Red Wolf
- January 10, 2024
- 0 comment
The red wolf, scientifically classified as Canis rufus, is a captivating and endangered species native to North America. Its unique reddish-brown coat sets it apart, showcasing distinctive physical traits. Historically intertwined with the cultural fabric of the Southeastern United States, the red wolf has faced a significant reduction in its original range. Known for its strategic hunting techniques and preference for specific prey, the red wolf plays a crucial role in controlling prey populations, earning it the status of a keystone species in the ecosystem. However, numerous challenges, including habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and genetic issues, have led to its endangered status.
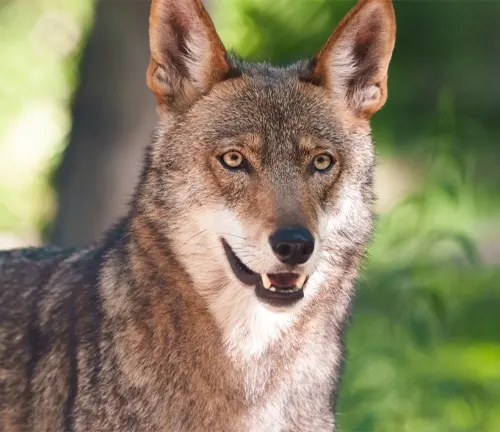

Conservation efforts are underway to safeguard and restore red wolf populations, with various projects and programs showcasing positive outcomes. The species’ significance in Native American culture adds a cultural dimension to its conservation, as it is symbolized in folklore and holds importance in indigenous traditions. Despite facing reproductive challenges, the red wolf’s unique mating behavior and social structure contribute to its evolutionary adaptability. Understanding the distinctions between red wolves and other canids, as well as the complexities of human-wildlife conflict, is essential for successful conservation.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Canis rufus |
| Common Name | Red Wolf |
| Coat Color | Reddish-brown |
| Size and Weight | Moderate size; Varied weight, typically 45-80 pounds |
| Geographic Range | Originally Southeastern United States |
| Current Distribution | Limited, facing habitat loss and fragmentation |
| Diet | Primarily specific prey species |
| Hunting Behavior | Stealthy, strategic |
| Conservation Status | Endangered |
| Threats | Habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, genetic issues |
| Keystone Species | Yes, influences prey population control |
| Reproduction | Faces challenges; Unique mating behavior |
| Significance in Culture | Symbolic in Native American traditions |
| Human-Wildlife Conflict | Historically faced challenges, ongoing initiatives |
| Conservation Efforts | Ongoing projects and programs, some with success |
| Public Awareness | Advocacy campaigns and educational initiatives |
Red Wolf: A Comprehensive Exploration
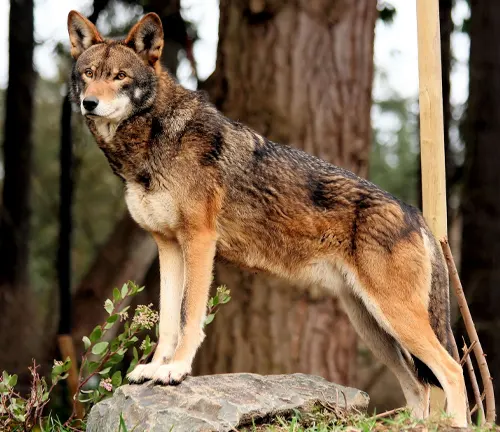

Definition of Red Wolf
The red wolf, scientifically known as Canis rufus, is a fascinating and endangered species native to North America. This article delves into its unique characteristics, ecological significance, and the challenges it faces in the modern world.
Historical Background
Tracing its roots back to early American history, the red wolf’s presence has been entwined with the cultural and ecological fabric of the region. Understanding its historical significance is crucial to appreciating its current conservation status.
Physical Characteristics
Size and Weight
Unlike its gray wolf counterparts, the red wolf exhibits distinct physical traits in terms of size and weight. Exploring these differences provides insights into its evolutionary adaptations.
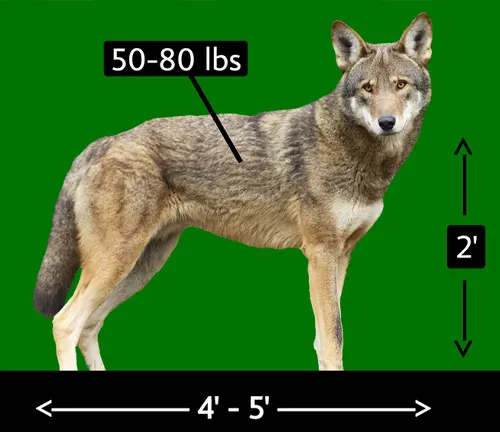
Coat Color and Fur Texture
The red wolf’s coat, a blend of reddish-brown hues, plays a vital role in its survival. Examining the coat color and fur texture sheds light on its ecological niche.

Habitat and Distribution
Original Range
Once widespread across the Southeastern United States, the red wolf has seen a significant reduction in its original range. Understanding its historical habitat provides context for ongoing conservation efforts.
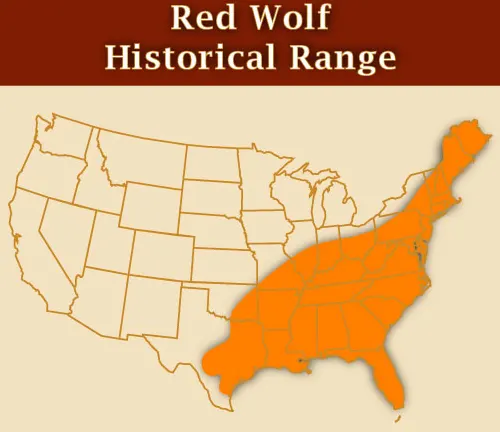
Current Geographic Distribution
Examining the red wolf’s current distribution highlights the challenges it faces due to habitat loss and fragmentation. This section explores the current status of red wolf populations.
Diet and Hunting Behavior
Primary Prey
The red wolf’s diet primarily consists of specific prey species. Analyzing its dietary preferences contributes to a holistic understanding of its role in the ecosystem.
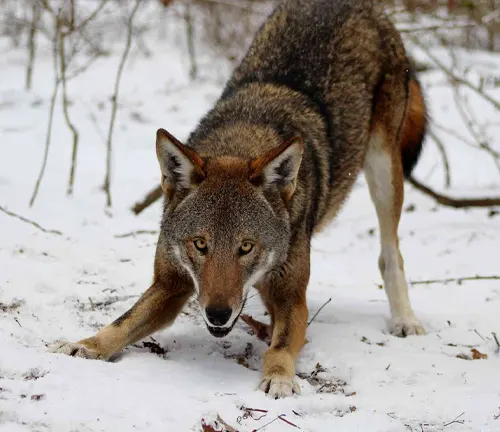

Hunting Techniques
Known for its stealth and strategic hunting methods, the red wolf’s hunting behavior reflects its evolutionary adaptations. Unraveling these techniques provides a glimpse into its survival strategies.
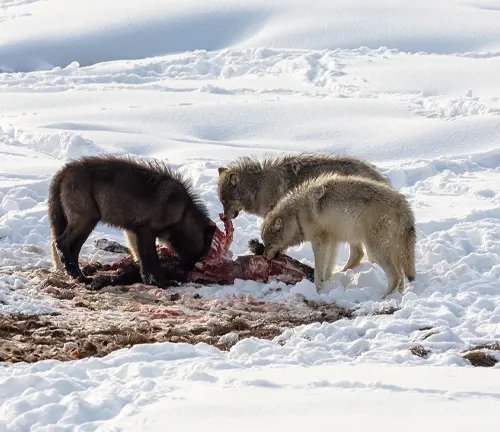

Conservation Status
Threats to Red Wolf Population
Various factors, including habitat destruction and human-wildlife conflict, pose significant threats to the red wolf population. Identifying these challenges is crucial for effective conservation.
Conservation Efforts
Diving into the ongoing conservation initiatives offers hope for the red wolf’s future. This section explores the collaborative efforts to safeguard and restore red wolf populations.
Role in Ecosystem
Impact on Prey Population
As a predator, the red wolf plays a vital role in controlling prey populations. Examining its impact on the ecosystem underscores its significance as a keystone species.
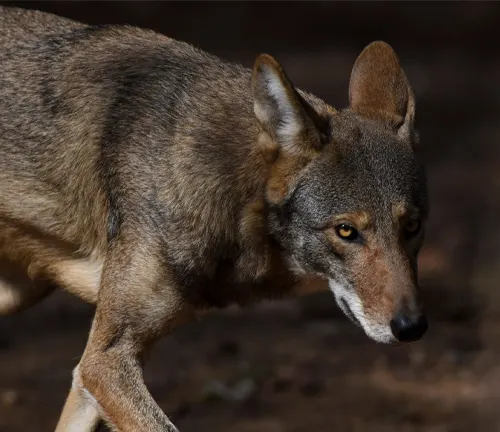

Keystone Species Status
Delving into the concept of keystone species, this section discusses how the red wolf’s presence influences the entire ecosystem.
Interaction with Humans
Historical Perception
Historically, the red wolf has faced challenges due to human perception. Understanding the historical dynamics between red wolves and humans is crucial for informed conservation strategies.
Current Conservation Initiatives
Contemporary conservation initiatives strive to reshape the relationship between red wolves and humans. This section explores projects and programs aimed at fostering coexistence.
Breeding and Reproduction
Mating Behavior
The red wolf’s mating behavior is a critical aspect of its reproductive cycle. Examining mating rituals and behaviors provides insights into its unique social structure.
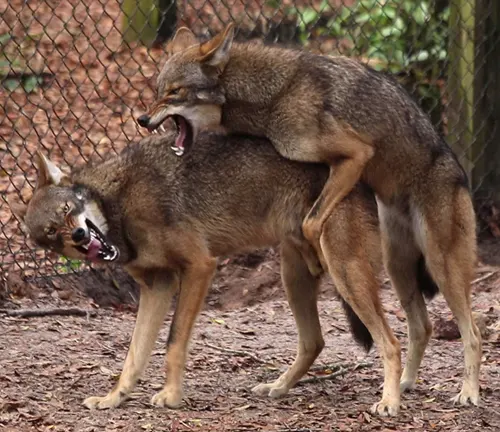

Reproductive Challenges
Despite conservation efforts, red wolves face reproductive challenges. This section discusses the hurdles hindering successful reproduction and potential solutions.
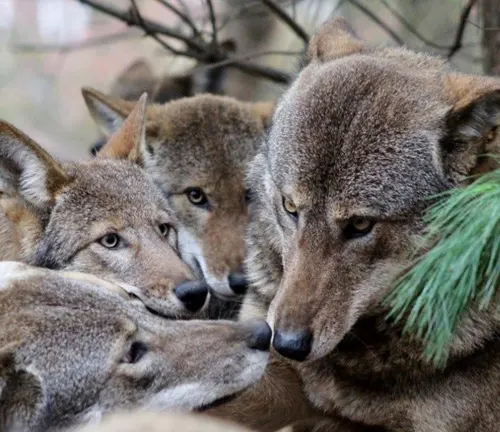

Red Wolf vs. Other Canids
Distinguishing Features
Comparing red wolves to other canids, such as gray wolves and coyotes, highlights their unique characteristics. Understanding these distinctions aids in species identification and conservation efforts.
Behavioral Contrasts
Examining behavioral contrasts among different canid species offers insights into the red wolf’s ecological niche and evolutionary adaptations.
Significance in Native American Culture
Symbolism and Folklore
The red wolf holds cultural significance in Native American traditions. Unraveling the symbolism and folklore surrounding the red wolf showcases its importance in indigenous cultures.
Importance in Indigenous Traditions
Exploring the red wolf’s role in various indigenous traditions deepens our understanding of the cultural bond between native communities and this iconic species.
Public Awareness and Education
Advocacy Campaigns
Raising public awareness through advocacy campaigns is essential for red wolf conservation. This section explores successful campaigns and their impact on public perception.
Educational Initiatives
Educational programs play a crucial role in shaping attitudes towards red wolf conservation. This section discusses initiatives aimed at fostering a deeper understanding of the species.
Future Prospects
Potential Threats
Identifying potential threats to red wolf populations is essential for proactive conservation. This section explores emerging challenges and strategies for mitigation.
Strategies for Continued Conservation
Proposing strategies for continued red wolf conservation ensures a sustained effort towards protecting this iconic species. This section discusses collaborative approaches for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why is the red wolf endangered?
The red wolf faces endangerment due to factors such as habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and genetic challenges, leading to a decline in its population. - How can individuals contribute to red wolf conservation?
Individuals can contribute by supporting conservation organizations, raising awareness about red wolf conservation issues, and advocating for policies that protect red wolf habitats. - What is the red wolf’s role as a keystone species?
The red wolf is considered a keystone species as its presence helps control prey populations, influencing the balance of the ecosystem. - Are there successful examples of red wolf conservation?
Yes, several conservation projects and programs have yielded positive outcomes, showcasing the potential for successful red wolf recovery. - Can red wolves coexist with humans?
With proper conservation measures and awareness, red wolves can coexist with humans, fostering a balanced and harmonious relationship. - What are the primary threats to red wolf populations?
The main threats include habitat destruction, human-wildlife conflict, and genetic issues that impact the red wolf’s survival. - How large is the red wolf’s historical range?
Originally, red wolves were widespread across the Southeastern United States, but their range has significantly diminished over time. - What distinguishes the red wolf from other canids?
Red wolves have unique physical and behavioral characteristics that differentiate them from other canids, such as gray wolves and coyotes. - What are the challenges in red wolf breeding and reproduction?
Red wolves face reproductive challenges, including issues related to mating behavior and successful reproduction in captivity. - How is the red wolf culturally significant?
The red wolf holds cultural importance in Native American traditions, symbolizing various aspects in folklore and indigenous cultures. - What conservation efforts are in place to protect red wolves?
Various conservation initiatives, projects, and programs are ongoing to protect and restore red wolf populations and their habitats. - How do red wolves impact the ecosystem?
Red wolves play a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling prey populations, influencing the balance of the food chain. - Are there educational programs about red wolf conservation?
Yes, there are educational initiatives aimed at raising awareness and understanding about red wolves and their conservation needs. - What are the prospects for the future of red wolf populations?
The future prospects depend on continued conservation efforts, addressing emerging threats, and implementing strategies for sustained recovery. - How do red wolves adapt to their changing environments?
Red wolves exhibit adaptive behaviors to cope with environmental changes, showcasing their resilience in the face of challenges.














Leave your comment