Indian Violet Tarantula
- March 12, 2024
- 0 comment
The Indian Violet Tarantula, scientifically known as Chilobrachys fimbriatus, is a captivating arachnid species native to the Indian subcontinent. What sets this tarantula apart is its striking appearance, characterized by a vivid violet-colored exoskeleton adorned with intricate patterns and markings. Found primarily in regions with tropical climates, such as dense forests and grasslands, these solitary creatures are nocturnal hunters, relying on their keen senses to locate prey under the cover of darkness.
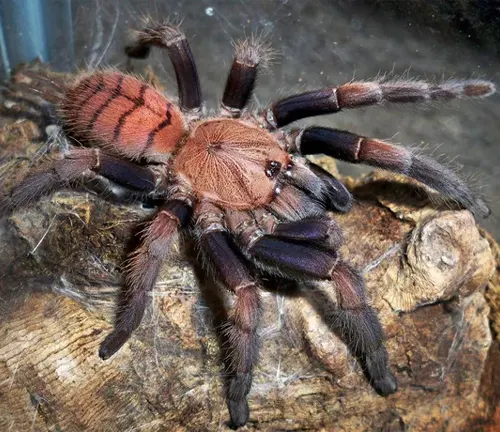

Despite their formidable appearance, Indian Violet Tarantulas are generally docile and pose minimal threat to humans. They play a vital role in their ecosystems as predators, feeding on a variety of prey including insects, small rodents, and other arachnids. As with many tarantula species, their venom is primarily designed for subduing prey and is rarely harmful to humans. However, habitat loss and human encroachment pose significant threats to their survival, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts to protect these fascinating creatures and their natural habitats.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Chilobrachys fimbriatus |
| Common Name | Indian Violet Tarantula |
| Color | Vivid violet exoskeleton with intricate markings |
| Habitat | Tropical regions, dense forests, grasslands |
| Distribution | Indian subcontinent, parts of Sri Lanka, Bangladesh |
| Behavior | Solitary, nocturnal, ambush predator |
| Diet | Insects, small rodents, other arachnids |
| Venom | Mildly venomous, primarily for subduing prey |
| Threats | Habitat loss, human encroachment |
| Conservation Status | Not listed as endangered, but facing threats |
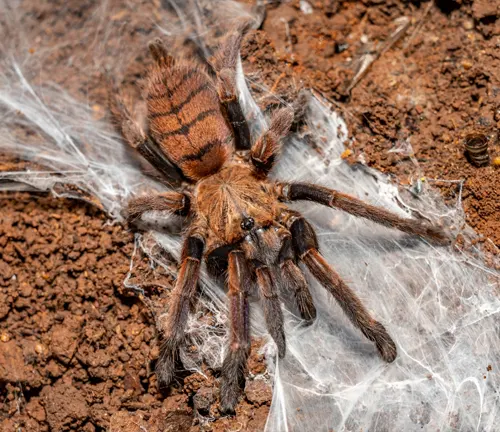

The Indian Violet Tarantula, scientifically known as Chilobrachys fimbriatus, is a captivating and enigmatic species of tarantula found primarily in the Indian subcontinent. With its striking appearance and intriguing behaviors, this arachnid has fascinated both researchers and enthusiasts alike.
Appearance and Behavior
Vivid Colors and Markings
The Indian Violet Tarantula is renowned for its stunning appearance, characterized by vivid colors and intricate markings. Its exoskeleton often displays shades of purple or violet, which contrast beautifully with the surrounding environment. These vibrant hues, combined with intricate patterns and markings, make the Indian Violet Tarantula a captivating sight to behold.
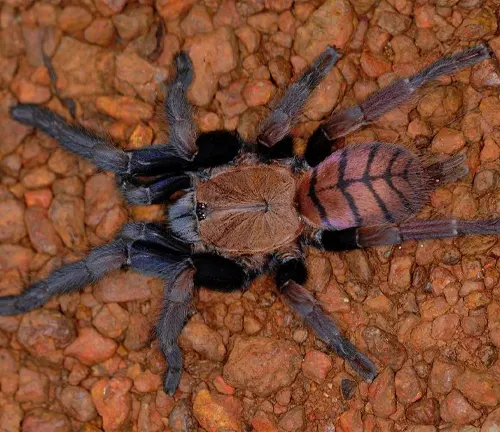
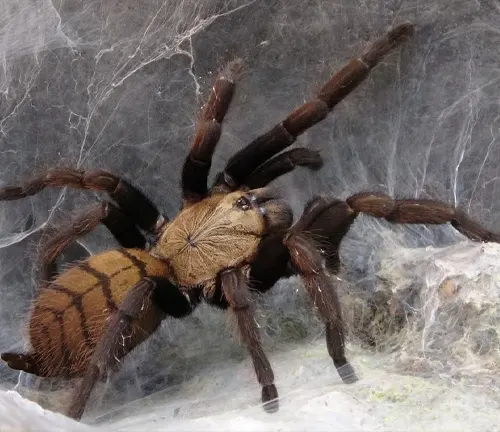


Solitary Nature
In the wild, the Indian Violet Tarantula is known for its solitary nature. Unlike some other spider species that may live in colonies or communal webs, the Indian Violet Tarantula prefers to live alone. It typically establishes its territory in burrows or hidden crevices, where it can hunt and rest without the presence of competing individuals. This solitary lifestyle allows the tarantula to avoid conflicts with other spiders and maximize its chances of survival in its natural habitat.
Habitat and Distribution
Natural Habitat
The natural habitat of the Indian Violet Tarantula encompasses a variety of environments typically found in the Indian subcontinent. These tarantulas are often found in regions with tropical climates, including dense forests, grasslands, and scrublands. They thrive in areas with ample vegetation and humidity, where they can find suitable shelter and hunting grounds. Within their natural habitat, Indian Violet Tarantulas may inhabit burrows, crevices, or other secluded areas where they can retreat and remain concealed during the day.
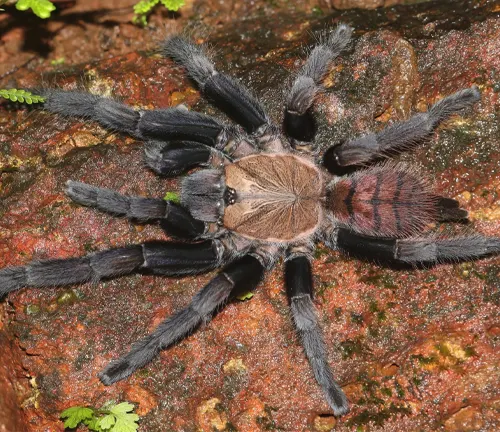

Geographic Range
The geographic range of the Indian Violet Tarantula spans various parts of the Indian subcontinent, including regions of India such as Kerala and Karnataka. Additionally, these tarantulas can be found in neighboring countries such as Sri Lanka and Bangladesh. While they are primarily distributed in specific regions within the Indian subcontinent, Indian Violet Tarantulas may also inhabit nearby areas with similar environmental conditions. Their geographic range may be influenced by factors such as habitat availability, climate, and prey abundance.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Carnivorous Appetite
The Indian Violet Tarantula possesses a carnivorous appetite, feeding primarily on a diet of small animals and insects. As an ambush predator, it relies on stealth and patience to capture its prey. Indian Violet Tarantulas are known to consume a diverse array of creatures, including insects like crickets, grasshoppers, and beetles, as well as small rodents and other arachnids. They use their keen senses to detect movement and vibrations, allowing them to locate and ambush prey with precision. This carnivorous diet provides the tarantula with essential nutrients and energy needed for survival and growth.
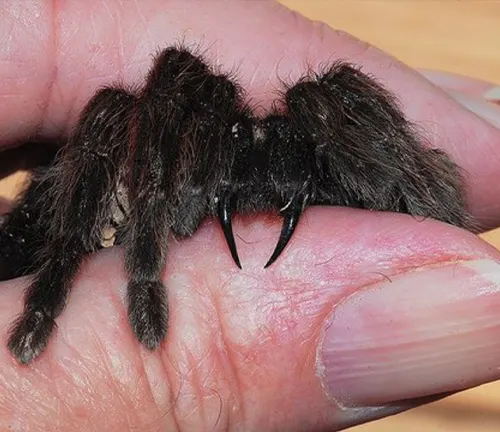


Venomous Bite
Like many tarantula species, the Indian Violet Tarantula possesses venomous fangs used to incapacitate its prey. While their venom is primarily designed for subduing small animals, it also serves as a defensive mechanism against potential threats. The venom of the Indian Violet Tarantula is considered mild and is not typically harmful to humans. Bites from these tarantulas are rare, as they usually only occur when the spider feels threatened or provoked. In most cases, the effects of a bite are minimal, causing mild discomfort or irritation similar to that of a bee sting.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
Courtship Rituals
During the breeding season, Indian Violet Tarantulas engage in elaborate courtship rituals to attract potential mates. Male tarantulas often perform intricate dances and displays to impress females and signal their readiness to mate. These rituals may involve tapping their legs on the ground, vibrating their abdomens, and producing pheromones to communicate their intentions. Female tarantulas carefully assess the displays of potential mates before choosing a suitable partner. Successful courtship rituals culminate in mating, allowing the female to produce fertilized eggs and continue the reproductive cycle.
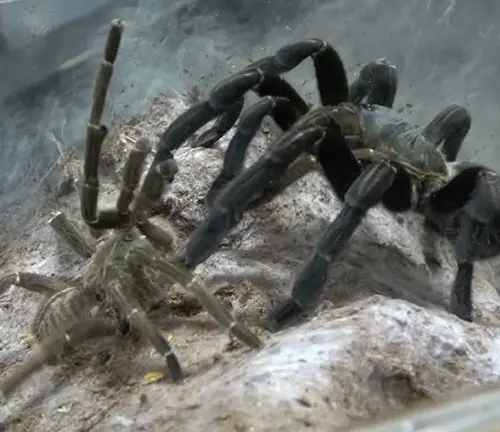
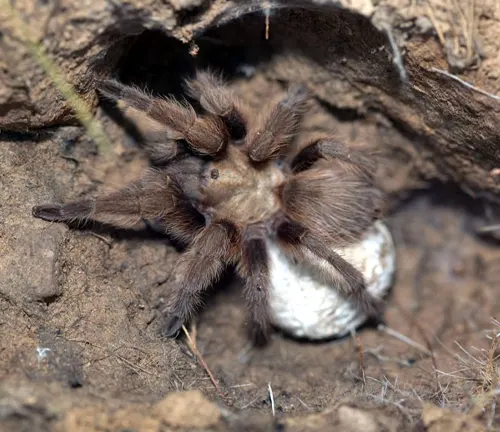


Egg Laying and Incubation
After mating, female Indian Violet Tarantulas lay eggs within silk-lined egg sacs, which they carefully guard until hatching. The process of egg laying and incubation varies depending on environmental conditions and the species of tarantula. Females may construct multiple egg sacs, each containing hundreds of eggs, to ensure the survival of their offspring. During incubation, the female tarantula provides warmth and protection to the eggs, often carrying the egg sac with her or attaching it to a secure location within her burrow. The length of the incubation period can range from several weeks to several months, depending on factors such as temperature and humidity levels. Once the eggs hatch, the young spiderlings emerge and begin their journey into the world.
Defense Mechanisms
Threat Displays
When faced with potential threats, such as predators or perceived dangers, Indian Violet Tarantulas may exhibit various defensive behaviors known as threat displays. These displays are aimed at deterring threats and avoiding confrontation whenever possible. Common threat displays include rearing up on their hind legs to appear larger and more intimidating, displaying their fangs as a warning, and emitting audible hisses or vibrations to signal aggression. Additionally, Indian Violet Tarantulas may release urticating hairs from their abdomens as a form of defense, which can irritate the skin or mucous membranes of potential predators. By showcasing these behaviors, Indian Violet Tarantulas effectively communicate their readiness to defend themselves and ward off potential threats without resorting to physical confrontation.
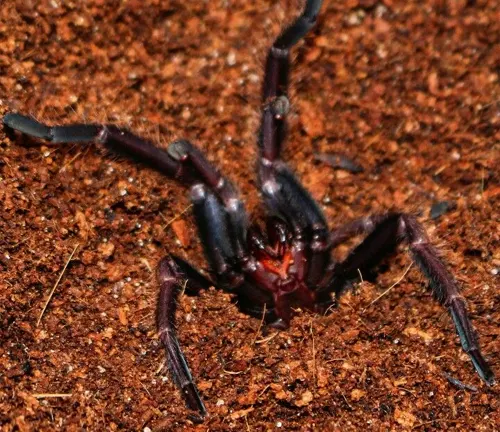

Conservation Status
Vulnerable Habitat
The natural habitat of the Indian Violet Tarantula is increasingly vulnerable to various threats, including habitat loss and degradation. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion have led to significant loss and fragmentation of the tarantula’s habitat. As forests are cleared for timber harvesting, agricultural development, and infrastructure projects, the available habitat for Indian Violet Tarantulas diminishes, putting pressure on local populations. Fragmentation of habitat isolates populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of local extinctions. Additionally, changes in land use and habitat alteration can disrupt crucial ecological processes, such as prey availability and microclimate regulation, further impacting the survival of Indian Violet Tarantulas. Conservation efforts focused on habitat protection, restoration, and sustainable land management are essential to safeguarding the remaining habitats of Indian Violet Tarantulas and ensuring their long-term survival in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.
Interactions with Humans
Cultural Significance
The Indian Violet Tarantula holds cultural significance in certain communities, where it is often intertwined with folklore, traditions, and beliefs. In some indigenous cultures, tarantulas are revered as symbols of patience, wisdom, or protection. They may feature prominently in myths, legends, and spiritual practices, serving as guardians or spiritual guides. Additionally, tarantulas may play a role in traditional medicine or rituals, believed to possess healing powers or supernatural abilities. In regions where the Indian Violet Tarantula is found, local communities may have developed unique customs or ceremonies associated with these fascinating creatures. By recognizing and respecting the cultural significance of the Indian Violet Tarantula, we gain a deeper understanding of its place in the cultural fabric of the region and its importance to local communities.
Myths and Misconceptions
Misunderstood Creatures
Tarantulas, including the Indian Violet Tarantula, are often misunderstood creatures surrounded by myths and misconceptions. Despite their fearsome appearance, tarantulas are generally docile and non-aggressive toward humans. Contrary to popular belief, they do not actively seek out human interaction or attack without provocation. Additionally, the venom of most tarantula species, including the Indian Violet Tarantula, is relatively mild and poses little threat to humans, causing only minor discomfort at most. Despite their important role in controlling insect populations and maintaining ecological balance, tarantulas are sometimes subjected to irrational fears and persecution. By dispelling myths and educating the public about the true nature of tarantulas, we can foster greater appreciation and coexistence with these fascinating creatures.
Research and Discoveries
Scientific Exploration
Ongoing scientific exploration into the biology and behavior of the Indian Violet Tarantula provides valuable insights into its ecology, evolutionary adaptations, and conservation needs. Researchers conduct field studies, laboratory experiments, and genetic analyses to better understand various aspects of tarantula biology, including their habitat requirements, feeding behaviors, reproduction, and response to environmental changes. By studying Indian Violet Tarantulas in their natural habitat and in controlled settings, scientists can identify threats to their survival, assess population dynamics, and develop conservation strategies to mitigate human impacts. Recent discoveries in tarantula research have expanded our knowledge of their ecological roles, evolutionary history, and potential contributions to biotechnology and medicine. By supporting scientific exploration and conservation efforts, we can ensure the long-term survival of the Indian Violet Tarantula and other species in their ecosystems.
Captivity and Pet Care
Popular Pets
Indian Violet Tarantulas are popular among exotic pet enthusiasts due to their striking appearance, manageable size, and relatively low maintenance requirements. As captivating display pets, these tarantulas fascinate hobbyists with their vivid colors and intriguing behaviors. With proper care and habitat setup, Indian Violet Tarantulas can thrive in captivity, providing enthusiasts with an opportunity to observe and appreciate these fascinating creatures up close. Additionally, their docile nature and minimal handling requirements make them suitable pets for individuals seeking an alternative to traditional pets like dogs or cats. However, it’s essential for prospective owners to research tarantula care thoroughly and ensure they can provide a suitable environment before acquiring one as a pet. With responsible ownership and proper care, Indian Violet Tarantulas can make rewarding and captivating pets for enthusiasts of all ages.
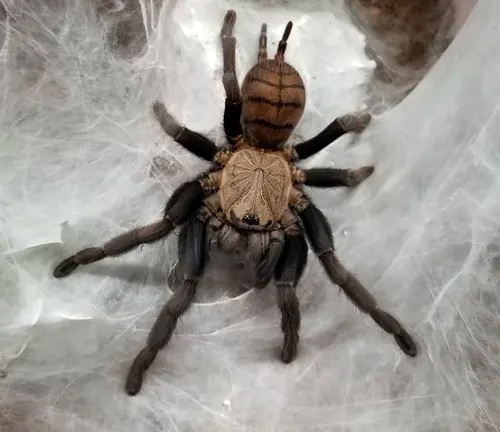

Different Species
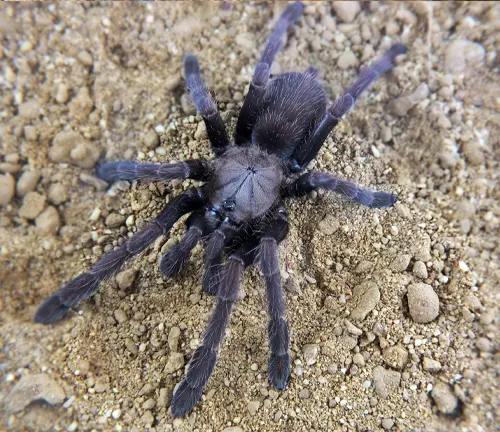
Chilobrachys fimbriatus
(Indian Violet Earth Tiger)
While not exclusively violet, this species is commonly referred to as the Indian Violet Earth Tiger due to its dark coloration, which may include shades of violet or purple.
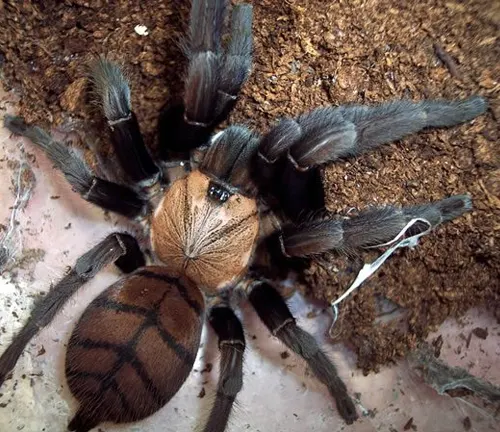
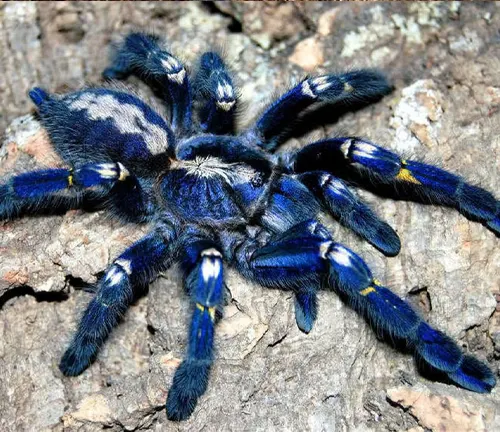


Thrigmopoeus psychedelicus
(Peacock Tarantula)
Found in southern India, this species is known for its striking metallic blue and violet colors, resembling the vibrant plumage of a peacock.
Poecilotheria metallica
(Gooty Sapphire Ornamental)
Although primarily blue, this tarantula species native to the Gooty region of India can exhibit iridescent hues of violet and purple under certain lighting conditions.
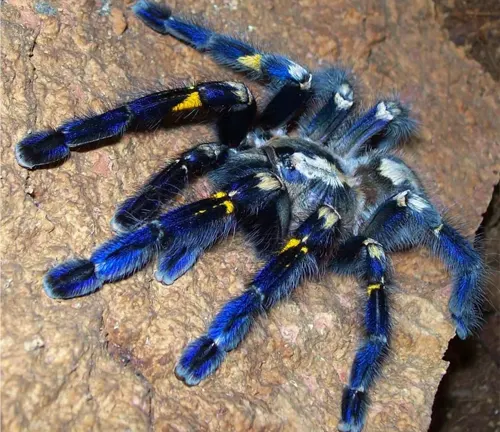


Thrigmopoeus truculentus
(Indian Violet Tarantula)
This species, sometimes referred to as the Indian Violet Tarantula, has a dark-colored body with subtle violet undertones. It is native to parts of southern India.
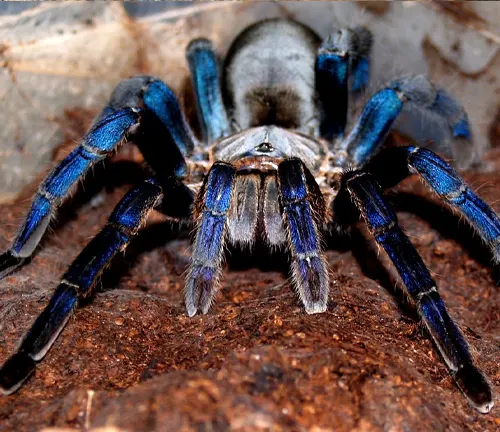
Haplopelma lividum
(Cobalt Blue Tarantula)
While not native to India, this species is sometimes kept as a pet in the country. It features a stunning cobalt blue coloration, reminiscent of violet hues.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are Indian Violet Tarantulas venomous?
Yes, Indian Violet Tarantulas possess venom, but it is primarily used to subdue prey rather than for defense against humans. Their venom is considered mild, with effects similar to a bee sting for most individuals. - How often do Indian Violet Tarantulas molt?
Indian Violet Tarantulas undergo molting, shedding their old exoskeleton to accommodate growth. The frequency of molting varies depending on factors such as age, diet, and environmental conditions. - What type of habitat do Indian Violet Tarantulas prefer in captivity?
In captivity, Indian Violet Tarantulas require an enclosure with substrate for burrowing, hiding places, and appropriate humidity levels. Providing a secure and stress-free environment is essential for their well-being. - Can Indian Violet Tarantulas be housed together?
It is generally not recommended to house Indian Violet Tarantulas together, as they are solitary creatures and may exhibit territorial behavior or cannibalism when kept in close proximity to one another. - How long do Indian Violet Tarantulas live?
Indian Violet Tarantulas have a lifespan of several years, with females typically living longer than males. Proper care and a suitable environment can contribute to their longevity in captivity. - Do Indian Violet Tarantulas make good display pets?
Yes, Indian Violet Tarantulas can make fascinating display pets due to their striking appearance and intriguing behaviors. However, it’s essential to research their care requirements thoroughly before keeping them. - Are Indian Violet Tarantulas difficult to care for?
While Indian Violet Tarantulas have specific care needs, they are not necessarily difficult to care for with proper knowledge and attention to detail. Providing suitable housing, diet, and environmental conditions is key to their well-being. - Do Indian Violet Tarantulas require special lighting?
No, Indian Violet Tarantulas do not require special lighting, as they are nocturnal creatures. However, providing a natural day-night cycle can help regulate their behavior and biological rhythms. - Can Indian Violet Tarantulas be handled?
While some tarantula enthusiasts may choose to handle their pets, it’s important to remember that Indian Violet Tarantulas, like all tarantulas, can be delicate and easily stressed. Handling should be done sparingly and with caution to avoid injury to the tarantula and minimize stress. - What are the signs of illness or distress in Indian Violet Tarantulas?
Signs of illness or distress in Indian Violet Tarantulas may include lethargy, loss of appetite, abnormal behavior, or visible physical abnormalities. If any of these signs are observed, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a veterinarian experienced in exotic pets.














Leave your comment