Wood Thrush
- December 6, 2023
- 0 comment
Thrushes, members of the Turdidae family, constitute a diverse and captivating group of birds found across the globe. Renowned for their melodious songs and distinctive plumage, thrushes have adapted to a wide range of environments, showcasing a remarkable spectrum of shapes, sizes, and habits.
Physical Appearance
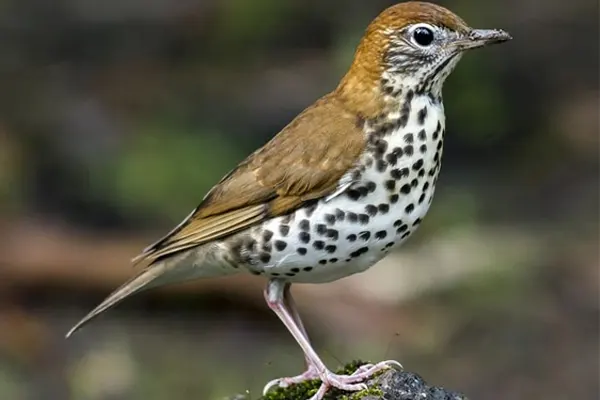

Wood Thrush
- Lifespan: 10 years 8 months
- Habitat: Woodlands
- Diet: Beetles, Caterpillars, Ants, Crickets, Moths also Spiders, Earthworms, and Snails.
- Size: 13 to 30 cm
- Weight: 128 to 175 g
- Wingspan: 12 cm
- Conservation Status: Deforestation due to Agricultural Land, Near Threatened
- Population Trend: The population trends of thrushes vary among species and geographic regions. Some species may be stable, while others may experience declines or increases in population.
Thrushes are characterized by their medium-sized bodies, slender bills, and often spotted or speckled plumage. Notable features include a strong, melodious song, an adaptation that plays a crucial role in communication and mate attraction.
Species Type
The Wood Thrush (Hylocichla mustelina) is a medium-sized songbird belonging to the family Turdidae, which includes a diverse group of thrushes. Here are some key characteristics and features of the Wood Thrush.
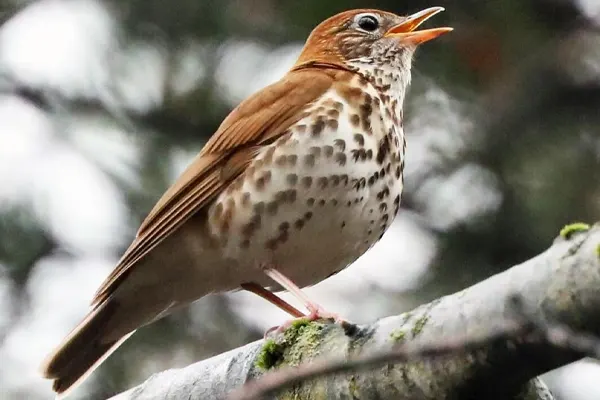

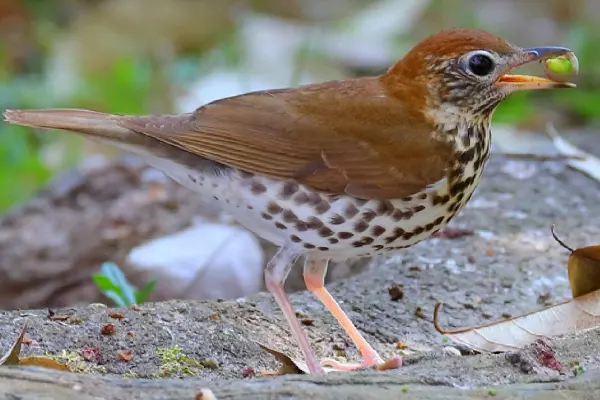
Feather Coloration
Cinnamon-Brown: The upper parts of the Wood Thrush’s body, including the back and wings, are characterized by a warm cinnamon-brown color. This rich and earthy hue gives the bird a visually appealing and camouflaged appearance within its woodland habitat.
Dark Spots: One of the most prominent features of the Wood Thrush’s plumage is the presence of bold, dark spots on its upperparts. These spots are scattered across the back, wings, and tail, creating a distinctive pattern that helps with camouflage in the dappled light of the forest.
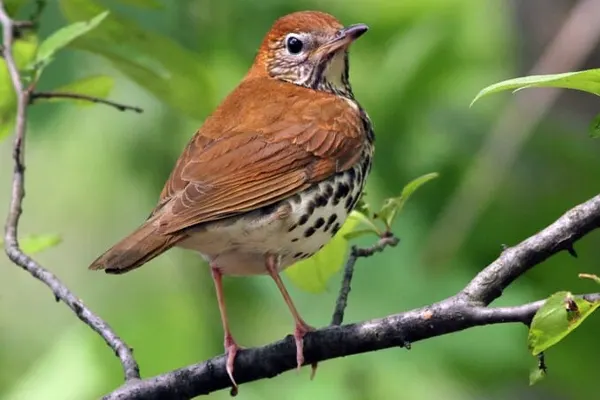
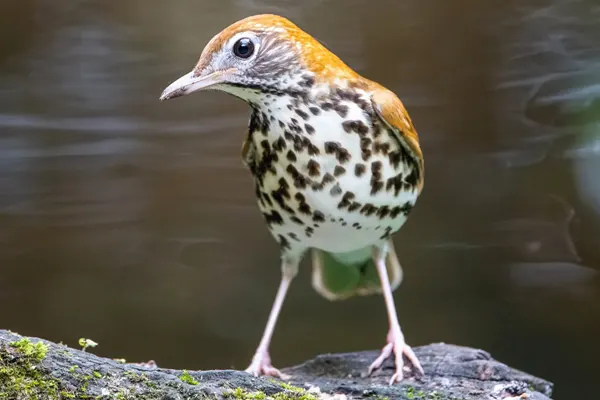


The Wood Thrush is renowned for its flute-like and complex song, which is often considered one of the most beautiful bird songs in North America. It consists of a series of clear, musical phrases and is used for mate attraction, territorial communication, and general vocalization within its habitat.
The Wood Thrush, with its captivating song and distinctive plumage, holds significance as a symbol of North American woodlands. Conservation efforts are vital to addressing the challenges facing Wood Thrush populations and ensuring their continued presence in their natural habitats.
Flight Characteristics
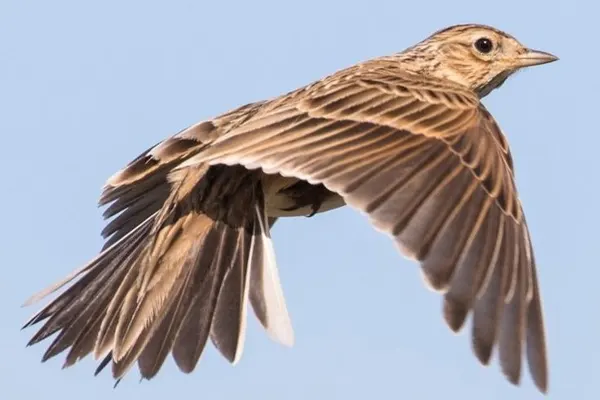

The Wood Thrush is known for its undulating flight pattern. This type of flight involves a series of rising and falling movements as it moves through the air. This undulation is often observed during both short flights within the forest and longer migratory journeys. Adept at maneuvering through dense vegetation in wooded environments. Their flight is characterized by agility, allowing them to navigate effortlessly around trees and branches as they move through the forest.
Migration Patterns
- Long-Distance Migration: Wood Thrushes are known for undertaking long-distance migrations between their breeding grounds in North America and their wintering grounds in Central America and southern Mexico.
- Nocturnal Migration: Wood Thrushes are primarily nocturnal migrants, meaning they undertake their journeys during the night. This behavior is thought to reduce the risk of predation and optimize energy conservation.
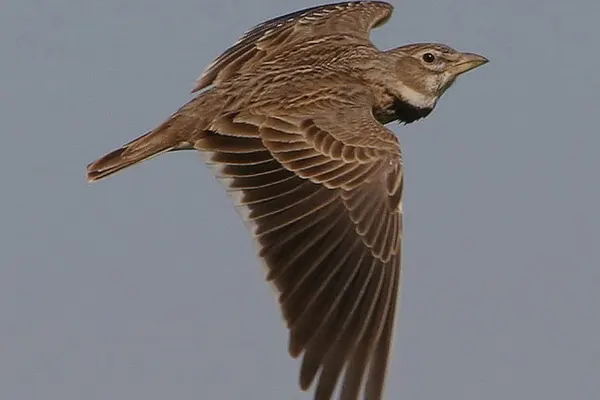
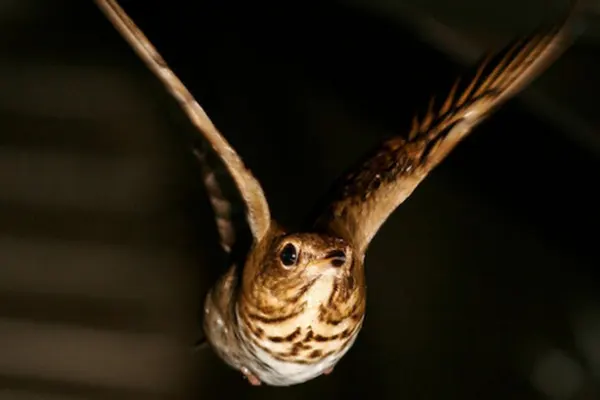
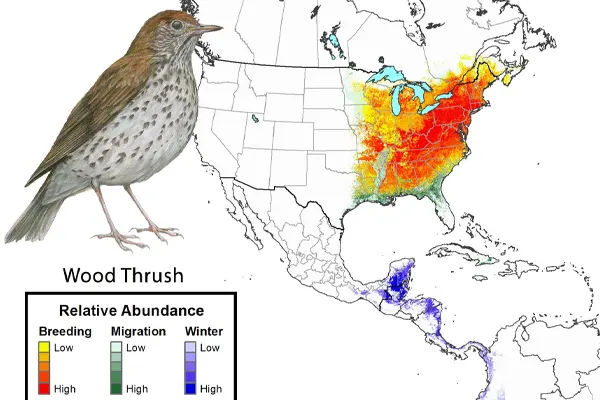


Habitat & Distribution
Habitat: Wood Thrushes show a preference for moist areas within their habitats, such as damp woodlands, riverine forests, and areas with a high abundance of leaf litter. It thrives in habitats with a well-developed understory, providing suitable locations for foraging and nesting.
Distribution: The Wood Thrush highlights the importance of maintaining healthy, mature forests with a well-developed understory. Conservation efforts focus on protecting and restoring these woodland habitats, both in their breeding range and along their migratory routes, to ensure the continued well-being of Wood Thrush populations. Conserving suitable habitats is essential for supporting their breeding activities, foraging needs, and successful migration.
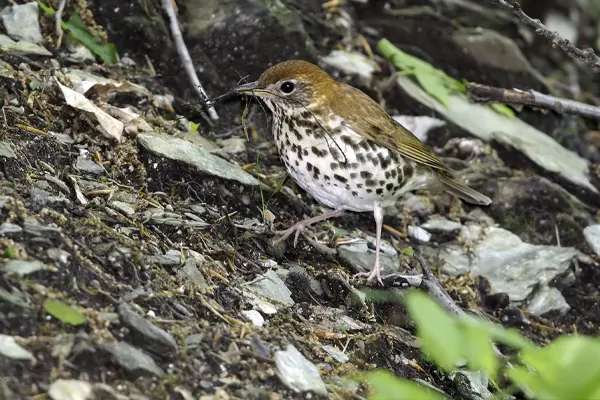
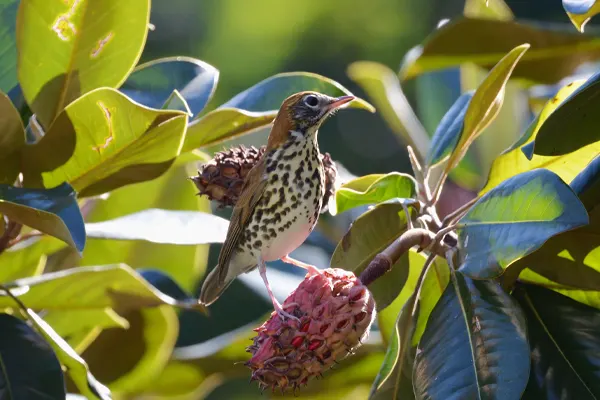


Behavioral Traits
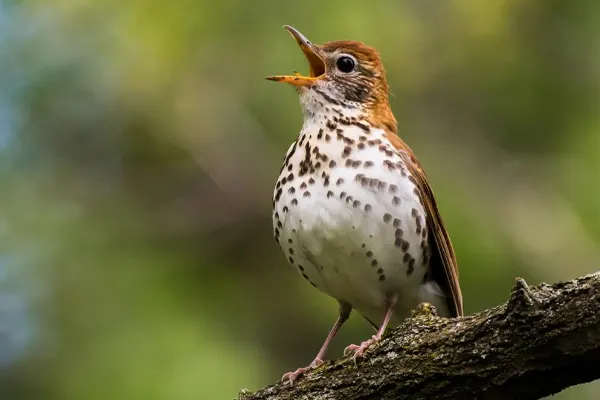

The song of the Wood Thrush is a melodic masterpiece, consisting of a sequence of clear, flute-like phrases. This musical repertoire is not only aesthetically pleasing but also carries important biological significance for the bird.
Male Wood Thrushes utilize their melodious songs as a means of establishing and defending territories. During the breeding season, each male stakes out a specific area within the forest, and the song serves as a vocal boundary. By proclaiming their presence through song, males deter other males from encroaching on their territories.
Beyond territorial and reproductive purposes, the Wood Thrush employs its song for general communication within its habitat. This can include signaling the presence of food, alerting others to potential threats, or simply maintaining contact with neighboring individuals.
The melodious song of the Wood Thrush is not only a testament to the beauty of avian vocalizations but also a crucial element of its behavioral repertoire. This vocal prowess plays a pivotal role in the bird’s ability to navigate its environment, establish territories, attract mates, and contribute to the overall vitality of its woodland ecosystem. Conservation efforts often focus on preserving the habitats that enable Wood Thrushes to engage in their intricate singing behavior, ensuring the continued presence of this iconic songster in North American forests.
Role in Ecosystem
The Wood Thrush’s ecological role extends beyond its individual existence, influencing the dynamics and health of the entire woodland ecosystem. The preservation of suitable habitats for Wood Thrushes is integral to maintaining the delicate balance of North American woodlands.
Dietary Habits
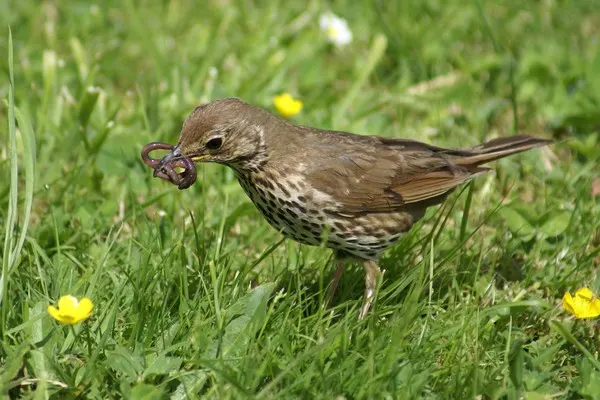


Wood Thrush in the ecosystem emphasizes the importance of conserving mature forests and maintaining the ecological integrity of these habitats. The preservation of suitable environments for Wood Thrushes ensures the continuation of their ecological contributions and supports the overall health and diversity of North American woodlands.
Seed Dispersers Wood Thrushes inadvertently aid in seed dispersal. Seeds of plants and fruits consumed by the birds can be dispersed across different areas of the forest, contributing to the regeneration of plant species.
Wood Thrushes primarily feed on insects, spiders, and other invertebrates found on the forest floor. Their foraging activities help regulate insect populations, contributing to the overall balance of the ecosystem. By consuming insects, Wood Thrushes play a role in controlling pest species that could otherwise negatively impact the health of the forest.
Interesting Facts
These fascinating facts the importance of Wood Thrushes in North American ecosystems and highlight the need for conservation efforts to protect their habitats and ensure the continued presence of these remarkable songbirds.
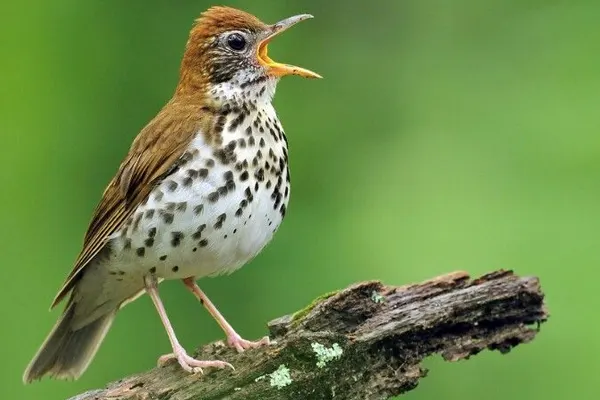

In addition to singing while perched, Wood Thrushes are known for a unique behavior—they continue to sing even during flight. This behavior is particularly pronounced during the breeding season. Singing in flight allows the Wood Thrush to communicate its presence and territorial boundaries to a broader audience within the forest.
- Mate Attraction: The melodious song of the Wood Thrush is a potent tool for attracting potential mates. Females are known to be drawn to males with strong, clear songs, as the quality of the song can be an indicator of the male’s health and genetic fitness. Males engage in elaborate singing displays to showcase their reproductive prowess and attract females for courtship.
- Communication: The Wood Thrush employs its song for general communication within its habitat. This can include signaling the presence of food, alerting others to potential threats, or simply maintaining contact with neighboring individuals.
- Territorial Establishment and Defense: Male Wood Thrushes utilize their melodious songs as a means of establishing and defending territories. During the breeding season, each male stakes out a specific area within the forest, and the song serves as a vocal boundary. By proclaiming their presence through song, males deter other males from encroaching on their territories.
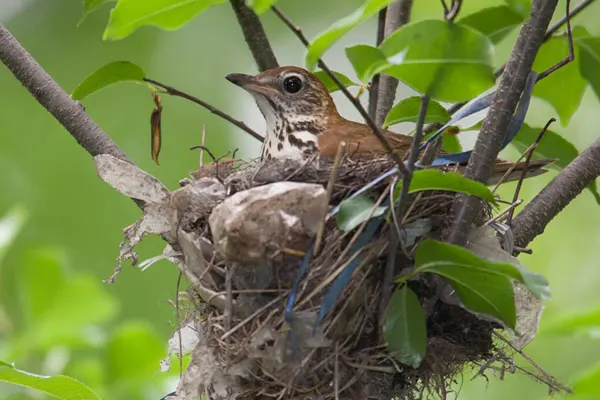
Nesting Habits
Wood Thrushes build cup-shaped nests, typically positioned in the lower branches of trees or within the understory. The nest construction involves a combination of twigs, leaves, and mud, creating a sturdy and well-insulated structure. The chosen nest location is often in the vicinity of the forest floor, providing convenient access to the ground for foraging and allowing the nest to blend into the understory vegetation.
Melodious Song & Vocalizations
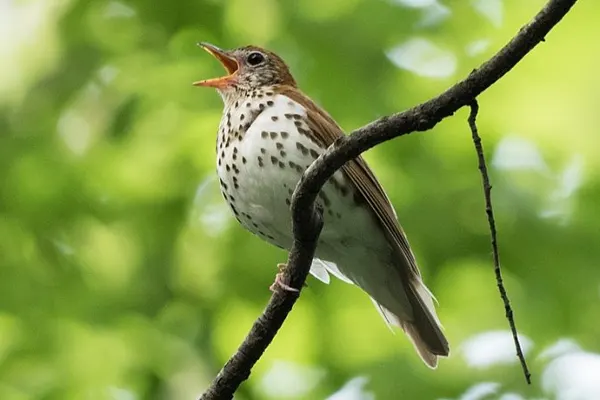

The song of the Wood Thrush is often described as a series of clear, flute-like notes that are delivered with a distinctive, ventriloquial quality. The bird’s musical repertoire consists of phrases that are repeated in a structured and rhythmic manner. The song is both powerful and serene, creating a soothing ambiance in the forest.
The Wood Thrush typically sings from elevated perches, such as the branches of tall trees, allowing its song to carry over long distances. The quality of the song is not only aesthetically pleasing to human ears but also serves a crucial role in the bird’s communication with potential mates and rivals.
Ecological Significance
Educational and Recreational Value Wood Thrushes, with their beautiful song and visible presence, contribute to the educational and recreational value of natural areas. They attract birdwatchers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts, fostering a connection between people and the natural world.
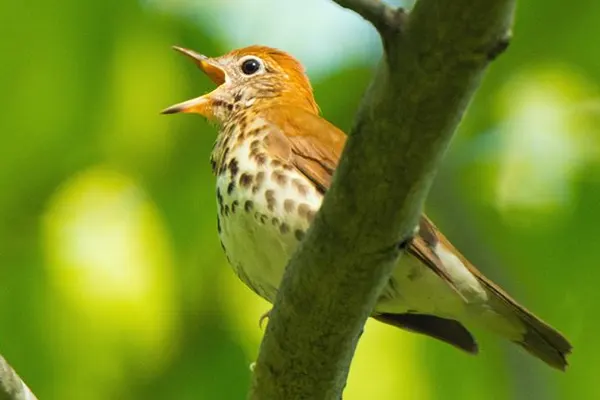

The presence and behavior of Wood Thrushes can serve as indicators of the health of their habitats. They are sensitive to changes in forest structure, and declines in their populations may signal broader ecological imbalances or threats, such as habitat fragmentation, pollution, or climate change.
Conservation Status
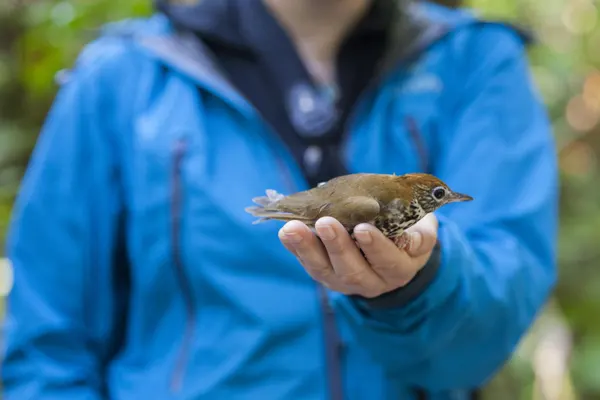


As update in January 2022, the conservation status of the Wood Thrush (Hylocichla mustelina) was assessed as “Near Threatened” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. However, it’s important to note that conservation statuses can change over time as new data becomes available, and I recommend checking more recent sources for the latest information.
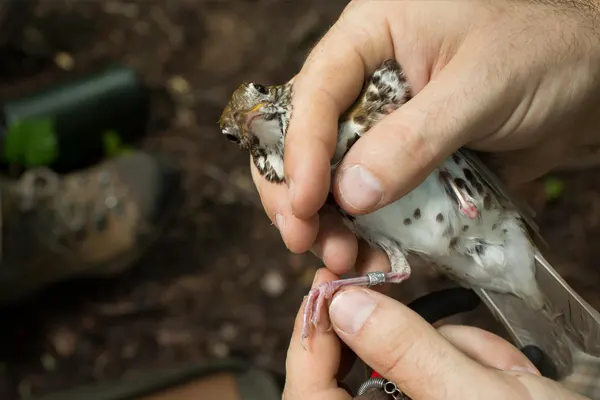
Research and Ongoing Studies

Researchers often collaborate with conservation organizations, government agencies, and citizen science initiatives to gather data on Wood Thrush populations across their range. Continued monitoring and research efforts are critical to adapting conservation strategies as new information emerges and as environmental conditions change.
Educational and Ecotourism Opportunities

Wood Thrushes offer excellent opportunities for both education and ecotourism due to their distinctive characteristics, melodious song, and the rich ecosystems they inhabit. Here are ways in which the Wood Thrush contributes to educational and ecotourism experiences like.
- Birdwatching and Nature Tours: Wood Thrushes are popular among birdwatchers, offering opportunities for people to observe and appreciate their behavior, nesting habits, and song.
- Guided Tours: Nature tours led by knowledgeable guides can provide insights into the ecology of Wood Thrushes, their role in the ecosystem, and the importance of conserving their habitats.
- Photography and Artistic Pursuits: Wood Thrushes provide excellent subjects for wildlife photography. Photography workshops can be organized to teach techniques for capturing these birds in their natural habitats.
- Art Exhibitions: Artists can draw inspiration from Wood Thrushes for exhibitions that blend art with ecological awareness, fostering a deeper connection between people and nature.
Conclusion
The Wood Thrush (Hylocichla mustelina) stands as a symbol of both the beauty and fragility of our natural world. With its enchanting flute-like song and ecological significance, this bird has captivated the hearts of birdwatchers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike. However, the Wood Thrush is not merely a source of aesthetic pleasure; it plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems through insect control, seed dispersal, and its contribution to overall biodiversity.
Despite its importance, the Wood Thrush faces an array of challenges that threaten its existence. Habitat loss, climate change, and other anthropogenic factors pose significant threats to these birds and the ecosystems they inhabit. Ongoing research endeavors seek to deepen our understanding of their ecology, behavior, and migration patterns, providing essential insights for conservation efforts.














Leave your comment