revenue streams, forestry operations can enhance their financial resilience and ensure long-term sustainability.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also contribute to cost control and financial optimization.
- Resource Conservation: Implementing practices that conserve resources, such as water, energy, and materials, to reduce costs.
- Waste Reduction: Reducing waste and recycling materials to minimize disposal costs and enhance environmental sustainability.
- Sustainable Procurement: Sourcing materials and services from sustainable suppliers to reduce costs and enhance environmental performance.
By focusing on cost control and optimization, forestry operations can improve their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Risk Management in Forestry
Forestry operations face a variety of risks that can impact their financial performance and sustainability. Effective risk management involves identifying potential risks and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact.
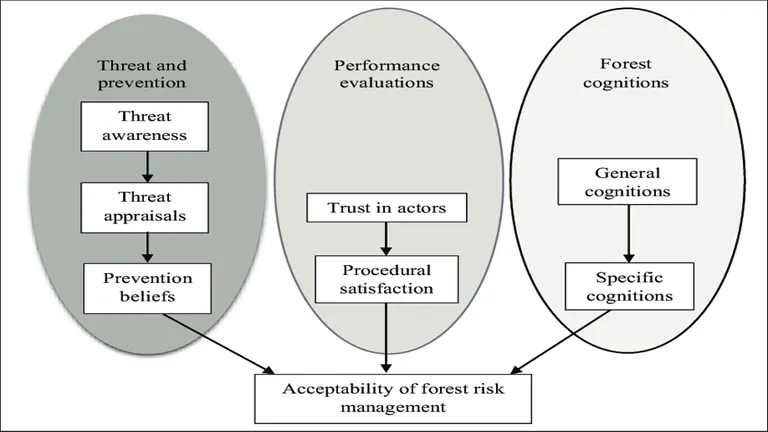
Types of Risks
- Natural Risks: Risks related to natural events, such as wildfires, storms, pests, and diseases, that can damage forests and reduce timber yields.
- Market Risks: Risks related to fluctuations in timber prices, demand, and supply, which can impact revenue and profitability.
- Operational Risks: Risks related to operational activities, such as equipment failure, accidents, and labor shortages, that can disrupt forestry operations.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Diversification: Diversifying income streams and activities to reduce reliance on a single source of revenue and mitigate financial risks.
- Insurance: Obtaining insurance coverage to protect against potential losses from natural events, market fluctuations, and operational disruptions.
- Contingency Planning: Developing contingency plans to address potential risks and ensure continuity of operations in the event of disruptions.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitoring risks and reporting potential threats to stakeholders to ensure timely response and mitigation.
By implementing effective risk management strategies, forestry operations can protect their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Investment Strategies in Forestry
Investment strategies play a crucial role in ensuring the financial success and sustainability of forestry operations. By making informed investment decisions, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and achieve long-term goals.
Long-term vs Short-term Investments
- Long-term Investments: Investments aimed at achieving long-term goals, such as reforestation, infrastructure development, and technology adoption, that enhance the sustainability and productivity of forestry operations.
- Short-term Investments: Investments aimed at achieving short-term goals, such as equipment upgrades, process improvements, and marketing initiatives, that enhance the financial performance of forestry operations.
Evaluating Investment Opportunities
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Assessing the costs and benefits of potential investments to determine their feasibility and expected returns.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the risks associated with potential investments and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact.
- Market Analysis: Monitoring market trends and developments to identify investment opportunities that align with organizational goals and objectives.
Impact of Market Trends
Understanding market trends and developments is essential for making informed investment decisions in forestry operations.
- Demand and Supply: Analyzing demand and supply trends to identify opportunities for revenue generation and cost control.
- Technological Advancements: Monitoring technological advancements to identify opportunities for process improvements and efficiency gains.
- Regulatory Changes: Keeping abreast of regulatory changes to identify opportunities for compliance and competitive advantage.
By developing and implementing effective investment strategies, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Sustainable Practices and Financial Outcomes
Sustainable practices are essential for ensuring the long-term financial success and environmental health of forestry operations. By balancing environmental and financial goals, forestry operations can achieve positive financial outcomes and enhance their sustainability.

Balancing Environmental and Financial Goals
- Resource Conservation: Implementing practices that conserve resources, such as water, energy, and materials, to reduce costs and enhance environmental sustainability.
- Ecosystem Protection: Protecting and maintaining ecosystems and biodiversity to ensure long-term environmental health and resilience.
- Sustainable Procurement: Sourcing materials and services from sustainable suppliers to reduce costs and enhance environmental performance.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in forest management and income-generating activities, fostering social and economic development.
Impact of Sustainability on Profitability
Sustainability can have a positive impact on the profitability of forestry operations by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving market access.
- Efficiency Gains: Implementing sustainable practices can improve efficiency and reduce costs, enhancing financial performance.
- Market Access: Achieving certification for sustainable forest management practices can enhance market access and command premium prices.
- Reputation and Brand Value: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability can enhance reputation and brand value, attracting customers and investors.
Sustainability Initiatives
Implementing sustainability initiatives can enhance the financial performance and environmental health of forestry operations.
- Carbon Sequestration: Participating in carbon credit programs that compensate forest owners for carbon sequestration and storage.
- Water Management: Implementing practices that enhance water management and watershed protection, providing clean water to downstream communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Protecting and maintaining biodiversity to ensure long-term environmental health and resilience.
By implementing sustainable practices, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Technology and Innovation in Forestry Finance
Technology and innovation are transforming the financial management of forestry operations, providing new tools and insights for optimizing resource allocation and achieving financial goals.

Emerging Technologies
- Remote Sensing: Using satellite and aerial imagery to monitor forest conditions and assess changes over time.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics to analyze financial performance and identify trends, deviations, and areas for improvement.
- Automation: Implementing automation to streamline processes and reduce labor costs.
- Blockchain: Using blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability in forestry operations.
Use of Data Analytics
Data analytics provides valuable insights into the financial performance and position of forestry operations, enabling informed decision-making and optimization.
- Performance Monitoring: Analyzing financial performance to identify trends, deviations, and areas for improvement.
- Cost Analysis: Conducting a thorough analysis of costs to identify areas for improvement and potential cost-saving opportunities.
- Revenue Forecasting: Predicting future trends and developments in the forestry industry to make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment.
Impact of Technology on Financial Management
Technology is transforming the financial management of forestry operations, providing new tools and insights for optimizing resource allocation and achieving financial goals.

- Efficiency Improvements: Utilizing technology and automation to streamline processes and reduce labor costs.
- Risk Management: Implementing technology to monitor risks and enhance risk mitigation strategies.
- Transparency and Reporting: Using technology to enhance transparency and reporting, ensuring accountability and building trust with stakeholders.
By embracing technology and innovation, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Government Policies and Financial Implications
Government policies play a significant role in shaping the financial management of forestry operations, providing incentives, regulations, and support for sustainable practices.
Regulatory Environment
- Environmental Regulations: Government regulations that promote environmental protection and sustainable forest management.
- Land Use Policies: Policies that govern land use and zoning, impacting the planning and development of forestry operations.
- Labor Regulations: Regulations that govern labor practices and ensure fair wages and working conditions.
Incentives and Subsidies
Government incentives and subsidies can provide financial support for sustainable forestry practices, enhancing the financial performance of forestry operations.
- Tax Incentives: Tax breaks and deductions for sustainable practices, such as reforestation and conservation initiatives.
- Grants and Loans: Financial assistance for forestry operations that implement sustainable practices and contribute to environmental health.
- Subsidies: Financial support for activities that enhance biodiversity, protect watersheds, and promote ecosystem services.
Impact of Policies on Financial Planning
Government policies can have a significant impact on the financial planning and performance of forestry operations, influencing resource allocation and investment decisions.
- Compliance Costs: The cost of complying with government regulations, impacting the financial performance of forestry operations.
- Market Access: Policies that promote sustainable practices can enhance market access and command premium prices.
- Risk Mitigation: Government policies can provide support for risk mitigation strategies, such as insurance and contingency planning.
By understanding and navigating the regulatory environment, forestry operations can optimize their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Case Studies: Successful Forestry Financial Management
Analyzing case studies of successful forestry operations provides valuable insights into effective financial management strategies and lessons learned from failures.
Examples of Successful Forestry Operations
- Sustainable Timber Production: A forestry operation that achieved financial success through sustainable timber production and value-added products.
- Community-based Forest Management: A forestry operation that engaged local communities in forest management and income-generating activities, fostering social and economic development.
- Ecosystem Service Payments: A forestry operation that monetized ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration and watershed protection, to generate additional income.
Lessons Learned from Failures
- Financial Mismanagement: A forestry operation that experienced financial difficulties due to poor financial planning and inadequate risk management.
- Market Fluctuations: A forestry operation that faced financial challenges due to reliance on a single source of revenue and lack of diversification.
- Regulatory Compliance: A forestry operation that incurred significant costs due to non-compliance with government regulations and environmental standards.
By analyzing successful case studies and learning from failures, forestry operations can develop effective financial management strategies and enhance their financial performance.
The Future of Financial Management in Forestry
The future of financial management in forestry is shaped by emerging trends, future challenges, and opportunities for innovation and sustainability.

Emerging Trends
- Digital Transformation: The adoption of digital technologies and automation to enhance financial management and operational efficiency.
- Sustainability and Resilience: The increasing focus on sustainability and resilience in forestry operations, driving innovation and best practices.
- Collaborative Partnerships: The development of collaborative partnerships between governments, businesses, and communities to promote sustainable forestry practices.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
- Climate Change: The impact of climate change on forestry operations, creating challenges and opportunities for adaptation and mitigation.
- Market Volatility: The potential for market volatility and fluctuations in timber prices, impacting financial performance and sustainability.
- Regulatory Changes: The potential for regulatory changes that impact the financial management and sustainability of forestry operations.
Preparing for Future Changes
- Strategic Planning: Developing long-term plans that account for future challenges and opportunities, ensuring the sustainability and resilience of forestry operations.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Embracing innovation and adaptation to enhance financial management and operational efficiency.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders in the planning and decision-making process to ensure transparency and accountability.
By preparing for future changes and embracing innovation, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Mastering Financial Management in Forestry
Mastering financial management is essential for ensuring the sustainability and success of forestry operations. By implementing key strategies, forestry operations can optimize resource allocation, enhance financial performance, and achieve long-term goals.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive Budgeting: Creating and maintaining a comprehensive budget to optimize resource allocation and achieve financial goals.
- Revenue Diversification: Diversifying revenue streams to reduce financial risks and ensure sustainability.
- Cost Control and Optimization: Implementing practices that reduce costs and enhance efficiency, improving financial performance.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks to protect financial performance and sustainability.
- Investment Strategies: Developing and implementing investment strategies that enhance financial performance and achieve long-term goals.
- Financial Analysis and Reporting: Conducting regular financial analysis and reporting to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementing sustainable practices that enhance financial performance and environmental health.
Summary of Strategies
Mastering financial management in forestry involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses budgeting, revenue diversification, cost control, risk management, investment strategies, financial analysis, and sustainable practices. By implementing these strategies, forestry operations can optimize resource allocation, enhance financial performance, and achieve long-term goals.
Final Thoughts
Effective financial management is essential for ensuring the sustainability and success of forestry operations. By implementing key strategies and embracing innovation, forestry operations can enhance their financial performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
Mastering financial management is crucial for the sustainability and success of forestry operations. By implementing key strategies, such as budgeting, revenue diversification, cost control, risk management, and investment strategies, forestry operations can optimize resource allocation, enhance financial performance, and achieve long-term goals. The future of financial management in forestry is shaped by emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities for innovation and sustainability, ensuring that forestry operations remain resilient and adaptable in the face of changing circumstances.
FAQs
- What is the importance of financial management in forestry? Financial management is essential for optimizing resource allocation, controlling costs, generating revenue, and ensuring the sustainability and success of forestry operations.
- How can forestry operations diversify their revenue streams? Forestry operations can diversify their revenue streams by tapping into various income sources, such as timber sales, non-timber products, ecosystem services, agroforestry, and community-based enterprises.
- What are the key components of a comprehensive budget for forestry operations? A comprehensive budget for forestry operations includes revenue estimation, expense estimation, financial goals, budget allocation, and monitoring and evaluation.
- How can forestry operations implement sustainable practices? Forestry operations can implement sustainable practices by conserving resources, protecting ecosystems, engaging communities, and sourcing materials and services from sustainable suppliers.
- What are the key financial metrics used in forestry operations? Key financial metrics used in forestry operations include revenue, expenses, profitability, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow.
- How can technology and innovation enhance financial management in forestry operations? Technology and innovation can enhance financial management in forestry operations by providing new tools and insights for optimizing resource allocation, improving efficiency, and achieving financial goals.
- How can forestry operations control costs effectively? Forestry operations can control costs by conducting thorough cost analyses, optimizing processes, negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, and implementing sustainable practices that conserve resources and reduce waste. Regular monitoring and adjustments to budgets help maintain financial discipline and efficiency.
- What are the main risks associated with forestry operations? Forestry operations face natural risks such as wildfires, storms, pests, and diseases; market risks including fluctuations in timber prices; and operational risks related to equipment failure and labor shortages. Effective risk management involves diversification, insurance, contingency planning, and regular monitoring to mitigate these risks.
- How do government policies impact financial management in forestry? Government policies can significantly impact financial management by influencing regulatory compliance costs, providing incentives and subsidies for sustainable practices, and shaping market access. Staying informed about policy changes helps forestry operations plan strategically and leverage available financial support.
- Why is it important to diversify revenue streams in forestry? Diversifying revenue streams helps reduce financial risks and ensures the sustainability of forestry operations. By generating income from multiple sources like non-timber products, ecosystem services, and agroforestry, operations can better withstand market fluctuations and enhance long-term financial stability.
Mastering financial management is not just an option—it’s a necessity. By implementing strategic financial practices, forestry operations can not only ensure profitability but also contribute to environmental sustainability and community well-being. From budgeting and cost control to risk management and innovative investment strategies, each component of financial management plays a crucial role in securing the future of forestry operations.

James Wilson
Forestry AuthorJames Wilson has over 15 years of experience in forestry economics, specializing in sustainable practices, investment opportunities, and financial management. He has contributed to notable publications like "Forestry Today" and "EcoFinance Journal" and is known for providing practical and insightful advice. With a degree in Environmental Economics, James stays updated through continuous learning and active participation in industry discussions. Outside work, he enjoys hiking and nature photography, bringing a well-rounded perspective to his professional role.



Leave your comment