Langurs Monkey
- January 16, 2024
- 0 comment
Langurs monkeys, scientifically classified under the genus Semnopithecus, emerge as captivating members of the primate family, displaying a unique blend of physical distinctiveness and social intricacies. Found primarily in South Asia, langurs are renowned for their elegant gray fur and distinctive facial features. The genus encompasses various species, such as the Gray Langur (Semnopithecus entellus), showcasing adaptability to diverse habitats, from dense forests to urban environments. Social bonds among langurs are a key aspect of their behavior, forming cohesive groups led by dominant males.
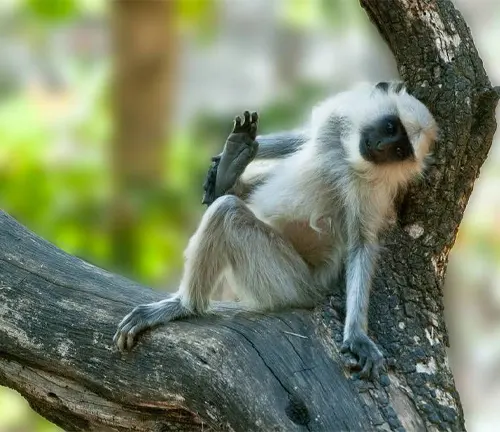

Communication within these groups involves a rich repertoire of vocalizations and expressive body language. As herbivores, langurs play a vital role in shaping ecosystems through seed dispersal and influencing vegetation patterns. Despite their ecological contributions, langurs face challenges like habitat loss, poaching, and human conflicts, necessitating concerted conservation efforts. Ongoing research endeavors delve into their biology, behavior, and the intricate dynamics of primate societies. In essence, langurs, with their cultural significance, ecological roles, and enigmatic presence, beckon us to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of their existence within the diverse landscapes they inhabit.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Genus | Semnopithecus |
| Species (Example) | Semnopithecus entellus (Gray Langur) |
| Geographic Range | South Asia and Southeast Asia |
| Fur Color | Typically gray, with variations in shades |
| Facial Features | Expressive faces with distinctive features |
| Social Structure | Highly social; form groups led by dominant males |
| Communication | Vocalizations, facial expressions, body language |
| Habitat | Diverse, including forests, plains, and urban areas |
| Dietary Habits | Herbivores, consuming leaves, fruits, and flowers |
| Ecological Role | Seed dispersal, influencing vegetation patterns |
| Conservation Status | Varies among species; some face endangerment |
| Main Threats | Habitat loss, poaching, conflicts with humans |
| Cultural Significance | Often holds cultural significance in local myths |
| Ongoing Research | Studies on behavior, biology, and societal dynamics |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat protection, awareness, community engagement |
| Importance | Integral to biodiversity, requiring conservation |
Langurs Monkey: Exploring the Fascinating World of these Primate Wonders
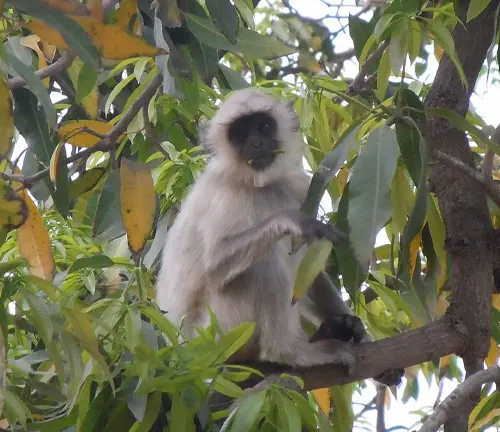

Langurs monkeys, an integral part of the primate family, have captivated the attention of researchers, wildlife enthusiasts, and casual observers alike. From their unique physical characteristics to their intricate social structures, langurs present a captivating study in the world of wildlife. Let’s delve into the fascinating aspects of these remarkable creatures.
Physical Characteristics
Langurs boast a distinctive appearance with their vibrant fur colors and tufted tails. The texture of their fur varies among species, ranging from sleek and shiny to long and coarse. Their expressive faces and prominent features make them easily recognizable in their natural habitats.

Habitat and Distribution
These agile primates inhabit a diverse range of environments, from lush forests to arid plains. Their geographic distribution spans various countries, with each species adapting to the specific conditions of their preferred habitats. Understanding their habitat preferences is crucial for effective conservation strategies.
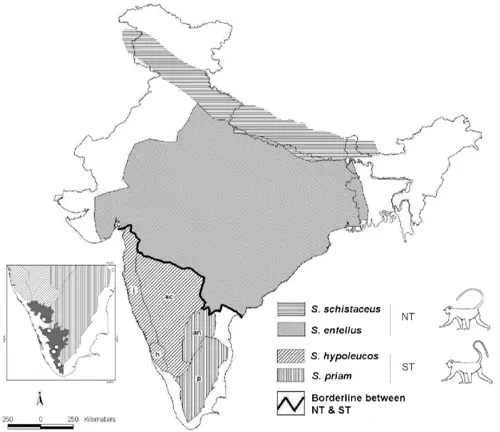
Social Structure
Langurs are social animals, forming close-knit groups led by a dominant male. The intricate communication methods within these groups include vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language. Studying their social dynamics sheds light on the complexity of primate societies.
Dietary Habits
Langurs are primarily herbivores, consuming a diet rich in leaves, fruits, and flowers. Their foraging behavior is both fascinating and essential for maintaining ecological balance within their habitats. Exploring their dietary habits provides insights into the interconnectedness of ecosystems.

Reproductive Behavior
Mating rituals among langurs involve elaborate displays and rituals, showcasing the importance of courtship in their communities. The gestation period and birth bring another dimension to their lives, highlighting the challenges faced by langur mothers in ensuring the survival of their offspring.
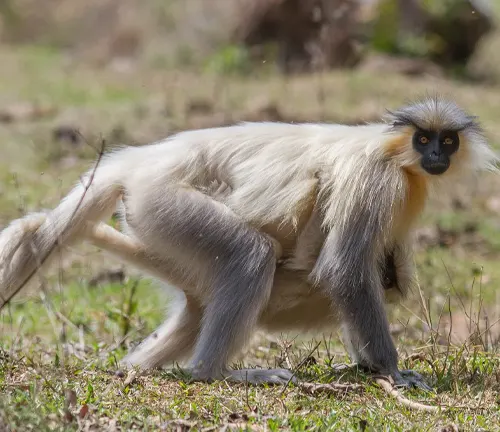

Predators and Threats
While langurs have natural predators in the wild, human-induced threats pose a significant danger to their populations. Understanding the factors contributing to their vulnerability is crucial for implementing effective conservation measures.
Conservation Status
The current population status of langurs varies among species, with some facing imminent threats. Conservation efforts, including habitat protection and community engagement, play a pivotal role in ensuring the survival of these primate wonders.
Cultural Significance
Langurs hold cultural significance in various regions, often appearing in myths and folklore. Understanding the historical beliefs associated with these creatures adds depth to our appreciation of their role in local traditions.
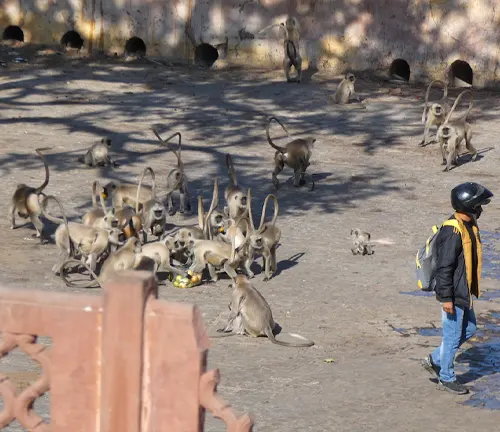

Interactions with Humans
As human development encroaches on langur habitats, encounters between humans and langurs become more frequent. Raising awareness among local communities about coexistence and conservation is crucial to minimizing conflicts.
Different Species
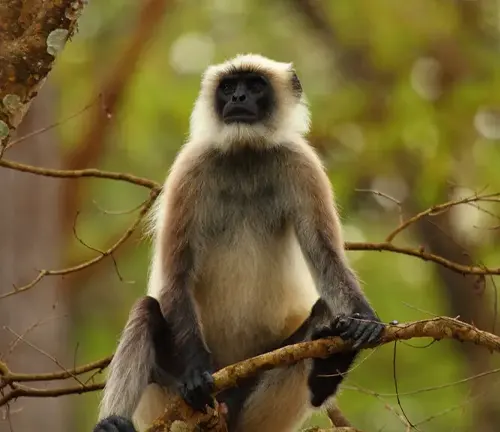
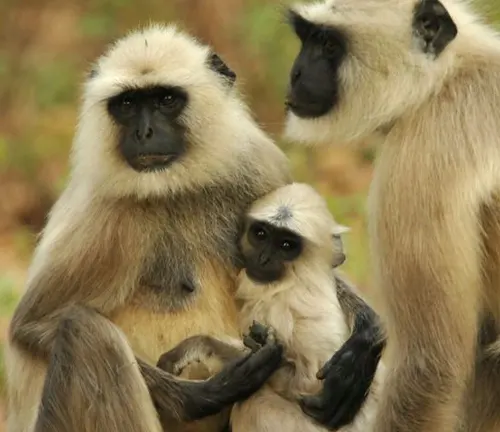
Gray Langur
(Semnopithecus entellus)
Found in South Asia, this species is known for its gray fur and long tail. It inhabits a variety of environments, from forests to urban areas.
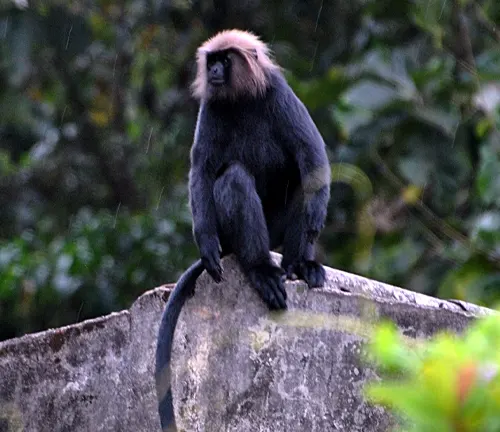


Black Langur
(Trachypithecus spp.)
Also known as leaf monkeys, black langurs are recognized for their dark-colored fur. Different species exist, such as the Francois’ langur and the ebony langur.
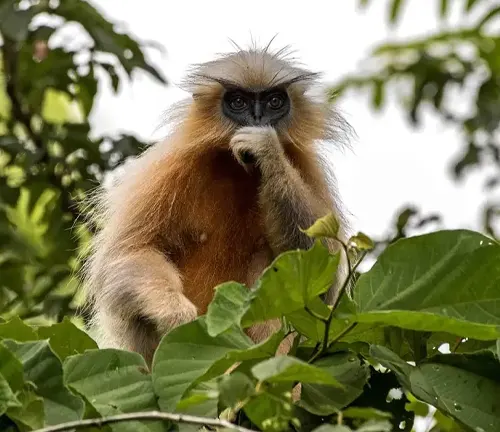
Golden Langur
(Trachypithecus geei)
Endemic to the northeastern regions of India, the golden langur is characterized by its vibrant golden-yellow fur. It resides in dense, hilly forests.


Purple-faced Langur
(Trachypithecus vetulus)
Native to Sri Lanka, this langur species is easily identified by its distinctively colored face, which ranges from purple to pink. They inhabit both lowland and montane forests.
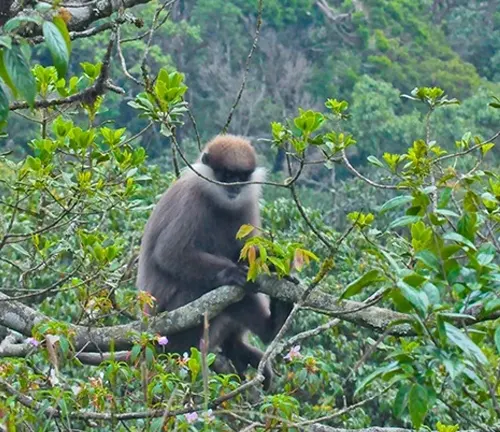
Hanuman Langur
(Semnopithecus spp.)
Named after the Hindu monkey god Hanuman, these langurs are widespread in South Asia. They have a grayish-brown coat and a characteristic crown of fur on their heads.
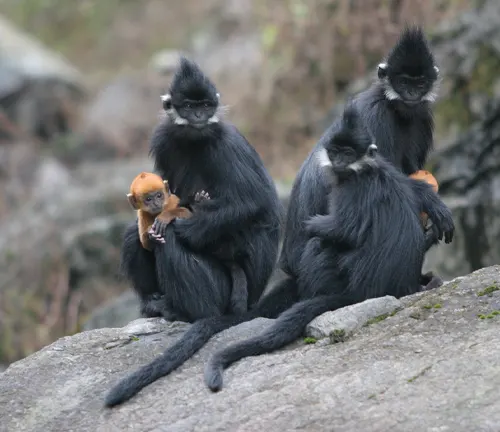


Francois’ Langur
(Trachypithecus francoisi)
Found in parts of China and Vietnam, Francois’ langur is known for its striking black fur and white face. They primarily inhabit limestone forests.
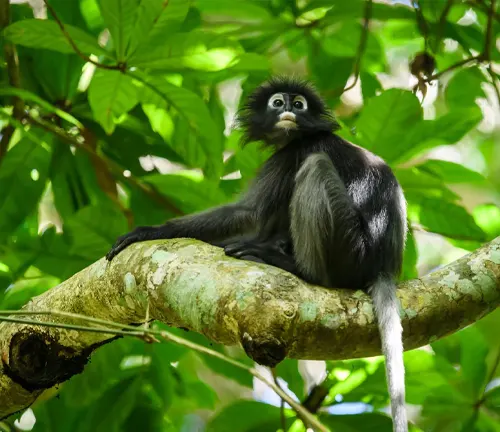
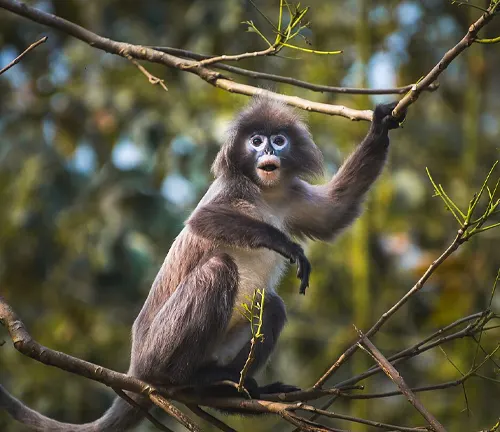
Dusky leaf monkey
(Trachypithecus obscurus)
Another species with a purple face, this langur is found in Myanmar and Thailand. It prefers tropical and subtropical forests.


Phayre’s Langur
(Trachypithecus phayrei)
Native to Southeast Asia, Phayre’s langur has a mix of gray, black, and white fur. It resides in a variety of habitats, including evergreen and deciduous forests.
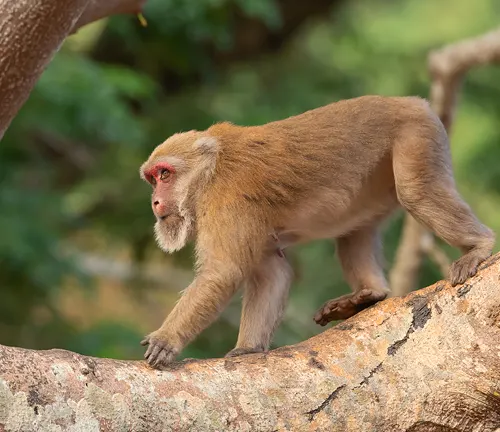
Assam Macaque
(Macaca assamensis)
While not technically a langur, the Assam macaque is often associated with them. Found in Southeast Asia, it has a short tail and a distinctive crest of hair on its head.


Hatinh langur
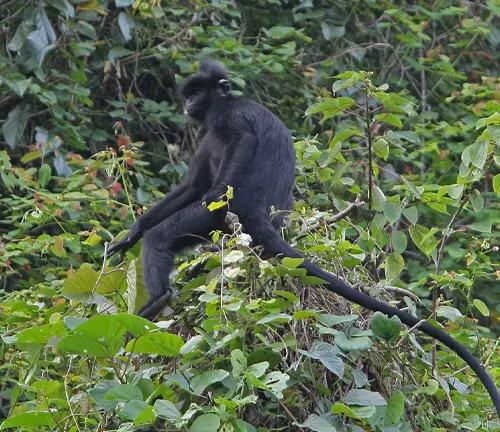
(Trachypithecus hatinhensis)
Endemic to Vietnam, this langur species has a purple face and is found in limestone areas. It is considered critically endangered.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the typical lifespan of langur monkeys in the wild?
The lifespan of langur monkeys varies by species but generally ranges from 20 to 30 years in their natural habitats. - How do langurs adapt to different climates and environments?
Langurs are adaptable primates, and different species have evolved to thrive in diverse climates, from tropical rainforests to arid plains. - Do langurs have natural predators, and what are they?
While langurs may face threats from large predators such as big cats and birds of prey, their main threats often come from human activities. - What is the significance of langurs in maintaining ecological balance?
Langurs play a crucial role in seed dispersal and maintaining the health of forests, contributing to the overall biodiversity of their habitats. - Are there any ongoing conservation projects specifically focused on langur monkeys?
Yes, various conservation organizations are actively engaged in projects aimed at protecting langur habitats, raising awareness, and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts. - How do langurs contribute to the tourism industry in regions where they are found?
Langurs, being charismatic primates, attract wildlife enthusiasts and tourists, contributing to ecotourism and local economies. However, responsible tourism practices are crucial to minimize negative impacts. - Do langurs exhibit tool use or other advanced cognitive abilities?
While langurs are not known for extensive tool use, they do display a range of cognitive abilities, including problem-solving and social intelligence. - Can langurs be kept as pets, and is it legal to do so?
Keeping langurs as pets is not only ethically questionable but is often illegal due to conservation concerns and the well-being of the primates. - How do langurs contribute to the overall biodiversity of their ecosystems?
Langurs, as herbivores, play a crucial role in shaping vegetation patterns, influencing the diversity of plant species and supporting other wildlife. - What is the role of international collaboration in langur conservation efforts?
International cooperation is essential for sharing knowledge, resources, and strategies to ensure the effective conservation of langur species that span multiple countries.














Leave your comment