Why Forest Biodiversity Matters
- August 21, 2024
- 0 comment
Forest biodiversity is a vital component of Earth’s ecological balance, encompassing the variety of life forms found within forested regions. From the towering trees and vibrant plants to the myriad animal species and unseen microorganisms, these ecosystems represent some of the planet’s most complex and dynamic environments.

Forest biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and water regulation. The rich diversity found in forests not only supports countless species but also underpins human livelihoods and cultures by providing resources, regulating climate, and offering recreational opportunities. As threats such as deforestation and climate change loom large, understanding and conserving forest biodiversity is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Understanding Forest Biodiversity
What Is Forest Biodiversity?
Forest biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms within forest ecosystems, including the diversity of species, genetic variation, and the complexity of ecological processes. It encompasses all life forms within a forest, from the smallest microbes to the largest trees and mammals. This diversity is crucial for maintaining the balance and functionality of ecosystems.

The Components of Forest Biodiversity
- Species Diversity: Refers to the variety of species within a forest. This includes trees, shrubs, animals, insects, fungi, and microorganisms. Each species plays a unique role in the ecosystem, contributing to its stability and productivity.
- Genetic Diversity: Within each species, there is genetic variation that allows populations to adapt to changing environments. Genetic diversity is essential for resilience against diseases, pests, and environmental changes.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This involves the variety of ecosystems within a forest region, such as wetlands, rivers, and grasslands. Each ecosystem supports different communities of organisms and ecological processes.
The Ecological Importance of Forest Biodiversity
Enhancing Ecosystem Productivity
Biodiverse forests are more productive and efficient in capturing sunlight, nutrients, and water. This productivity supports a greater number of species and higher biomass, which in turn stabilizes the ecosystem.
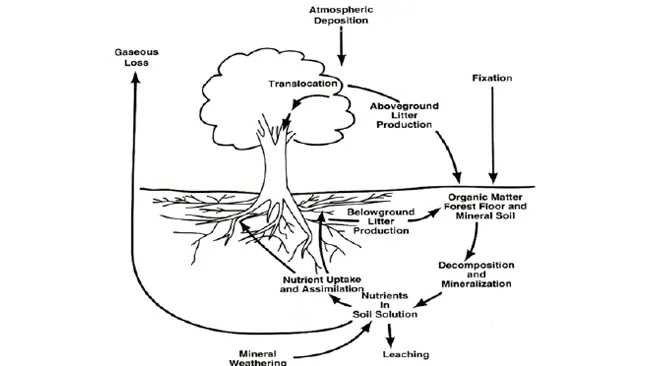
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse plant and animal species contribute to the cycling of nutrients through decomposition and other processes, maintaining soil fertility and ecosystem health.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Many forest species are interdependent, relying on each other for pollination and seed dispersal. This mutual relationship ensures the regeneration and sustainability of forests.
Supporting Ecosystem Services
Forests provide numerous ecosystem services that benefit humans and the planet. Biodiversity enhances these services, ensuring they are sustainable and resilient.

- Carbon Sequestration: Forests are vital carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. A diverse forest captures more carbon due to its varied plant species, helping mitigate climate change.
- Water Regulation: Forest ecosystems regulate water cycles by controlling precipitation, evaporation, and river flows. Biodiversity ensures these processes function efficiently.
- Soil Stabilization: Diverse root systems of different plant species help prevent soil erosion, maintaining land stability and fertility.
The Role of Forest Biodiversity in Climate Regulation
Climate Mitigation
Biodiverse forests play a significant role in climate regulation by capturing carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas. Forests with a high diversity of species are more effective at sequestering carbon, thereby reducing the impact of climate change.
Resilience to Climate Change
Diverse forests are more resilient to climate extremes and disturbances. Genetic diversity within species allows forests to adapt to changing conditions, enhancing their ability to withstand droughts, storms, and diseases.
Biodiversity as a Buffer
A diverse array of species acts as a buffer against environmental changes. If one species is affected by climate change, others can fill its ecological role, maintaining ecosystem stability and functionality.
The Economic and Social Benefits of Forest Biodiversity
Sustainable Resources
Forests provide a wealth of resources, including timber, non-timber forest products, and medicinal plants. Biodiversity ensures these resources are sustainable and available for future generations.

- Timber and Non-Timber Products: Diverse forests produce high-quality timber and a variety of non-timber products such as fruits, nuts, resins, and fibers, which support local economies.
- Medicinal Plants: Many forest plants have medicinal properties, contributing to health care and pharmaceutical industries. Biodiversity increases the potential for discovering new medicines.
Cultural and Recreational Value
Forests hold cultural significance for many communities and offer recreational opportunities that enhance human well-being.
- Cultural Heritage: Many indigenous communities have deep cultural and spiritual connections to forests, relying on their biodiversity for traditional practices and livelihoods.
- Recreation and Tourism: Biodiverse forests attract tourists, providing recreational activities such as hiking, bird-watching, and wildlife observation, which generate economic benefits.
Threats to Forest Biodiversity
Deforestation and Habitat Loss
Human activities such as logging, agriculture, and urban expansion lead to deforestation and habitat destruction, reducing biodiversity and threatening ecosystem services.
Climate Change
Climate change alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting species distribution and ecosystem dynamics. Forests with low biodiversity are less capable of adapting to these changes.
Pollution and Invasive Species
Pollution from industrial activities and the introduction of invasive species can disrupt forest ecosystems, outcompeting native species and altering ecological processes.
Conservation Strategies for Forest Biodiversity
Protected Areas and Reserves
Establishing protected areas and reserves helps conserve critical habitats and species, ensuring the preservation of forest biodiversity.

- National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries: These areas protect biodiversity by restricting human activities and providing a refuge for species.
- Biosphere Reserves: Biosphere reserves promote sustainable development and conservation, balancing human needs with ecosystem protection.
Sustainable Forest Management
Sustainable forest management practices balance the extraction of forest resources with the conservation of biodiversity.
- Reduced Impact Logging: This practice minimizes damage to the forest during logging, preserving habitat and biodiversity.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and provides economic benefits.
Community Involvement and Education
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and educating the public about the importance of biodiversity fosters a sense of stewardship and responsibility.

- Community-Based Conservation: Empowering local communities to manage and protect forests ensures sustainable use and conservation of biodiversity.
- Environmental Education: Raising awareness about the importance of forest biodiversity encourages support for conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Forest biodiversity is the key to a thriving ecosystem, providing essential services that support life on Earth. It enhances ecosystem productivity, regulates climate, and offers economic and social benefits. However, biodiversity faces significant threats from human activities and environmental changes. Conserving forest biodiversity requires concerted efforts to protect habitats, manage resources sustainably, and engage communities in conservation initiatives. By valuing and protecting forest biodiversity, we ensure the health and resilience of our planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is forest biodiversity?
Forest biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms found within forest ecosystems, including trees, plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. It encompasses the diversity of species, genetic variation, and ecological processes that sustain life in forests. - Why is forest biodiversity important?
Forest biodiversity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. It supports essential ecological processes like nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and water regulation. Diverse forests are more resilient to environmental changes and provide numerous resources and services that benefit humans and other species. - How does forest biodiversity affect climate change?
Forest biodiversity helps mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration. Diverse plant species capture more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, reducing greenhouse gas levels. Biodiverse forests are also more adaptable to climate changes, helping to maintain ecosystem stability. - What are the main threats to forest biodiversity?
The primary threats to forest biodiversity include deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and the introduction of invasive species. These factors disrupt ecosystems, reduce species diversity, and threaten the services forests provide. - How can we conserve forest biodiversity?
Conserving forest biodiversity requires protecting habitats through the establishment of protected areas and reserves, promoting sustainable forest management practices, and engaging local communities in conservation efforts. Educating the public about the importance of biodiversity is also crucial for fostering stewardship. - What role do forests play in the global ecosystem?
Forests play a critical role in the global ecosystem by providing habitat for numerous species, regulating the climate, and supporting water cycles. They offer ecosystem services such as carbon storage, oxygen production, and soil stabilization, which are essential for the well-being of the planet and its inhabitants. - How does forest biodiversity support human livelihoods?
Forest biodiversity supports human livelihoods by providing resources such as timber, non-timber forest products, and medicinal plants. It also offers recreational opportunities and cultural value, contributing to local economies and human well-being. - What is the relationship between forest biodiversity and ecosystem services?
Forest biodiversity enhances ecosystem services by ensuring the efficient functioning of ecological processes. Diverse species contribute to nutrient cycling, water regulation, and carbon sequestration, which are essential for maintaining healthy and productive ecosystems that benefit humans and other species. - How do invasive species impact forest biodiversity?
Invasive species can significantly impact forest biodiversity by outcompeting native species, altering habitats, and disrupting ecological processes. This can lead to a reduction in species diversity and the loss of ecosystem services provided by native species. - Why should we prioritize forest biodiversity conservation?
Prioritizing forest biodiversity conservation is essential for sustaining ecosystems and the services they provide. Healthy, biodiverse forests are more resilient to environmental changes and support a wide range of species, including humans. Protecting forest biodiversity ensures a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
We hope this exploration of forest biodiversity has deepened your understanding of its vital role in sustaining our planet’s ecosystems. Have you observed the impact of biodiversity in your local forests or participated in any conservation efforts? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below, and join the discussion on how we can collectively protect and preserve our natural heritage. Your contributions can inspire others to take action and help shape future conservation initiatives. Don’t forget to share this article with fellow nature enthusiasts and environmental advocates to spread awareness about the importance of forest biodiversity.

Evan Bennett
Forestry AuthorEvan Bennett brings over a decade of expertise in forestry wildlife management to the forefront, specializing in habitat conservation, biodiversity, and human-wildlife interaction. Evan's work ensures harmonious coexistence between wildlife and human communities through effective and sustainable practices. Continuously engaging in research and workshops, Evan stays at the cutting edge of wildlife management advancements. As a trusted advisor and contributor to leading environmental journals, Evan is dedicated to preserving the natural world for future generations.










Leave your comment