African Forest Elephant
- January 30, 2024
- 0 comment
The African Forest Elephant, scientifically known as Loxodonta cyclotis, is a captivating and enigmatic species that dwells within the lush rainforests of Central and West Africa. Unlike its larger counterpart, the savanna elephant, African forest elephants are known for their smaller stature, standing at an average of 7 to 10 feet and weighing between 2,000 to 6,000 pounds. Their remarkable adaptation to the dense rainforest environment includes large, fan-shaped ears that aid in temperature regulation.
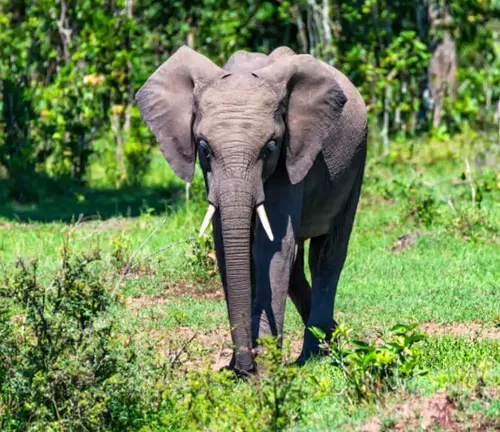

These gentle giants play a pivotal role in the rainforest ecosystem by facilitating seed dispersal through their diet of leaves, fruits, bark, and other vegetation. Despite their vital ecological importance, African forest elephants face significant threats, such as illegal ivory poaching and habitat loss due to deforestation. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these magnificent creatures and preserve the delicate balance of the rainforest they call home.
| Attribute | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Loxodonta cyclotis |
| Average Height | 7 to 10 feet |
| Average Weight | 2,000 to 6,000 pounds |
| Habitat | Central and West African Rainforests |
| Ivory Characteristics | Harder, denser, and darker than savanna |
| elephant ivory | |
| Social Behavior | Solitary or small family groups |
| Primary Diet | Leaves, fruit, bark, and vegetation |
| Ecological Role | Seed dispersal and rainforest health |
| Conservation Status | Critically endangered |
| Major Threats | Illegal ivory poaching, habitat loss due |
| to deforestation | |
| Conservation Initiatives | Protected areas, anti-poaching measures, |
| combating ivory trafficking |
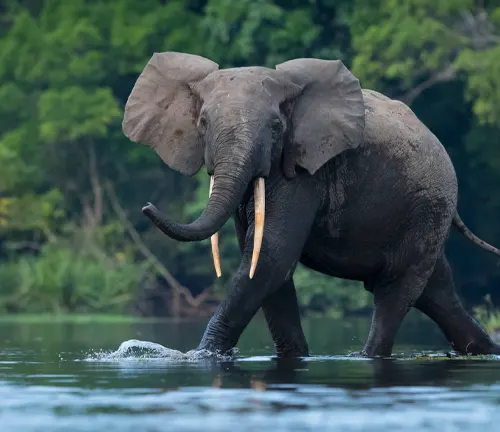

The African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis) is one of the two recognized subspecies of African elephants, the other being the African savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana). These majestic beings are primarily found in the dense, lush rainforests of Central and West Africa, where their size and elusive nature make them a captivating enigma.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Build
African forest elephants are relatively smaller than their savanna counterparts, standing at an average height of 7 to 10 feet and weighing between 2,000 to 6,000 pounds. Their compact size allows them to navigate through the dense underbrush of the rainforest with ease.
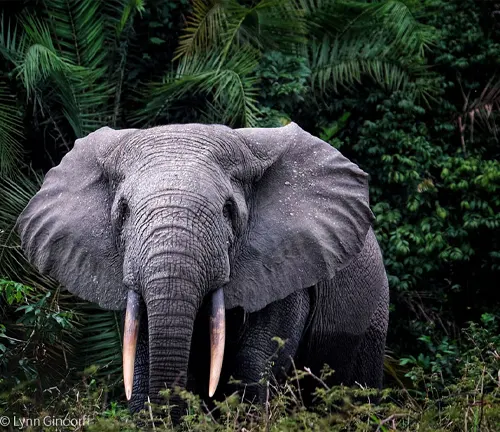
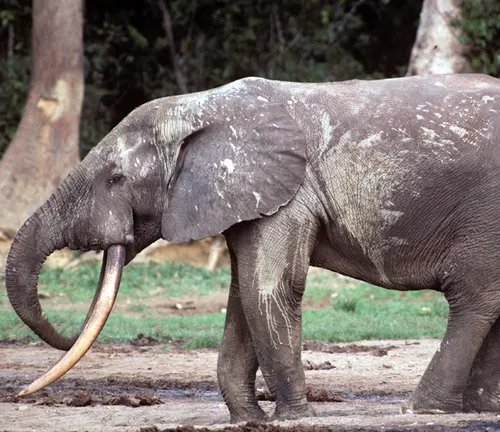


Unique Ivory
One distinctive feature of the African forest elephant is its ivory. Their ivory is harder, denser, and darker than that of the savanna elephant, making it highly sought after. Unfortunately, this has made them a target for illegal ivory poaching.
Habitat and Distribution
Rainforest Dwellers
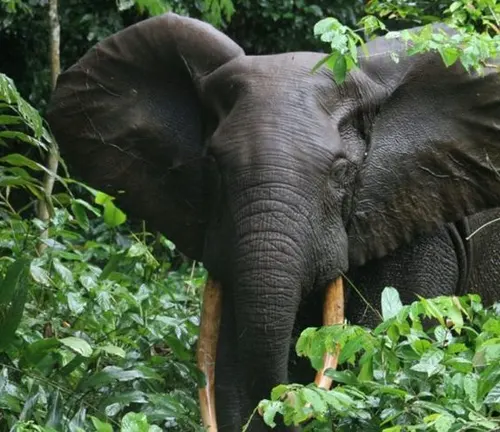
These elephants are perfectly adapted to the rainforest environment. Their large, fan-shaped ears help regulate body temperature in the humid and hot rainforest climate. They also play a pivotal role in shaping the rainforest ecosystem.

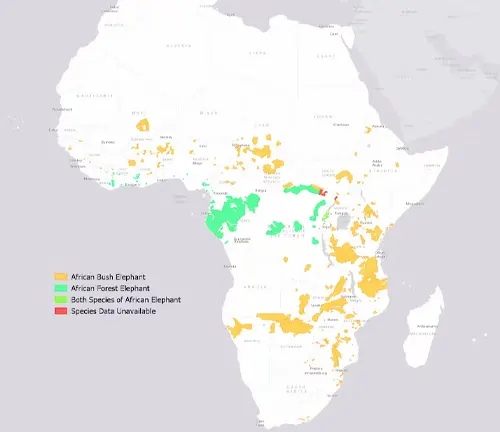
Range
African forest elephants can be found in the dense rainforests of countries like Cameroon, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Central African Republic. Their elusive nature makes them challenging to study and protect effectively.
Behavior and Social Structure
Solitary Nature
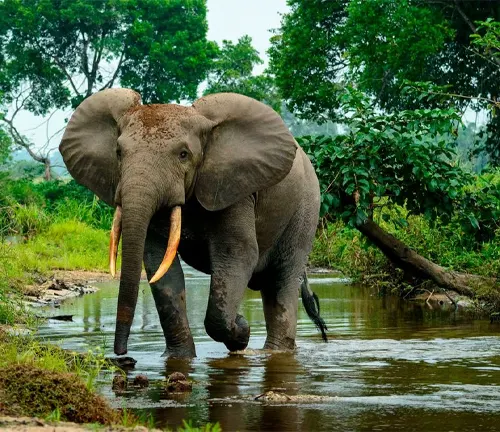
Unlike the savanna elephants that often form large herds, African forest elephants are typically solitary or found in small family groups. This behavior is likely an adaptation to the dense and challenging terrain of the rainforest.


Communication
These elephants communicate through a variety of vocalizations, including low-frequency rumbles that can travel long distances through the forest. They also use body language to convey their intentions and emotions.
Diet and Feeding Habits
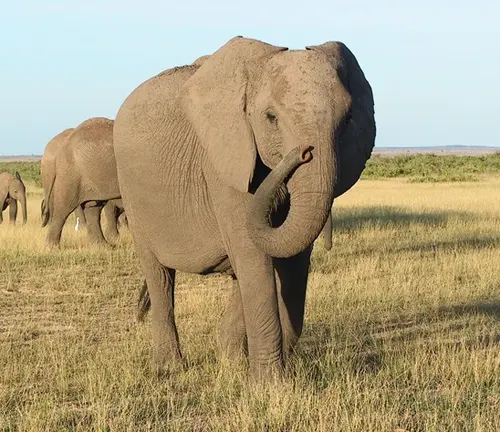
Herbivores of the Rainforest
African forest elephants are herbivores, primarily feeding on leaves, fruit, bark, and other plant materials. Their diet plays a crucial role in shaping the rainforest vegetation.
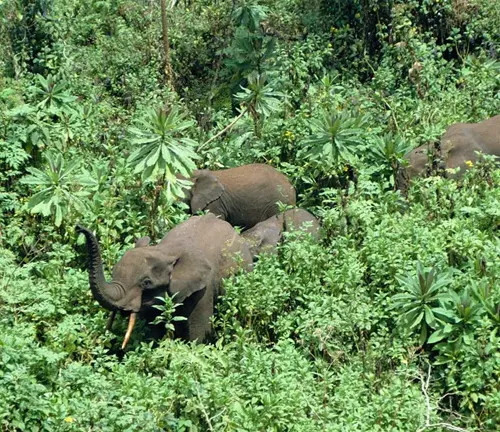
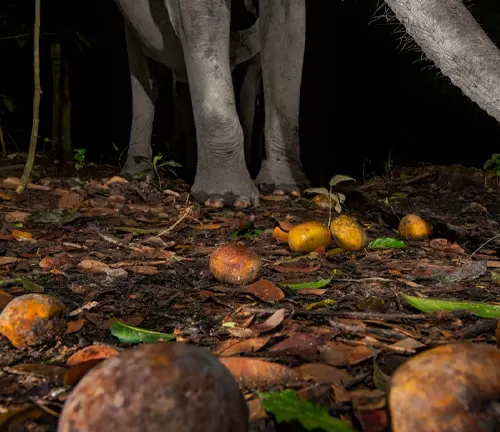


Seed Dispersal
One of their essential ecological roles is seed dispersal. As they consume fruits and plants, they help disperse seeds throughout the rainforest, contributing to the forest’s diversity and health.
Conservation Challenges
Poaching
The African forest elephant faces a grave threat from poaching due to the high demand for their ivory. Conservation efforts are ongoing to combat this illegal trade and protect these magnificent creatures.
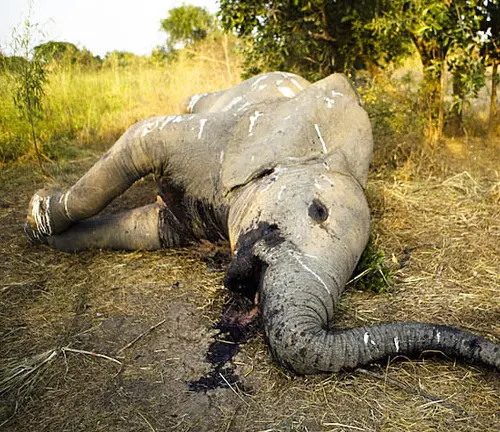
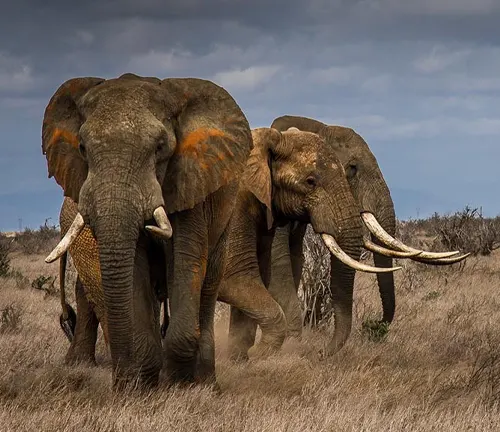


Habitat Loss
Deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose a significant challenge to their survival. As the rainforests continue to shrink, the available habitat for these elephants decreases, leading to human-elephant conflicts.
Conservation Efforts
Protected Areas
Several national parks and reserves have been established to safeguard the habitat of African forest elephants. These protected areas play a crucial role in their conservation.
Anti-Poaching Measures
Rigorous anti-poaching efforts, including increased surveillance and penalties for ivory trafficking, are being implemented to protect these elephants from illegal hunting.
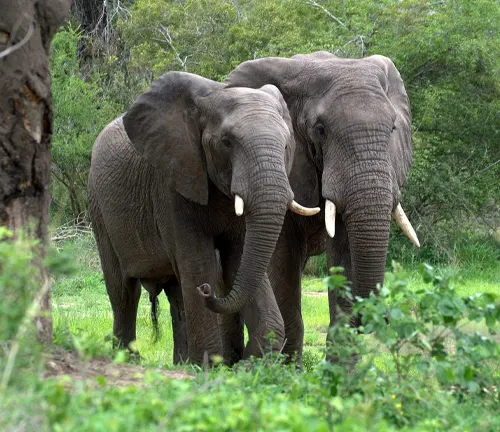
Different Species
The African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis) is a single species, but it is important to note that there are no distinct subspecies or separate species recognized within the African forest elephant category.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the African forest elephant, and how does it differ from the savanna elephant?
The African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis) is a distinct subspecies known for its smaller size and adaptation to rainforest habitats, while the savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana) is larger and inhabits open savannas. - Where can I find African forest elephants in the wild?
African forest elephants are primarily found in the dense rainforests of Central and West Africa, including countries like Cameroon, Gabon, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. - What is the size and weight range of African forest elephants?
African forest elephants typically stand at an average height of 7 to 10 feet and weigh between 2,000 to 6,000 pounds, making them smaller than savanna elephants. - What makes African forest elephant ivory unique, and why is it targeted by poachers?
African forest elephant ivory is harder, denser, and darker than savanna elephant ivory, making it highly sought after in the illegal ivory trade, which poses a significant threat to their survival. - How do African forest elephants contribute to the rainforest ecosystem?
African forest elephants play a crucial role in seed dispersal, helping maintain the health and diversity of rainforest vegetation. - Are African forest elephants solitary or social animals?
African forest elephants are typically solitary or found in small family groups, which is an adaptation to the challenging terrain of the rainforest. - What are some of the vocalizations and communication methods used by African forest elephants?
They communicate through low-frequency rumbles that can travel long distances through the forest and use body language to convey their intentions and emotions. - What is the impact of habitat loss and deforestation on African forest elephants?
Deforestation and habitat loss due to human activities threaten the available habitat for African forest elephants, leading to increased human-elephant conflicts. - What conservation efforts are in place to protect African forest elephants?
Conservation initiatives include the establishment of protected areas, anti-poaching measures, and efforts to combat illegal ivory trafficking. - How can individuals support the conservation of African forest elephants?
People can support conservation organizations, raise awareness about the issue, and avoid purchasing products made from ivory. - Are African forest elephants considered a keystone species in the rainforest ecosystem?
Yes, they are considered a keystone species because of their vital role in shaping the rainforest ecosystem through seed dispersal and other ecological contributions.| - What is the current population status of African forest elephants, and are they endangered?
African forest elephants are listed as critically endangered due to the significant decline in their population, primarily driven by poaching and habitat loss.














Leave your comment