Cinchona Bark
- December 20, 2023
- 1 comment
Cinchona bark, derived from the evergreen trees of the Cinchona genus native to the Andean forests of South America, holds a rich history and significance in the realm of medicine and beyond. Revered for its therapeutic properties, the bark is a primary source of quinine, a compound renowned for its antimalarial properties.
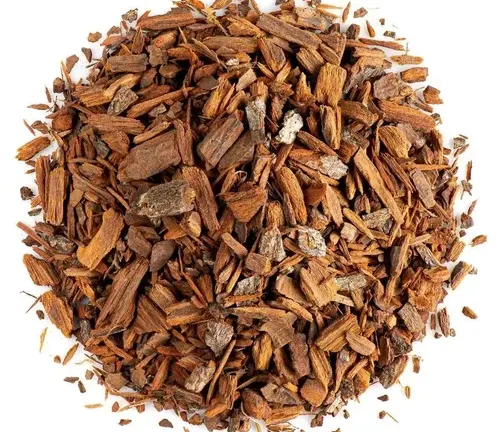
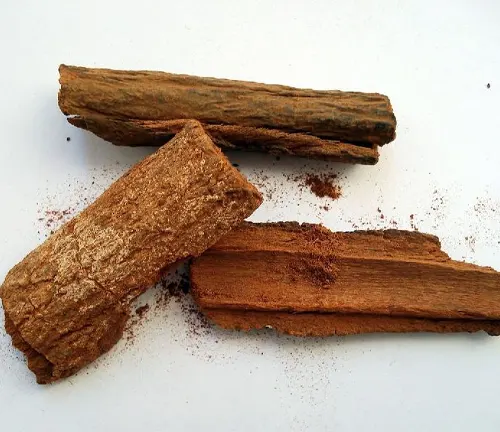


Historically, indigenous people of South America had long recognized the bark’s medicinal potential, but it gained widespread attention in the 17th century when it was introduced to Europe. Cinchona bark became a pivotal tool in combating malaria, a disease that had long plagued tropical regions. Over the years, its applications have expanded beyond malaria treatment, finding use in the production of tonic water and various pharmaceuticals.
Beyond its utilitarian value, cinchona bark has also woven itself into the fabric of cultural narratives, symbolizing the intersection of nature and human ingenuity in the pursuit of health and well-being.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cinchona spp. |
| Family | Rubiaceae |
| Native Region | Andean forests of South America |
| Key Compound | Quinine |
| Medicinal Use | Antimalarial properties |
| Historical Significance | Introduced to Europe in the 17th century |
| Applications | Malaria treatment, tonic water, pharmaceuticals |
| Cultural Significance | Symbolises the intersection of nature and human ingenuity |
| Source | Bark of evergreen trees belonging to the Cinchona genus |
Botanical Beauty of Cinchona Bark
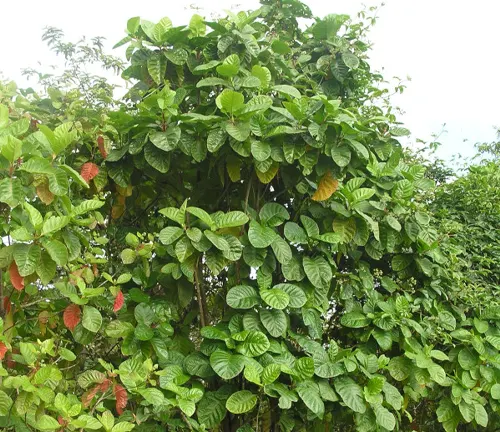

Cinchona bark, extracted from the evergreen trees of the Cinchona genus, unveils a botanical beauty that has captivated both indigenous communities and global enthusiasts. Residing in the enchanting Andean forests of South America, these trees boast lush greenery and delicate blooms, creating a picturesque scene that adds to the allure of the Cinchona bark. Beyond its medicinal significance, the botanical beauty of Cinchona bark contributes to the rich biodiversity of the ecosystems it inhabits.
Woodland Elegance
Within the sprawling Andean forests, Cinchona trees exude woodland elegance with their tall, slender trunks and gracefully arching branches. The bark, with its distinctive texture and hues ranging from deep reds to browns, adds a touch of sophistication to the forest landscape. This woodland elegance extends beyond the visual realm, as the aromatic compounds within the bark fill the air with a subtle, earthy fragrance, creating a sensorial experience that enhances the overall ambiance of the wooded environment.
Ecological Importance
Cinchona trees play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance within their native habitats. Their presence supports diverse flora and fauna, creating a thriving ecosystem. The trees provide habitat and sustenance for various wildlife, contributing to the overall health of the Andean forests. Moreover, the Cinchona trees actively participate in nutrient cycling, further emphasizing their ecological importance in the intricate web of life within these biodiverse regions.
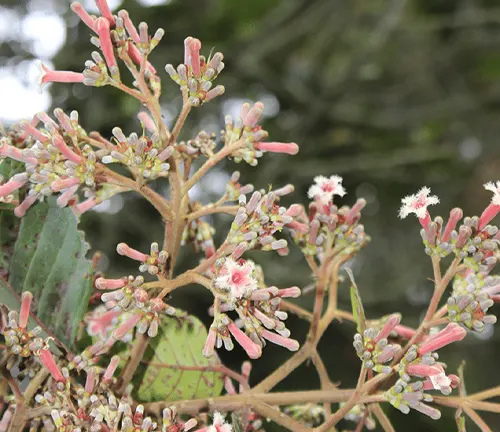

Cultivation and Conservation
As the demand for Cinchona bark has risen due to its medicinal properties, cultivation practices have evolved to meet these needs sustainably. Conservation efforts are underway to ensure the survival of Cinchona species in their natural habitats. Sustainable cultivation practices, coupled with responsible harvesting, aim to balance the medicinal requirements with the preservation of these remarkable trees.
Soil Stabilization
Beyond its aesthetic and ecological contributions, Cinchona trees play a pivotal role in soil stabilization. Their extensive root systems help prevent soil erosion, especially in the steep and hilly terrains of the Andean forests. This soil stabilization feature is a testament to the trees’ ability to harmonize with their environment and contribute to the overall stability of the ecosystem.
Common Uses

The applications of Cinchona bark extend far beyond its natural habitat. Historically, it gained fame for its role in treating malaria, introducing a powerful weapon against a widespread disease. In contemporary times, Cinchona bark is a key ingredient in the production of tonic water, offering a unique flavor profile and a subtle bitterness. Its versatility extends to the pharmaceutical industry, where its compounds are harnessed for various medicinal purposes.
Benefits
The benefits of Cinchona bark are diverse and impact. Primarily known for its antimalarial properties, the bark’s compounds have saved countless lives. Additionally, the bark contributes to soil conservation, showcasing its environmental benefits. The aromatic qualities and aesthetic appeal add an extra layer of value, making Cinchona bark a remarkable botanical resource with far-reaching positive effects.
Biological Marvel of Cinchona Bark

Cinchona bark, derived from the majestic Cinchona trees of the Andean forests, unfolds as a biological marvel. Within its fibrous layers lie compounds that have intrigued scientists and healers alike. The intricate biological composition of Cinchona bark, rich in alkaloids such as quinine, forms the cornerstone of its medicinal prowess. As we delve into the biological intricacies, a deeper appreciation for the synergistic relationship between this botanical marvel and human health emerges.
Navigating the Andean Canopy
The Cinchona trees create a botanical tapestry within the Andean forests, and understanding their habitat is akin to navigating a living map. These trees thrive in specific altitudes and climatic conditions, creating a unique ecosystem. The habitat map of Cinchona showcases its adaptability and resilience, providing valuable insights into how these trees have seamlessly integrated into the diverse landscapes of the Andes. This exploration unveils the interconnected dance between flora and environment that sustains this botanical treasure.
Unraveling the Alkaloid Symphony
At the heart of Cinchona’s therapeutic magic lies a symphony of alkaloids, each playing a distinct role in its medicinal profile. Quinine, the most renowned compound, takes center stage for its antimalarial properties, but the bark hosts a chorus of other alkaloids, contributing to its holistic efficacy. Unraveling this alkaloid symphony provides a glimpse into the complex biochemical dance that renders Cinchona bark a potent healer. As science continues to unlock the secrets within, the potential applications of these compounds may extend beyond traditional medicine.
Navigating the Healing Path
While Cinchona bark holds a formidable reputation as a healer, understanding potential side effects is crucial for responsible use. Exploring the nuanced landscape of side effects associated with Cinchona bark reveals the importance of proper dosage and administration. From mild reactions to more severe effects, awareness empowers both practitioners and patients to navigate the healing path safely. This section sheds light on the nuanced considerations that accompany the use of Cinchona bark, emphasizing the importance of informed choices in harnessing its medicinal benefits.
Different Species
Cinchona pubescens
(Red Cinchona or Quina Roja)
This species is one of the most well-known and widely cultivated for its high quinine content. It has distinctive red or maroon-colored bark.
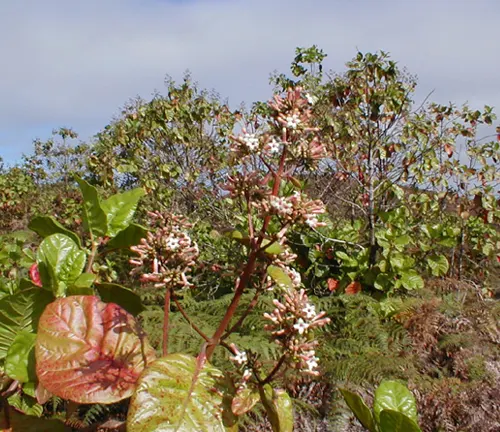
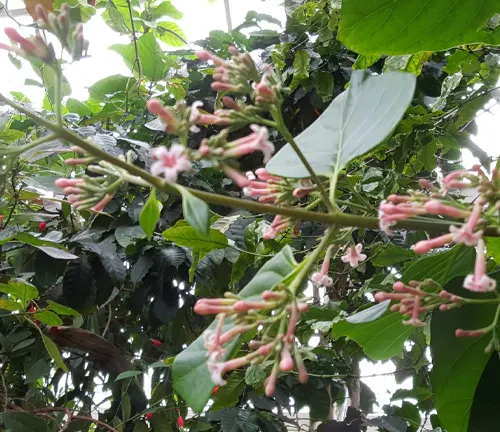


Cinchona officinalis
(Peruvian Bark)
Historically significant, this species played a crucial role in the treatment of malaria. It has pale yellow or light-colored bark and is native to the Andes.
Cinchona ledgeriana
(Ledger’s Cinchona)
Recognized for its high quinine content, this species has been extensively used in the production of antimalarial drugs. It has dark brown to blackish bark.
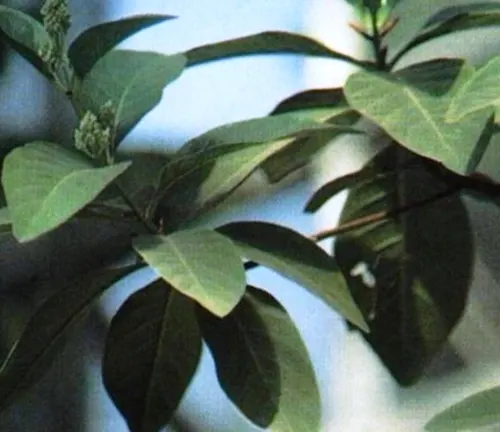
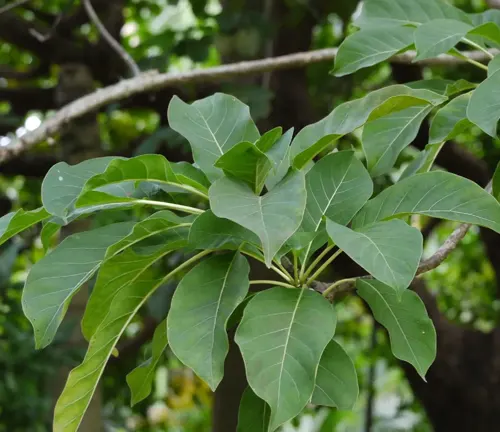


Cinchona calisaya
(Yellow Cinchona)
Native to Peru and Bolivia, this species is prized for its high alkaloid content, including quinine. Its bark is yellowish, and it has been historically important in the pharmaceutical industry.
Cinchona ledgeriana var. pubescens: This variety is a hybrid of Cinchona ledgeriana and Cinchona pubescens. It combines the high quinine content of ledgeriana with the adaptability of pubescens.
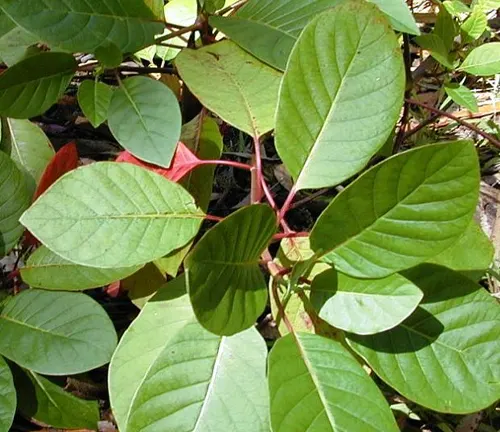
Cinchona pitayensis
(Pitayo Cinchona)
Found in Ecuador, this species is characterised by its pink bark. It is one of the less common species but has contributed to the diversity of Cinchona bark sources.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Cinchona Bark?
Cinchona bark is the bark obtained from trees of the Cinchona genus, primarily found in the Andean forests of South America. It is known for containing medicinal compounds, including quinine, and has been historically used in the treatment of malaria. - What are the Main Medicinal Compounds in Cinchona Bark?
The primary medicinal compound in Cinchona bark is quinine, which exhibits antimalarial properties. Additionally, the bark contains other alkaloids contributing to its therapeutic effects. - How is Cinchona Bark Used in Medicine?
Cinchona bark has been traditionally used to treat malaria due to its antimalarial properties. It is also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of drugs treating various ailments. - What Species of Cinchona Trees Produce the Bark?
Several species within the Cinchona genus produce Cinchona bark, including Cinchona pubescens, Cinchona officinalis, Cinchona ledgeriana, Cinchona succirubra, Cinchona calisaya, and others. - Are There Different Varieties of Cinchona Bark?
Yes, there are different varieties and species of Cinchona bark, each with unique characteristics. These varieties may vary in color, alkaloid content, and specific medicinal properties. - What is the Historical Significance of Cinchona Bark?
Cinchona bark has a significant historical role in combating malaria. Its introduction to Europe in the 17th century revolutionized the treatment of the disease and had a profound impact on global health. - How is Cinchona Bark Cultivated and Harvested?
Cinchona trees are cultivated in regions with suitable climates, and the bark is typically harvested from mature trees. Sustainable cultivation practices are employed to balance medicinal demand with environmental conservation. - What Are the Common Uses of Cinchona Bark Besides Medicine?
In addition to its medicinal uses, Cinchona bark is employed in the production of tonic water, providing a unique flavor profile. It is also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for various applications. - Are There Side Effects Associated with Cinchona Bark?
While generally safe when used in appropriate doses, Cinchona bark may have side effects, including digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. It’s essential to use it under proper guidance and supervision. - Is Cinchona Bark Endangered?
Some species of Cinchona trees are considered threatened due to overharvesting and habitat loss. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these valuable trees and ensure their sustainable use.














This is a pretty great explanation of the Cinchona/Chinchóna tree. I can't help but think that if you wanted to cultivate it to produce potent bark, you'd make a bit of a sterile house off the side and methodically alter harvesting bark induced to grow in combs to one side or another, including roots and transition matter if in the harvest profile.
Dave Nordquist
October 29, 2024 8:55 am