Agile Gibbon
- January 17, 2024
- 0 comment
The Agile Gibbon, scientifically known as Hylobates agilis, is a captivating and agile primate found in the lush rainforests of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. Renowned for its remarkable agility in navigating the treetops, this small, tree-dwelling ape belongs to the Hylobates genus. Agile Gibbons exhibit distinctive features, with adults reaching an average height of 17 to 25 inches and boasting a slender build, long arms, and gripping hands and feet that facilitate their adept movement through the forest canopy. Their fur varies in color, ranging from dark brown to light tan, contributing to effective camouflage in their tropical habitats.
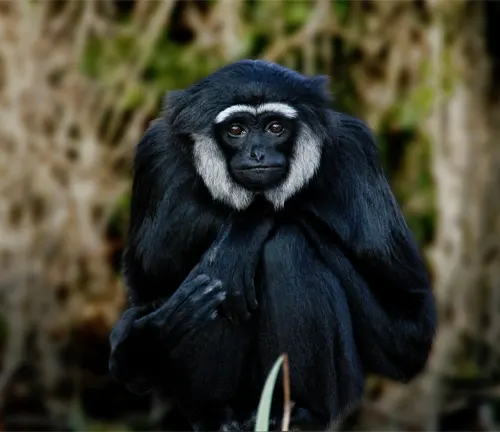

Agile Gibbons are known for their unique vocalizations, engaging in elaborate songs that serve as a means of communication, territory marking, and reinforcing social bonds within their monogamous family units. With a frugivorous diet, Agile Gibbons play a crucial role in their ecosystems by contributing to seed dispersal and maintaining ecological balance. Unfortunately, these fascinating primates face significant threats, including habitat loss due to deforestation, illegal pet trade, and hunting, leading to their classification as endangered. Conservation efforts are underway to protect Agile Gibbons and their habitats, emphasizing the importance of raising awareness and fostering collaborative initiatives to ensure the survival of this remarkable species.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hylobates agilis |
| Average Height | 17 to 25 inches |
| Physical Features | Slender build, long arms, gripping hands and feet |
| Fur Color | Dark brown to light tan |
| Habitat Range | Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand) |
| Preferred Habitat | Primary and secondary rainforests |
| Social Structure | Monogamous family units |
| Communication | Unique vocalizations, including elaborate songs |
| Diet | Frugivorous, primarily consuming fruits |
| Notable Behavior | Remarkable agility in navigating treetops |
| Conservation Status | Endangered |
| Threats | Habitat loss, illegal pet trade, hunting |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat protection, anti-poaching, awareness |
| Cultural Significance | Featured in folklore and traditions in some cultures |
| Ecological Role | Contributes to seed dispersal and ecosystem balance |
Agile Gibbon: Unlocking the Mysteries of a Unique Primate
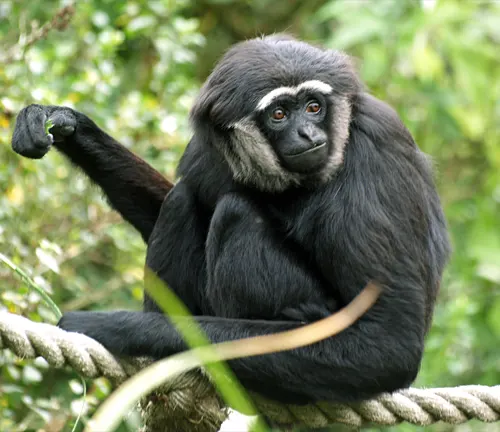

The natural world is filled with fascinating creatures, each with its own set of unique characteristics. Among the lesser-known inhabitants of our planet is the Agile Gibbon (Hylobates agilis), a primate that captivates both researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Agile Gibbons, exploring their physical attributes, behavior, conservation status, and the critical role they play in ecosystems.
Agile Gibbons, scientifically known as Hylobates agilis, are small, arboreal apes native to Southeast Asia. Their name is derived from their remarkable agility in navigating the treetops with astonishing grace.
What sets Agile Gibbons apart from other primates? Their unique vocalizations, tight-knit social structure, and remarkable adaptability make them a subject of interest for researchers and wildlife enthusiasts worldwide.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Appearance
Agile Gibbons are relatively small, with adults reaching an average height of 17 to 25 inches. Their slender bodies, long arms, and gripping hands and feet make them well-adapted to a life spent swinging through the trees.
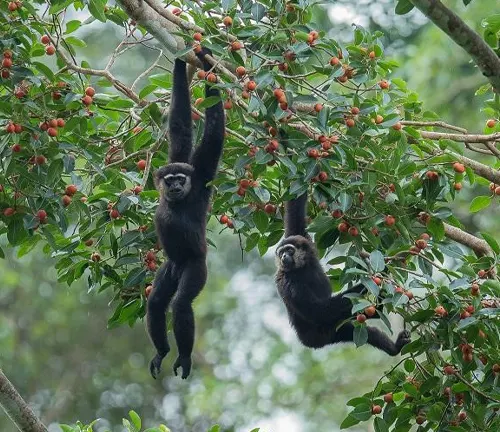
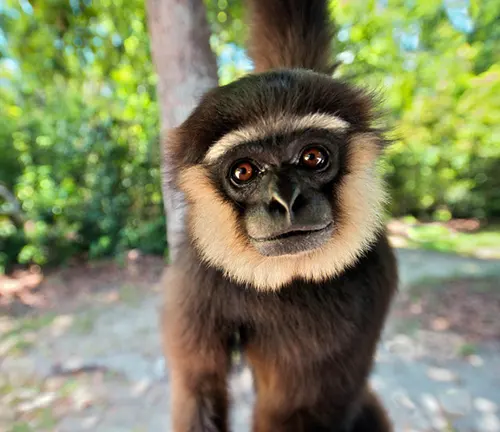


Coloration and Fur Texture
The fur of Agile Gibbons varies in color, ranging from dark brown to light tan. Their soft, dense fur provides insulation in their tropical habitats, while the lighter coloration aids in camouflage within the foliage.
Habitat and Distribution
Native Regions
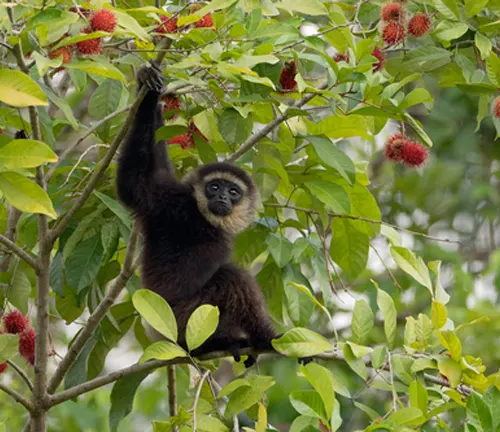
Agile Gibbons are primarily found in the rainforests of Southeast Asia, including parts of Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. These regions offer the dense canopy and diverse plant life that support the Gibbons’ arboreal lifestyle.
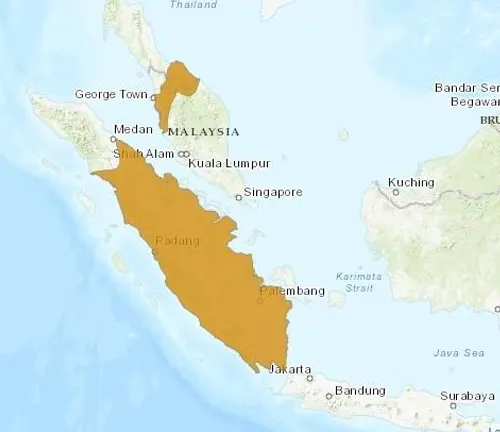

Preferred Environments
Within their native range, Agile Gibbons show a preference for primary and secondary rainforests, where they can find an abundance of fruit-bearing trees and navigate through the forest canopy with ease.
Behavior and Social Structure
Agile Gibbon Vocalizations
One of the most intriguing aspects of Agile Gibbon behavior is their vocalizations. Gibbons use elaborate songs to communicate with each other, establishing territory boundaries and strengthening social bonds.
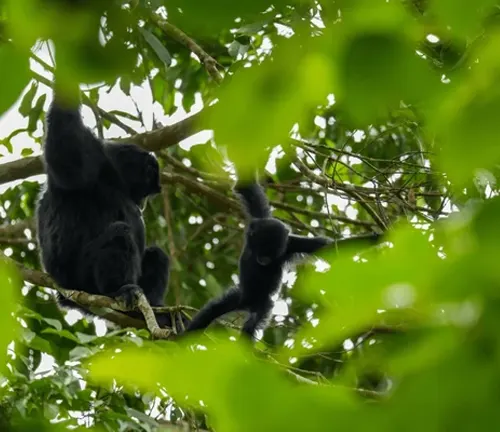
Social Bonds and Family Units
Agile Gibbons form monogamous pairs, and their family units typically consist of a mated pair and their offspring. The strong social bonds within these family units contribute to the Gibbons’ ability to thrive in their complex rainforest environment.

Diet and Feeding Habits

Primary Food Sources
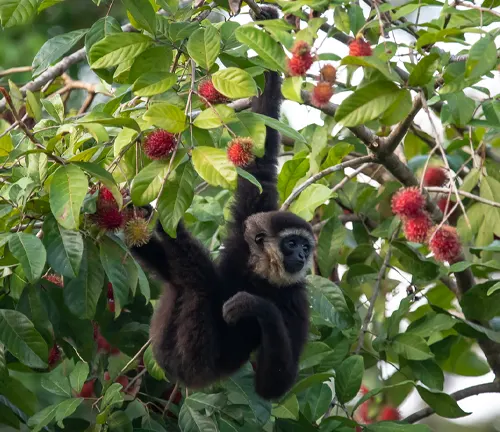
The Agile Gibbon’s diet is predominantly frugivorous, consisting of various fruits, leaves, and flowers. Their keen agility allows them to access a wide range of food sources within the forest canopy.
Foraging Techniques
Gibbons are expert foragers, using their dexterous hands and nimble movements to pluck fruits and navigate through the treetops. This foraging behavior plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitat.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Mating Rituals
Agile Gibbons engage in elaborate mating rituals, including vocal duets and physical displays. These rituals strengthen the bond between mates and contribute to the overall stability of their social structure.
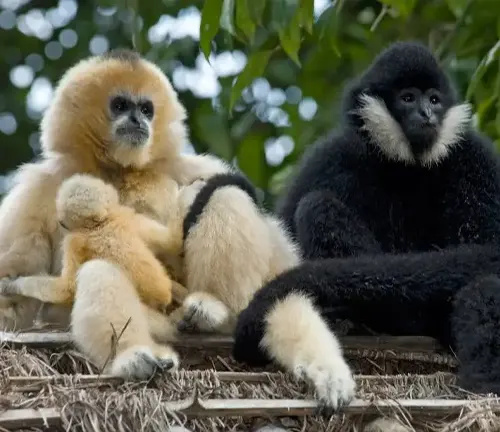

Gestation Period and Offspring Care
After a gestation period of around seven months, Agile Gibbons give birth to a single offspring. The attentive parents invest significant time and effort into caring for their young, ensuring their survival in the challenging rainforest environment.
Conservation Status
Threats to Agile Gibbon
Despite their adaptability, Agile Gibbons face numerous threats, including habitat loss due to deforestation, illegal pet trade, and hunting.
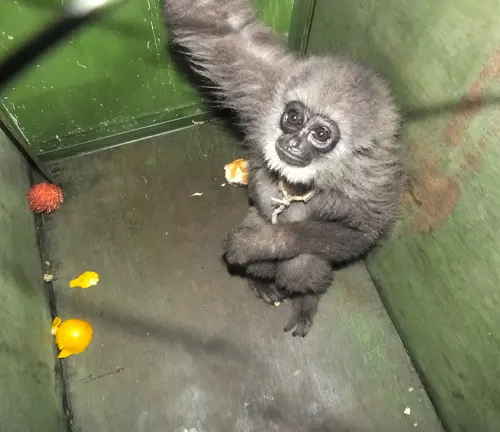

Conservation Efforts
Conservation organizations and researchers are actively working to protect Agile Gibbons and their habitats. Efforts include habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and community education programs to promote coexistence.
Interactions with Humans
Cultural Significance
Agile Gibbons hold cultural significance in some Southeast Asian communities, where they are featured in folklore and traditions.
Human-Induced Challenges
Human activities, such as logging and agricultural expansion, pose significant challenges to the survival of Agile Gibbons. Increased awareness and sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating these threats.
Popular Myths and Misconceptions
Addressing Common Misbeliefs
Dispelling myths surrounding Agile Gibbons, such as misconceptions about their behavior or perceived threats, is crucial for fostering accurate understanding and informed conservation efforts.
Captive Agile Gibbons
Zoos and Conservation Centers
Some Agile Gibbons reside in zoos and conservation centers, where they play a role in educational programs and captive breeding efforts.
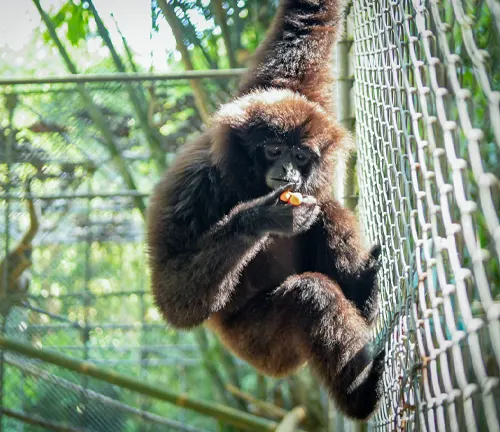

Challenges and Benefits
Captive settings present both challenges and benefits for Agile Gibbons, raising important ethical considerations regarding their well-being and conservation impact.
The Agile Gibbon’s Contribution to Ecosystems
Ecological Importance
Agile Gibbons play a vital role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems through seed dispersal and shaping vegetation dynamics.
Biodiversity Impact
The presence of Agile Gibbons contributes to the overall biodiversity of their habitats, influencing the abundance and distribution of various plant and animal species.
Different Species
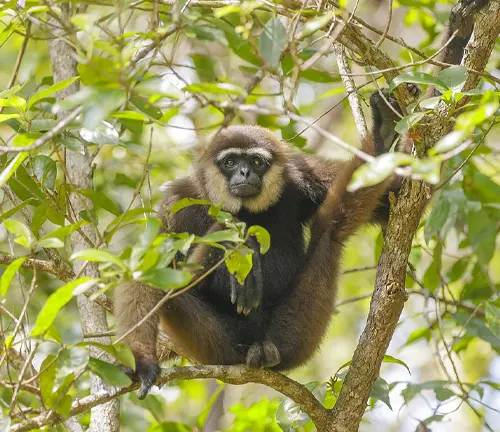
Hylobates albibarbis
(White-bearded Gibbon)
Found in parts of Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula, the White-bearded Gibbon is known for its distinct white facial hair.
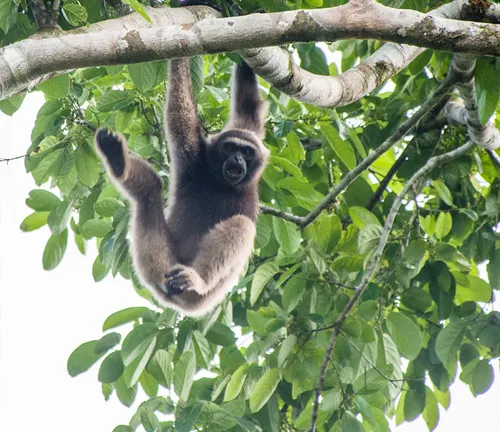


Hylobates funereus
(Müller’s Bornean Gibbon)
Native to Borneo, Müller’s Bornean Gibbon has a dark-colored fur coat and plays a vital role in the ecological balance of Bornean rainforests.
Hylobates klossii
(Kloss’s Gibbon)
Inhabiting the islands of Java and Borneo, Kloss’s Gibbon is recognized by its dark fur and is considered endangered due to habitat loss.
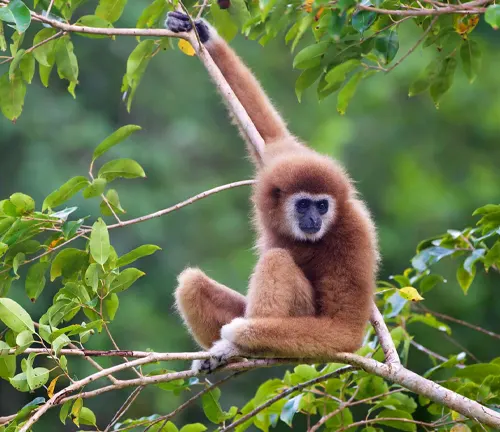


Hylobates lar
(Lar Gibbon)
Also known as the White-handed Gibbon, it is distributed across Southeast Asia and is easily identified by its distinctive light-colored hands.
Hylobates moloch
(Javan Gibbon)
Endemic to Java, the Javan Gibbon is recognized by its black fur and is critically endangered due to habitat destruction.
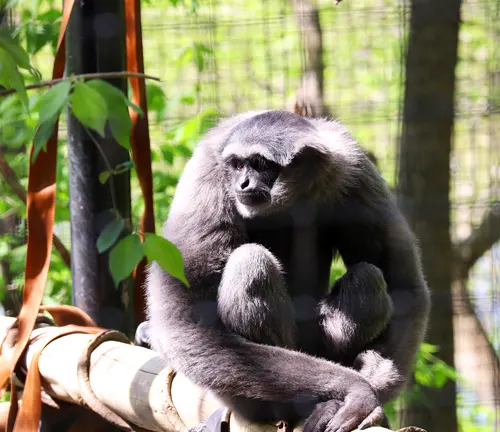
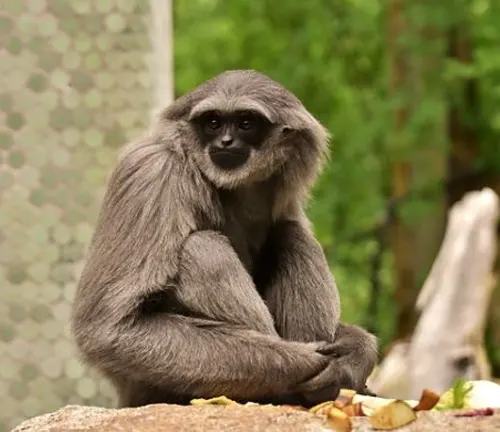


Hylobates muelleri
(Silvery Gibbon)
Found on Sumatra, the Silvery Gibbon has a distinctive silvery-gray fur coloration, and like many gibbon species, it faces threats from habitat loss.
Hylobates pileatus
(Capped Gibbon)
Inhabiting the island of Borneo, the Capped Gibbon has a cap-like fur pattern on its head, making it visually distinct.


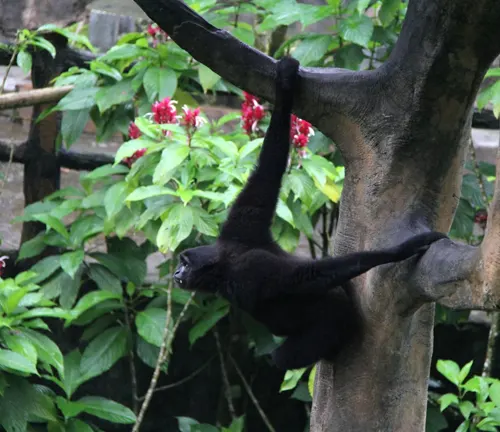
Hylobates syndactylus
(Siamang)
While not technically a “Gibbon,” the Siamang is closely related and is the largest of the gibbons. It has distinctive throat sacs and is found in the forests of Malaysia and Sumatra.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the average lifespan of Agile Gibbons?
Agile Gibbons typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years in the wild, depending on various factors such as habitat conditions and threats. - How do Agile Gibbons communicate with each other?
Agile Gibbons communicate using intricate vocalizations, often engaging in duets that play a crucial role in establishing territory and strengthening social bonds. - Are Agile Gibbons solitary or social animals?
Agile Gibbons are social animals and typically form monogamous pairs, consisting of a mated male and female along with their offspring. - What are the primary threats to Agile Gibbons in the wild?
The main threats to Agile Gibbons include habitat loss due to deforestation, illegal pet trade, and hunting. - How fast and far can Agile Gibbons swing through trees?
Agile Gibbons are incredibly nimble and can swing at high speeds, covering distances of up to 30 feet in a single swing. - Do Agile Gibbons build nests in trees?
Agile Gibbons do not build nests like some other primates. They primarily rest and sleep on sturdy branches in the trees. - Are Agile Gibbons considered endangered?
Yes, Agile Gibbons are listed as endangered due to the ongoing threats they face, particularly habitat loss and human-related activities. - How do Agile Gibbons contribute to the ecosystems they inhabit?
Agile Gibbons play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by dispersing seeds through their foraging and contributing to forest regeneration. - Can Agile Gibbons be kept as pets?
Keeping Agile Gibbons as pets is illegal in many countries due to the conservation concerns and the specialized care they require. - What is the significance of Agile Gibbons in local cultures?
Agile Gibbons hold cultural significance in some Southeast Asian communities, featuring in folklore and traditions. - How do Agile Gibbons adapt to changes in their natural habitat?
Agile Gibbons exhibit adaptability by adjusting their foraging patterns and social behaviors in response to changes in the environment. - What role do Agile Gibbons play in seed dispersal?
Agile Gibbons contribute significantly to seed dispersal by consuming fruits and then spreading seeds across different areas as they move through the forest canopy. - Are there any captive breeding programs for Agile Gibbons?
Yes, some conservation centers and zoos participate in captive breeding programs for Agile Gibbons to support genetic diversity and raise awareness about their conservation. - How do conservation organizations monitor Agile Gibbon populations in the wild?
Conservation organizations often use a combination of field surveys, camera traps, and vocalization studies to monitor Agile Gibbon populations and assess their well-being. - What are the key factors influencing Agile Gibbon conservation success?
Successful Agile Gibbon conservation relies on habitat protection, anti-poaching efforts, community involvement, and international collaboration among conservation organizations.














Leave your comment