African Bush Elephant
- January 30, 2024
- 0 comment
The African Bush Elephant, a magnificent giant of the wild, stands as the largest land animal on Earth. These majestic creatures, known scientifically as Loxodonta africana, roam the vast landscapes of sub-Saharan Africa. They are easily recognized by their impressive size, with males reaching heights of up to 4 meters and weighing as much as 6,000 kg. Their distinctive features include large ears that resemble the African continent, long, curved tusks, and a robust body covered in rough, grey skin.
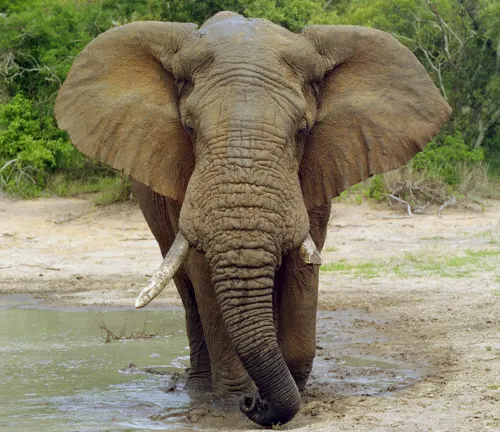

These elephants are not just known for their size but also for their complex social structure. They live in matriarchal herds led by an experienced female, showcasing deep familial bonds and sophisticated communication skills. They communicate through a range of vocalizations and seismic signals transmitted through the ground, a testament to their intelligence and social complexity.
The diet of the African Bush Elephant is primarily herbivorous, consisting of leaves, bark, and fruits, which they deftly handle with their versatile trunks. Their feeding habits significantly impact the environment, making them a keystone species in their ecosystem. By uprooting trees and spreading seeds, they play a crucial role in shaping the African savannas and forests.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Loxodonta africana |
| Common Name | African Bush Elephant |
| Size (Height) | Up to 4 meters (13 feet) for males; females slightly smaller |
| Weight | Males: Up to 6,000 kg (13,228 lbs); Females: Slightly less |
| Lifespan | Up to 60-70 years in the wild |
| Diet | Herbivorous, including leaves, bark, fruit, and grasses |
| Habitat | Sub-Saharan Africa, including savannas, grasslands, and forests |
| Social Structure | Matriarchal herds consisting of females and their offspring; solitary or small groups for males |
| Reproduction | Gestation period of about 22 months, usually birthing a single calf |
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable, primarily due to poaching and habitat loss |
| Distinctive Features | Large ears that help with thermoregulation, long tusks, muscular trunk |
| Behavior | Highly social, intelligent, displays complex communication and emotional bonds |
| Role in Ecosystem | Keystone species, influencing vegetation patterns and biodiversity |
| Threats | Poaching for ivory, habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict |
| Cultural Significance | Symbol of wisdom and strength in many African cultures; a global icon for conservation efforts |
African Bush Elephant: Majestic Giants of the Wild
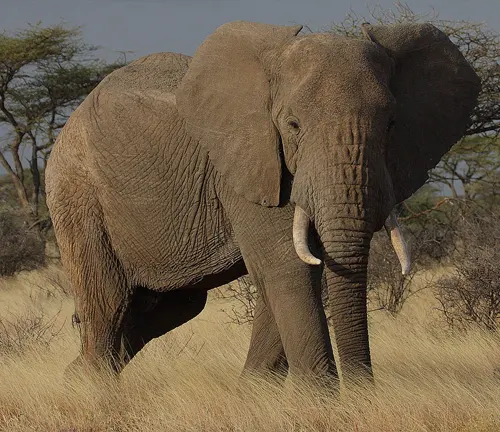

The African bush elephant, a majestic creature, stands as the largest land animal on our planet. Belonging to the family Elephantidae, these elephants have roamed the African savannas and forests for centuries, symbolizing strength and wisdom in various cultures.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Appearance
The African bush elephant, the largest of all terrestrial animals, stands as a symbol of grandeur and strength. These magnificent creatures can reach up to 4 meters in height and weigh as much as 6,000 kg. Their massive bodies are covered in wrinkled, grey skin, with large, flapping ears that radiate excess heat.
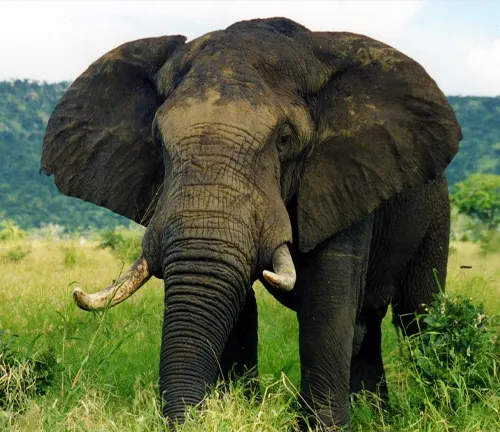


Distinctive Features Compared to Other Elephants
What sets them apart from their Asian cousins and even the African forest elephants are their enormous tusks, which are both longer and heavier, serving as tools for digging and weapons in conflicts.
Habitat and Distribution
Geographical Range
The African bush elephant roams across a vast expanse of sub-Saharan Africa, with populations found from Mali in the west to Ethiopia in the east, and southward to South Africa.
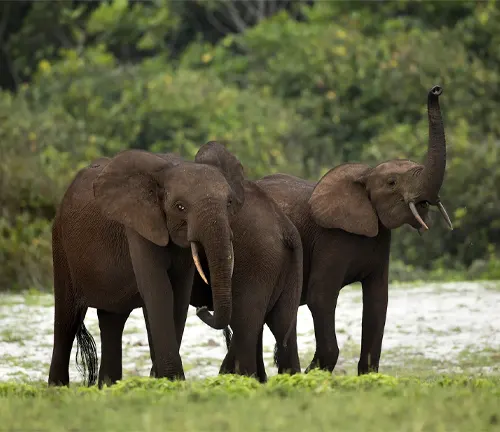

Types of Habitats
These elephants are adaptable, living in varied habitats ranging from grasslands and savannas to swamps and dense forests, wherever they can find ample food and water.
Diet and Feeding Habits
What Do They Eat?
Primarily herbivores, these elephants feed on a diet of leaves, bark, and fruits, occasionally grazing on grasses. Their large size demands a massive intake of food, which can be up to 150 kg per day.
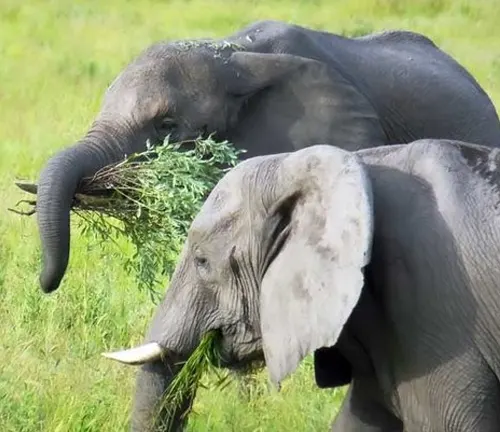


Feeding Behaviors
They play a pivotal role in their ecosystems, not only as mega-herbivores but also as environmental engineers. Their feeding habits help in shaping the landscape, dispersing seeds, and creating pathways in dense vegetation.
Social Structure and Behavior
Herd Dynamics
African bush elephants are profoundly social, typically seen in matriarchal herds consisting of females and their offspring. These herds are led by the eldest female, known as the matriarch.
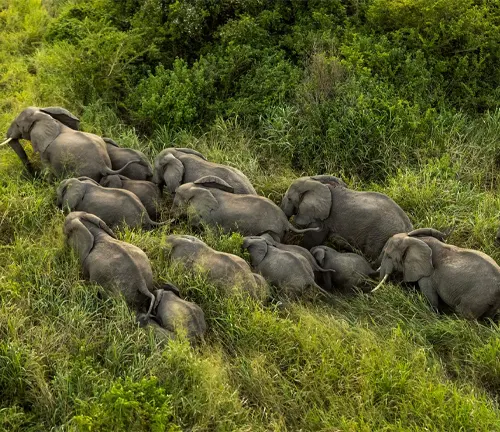
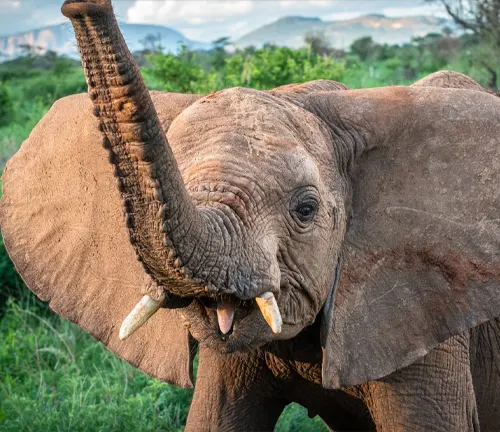


Communication Methods
Communication among them is sophisticated, involving a range of vocalizations, from trumpeting to rumbling, as well as non-verbal cues like body language and seismic signals transmitted through the ground.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Mating Rituals
Mating in these elephants is a complex affair, with males (bulls) seeking out females (cows) in estrus. Bulls will often compete for mating rights, showcasing their strength and dominance.
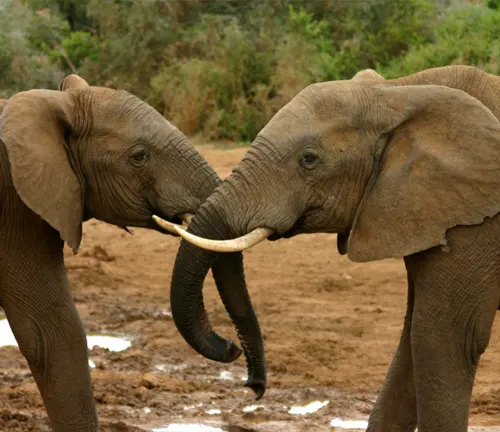

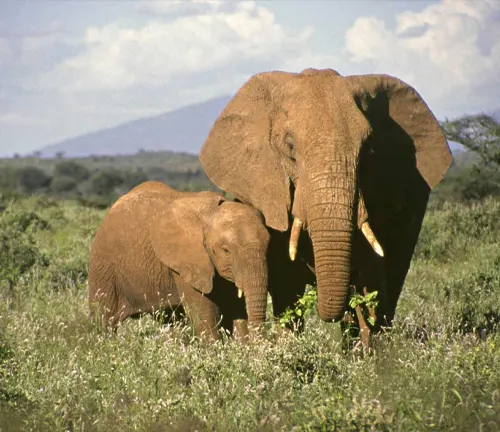
Parenting and Offspring
Calves are born after a lengthy gestation period of 22 months, and they receive extensive care not only from their mothers but also from other females in the herd, in a communal parenting approach.

Conservation Status
Current Threats
Their existence is perilously threatened by habitat loss due to expanding human activities and poaching for ivory, which has seen their populations decline drastically.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation strategies include anti-poaching patrols, habitat preservation, and international efforts to control the ivory trade.
Human and Elephant Conflict
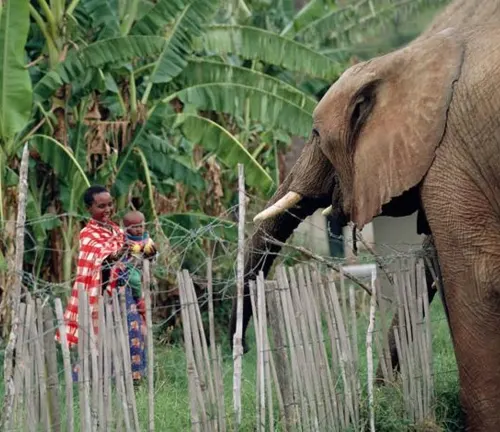

Causes of Conflicts
As human populations expand, encroaching on elephant habitats, conflicts arise. Elephants raid crops, causing economic losses, while humans retaliate, sometimes lethally.
Impact on Local Communities
These conflicts can have profound impacts on local communities, not just economically but also in terms of safety, requiring innovative solutions to promote coexistence.
Cultural Significance
In African Cultures
In African societies, the elephant is revered and often associated with wisdom, memory, and longevity. They feature prominently in folklore and are considered sacred in some cultures.
In Global Perspective
Globally, the African bush elephant has become an icon for wildlife conservation, representing the urgent need to protect our natural world.
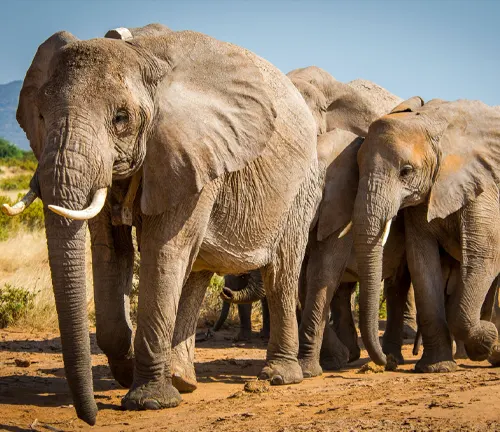

Elephant Tourism
Ethical Considerations
Elephant tourism, if not managed ethically, can lead to exploitation and harm. It’s crucial to ensure that any interaction with these wild animals is conducted in a way that prioritizes their welfare.
How to Responsibly Observe Elephants
Responsible tourism involves observing elephants in their natural habitats without intruding or causing stress, thereby contributing to conservation efforts and local economies.
Different Species
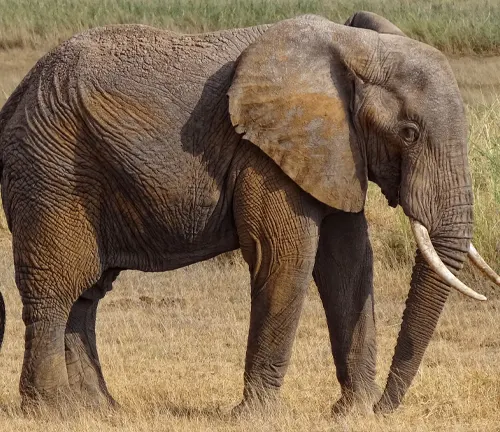
African Bush Elephant (Loxodonta africana)
Habitat: Primarily found in savannas, grasslands, and woodlands of sub-Saharan Africa.
Physical Characteristics: Larger in size compared to the forest elephant, with bulls reaching up to 4 meters in height and weighing as much as 6,000 kg. They have larger ears and tusks.
Behavior: Known for their long migrations in search of food and water.
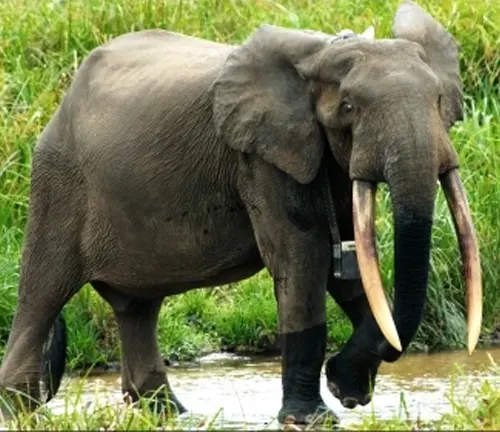


African Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis)
Habitat: Lives in the dense rainforests of west and central Africa.
Physical Characteristics: Smaller and more compact than their bush counterparts, with straighter tusks and rounded ears. Their skin is usually darker with a more pinkish undertone.
Behavior: They have a more restricted range due to their reliance on forest environments. Their diet consists more of fruit, which plays a crucial role in seed dispersal in their habitats.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the African Bush Elephant?
The African Bush Elephant (Loxodonta africana) is the largest land mammal on Earth, native to various habitats in sub-Saharan Africa. - How large can African Bush Elephants grow?
Adult males can reach up to 4 meters in height and weigh as much as 6,000 kg, making them significantly larger than females. - What is the natural habitat of the African Bush Elephant?
They primarily inhabit savannas, grasslands, and woodlands, but they can also be found in deserts and marshes. - What do African Bush Elephants eat?
They are herbivores and mainly consume leaves, bark, fruit, and grass. - How do African Bush Elephants communicate?
They communicate through a range of vocalizations, body language, and seismic vibrations transmitted through the ground. - What is the social structure of African Bush Elephants?
They live in matriarchal herds composed of females and their young, while adult males often lead solitary lives or form bachelor groups. - How long is the gestation period of an African Bush Elephant?
The gestation period lasts about 22 months, one of the longest of any land animal. - Are African Bush Elephants endangered?
They are currently classified as vulnerable, mainly due to poaching for ivory and habitat loss. - What are the primary threats to African Bush Elephants?
The major threats include poaching for their ivory tusks and habitat destruction due to human activities. - What is the lifespan of an African Bush Elephant?
They can live up to 60-70 years in the wild. - How do African Bush Elephants contribute to their ecosystem?
As a keystone species, they play a critical role in their ecosystem by modifying their habitat, which benefits other species. - Can African Bush Elephants be domesticated?
They are not typically domesticated due to their size, wild nature, and the specific environmental and social needs they have. - What efforts are being made to conserve African Bush Elephants?
Conservation efforts include anti-poaching measures, habitat preservation, and international trade regulations on ivory. - How does climate change affect African Bush Elephants?
Climate change impacts their food and water sources, habitat, and could lead to increased conflicts with humans as they search for resources. - How can individuals contribute to the conservation of African Bush Elephants?
People can help by supporting conservation organizations, advocating for policies that protect elephant habitats, and promoting responsible eco-tourism.














Leave your comment