Asiatic Black Bear
- January 11, 2024
- 0 comment
The Asiatic Black Bear, scientifically known as Ursus thibetanus, is a captivating species that inhabits a diverse range of environments across Asia. Often referred to as the “moon bear” due to the distinct crescent-shaped white mark on its chest, this bear species is characterized by a robust build and a variable coat color ranging from black to brown. Adapted to a variety of landscapes, including dense forests, mountainous regions, and high-altitude plateaus, the Asiatic Black Bear showcases remarkable versatility in its habitat choices. With a penchant for climbing trees and proficient swimming abilities, these bears navigate their surroundings with ease.
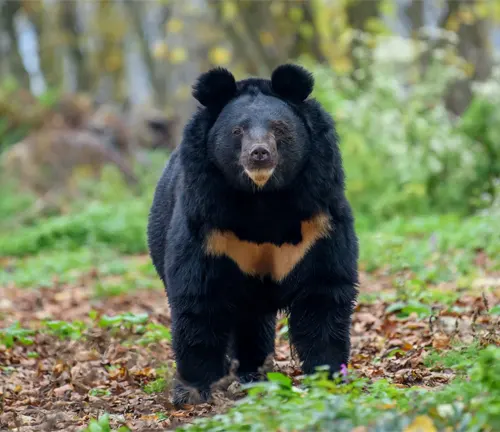

Beyond their physical prowess, Asiatic Black Bears play a vital role in ecosystems, contributing to seed dispersal and controlling insect populations. Unfortunately, the species faces significant threats, including habitat loss and poaching, leading to conservation concerns. Efforts to protect and preserve these iconic bears involve a combination of conservation initiatives, community engagement, and raising awareness about the importance of coexisting with wildlife. The Asiatic Black Bear stands not only as a symbol of wildlife resilience but also as a reminder of the delicate balance between human activities and the natural world.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ursus thibetanus |
| Common Name | Asiatic Black Bear |
| Distinctive Marking | White crescent-shaped mark on the chest |
| Coat Color | Variable, ranging from black to brown |
| Habitat | Diverse, including dense forests and mountains |
| Geographic Range | Across Asia, from the Himalayas to Russian Far East |
| Adaptations | Skilled climber, proficient swimmer |
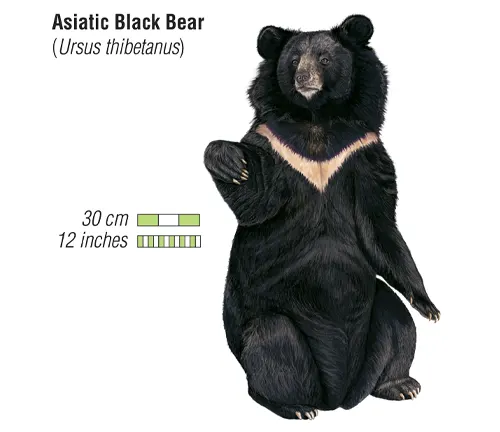
| Average Weight | 200 to 440 pounds (varies by gender) |
| Lifespan in the Wild | 25 to 30 years |
| Behavioral Traits | Social, communication through vocalizations |
| Diet | Omnivorous, includes fruits, nuts, and small mammals |
| Reproduction | Involves intricate processes, cubs are raised by mothers |
| Conservation Status | Varies by subspecies; some listed as vulnerable |
| Threats | Habitat loss, poaching, human-wildlife conflicts |
| Cultural Significance | Featured in folklore and mythology, symbolizing strength and resilience |
| Role in Ecosystem | Seed dispersal, insect population control |
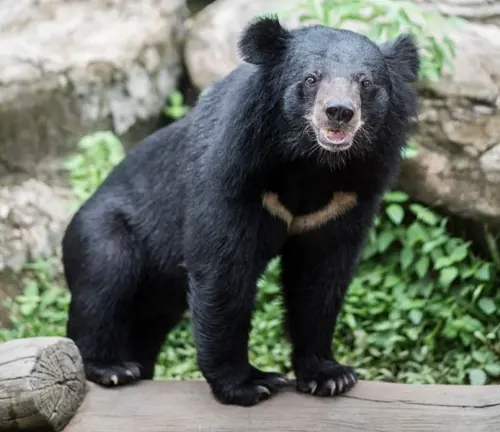

The Asiatic Black Bear, also known as the moon bear, is a fascinating species that captures the attention of wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists alike. In this article, we’ll delve into various aspects of this bear species, from its taxonomy to its role in ecosystems.
Taxonomy and Classification
The Asiatic Black Bear falls under the scientific classification of Ursus thibetanus. This species is further divided into several subspecies, each adapted to its unique environment.
Physical Characteristics
Standing out with its distinctive V-shaped white chest mark, the Asiatic Black Bear possesses a robust build and a coat that ranges from black to brown. Understanding its physical characteristics is crucial for identifying and studying this species in the wild.

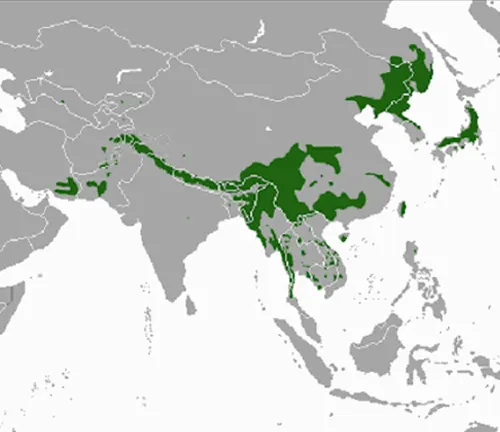
Geographic Distribution
Found across a diverse range of habitats, from dense forests to mountainous regions, the Asiatic Black Bear has a wide distribution. Exploring where these bears are located helps us comprehend their adaptability to various landscapes.
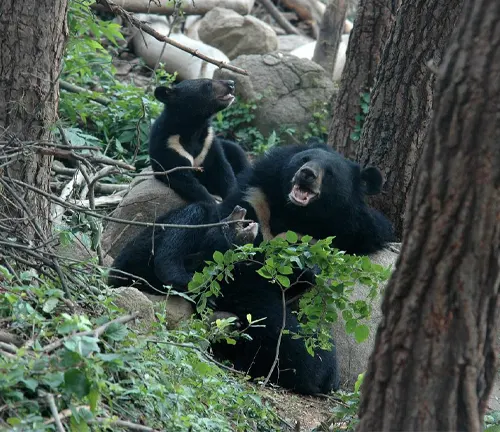
Habitat and Environment
Delving into the specific habitats and environments preferred by Asiatic Black Bears provides insights into their ecological roles and the conservation challenges they face due to habitat loss.
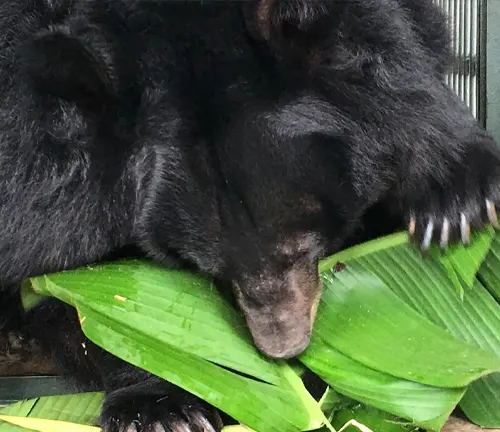


Diet and Feeding Habits
Unraveling the dietary preferences and feeding habits of these bears sheds light on their role as omnivores and their impact on local ecosystems. From fruits and nuts to small mammals, understanding their diet is vital.
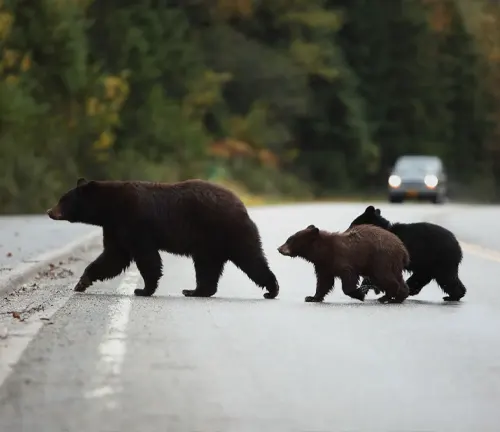
Reproduction and Life Cycle
The life cycle of Asiatic Black Bears involves intricate reproductive processes and parenting behaviors. Exploring their reproduction and life cycle unveils the challenges faced by bear populations.

Behavioral Traits
Understanding the behavioral traits of the Asiatic Black Bear, including social interactions and communication methods, enhances our appreciation for the complexity of their lives in the wild.
Conservation Status
Examining the conservation status of this species highlights the need for protective measures. The Asiatic Black Bear faces threats like habitat destruction and poaching, necessitating conservation efforts.
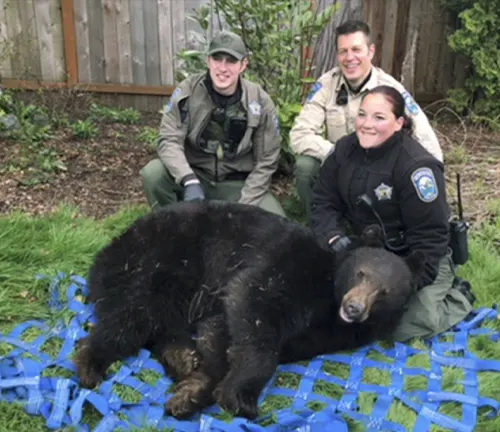

Human-Bear Conflicts
As human populations expand, conflicts between humans and Asiatic Black Bears arise. Investigating these conflicts provides valuable information on mitigating human-wildlife interactions.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve the Asiatic Black Bear involve various strategies, from protected reserves to community engagement. Unveiling these conservation initiatives showcases the dedication to preserving this iconic species.
Importance in Ecosystem
The Asiatic Black Bear plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance. Examining its ecological significance emphasizes the interconnectedness of wildlife and their environments.
Asiatic Black Bear in Culture
Throughout history, the Asiatic Black Bear has held cultural significance in various societies. Exploring its role in folklore and traditions adds a cultural dimension to our understanding of this species.
Challenges and Threats
Identifying the challenges and threats faced by Asiatic Black Bears, including illegal wildlife trade and habitat fragmentation, underscores the urgency of conservation actions.
Different Species
Ursus thibetanus thibetanus
This subspecies is commonly found in the eastern Himalayas, including parts of India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Tibet.
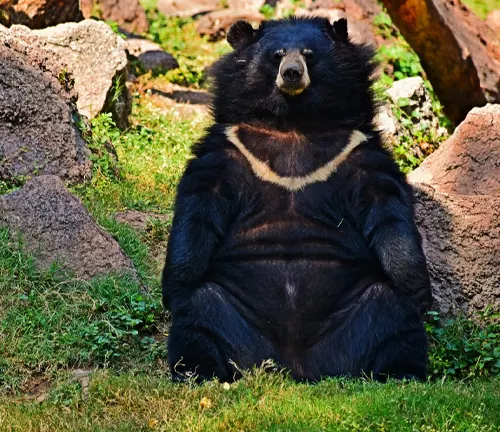
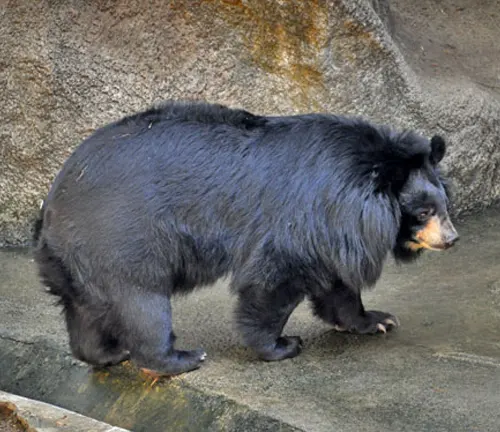


Ursus thibetanus laniger
Known as the Tibetan Black Bear, this subspecies inhabits the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas, displaying adaptations to high-altitude environments.
Ursus thibetanus mupinensis
Found in the Min Mountains of China, this subspecies is well-adapted to the forested and mountainous terrain of the region.
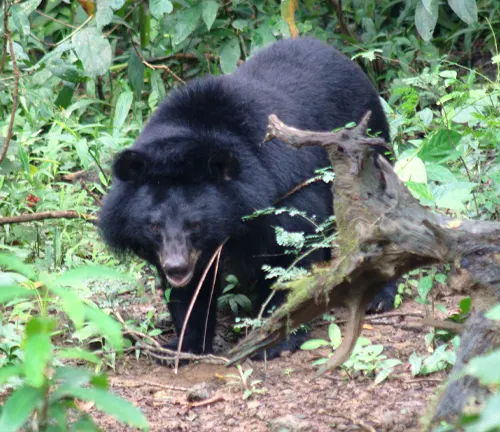
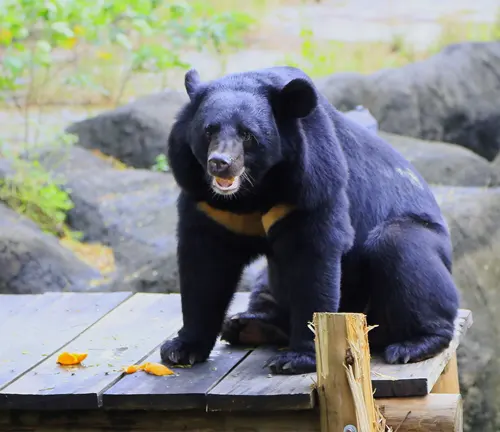


Ursus thibetanus formosanus
The Formosan Black Bear is native to Taiwan, distinguished by its smaller size and unique ecological adaptations.
Ursus thibetanus gedrosianus
Inhabiting parts of Iran, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, this subspecies is adapted to the varied landscapes of the region.
Ursus thibetanus japonicus
The Japanese Black Bear is found in Japan and exhibits specific characteristics influenced by the country’s diverse ecosystems.
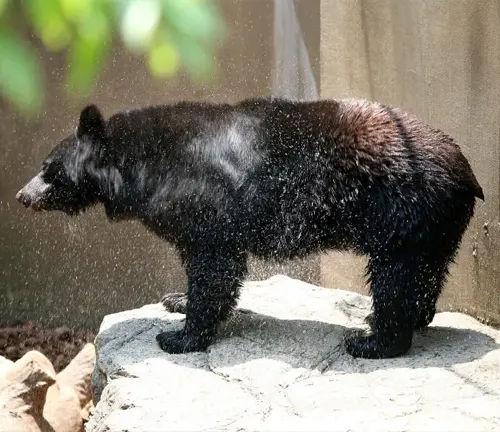
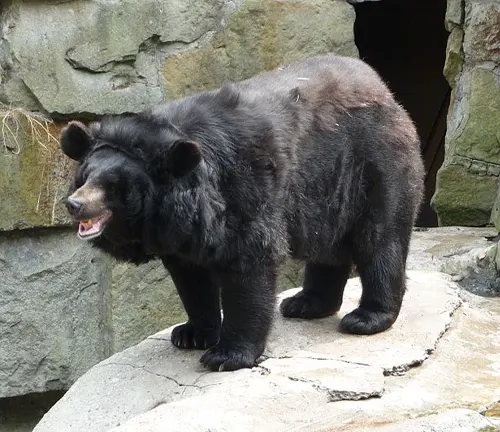


Ursus thibetanus ussuricus
Inhabiting the Russian Far East, China, and North Korea, this subspecies is adapted to the boreal forests and taiga of the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How many Asiatic Black Bear subspecies are there?
The Asiatic Black Bear has several subspecies, each adapted to different regions. Common ones include thibetanus, laniger, formosanus, and ussuricus. - What is the Asiatic Black Bear’s conservation status?
The conservation status of Asiatic Black Bears varies across subspecies. Some are listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss and poaching. - Do Asiatic Black Bears have any natural predators?
Apart from humans, Asiatic Black Bears generally don’t have natural predators. However, young cubs may be vulnerable to larger predators. - What is the average lifespan of Asiatic Black Bears in the wild?
In the wild, Asiatic Black Bears typically live between 25 to 30 years, depending on factors such as habitat and food availability. - How do Asiatic Black Bears communicate with each other?
Asiatic Black Bears use vocalizations, body language, and scent marking to communicate. These behaviors play a crucial role in their social interactions. - Are Asiatic Black Bears good climbers?
Yes, Asiatic Black Bears are skilled climbers and often use trees for various purposes, including foraging and escaping predators. - Why are Asiatic Black Bears sometimes called “moon bears”?
The term “moon bear” comes from the crescent-shaped, white patch on their chest, resembling a crescent moon. This distinctive mark sets them apart. - How much can an adult Asiatic Black Bear weigh?
Adult Asiatic Black Bears can weigh anywhere from 200 to 440 pounds, with males generally being larger than females. - Do Asiatic Black Bears migrate seasonally?
While they may move to find food, Asiatic Black Bears don’t undergo extensive seasonal migrations. Their movements are often influenced by food availability. - Can Asiatic Black Bears swim?
Yes, Asiatic Black Bears are proficient swimmers. They use water bodies for cooling off and may swim for long distances if necessary. - What role do Asiatic Black Bears play in their ecosystems?
Asiatic Black Bears play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling insect populations and dispersing seeds through their feces. - Are there any cultural references to Asiatic Black Bears in folklore or mythology?
Yes, Asiatic Black Bears are often featured in various cultural tales and folklore, symbolizing strength, resilience, and the harmony between nature and humans.














Leave your comment