Somaliland Leopard
- February 14, 2024
- 0 comment
The Somaliland leopard, a subspecies of the majestic Panthera pardus, holds a significant place in the unique ecosystem of the Horn of Africa. Known for its adaptability to the semi-arid landscapes of Somaliland, this elusive feline species boasts a sandy or pale yellow coat adorned with distinctive rosettes and spots, providing excellent camouflage amidst the rocky outcrops and savannas it calls home. As a solitary and primarily nocturnal predator, the Somaliland leopard relies on stealth and ambush techniques to hunt its prey, which includes small to medium-sized mammals like gazelles and antelopes.
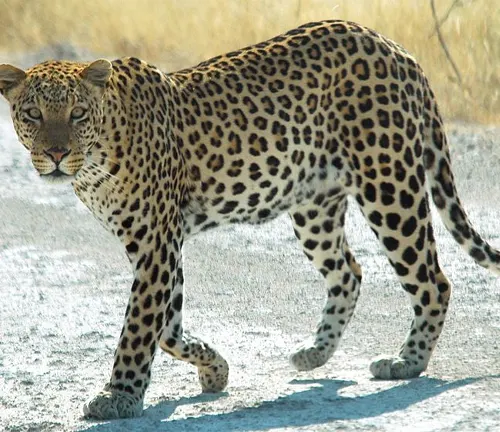

However, the survival of this iconic species is threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts, leading to its designation as “Endangered” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Conservation efforts are underway to protect the Somaliland leopard and its habitat, emphasizing the importance of community engagement, sustainable land-use practices, and raising awareness about the significance of preserving this emblematic predator for future generations.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Panthera pardus saxicolor |
| Habitat | Semi-arid landscapes, including mountainous regions, savannas, and rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Primarily found in Somaliland, with range extending to neighboring areas of Ethiopia and Djibouti |
| Coat Color | Sandy or pale yellow with distinctive rosettes and spots |
| Size | Variable; slightly smaller than other leopard subspecies |
| Behavior | Solitary and primarily nocturnal; relies on stealth and ambush to hunt prey |
| Prey | Small to medium-sized mammals like gazelles, antelopes, and occasionally livestock |
| Conservation Status | Listed as “Endangered” by the IUCN |
| Threats | Habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts |
| Conservation Efforts | Focus on habitat restoration, community-based conservation, anti-poaching efforts |
| Importance | Maintains ecological balance by regulating prey populations; cultural significance |
Preserving a Majestic Icon of the Wild
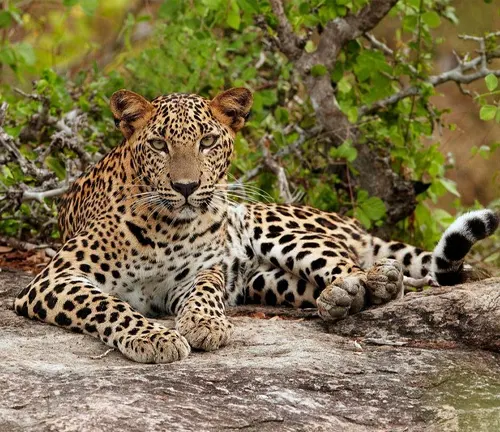

The Somaliland leopard, scientifically known as Panthera pardus saxicolor, is a subspecies of leopard found in the Horn of Africa. This elusive feline holds a significant place in the region’s ecosystem and cultural heritage. Let’s delve deeper into the world of the Somaliland leopard to understand its importance and the conservation efforts aimed at its protection.
The Somaliland leopard is a majestic big cat native to the semi-arid landscapes of Somaliland, a self-declared independent state in the Horn of Africa. Renowned for its agility and stealth, this leopard species has adapted remarkably to its harsh habitat over centuries.
Habitat and Distribution
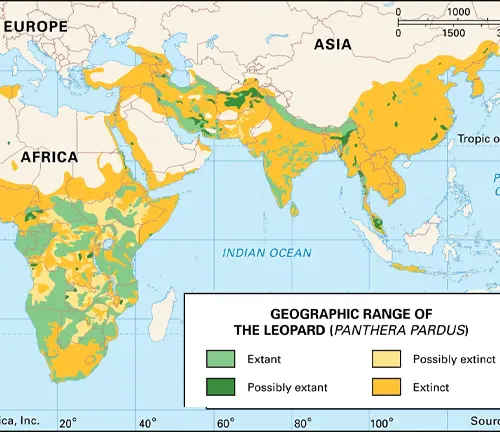
The habitat and distribution of the Somaliland Leopard are primarily centered around the semi-arid landscapes of Somaliland, a self-declared independent state in the Horn of Africa. These leopards inhabit diverse habitats within Somaliland, including mountainous regions, savannas, rocky outcrops, and scrublands. They have adapted remarkably to the challenging conditions of their environment, utilizing their agility and stealth to thrive in these rugged terrains.
Physical Characteristics
The Somaliland Leopard, exhibits distinct physical characteristics that enable it to thrive in the semi-arid landscapes of the Horn of Africa. Here are some notable features:
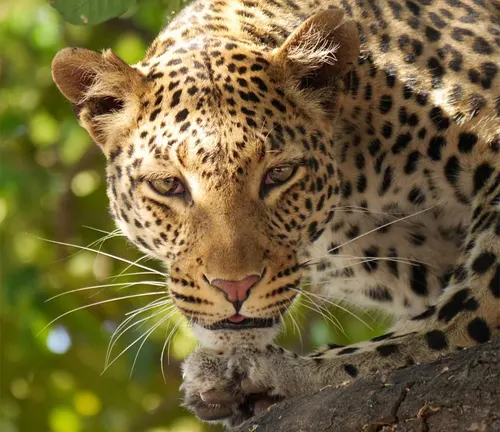

Coat Color
Somaliland Leopards typically have a sandy or pale yellow coat, which provides excellent camouflage in their arid surroundings. This coloration helps them blend seamlessly with the rocky outcrops and savannas where they reside.
Markings
Their coat is adorned with distinctive rosettes and spots, arranged in a pattern that varies from individual to individual. These markings serve as effective camouflage and aid in breaking up their silhouette, making them difficult to spot by potential prey and predators alike.
Size
Somaliland Leopards are generally slightly smaller in size compared to other Leopard subspecies. However, they still possess a powerful and agile build, well-suited for their predatory lifestyle.
Muscular Build
These leopards have a muscular and streamlined body, designed for stealthy movements and swift pursuits. Their strong limbs and sharp claws enable them to climb trees with ease, offering them vantage points for hunting and resting.
Facial Features
Somaliland Leopards have a distinctive facial structure, characterized by a broad skull, short muzzle, and keen eyesight. Their keen senses, particularly their acute vision and hearing, play a crucial role in locating prey and avoiding potential threats.
Adaptations
Over generations, Somaliland Leopards have evolved specific adaptations to cope with the harsh conditions of their environment. These include efficient water conservation mechanisms and the ability to regulate body temperature in extreme heat.
Sexual Dimorphism
Like other Leopard subspecies, Somaliland Leopards exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males typically being larger and heavier than females. This difference in size may be advantageous for males during territorial disputes and mating competitions.
Behavior and Diet
The behavior and diet of the Somaliland Leopard, also known as Panthera pardus saxicolor, are closely intertwined with its habitat and ecological niche in the semi-arid landscapes of the Horn of Africa. Here’s an overview:
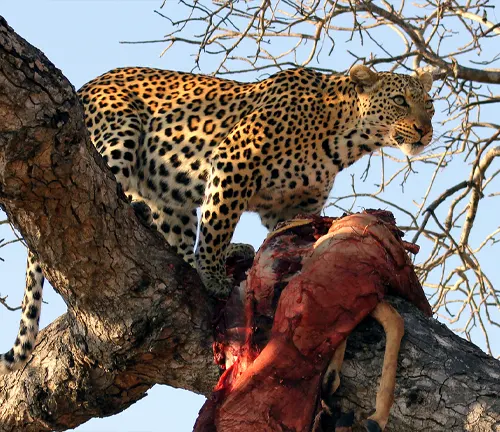
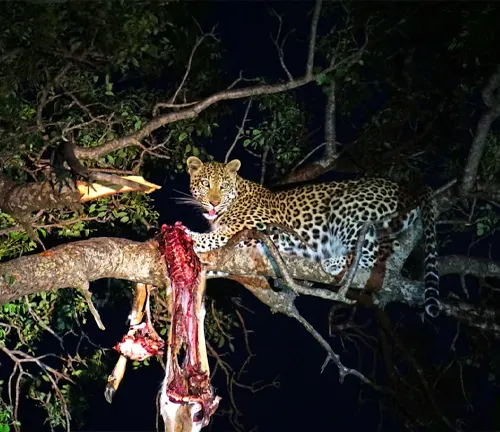


Behavior
- Nocturnal Predators: Somaliland Leopards are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active during the night. This behavioral adaptation allows them to avoid the scorching heat of the day and capitalize on the cover of darkness to hunt their prey.
- Solitary Lifestyle: These leopards are solitary animals, typically avoiding social interactions except during the mating season or when raising young cubs. They establish and defend territories, marking them with scent markings to deter intruders and communicate with potential mates.
- Stealthy Hunters: Somaliland Leopards are renowned for their stealth and agility, employing ambush tactics to surprise and overpower their prey. They rely on their keen senses of sight, hearing, and smell to locate potential prey items and stalk them with utmost patience and precision.
- Tree Climbing: Like other Leopard subspecies, Somaliland Leopards are adept climbers and often retreat to the safety of trees to rest, store their kills, or escape potential threats. Their muscular build and retractable claws make them highly proficient climbers.
Diet
- Versatile Predators: Somaliland Leopards have a diverse diet, feeding on a wide range of prey species depending on availability and opportunity. Their diet primarily consists of small to medium-sized mammals, including gazelles, antelopes, hares, rodents, and occasionally livestock such as goats and sheep.
- Opportunistic Feeders: These leopards are opportunistic hunters, capable of adapting their hunting strategies to exploit various prey sources. They may ambush their prey from trees, stalk them through dense vegetation, or patiently wait near water sources for potential targets to approach.
- Carnivorous Diet: As obligate carnivores, Somaliland Leopards rely exclusively on animal protein for sustenance. Their sharp teeth and powerful jaws are well-suited for tearing through flesh and consuming their prey.
- Role in Ecosystem: By regulating prey populations, Somaliland Leopards play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of their habitat. They help prevent overgrazing by herbivores, which in turn promotes vegetation growth and supports a diverse array of wildlife in the ecosystem.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the Somaliland Leopard, scientifically known as Panthera pardus saxicolor, is a matter of concern due to various threats facing the species. Here’s an overview of its conservation status:
Endangered Status
The Somaliland Leopard is classified as “Endangered” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. This designation signifies that the species faces a high risk of extinction in the wild if urgent conservation measures are not implemented.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
One of the primary threats to Somaliland Leopards is habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities such as agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development. The conversion of natural habitats into farmland and settlements diminishes the available range and suitable habitats for leopards, leading to population declines and increased isolation of remaining populations.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Poaching of Somaliland Leopards for their pelts, bones, and other body parts poses a significant threat to their survival. The illegal wildlife trade driven by demand for leopard skins and body parts in traditional medicine and trophy hunting markets further exacerbates the pressure on already vulnerable populations.
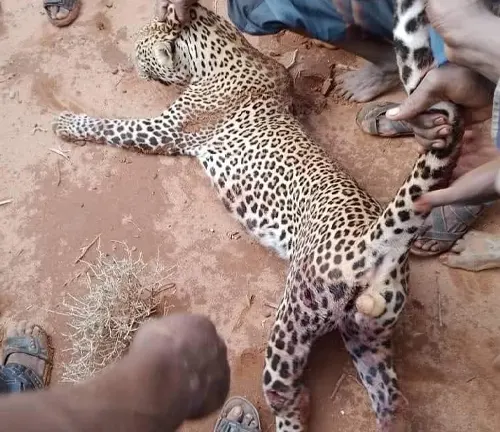

Human-Wildlife Conflicts
Conflict between humans and Somaliland Leopards, particularly livestock herders, is another significant conservation challenge. Retaliatory killings of leopards by farmers in response to livestock predation exacerbate population declines and undermine conservation efforts.
Limited Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting Somaliland Leopards and their habitat are hampered by limited funding, inadequate law enforcement, and socio-economic challenges. Without sufficient resources and political will, conservation initiatives struggle to address the underlying drivers of population decline effectively.
Fragmented Range
The range of Somaliland Leopards has become increasingly fragmented, further isolating populations and reducing genetic diversity. Fragmentation of habitat makes it more difficult for leopards to find suitable mates and maintain viable populations, increasing their vulnerability to extinction.
Different Species
African Leopard
(Panthera pardus pardus)
Found across sub-Saharan Africa, this is the most widespread subspecies of Leopard.


Indian Leopard
(Panthera pardus fusca)
Native to the Indian subcontinent, including countries like India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
Amur Leopard
(Panthera pardus orientalis)
Critically endangered subspecies found in the Russian Far East and parts of China.


Arabian Leopard
(Panthera pardus nimr)
Endangered subspecies found in the Arabian Peninsula, including Oman and Yemen.
Javan Leopard
(Panthera pardus melas)
Found on the island of Java in Indonesia, this subspecies is critically endangered due to habitat loss and poaching.


Sri Lankan Leopard
(Panthera pardus kotiya)
Native to Sri Lanka, this subspecies is classified as endangered due to habitat loss and human-wildlife conflicts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why are Somaliland leopards endangered?
This question addresses the factors contributing to the endangered status of Somaliland leopards, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. - How can I help conserve Somaliland leopards?
This question explores ways individuals can contribute to the conservation efforts aimed at protecting Somaliland leopards and their habitat, such as supporting conservation organizations and raising awareness. - Are Somaliland leopards aggressive towards humans?
This question delves into the behavior of Somaliland leopards in relation to human interaction, addressing concerns about potential conflicts and safety measures. - What is the role of traditional beliefs in endangering Somaliland leopards?
This question discusses the impact of traditional beliefs, particularly regarding the use of leopard body parts in traditional medicine or rituals, on the conservation status of Somaliland leopards. - How do Somaliland leopards contribute to ecosystem balance?
This question explores the ecological role of Somaliland leopards as apex predators and their influence on prey populations, vegetation dynamics, and overall ecosystem health. - What are the main threats to Somaliland leopards?
This question focuses on the primary factors posing threats to the survival of Somaliland leopards, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. - Where can Somaliland leopards be found?
This question addresses the geographical distribution of Somaliland leopards, including their habitat range in Somaliland and neighboring regions. - How do Somaliland leopards hunt?
This question explores the hunting behavior and strategies employed by Somaliland leopards to capture prey in their natural habitat. - What is being done to protect Somaliland leopards?
This question discusses the conservation efforts and initiatives aimed at safeguarding Somaliland leopards, including habitat conservation, anti-poaching measures, and community engagement. - What are the physical characteristics of Somaliland leopards?
This question describes the appearance and distinguishing features of Somaliland leopards, including their coat color, size, and markings. - Do Somaliland leopards have any predators?
This question explores the natural predators and threats faced by Somaliland leopards, such as larger carnivores or human activities.














Leave your comment