Philippine Tarsiers
- March 25, 2024
- 0 comment
The Philippine Tarsier, often regarded as one of the smallest primates in the world, is a captivating creature endemic to the lush rainforests of the Philippines. Renowned for its distinctively large eyes and remarkably small stature, this elusive primate inhabits select regions across the Philippine archipelago, including Bohol, Leyte, Samar, and Mindanao. These diminutive primates thrive in dense forest environments, where they spend their days nestled in concealed nests made of leaves and branches, emerging under the cloak of night to embark on their nocturnal adventures.
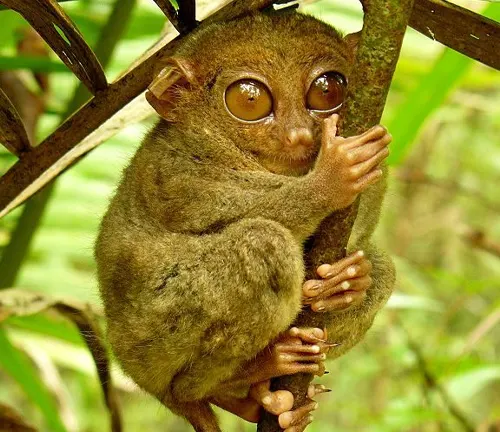

Despite their petite size, Philippine Tarsiers possess an impressive array of adaptations, including keen senses and agile limbs, enabling them to navigate their arboreal habitat with ease and precision. These remarkable creatures primarily subsist on a diet of insects, showcasing their prowess as skilled hunters within their ecosystem. However, despite their resilience, Philippine Tarsiers face myriad threats, including habitat loss, illegal pet trade, and disturbance from human activities. Consequently, concerted conservation efforts are essential to safeguard the future of these enchanting primates, ensuring that they continue to thrive in their natural habitat for generations to come.
Philippine Tarsiers Characteristics
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Carlito syrichta |
| Common Name | Philippine Tarsier |
| Family | Tarsiidae |
| Size | 3 to 6 inches (7.5 to 15 cm) in height |
| Weight | 80 to 160 grams |
| Habitat | Dense rainforests of the Philippines |
| Distribution | Islands of Bohol, Leyte, Samar, and Mindanao |
| Activity | Nocturnal |
| Diet | Mainly insects, such as crickets and beetles |
| Lifespan | 12 to 20 years |
| Gestation Period | Approximately 6 months |
| Reproduction | Usually give birth to a single offspring |
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable |
Exploring the Enigmatic Primates of the Philippines
The Philippine tarsier is one of the most intriguing and enigmatic creatures inhabiting the lush rainforests of the Philippines. In this article, we delve into the unique characteristics, behaviors, and conservation status of these fascinating primates.
Habitat and Distribution
Rainforests of the Philippines
The Philippines boasts a remarkable diversity of ecosystems, but perhaps none are as iconic as its rainforests. These dense and verdant forests cover vast stretches of the archipelago, nurturing a wealth of plant and animal species. Within this vibrant tapestry of life, the Philippine Tarsier finds its home, adapting to the unique challenges and opportunities offered by the rainforest environment.
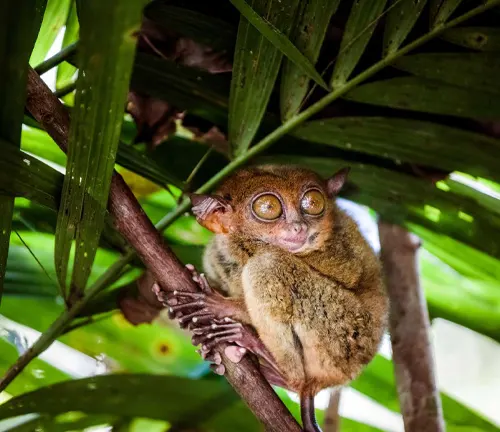

Specific regions where they are found
While Philippine Tarsiers can be found across various islands of the archipelago, there are specific regions where they are more commonly sighted. Among these regions are Bohol, Leyte, Samar, and Mindanao. Each of these islands harbors pockets of pristine rainforest habitat, providing ideal conditions for tarsiers to thrive.
Bohol: The Tarsier Sanctuary
Bohol stands out as one of the premier destinations for encountering Philippine Tarsiers in their natural habitat. Here, visitors can explore the Tarsier Sanctuary, a protected area dedicated to the conservation of these captivating creatures. Guided tours offer a glimpse into the tarsiers’ world, as knowledgeable guides lead visitors through the forest, pointing out these elusive primates along the way.

Leyte and Samar: Hidden Gems of Biodiversity
Leyte and Samar, neighboring islands in the Eastern Visayas region, are lesser-known but equally important habitats for Philippine Tarsiers. Here, amidst the rugged terrain and dense foliage, tarsiers find refuge in secluded pockets of forest. While sightings may be less common than in Bohol, the opportunity to encounter these creatures in their untamed wilderness adds to the allure of these islands for nature enthusiasts.
Mindanao: Diverse Habitats, Diverse Tarsiers
Mindanao, the southernmost major island of the Philippines, is renowned for its diverse ecosystems, ranging from lowland rainforests to mountainous terrain. Within this mosaic of habitats, various subspecies of Philippine Tarsiers have adapted to different environmental conditions. Exploring the forests of Mindanao offers a chance to encounter these distinct populations and witness their unique behaviors.
Physical Characteristics
The Philippine tarsier is known for its diminutive size and unique features.
Size and weight
Despite its diminutive stature, the Philippine Tarsier stands as a testament to nature’s ingenuity. Measuring a mere 3 to 6 inches in height, this tiny primate commands attention with its remarkable presence. Weighing in at a feather-light 80 to 160 grams, the tarsier’s petite frame belies its significance in the intricate web of life within the rainforests of the Philippines.
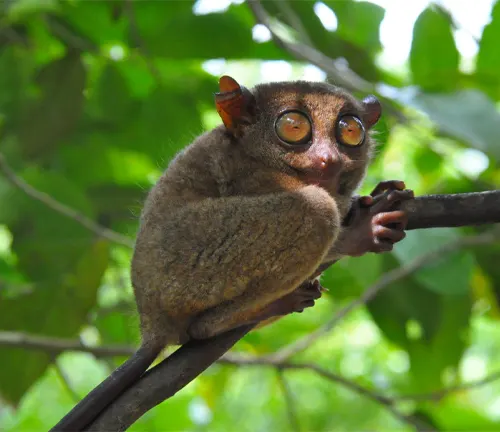
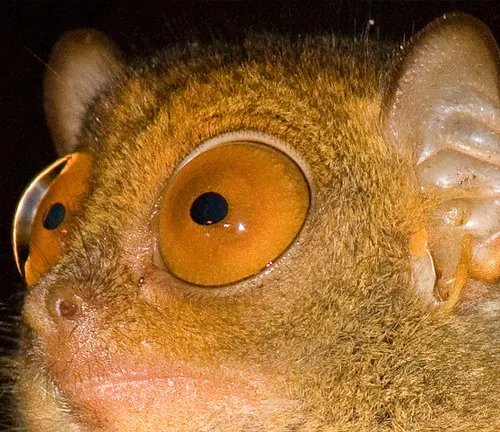


Large eyes and sensory organs
Among the most striking features of the Philippine Tarsier are its disproportionately large eyes and finely tuned sensory organs. Each eye, roughly the size of its brain, serves as a powerful tool for nocturnal navigation and hunting. Adapted to low light conditions, these oversized orbs allow the tarsier to perceive even the faintest glimmer of moonlight filtering through the dense canopy, granting it a distinct advantage in the darkness of the forest floor.
Complementing its extraordinary vision are the tarsier’s other sensory organs, finely attuned to the nuances of its environment. Its large ears swivel independently, detecting the subtlest rustle of leaves or the faintest chirp of an insect. Meanwhile, sensitive pads on its feet provide traction on the most precarious of branches, enabling the tarsier to navigate its arboreal realm with unparalleled grace and agility.
In the intricate tapestry of the rainforest, the Philippine Tarsier stands as a testament to the wonders of evolution, its unique features finely tuned to the demands of its environment. With each subtle movement and piercing gaze, it offers a glimpse into a world both ancient and awe-inspiring.
Behavior and Lifestyle
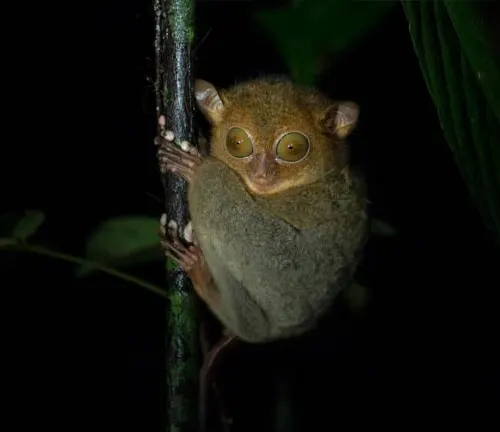

Nocturnal habits
As denizens of the night, Philippine Tarsiers emerge from their secluded nests under the cloak of darkness, embarking on their nightly forays through the rainforest canopy. While the sun sets and diurnal creatures retreat, these elusive primates come alive, their large eyes attuned to the faintest glimmers of moonlight filtering through the dense foliage. With stealth and precision, they navigate the labyrinthine branches, hunting for prey and marking their territory with eerie calls that echo through the darkness.
Communication methods
Despite their solitary nature, Philippine Tarsiers possess a rich repertoire of vocalizations, each serving a unique purpose in their intricate social fabric. From soft chirps to sharp clicks, these sounds convey messages of warning, attraction, and territoriality, echoing through the night air as tarsiers communicate with one another across the forest canopy. In addition to audible calls, tarsiers also emit ultrasonic vocalizations, beyond the range of human hearing, further enhancing their ability to navigate and interact in their nocturnal world.
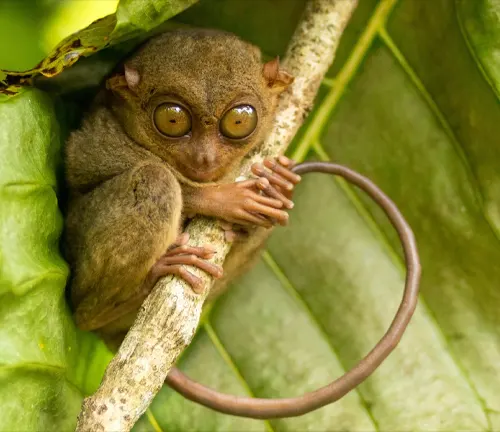
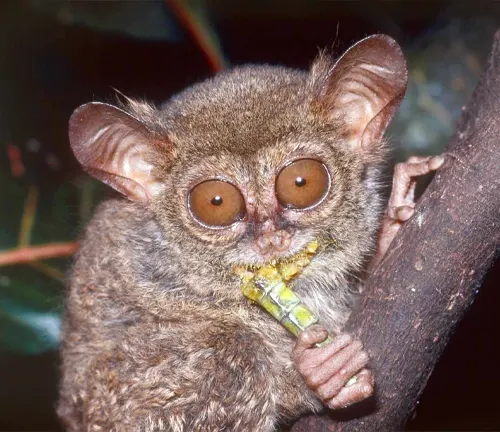


Diet and feeding habits
Philippine Tarsiers are consummate insect hunters, their sharp senses and agile limbs finely attuned to the pursuit of prey amidst the dense foliage. Under the cover of darkness, they stalk their quarry with stealth and precision, pouncing upon unsuspecting insects with lightning-fast reflexes.
From crickets to grasshoppers, beetles to moths, tarsiers feast on a diverse array of invertebrates, supplementing their diet with occasional small vertebrates such as lizards and small birds. With each successful hunt, they sustain themselves in the intricate web of life within the rainforest, playing a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of their ecosystem.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Gestation period
The journey of life for a Philippine Tarsier begins with the miracle of gestation. After a gestation period of approximately six months, female tarsiers give birth to a single offspring, ushering in a new generation of these fascinating primates. Throughout this period, mothers meticulously care for their developing young within the safety of their forest nests, ensuring their health and well-being as they prepare to enter the world.
Birth and infancy
The birth of a tarsier infant marks the beginning of a period of intense maternal care and bonding. Born relatively undeveloped, with closed eyes and sparse fur, newborn tarsiers rely entirely on their mother for sustenance and protection. Clinging tightly to her belly, they embark on a journey of growth and discovery, gradually opening their eyes to the wonders of their rainforest habitat and forging strong bonds with their caregivers.
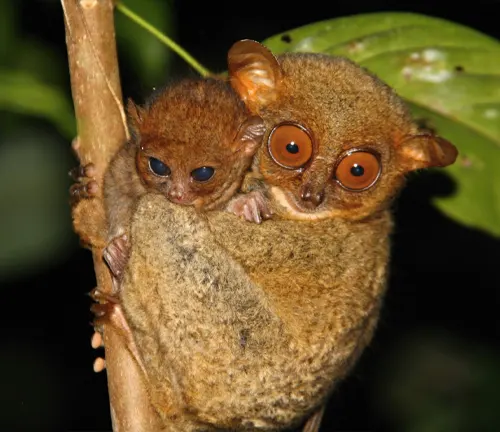
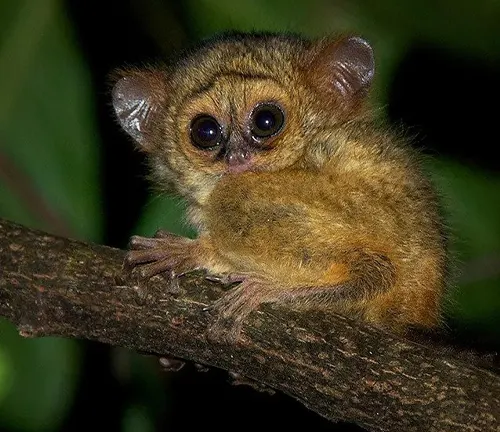


Maturity and lifespan
As tarsier infants grow and develop, they undergo a remarkable transformation, gradually maturing into independent adults capable of navigating the challenges of their rainforest home. By the age of one year, they reach sexual maturity, embarking on their own solitary journeys through the forest canopy. Despite the perils of their environment, Philippine Tarsiers can live for 12 to 20 years in the wild, their lifespan a testament to their resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.
Conservation Status
Threats to their survival
Despite their resilience, Philippine Tarsiers face a myriad of threats to their survival, primarily stemming from human activities and habitat destruction. Deforestation, driven by logging, agricultural expansion, and urbanization, poses a significant risk to tarsier populations, fragmenting their habitats and limiting their access to essential resources. Additionally, illegal hunting and the pet trade further exacerbate the decline of tarsier populations, as these charismatic primates fall victim to exploitation and captivity.
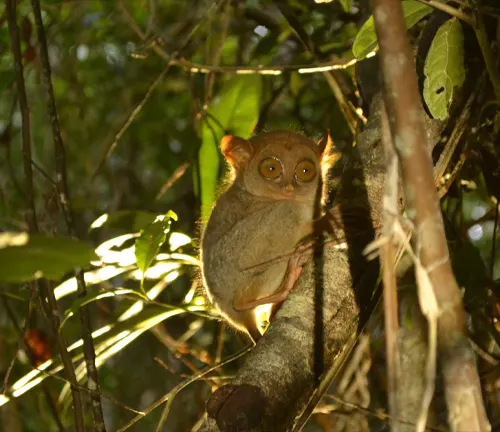

Conservation efforts and initiatives
In response to the escalating threats facing Philippine Tarsiers, conservationists and local communities have rallied together to implement various initiatives aimed at protecting these iconic creatures and their habitats. One such effort involves the establishment of protected areas and conservation reserves, where tarsiers can thrive free from the pressures of human encroachment. Through community-based conservation projects, stakeholders collaborate to raise awareness, enforce regulations, and promote sustainable land use practices that benefit both people and wildlife.
Furthermore, educational programs and ecotourism initiatives play a vital role in fostering appreciation for tarsiers and their habitats, generating economic opportunities for local communities while instilling a sense of stewardship for the natural world. By engaging stakeholders at all levels, from government agencies to grassroots organizations, conservationists strive to secure a brighter future for Philippine Tarsiers, ensuring that these captivating creatures continue to enchant and inspire generations to come.
Importance in Eco-tourism
Economic significance
The Philippine Tarsier not only holds ecological importance but also boasts significant economic potential through ecotourism. As one of the flagship species of the Philippines, tarsiers attract thousands of tourists each year, eager to catch a glimpse of these elusive creatures in their natural habitat. This influx of visitors translates into revenue for local communities, supporting livelihoods and fostering economic growth in tarsier-rich regions.
Responsible tourism practices
While tourism offers undeniable benefits, it also brings inherent challenges, particularly concerning the conservation of fragile ecosystems and sensitive wildlife like the Philippine Tarsier. To mitigate the negative impacts of tourism, stakeholders must embrace responsible practices that prioritize the well-being of tarsiers and their habitats.
Guided by principles of sustainable tourism, responsible tourism practices aim to minimize disturbance to tarsiers while maximizing the educational and recreational value of visitor experiences. This includes implementing visitor guidelines to minimize noise, maintaining safe distances from tarsiers, and adhering to designated trails to avoid habitat destruction.
Cultural Significance
Folklore and myths surrounding tarsiers
In the rich tapestry of Philippine folklore, Philippine Tarsiers occupy a prominent place, their enigmatic presence inspiring a plethora of myths and legends passed down through generations. According to local folklore, tarsiers are believed to possess supernatural abilities, with some tales depicting them as mystical guardians of the forest or harbingers of good fortune. In other stories, tarsiers are portrayed as mischievous tricksters, playing pranks on unsuspecting travelers who dare to venture into their domain. These captivating tales reflect the deep reverence and awe that tarsiers evoke among the people of the Philippines, highlighting their significance in the cultural fabric of the archipelago.
Role in local traditions and beliefs
Beyond folklore, Philippine Tarsiers hold a revered place in local traditions and beliefs, symbolizing the interconnectedness between humans and the natural world. In some indigenous communities, tarsiers are viewed as sacred beings, embodying the spirit of the forest and serving as guardians of the land. Rituals and ceremonies are held to honor these elusive creatures, seeking their blessings for bountiful harvests, successful hunts, and protection from harm.
Tarsiers are also believed to possess the power to ward off evil spirits, with their haunting calls serving as a potent talisman against malevolent forces. Through these cultural practices, tarsiers become woven into the fabric of daily life, their presence imbuing the landscape with a sense of magic and reverence that transcends generations.
Research and Scientific Significance
Contributions to science
Despite their diminutive size, Philippine Tarsiers have made significant contributions to scientific understanding, particularly in the fields of primatology, evolutionary biology, and ecology. As one of the oldest surviving primate lineages, tarsiers offer valuable insights into the early stages of primate evolution, shedding light on the transition from nocturnal to diurnal lifestyles and the development of specialized anatomical features such as large eyes and elongated limbs. By studying tarsiers’ unique adaptations to their environment, scientists gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
Studies on their behavior and biology
Numerous studies have focused on unraveling the intricate behaviors and biology of Philippine Tarsiers, providing invaluable data on their social structure, reproductive biology, communication, and feeding ecology. Through meticulous observation and field research, scientists have documented tarsiers’ complex vocalizations, elaborate courtship rituals, and intricate hunting techniques, offering insights into their evolutionary strategies and ecological roles within their rainforest habitats. Additionally, studies on tarsier genetics and population dynamics contribute to conservation efforts, informing management strategies aimed at safeguarding these charismatic primates and their ecosystems for future generations.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Continuing threats and challenges
Despite ongoing conservation efforts, Philippine Tarsiers continue to face a myriad of threats and challenges to their survival. Habitat loss and fragmentation remain persistent threats, driven by deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion. Additionally, illegal logging, mining, and land conversion further exacerbate the degradation of tarsier habitats, fragmenting populations and reducing their access to essential resources. Furthermore, the illegal pet trade continues to pose a significant risk to tarsier populations, with individuals being captured and sold as exotic pets, further threatening their long-term viability in the wild.
Potential avenues for conservation and research
In the face of these daunting challenges, concerted efforts are needed to safeguard the future of Philippine Tarsiers and their habitats. Key avenues for conservation and research include:
- Habitat Protection and Restoration: Prioritizing the establishment and management of protected areas and conservation reserves to safeguard critical tarsier habitats and mitigate the impacts of habitat loss and degradation.
- Community Engagement and Empowerment: Fostering partnerships with local communities to promote sustainable land use practices, raise awareness about the importance of tarsier conservation, and empower communities to actively participate in conservation efforts.
- Law Enforcement and Anti-Poaching Measures: Strengthening law enforcement efforts to combat illegal logging, poaching, and the illegal pet trade through enhanced surveillance, enforcement of regulations, and collaboration with law enforcement agencies and local authorities.
- Research and Monitoring: Investing in scientific research and monitoring programs to enhance understanding of tarsier ecology, behavior, genetics, and population dynamics, providing critical data to inform conservation strategies and management decisions.
- Education and Outreach: Implementing educational programs and outreach initiatives to engage stakeholders at all levels, including local communities, policymakers, tourists, and the general public, fostering a culture of conservation and stewardship for Philippine Tarsiers and their habitats.
Different Species
Spectral Tarsier
(Tarsius spectrum)
Found in Indonesia, including Sulawesi, Selayar, and Buton islands. They are slightly larger than Philippine Tarsiers and have a wider distribution range.
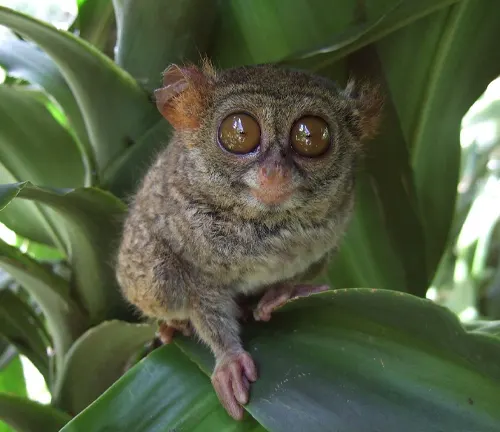
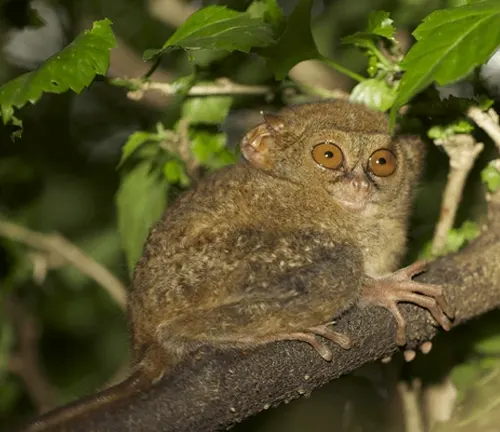


Dian’s Tarsier
(Tarsius dentatus)
Endemic to central Sulawesi, Indonesia, and known for their distinctive toothcomb.
Sangihe Tarsier
(Tarsius sangirensis)
Found on the Sangihe Islands, north of Sulawesi, Indonesia. They are relatively larger compared to other tarsier species.
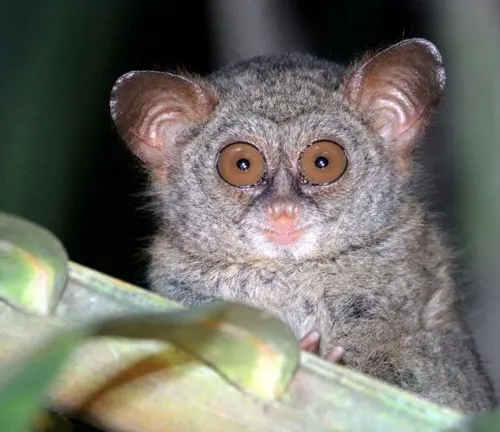
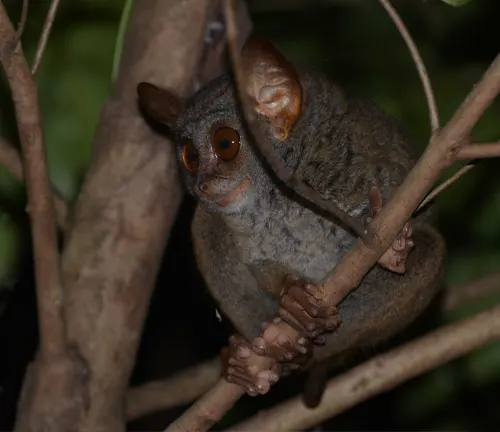


Tarsius tumpara
Discovered in 2014, this tarsier species is found in the central part of Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Pygmy Tarsier
(Tarsius pumilus)
Once thought to be extinct, this species was rediscovered in the highlands of Sulawesi, Indonesia. They are the smallest known primates.
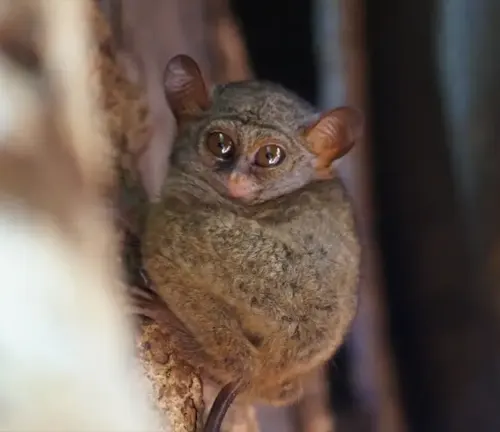
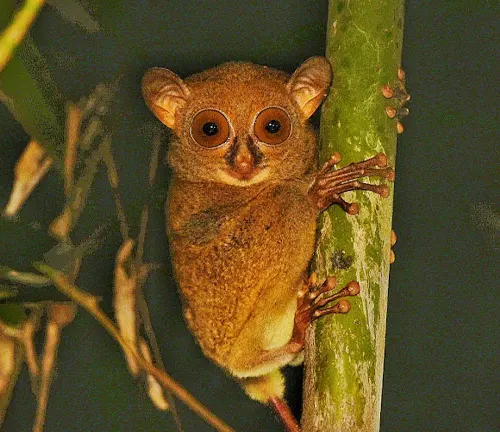


Horsfield’s Tarsier
(Cephalopachus bancanus)
Found in Indonesia and Malaysia, primarily on the islands of Borneo and Sumatra. They are larger than Philippine Tarsiers and have distinctive coloration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What do Philippine Tarsiers eat?
Philippine Tarsiers primarily feed on insects such as crickets, grasshoppers, beetles, and other small invertebrates found in their forest habitat. - How big are Philippine Tarsiers?
Philippine Tarsiers are small primates, measuring about 3 to 6 inches (7.5 to 15 cm) in height and weighing between 80 to 160 grams. - Where can I see Philippine Tarsiers in the wild?
Philippine Tarsiers can be observed in select regions of the Philippines, including Bohol, Leyte, Samar, and Mindanao. Guided tours in protected areas offer opportunities for wildlife sightings. - Why do Philippine Tarsiers have large eyes?
Philippine Tarsiers have large eyes adapted for nocturnal vision, allowing them to hunt for prey and navigate in low light conditions typical of their forest habitat. - How long do Philippine Tarsiers live?
Philippine Tarsiers have a lifespan of about 12 to 20 years in the wild, although this can vary depending on factors such as predation, habitat quality, and human disturbance. - Do Philippine Tarsiers have predators?
While Philippine Tarsiers are small and agile, they are preyed upon by larger birds of prey, snakes, and carnivorous mammals that inhabit their forest environment. - Are Philippine Tarsiers aggressive towards humans?
Philippine Tarsiers are generally shy and elusive animals. While they may exhibit defensive behavior if threatened, they are not aggressive towards humans unless provoked. - Do Philippine Tarsiers make good subjects for scientific research?
Yes, Philippine Tarsiers are of great interest to scientists studying primate behavior, ecology, and evolution due to their unique characteristics and evolutionary history. - Can Philippine Tarsiers swim?
While Philippine Tarsiers are primarily arboreal and not known for swimming, they are capable of crossing small bodies of water by leaping or climbing. - How do Philippine Tarsiers communicate?
Philippine Tarsiers communicate through a variety of vocalizations, including chirps, clicks, and ultrasonic calls, which they use to communicate with each other and establish territory.














Leave your comment