How Do Animals and Plants Depend on Each Other?
- February 27, 2024
- 2 comment
Animals and plants depend on each other in remarkable ways, showcasing plant and animal interdependence that supports life on Earth. This mutual relationship forms the backbone of ecosystems everywhere, from lush rainforests to arid deserts. Understanding how animals and plants coexist highlights the beauty of nature and the need to protect biodiversity for future generations.
Photosynthesis and Respiration
The relationship between plants and animals is deeply connected through plant and animal interdependence, especially in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Plants perform photosynthesis, using sunlight and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and glucose. This not only fuels their growth but also provides oxygen essential for animal survival.
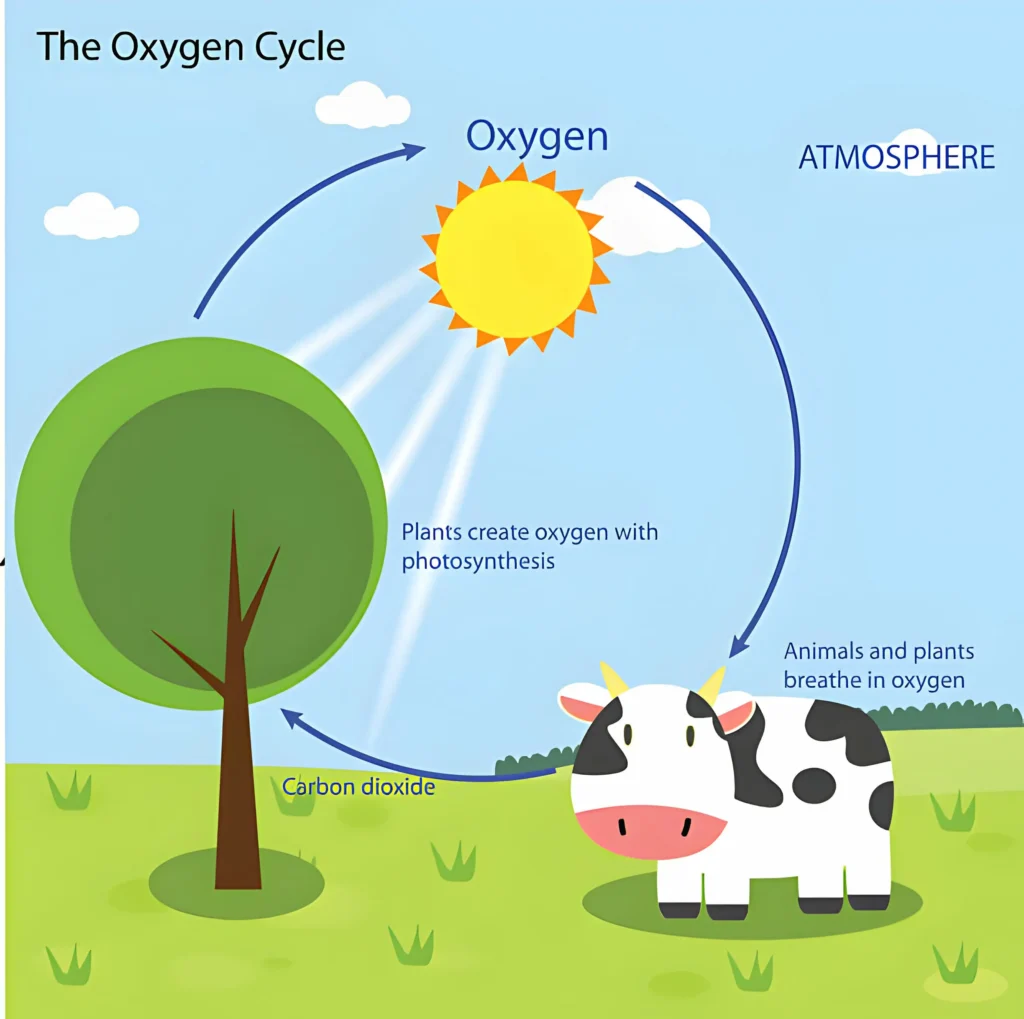
In return, animals breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, a byproduct for them but a crucial resource for plants. This natural exchange is a perfect example of ecosystem interdependence, highlighting how animals help plants grow and how plants help animals survive.
Dr. Ava Martinez, an ecologist with over 20 years of experience studying tropical rainforests, emphasizes the fragility of these ecosystems:
“The symbiotic relationships between animals and plants are not just fascinating; they’re pivotal for the ecosystem’s survival. A slight change in one species’ population can have a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem. It’s a delicate balance that we must strive to protect.“
Pollination
Pollination is a prime example of plant and animal interdependence, showcasing how animals and plants rely on each other for survival. Many plants depend on animals like bees, butterflies, birds, and even some mammals to transfer pollen between flowers, enabling reproduction and ensuring their species thrive.
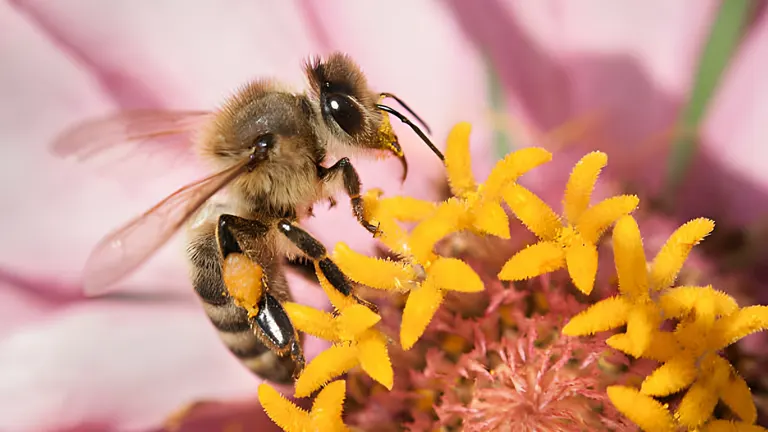

In return, pollinators benefit by collecting nectar and pollen as a food source. This mutual relationship is a clear example of symbiosis between plants and animals, illustrating how they co-evolve and adapt to meet each other’s needs, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
Professor Liam Chen, a conservation biologist, shares a similar sentiment:
“Pollinators like bees and butterflies are under threat from various factors including pesticide use and habitat loss. Without them, many of the plants we rely on for food, medicine, and clothing would struggle to reproduce. Preserving these pollinator species is not just about saving the bees; it’s about safeguarding our own future.“
Habitat Provision
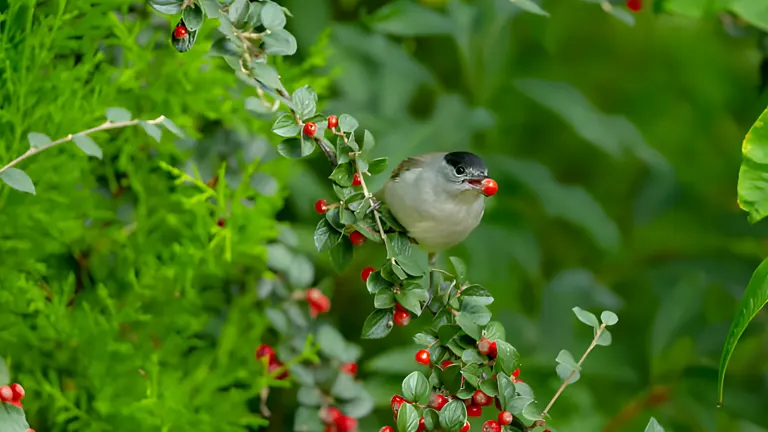

Plants play a vital role in supporting animal life by providing critical habitats. They offer shelter, breeding grounds, and protection from predators, illustrating the mutual relationship between plants and animals. Forests, wetlands, grasslands, and underwater ecosystems like kelp forests serve as essential environments for countless species.
These habitats are more than just homes they provide the conditions animals need to thrive, complete their life cycles, and nurture their young. This example of ecosystem interdependence highlights how plants help animals survive while benefiting from the animals that rely on them.
Food Chains and Webs
Food chains and webs demonstrate the intricate plant and animal interdependence at the core of every ecosystem. Plants, as primary producers, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain. Herbivores depend directly on plants for nourishment, while carnivores rely on herbivores to survive.
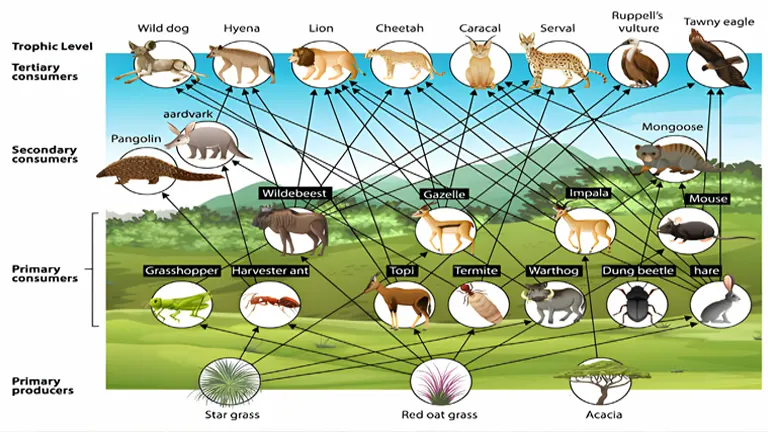
Omnivores, which consume both plants and animals, further emphasize the mutual relationship between plants and animals within these webs. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil to support plant growth. This cycle of energy flow showcases how plants help animals survive and how animals, in turn, support plants, ensuring balance within ecosystems.
Mutualism
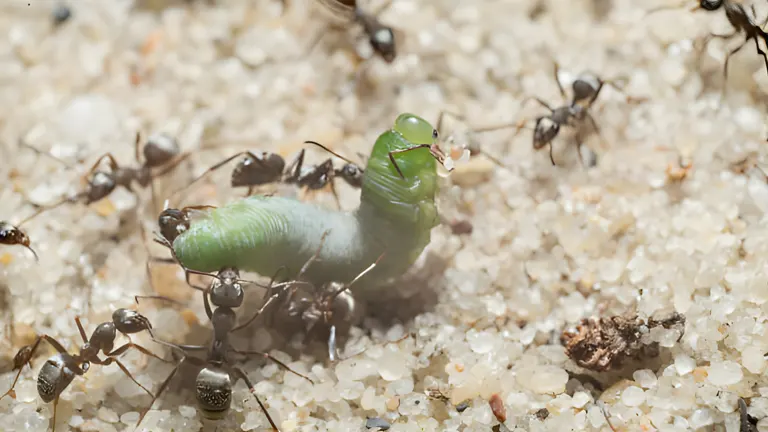

Mutualism offers fascinating examples of plant and animal interdependence, where both species benefit from their interactions. For instance, some ant species protect plants from herbivorous insects, receiving shelter and food in return. Similarly, certain fungi establish symbiosis between plants and animals, enhancing a plant’s nutrient uptake in exchange for carbohydrates.
These examples highlight the intricate mutual relationship between plants and animals, demonstrating how they co-adapt and support each other to thrive in diverse ecosystems.
Actionable Steps for Protecting Local Wildlife and Plant Life
- Creating Pollinator-Friendly Gardens: Creating pollinator-friendly gardens is a wonderful way to support local ecosystems. By planting native flowers, shrubs, and trees, you not only attract bees, butterflies, and birds but also provide them with the necessary resources to thrive. Native plants are particularly beneficial as they’re adapted to the local climate and soil, reducing the need for excessive watering or maintenance. To further support pollinators, it’s crucial to have a variety of plants that bloom at different times throughout the year, ensuring a continuous source of nourishment. Additionally, avoiding pesticides and herbicides can protect these vital insects and other beneficial creatures from harm.
- Building Habitats for Wildlife: Building habitats for wildlife can also significantly enhance local biodiversity. Installing structures like birdhouses, bat boxes, and insect hotels creates safe havens for various species, encouraging them to make a home in your garden. Allowing a part of your yard to remain wild provides a natural habitat for insects, birds, and small mammals, fostering a more diverse ecosystem right outside your door.
- Participating in Local Conservation Projects: Participation in local conservation projects offers a hands-on approach to environmental protection. Engaging in activities such as tree planting, beach clean-ups, and wildlife surveys not only benefits the environment but also connects you with a community of people who share your values. Supporting local parks, nature reserves, and conservation organizations through donations or advocacy raises awareness and contributes to the preservation of these vital green spaces.
- Practicing Sustainable Living: Practicing sustainable living is another key aspect of contributing to conservation efforts. By making conscious choices to reduce, reuse, and recycle, individuals can minimize their environmental footprint. Water conservation techniques, such as installing rain barrels and using drought-resistant plants, further reduce the ecological impact. Opting for sustainable products ensures that your consumption does not contribute to habitat destruction or harm to wildlife and human health.
- Advocating for Conservation: Finally, advocating for conservation can amplify your impact. Educating others about the importance of protecting local wildlife and ecosystems can inspire collective action. Utilizing social media, hosting educational events, or simply discussing these topics with friends and family can spread awareness. Engaging with policymakers to support environmental legislation helps protect natural habitats and promote biodiversity at a broader level.
Each of these practices, from creating pollinator-friendly gardens to advocating for conservation, plays a crucial role in protecting and enhancing local ecosystems. By incorporating these actions into daily life, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable and biodiverse world.
Conclusion
The interdependence of animals and plants showcases the intricate and resilient connections within ecosystems. Over millions of years, this mutual relationship between plants and animals has enabled both to thrive, maintaining the delicate balance of life on Earth. Understanding and preserving these relationships is essential for biodiversity, ecosystem stability, and the planet’s health.
Recognizing how plants help animals survive and how animals help plants grow is key to protecting these vital connections. As we move forward, safeguarding the symbiosis between plants and animals will play a crucial role in ensuring life continues to flourish for future generations.
FAQs
- How do animals and plants depend on each other?
Plants provide food and oxygen for animals; animals offer pollination, seed dispersal, and carbon dioxide for plants. Both are vital for ecosystem health. - How do animals contribute to plant diversity?
Animals play a crucial role in maintaining plant diversity through pollination, seed dispersal, and habitat creation. Their interactions with plants can lead to evolutionary changes, promoting diversity. For example, as animals move from one flower to another, they transport pollen, facilitating cross-pollination, which can result in stronger, more genetically diverse plant populations. - What is the most unusual plant-animal relationship known to science?
One of the most fascinating relationships is between the fig tree and the fig wasp. The fig tree relies on the wasp to pollinate its flowers, which are actually inside the fig fruit. In return, the fig provides a home for the wasp’s larvae. This mutual dependence has led to a highly specific and intricate co-evolutionary relationship. - Are there any animals that can photosynthesize like plants?
Some animals have developed unique relationships with photosynthetic organisms. For example, the Elysia chlorotica, a sea slug, can incorporate chloroplasts from the algae it eats into its own cells, allowing it to photosynthesize sunlight into energy, much like a plant. This is a rare instance of an animal harnessing the power of photosynthesis. - How does the extinction of a single species affect the plant-animal relationship web?
The extinction of a single species can have a ripple effect throughout an ecosystem, disrupting established relationships and leading to further losses in biodiversity. For instance, if a key pollinator species were to go extinct, plants that rely on that pollinator might also face extinction or a significant decrease in their populations, affecting other animals that depend on those plants for food or habitat. - Can plants communicate with animals?
Plants can’t communicate in the conventional sense, but they can send signals that affect animal behavior. For example, some plants release chemical signals when they are being eaten by herbivores, which can attract predators of the herbivores, effectively reducing the damage to the plant. Other plants may produce nectar or fragrances that attract pollinators. - What role do humans play in the plant-animal interdependence?
Humans have a profound impact on plant-animal relationships through activities such as agriculture, urban development, and conservation. While agricultural practices can disrupt natural relationships by favoring certain species over others, conservation efforts aim to protect these relationships by preserving habitats and fostering biodiversity. The choices humans make can either support or undermine the delicate balance of interdependence in nature.
As we’ve journeyed through the fascinating world of how animals and plants depend on each other, it’s clear that the tapestry of life is rich with interconnections. But this exploration is far from over, and your insights can make it even more vibrant. Have you observed any unique interactions between animals and plants in your own backyard or during your travels? Maybe you have thoughts on how we can better protect these vital relationships?
We’d love to hear your stories and ideas! Share your thoughts in the comments below and let’s continue this conversation. Together, we can deepen our appreciation for the natural world and work towards preserving its beauty for generations to come. Don’t forget to share this article with friends and family who might find it as intriguing as you did!

David Murray
Forestry AuthorI'm David Murry, a forestry equipment specialist with a focus on chainsaw operation. With over 13 years of experience, I've honed my skills in operating and maintaining a wide range of machinery, from chainsaws to log splitters. My passion for the outdoors and commitment to sustainable forestry drive my work, which emphasizes safety, efficiency, and staying updated with industry advancements. Additionally, I'm dedicated to sharing my expertise and promoting environmental awareness within the forestry community.
2 comments
Thanks for the information!













animals and plants
Falmi Fishe
April 25, 2024 3:37 am