Mountain Zebra
- January 30, 2024
- 0 comment
The mountain zebra, scientifically known as Equus zebra, is a distinctive species of zebra found in the mountainous regions of southern Africa, including Namibia, South Africa, and Angola. What sets them apart are their striking black and white stripes, serving both as a form of camouflage and a means to regulate their body temperature. Unlike their plains zebra counterparts, mountain zebras are smaller and stockier in build, standing about 3.9 to 4.9 feet tall at the shoulder.
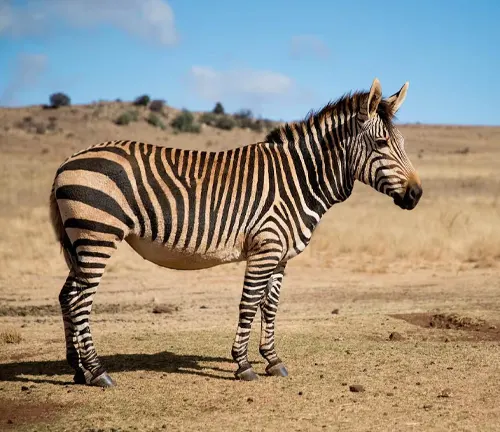

These creatures are known for their strong family bonds, living in small groups led by a dominant stallion in a social structure known as harems. Mountain zebras are herbivores, primarily grazing on tough grasses, leaves, and shrubs, which allows them to thrive in their challenging rocky habitat. Despite their unique features and significance in their ecosystem, mountain zebras are classified as a vulnerable species due to threats like habitat loss and poaching. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these majestic animals and ensure their survival for generations to come.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Equus zebra |
| Habitat | Mountainous regions of southern Africa |
| Range | Namibia, South Africa, Angola |
| Size at Shoulder | Approximately 3.9 to 4.9 feet |
| Physical Features | Black and white stripes for camouflage |
| Social Structure | Small family groups known as harems |
| Diet | Herbivorous, feeding on grasses and shrubs |
| Reproduction | Gestation period of about 12 months, single foal births |
| Conservation Status | Classified as vulnerable |
| Primary Threats | Habitat loss, poaching, competition for resources |
| Conservation Efforts | Habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, community education |
Majestic Mountain Zebra
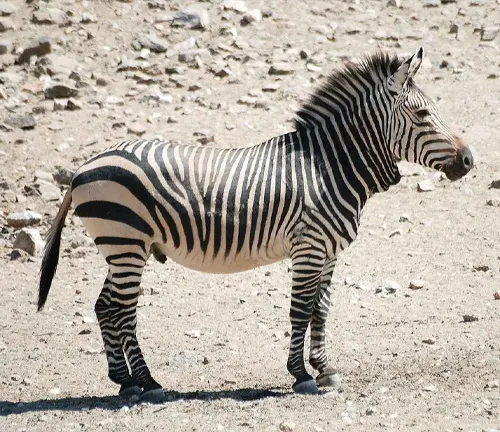

Mountain zebras, with their unique appearance and fascinating behavior, hold a special place in the animal kingdom. In this article, we will embark on a journey to discover the world of mountain zebras, exploring their habitat, behavior, conservation status, and much more. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of these majestic creatures.
The Mountain Zebra: A Distinctive Species
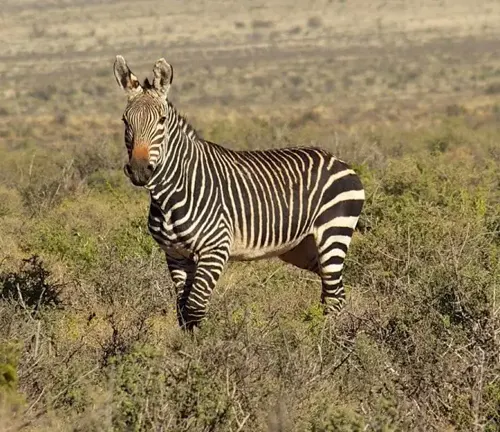
Mountain zebras (Equus zebra) are a distinct species of zebra found in southern Africa. They are easily recognizable by their striking black and white stripes, which make them stand out against the rugged terrain of their habitat.
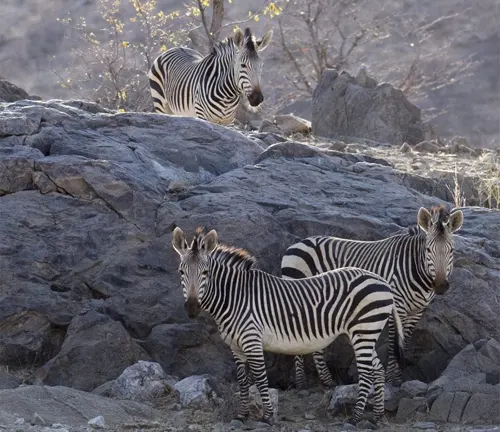

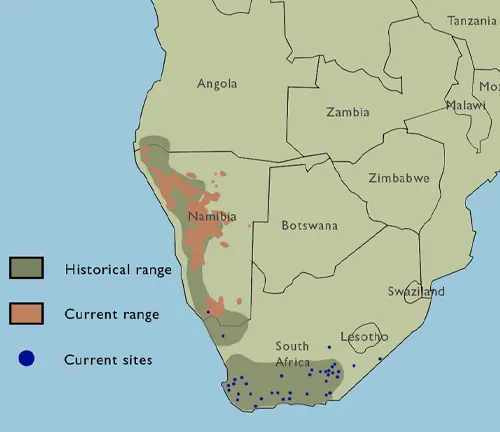
Habitat and Range
Mountain zebras primarily inhabit the mountainous regions of Namibia, South Africa, and Angola. They have adapted to living in rocky and challenging terrains, where they can find suitable food sources and evade predators.
Physical Characteristics
Mountain zebras are smaller than their plains zebra counterparts. They have a stockier build, with a height ranging from 3.9 to 4.9 feet at the shoulder. Their unique stripes are not just for show; they serve as a form of camouflage and can help regulate their body temperature.


Social Structure
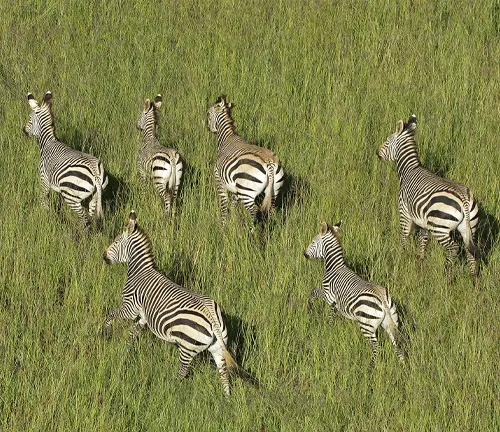
These zebras are known for their strong family bonds. They live in small family groups led by a dominant stallion. These groups are called harems and typically consist of one stallion, several mares, and their offspring.
Feeding Habits
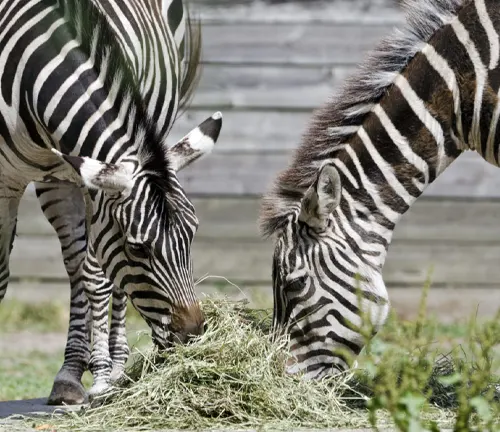
Mountain zebras are herbivores, primarily grazing on grasses, leaves, and shrubs. They have adapted to consuming tough, thorny plants that other herbivores might avoid. This specialized diet allows them to thrive in their harsh habitat.


Reproduction
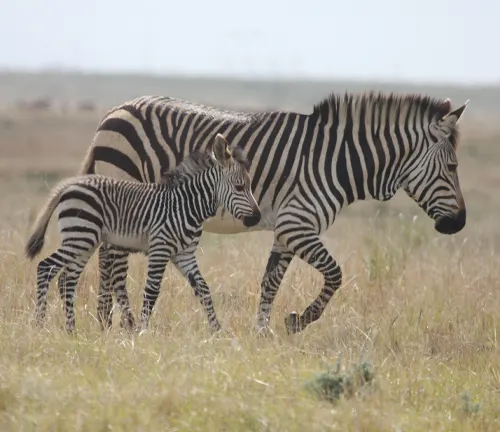
The reproduction cycle of mountain zebras is fascinating. Mares usually give birth to a single foal after a gestation period of about 12 months. The bond between the mother and her offspring is strong, and the young zebra relies on its mother for protection and nourishment.
Conservation Status
Despite their unique features and importance to the ecosystem, mountain zebras face several threats that have led to their classification as a vulnerable species. Habitat loss, poaching, and competition for resources are some of the challenges they encounter.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation organizations and governments in the region are working tirelessly to protect the mountain zebra population. Initiatives such as habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and community education have been implemented to ensure the survival of these remarkable creatures.
Different Species
Cape Mountain Zebra
(Equus zebra zebra)
This subspecies is found in South Africa, particularly in the Eastern Cape province and parts of the Western Cape. The Cape mountain zebra has distinctive narrow stripes and a slightly larger population compared to Hartmann’s mountain zebra. Conservation efforts have been successful in stabilizing their numbers.
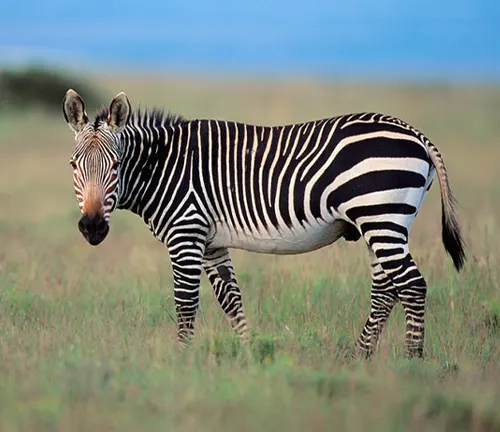
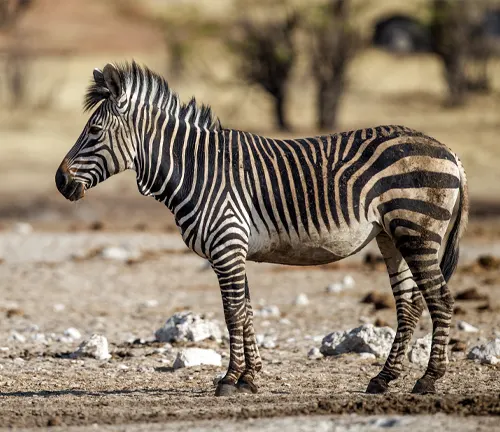


Hartmann’s Mountain Zebra
(Equus zebra hartmannae)
Hartmann’s mountain zebra is primarily found in Namibia and southwestern Angola. They have broader stripes and are slightly smaller in size compared to the Cape mountain zebra. This subspecies faces significant threats due to habitat loss and poaching, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a mountain zebra?
A mountain zebra (Equus zebra) is a species of zebra native to the mountainous regions of southern Africa. They are known for their distinctive black and white stripes, which serve as a form of camouflage and a means to regulate their body temperature. - Where are mountain zebras found in the wild?
Mountain zebras are primarily found in the mountainous regions of southern Africa, including Namibia, South Africa, and Angola. - What is the scientific name of the mountain zebra?
The scientific name of the mountain zebra is Equus zebra. - How do mountain zebras differ from other zebra species?
Mountain zebras are smaller and stockier compared to other zebra species. They have unique, narrow stripes and are adapted to rocky, challenging terrains. - What is the average size of a mountain zebra?
Mountain zebras typically stand between 3.9 to 4.9 feet tall at the shoulder. - What is the primary diet of mountain zebras?
Mountain zebras are herbivores, primarily feeding on grasses, leaves, and shrubs. They have adapted to consuming tough, thorny plants that other herbivores might avoid. - Are mountain zebras social animals?
Yes, mountain zebras are social animals. They live in small family groups known as harems, which are led by a dominant stallion. These groups consist of mares and their offspring. - How do mountain zebras reproduce and raise their young?
Mares have a gestation period of about 12 months and typically give birth to a single foal. The bond between the mother and foal is strong, and the mother provides protection and nourishment. - What are the major threats to mountain zebra populations?
Major threats to mountain zebra populations include habitat loss, poaching, and competition for resources with domestic livestock. - Why are mountain zebras classified as a vulnerable species?
Mountain zebras are classified as vulnerable due to the threats they face, primarily habitat loss and poaching. Their population is at risk, and conservation efforts are crucial. - What conservation efforts are in place to protect mountain zebras?
Conservation organizations and governments in the region are implementing initiatives such as habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and community education to protect mountain zebras. - Are mountain zebras kept in captivity or zoos?
Yes, mountain zebras are kept in captivity and can be found in zoos and wildlife reserves as part of conservation programs. - Do mountain zebras have any natural predators?
Mountain zebras may face predation from large carnivores such as lions and hyenas, as well as human-related threats like poaching. - How do mountain zebras adapt to their rugged mountainous habitat?
Mountain zebras have adapted to their habitat by developing strong, sturdy legs for navigating rocky terrain and consuming tough vegetation. - What is the lifespan of a mountain zebra in the wild?
In the wild, mountain zebras have an average lifespan of around 20 to 30 years. - Are there any specific adaptations that mountain zebras have developed to survive in their environment?
Mountain zebras have developed specialized dentition to consume tough, fibrous plants, and their stripes serve as a form of camouflage against predators. - How can I get involved in mountain zebra conservation efforts?
You can support mountain zebra conservation by donating to reputable organizations dedicated to their protection and spreading awareness about their importance in preserving biodiversity.














Leave your comment