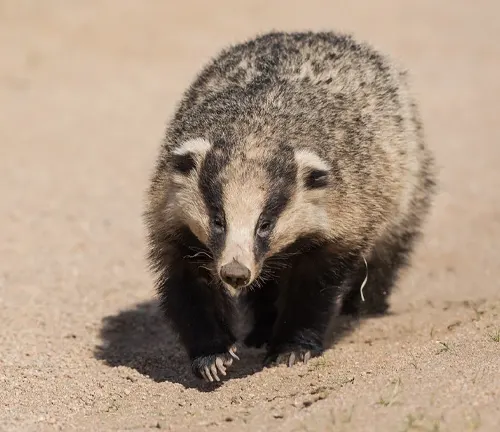
American Badger
- January 15, 2024
- 0 comment
The American badger, a captivating creature native to North America, is often a shadowy figure in the vast tapestry of the continent’s wildlife. Characterized by its robust build and distinctive black and white facial markings, this carnivorous mammal belongs to the weasel family and is scientifically known as Taxidea taxus. While not as heralded as some of its animal counterparts, the American badger’s enigmatic charm lies in its unique features and behaviors. Thriving in a diverse range of ecosystems, from grasslands to woodlands, these creatures display a remarkable adaptability.
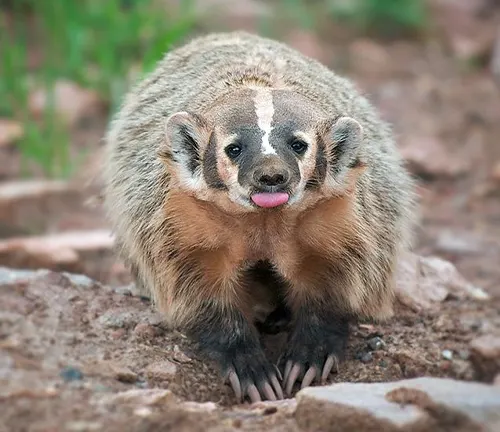

Nocturnal by nature, they reveal their activities under the cover of darkness, showcasing both solitary and social tendencies. Armed with formidable claws and a keen predatory instinct, American badgers are skilled hunters, preying on rodents, ground-dwelling birds, and insects. Their significance in controlling rodent populations highlights their role in maintaining ecological balance. Cultural significance is woven into their existence, with the badger featuring prominently in indigenous myths and symbolizing various attributes in different cultures. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these intriguing creatures, emphasizing the delicate balance required for their coexistence with human activities. The American badger, though often unseen, stands as a testament to the rich biodiversity of North America, deserving of appreciation and understanding.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Taxidea taxus |
| Family | Mustelidae |
| Size | Medium-sized mammal, typically 20-32 inches in length |
| Weight | Varied, ranging from 9 to 26 pounds |
| Color | Grizzled appearance with distinctive black and white facial markings |
| Habitat | Diverse ecosystems including grasslands, woodlands, and prairies |
| Distribution | North America, primarily in the United States and Canada |
| Activity | Nocturnal, with increased activity during warmer months |
| Behavior | Solitary but may exhibit social tendencies, territorial |
| Diet | Carnivorous, preying on rodents, ground-dwelling birds, and insects |
| Hunting Technique | Relies on strong digging capabilities and sharp claws |
| Reproduction | Mating season in late summer or early fall, with young born in spring |
| Lifespan | Around 4-5 years in the wild, longer in captivity |
| Cultural Significance | Featured in indigenous myths, symbolizing various attributes in different cultures |
| Conservation Status | Subject to conservation efforts due to habitat loss and human-related threats |
| Notable Feature | Excellent digging capabilities for burrowing and hunting |
Unveiling the Secrets of North America’s Stealthy Digger
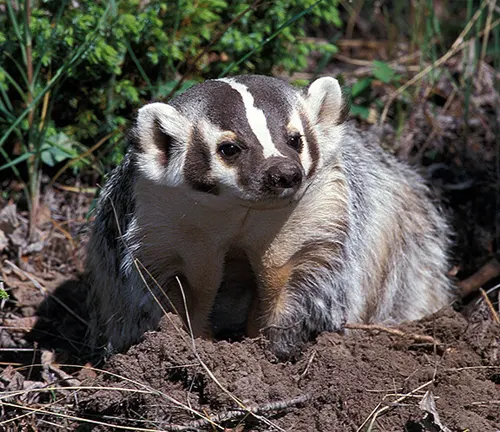

The American badger, often overshadowed by its more well-known counterparts in the animal kingdom, possesses a mystique that intrigues wildlife enthusiasts and researchers alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the fascinating world of the American badger, uncovering its physical characteristics, habitat, behavior, and its crucial role in the ecosystem.
Nestled in the heart of North America, the American badger (Taxidea taxus) is a creature of both mystery and importance. This article aims to shed light on its lesser-known aspects, highlighting the need for understanding and conservation efforts.
Physical Characteristics
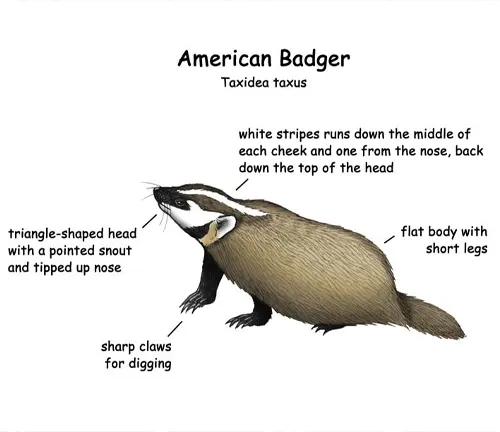
With a sturdy build, the American badger stands out for its distinctive black and white facial markings, setting it apart from its relatives. Despite its relatively small size, this carnivore possesses strength and agility, crucial for its survival in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
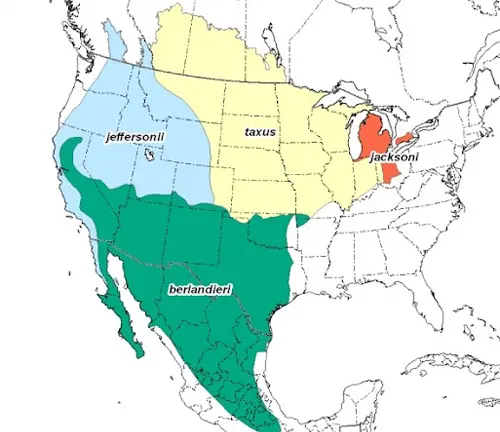
Thriving in a variety of ecosystems, from grasslands to woodlands, the American badger boasts a wide distribution across North America. Understanding its preferred habitats is key to preserving its natural environments.
Behavior and Lifestyle
As a nocturnal creature, the badger’s activities unfold under the cover of darkness. Known for both solitary and social tendencies, its behavior adds an extra layer of complexity to its enigmatic persona.
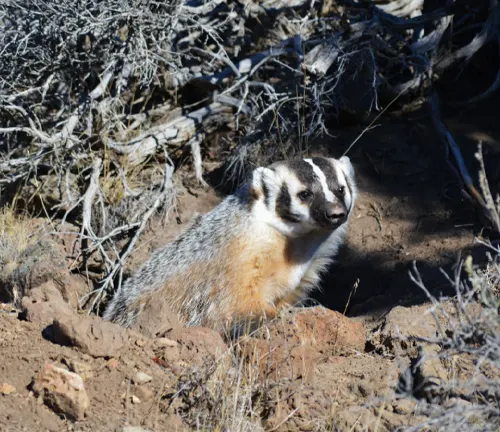

Hunting and Diet
Equipped with formidable claws and a predatory instinct, the badger employs unique hunting techniques. Exploring its diet and hunting habits unveils a captivating aspect of its role in the food chain.
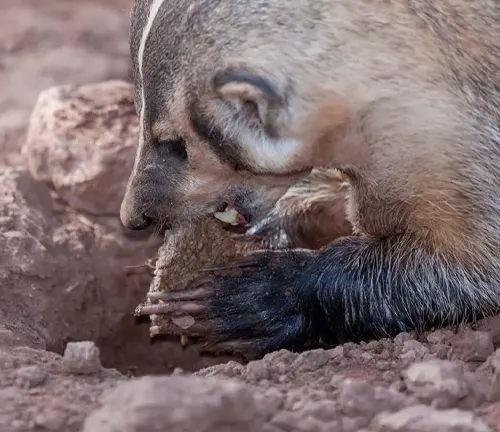

Reproduction
Mating season marks a crucial time in the badger’s life cycle. Delving into its reproductive patterns, we uncover the mysteries of gestation periods and the number of offspring born in a litter.
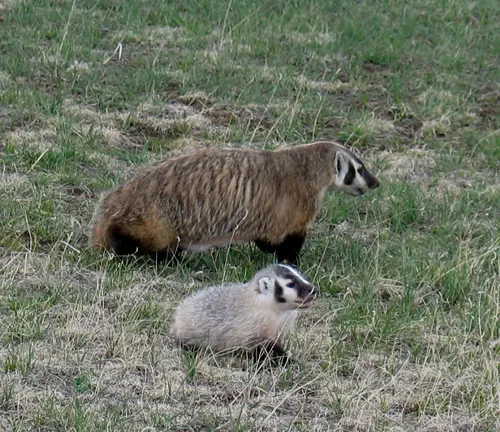

Adaptations and Survival Skills
The American badger’s specialized digging capabilities make it a formidable force in the wild. Examining its defense mechanisms against predators reveals a creature well-adapted to its surroundings.
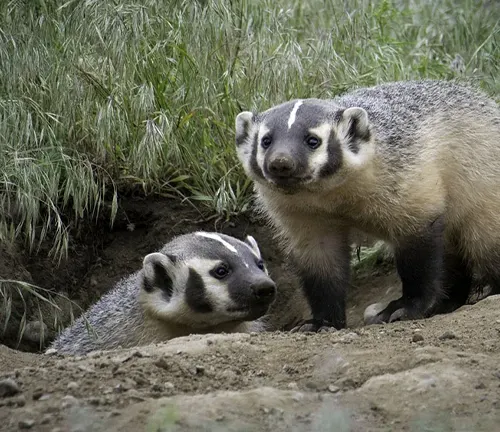

Human Interaction
While conservation efforts are underway to protect this species, challenges persist in fostering coexistence. Understanding the delicate balance between human activities and badger habitats is essential for future harmony.
Importance in Ecosystem
Beyond its captivating persona, the American badger plays a vital role in controlling rodent populations. Examining its ecological impact underscores the intricate web of life in which it participates.
Threats and Conservation Status
Human-related threats pose a challenge to the badger’s existence. Highlighting ongoing conservation measures is paramount to securing its future in the wild.
Different Species
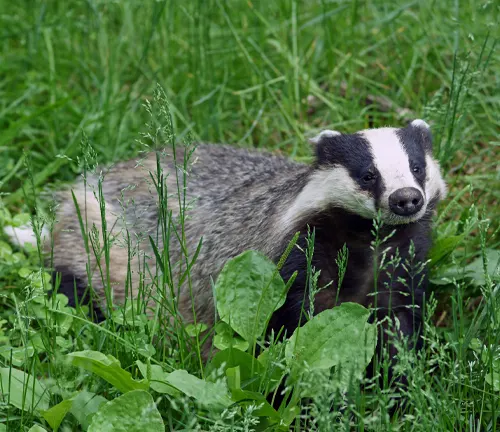
European Badger
(Meles meles)
Found across Europe and parts of Asia, the European badger is known for its distinctive black and white facial markings. It’s larger than the American badger and has a more varied diet.

Honey Badger
(Mellivora capensis)
Native to Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent, the honey badger is renowned for its fearless and aggressive nature. It has a unique resistance to venomous snake bites.

Asian Badger
(Arctonyx collaris)
Found in various regions of Asia, including the Indian subcontinent, the Asian badger has a distinct appearance with a white stripe running down its face and a stocky build.

Japanese Badger
(Meles anakuma)
Endemic to Japan, this badger species is smaller than its European counterpart. It has a thick coat and is often found in forested areas.

Sunda Stink Badger
(Mydaus javanensis)
Native to Southeast Asia, the Sunda stink badger, also known as the Indonesian stink badger, is characterized by its black fur and the strong-smelling secretion it produces for defense.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- Are American badgers dangerous to humans?
American badgers are generally not aggressive towards humans unless provoked. However, it’s essential to admire them from a safe distance in the wild. - How can I contribute to American badger conservation?
Supporting local wildlife conservation organizations and respecting their habitats during outdoor activities are impactful ways to contribute. - Do American badgers hibernate?
While they don’t undergo true hibernation, badgers may enter a state of torpor during harsh winter conditions. - What is the typical diet of an American badger?
American badgers are carnivores with a diet primarily consisting of rodents, ground-dwelling birds, and insects. - How fast can American badgers run?
American badgers are not known for their speed, but they are agile. They can run at moderate speeds when pursuing prey or avoiding predators. - Do American badgers live in family groups?
While they are generally solitary animals, female badgers may live with their offspring until the young are independent enough to venture out on their own. - What is the significance of the American badger in Native American folklore?
The American badger holds cultural importance in various Native American myths, often symbolizing attributes such as persistence and strength. - Q: Are American badgers good climbers?American badgers are not adept climbers. Their strength lies in digging, and they use their sharp claws for burrowing rather than climbing trees.
- How do American badgers contribute to rodent control in ecosystems?
American badgers play a vital role in controlling rodent populations, helping maintain ecological balance by preying on species that can be detrimental to crops and other wildlife. - Are American badgers territorial?
Yes, American badgers can be territorial, marking their territories with scent markings. They may defend their territory from other badgers. - Do American badgers have any natural predators?
While adult badgers have few natural predators, young badgers may be vulnerable to larger carnivores such as wolves, coyotes, and birds of prey. - Can American badgers swim?
Yes, American badgers are capable swimmers. They may swim across bodies of water if necessary, showcasing their adaptability. - What is the breeding season for American badgers?
The breeding season for American badgers typically occurs in the late summer or early fall, with females giving birth to their young in the spring. - Are American badgers more active during specific times of the year?
American badgers are generally active year-round, but their behavior may vary seasonally, with increased activity during the warmer months and potential torpor in winter.














Leave your comment