Black Slug
- April 1, 2024
- 0 comment
The black slug, scientifically known as Arion ater, is a fascinating creature found in various habitats around the world. Sporting a distinctive dark coloration ranging from deep black to dark brown, these slugs typically measure between 10 to 15 centimeters in length. They thrive in moist environments like woodlands, gardens, and fields, where they play vital roles as decomposers, aiding in nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
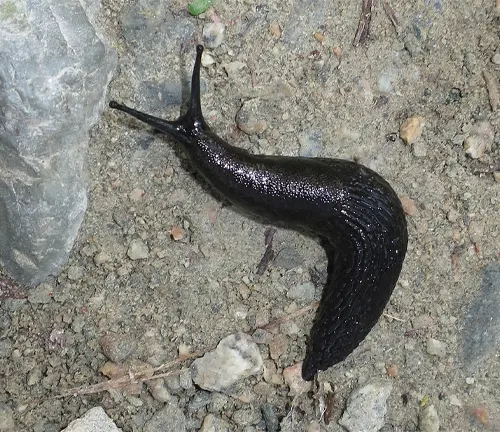

Despite their ecological importance, black slugs can be a nuisance in gardens and agricultural settings, where their herbivorous appetite for plants, including seedlings and tender shoots, can cause significant damage. Despite their pest status, understanding and managing black slug populations are essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and fostering coexistence with humans.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Black Slug |
| Scientific Name | Arion ater |
| Coloration | Deep black to dark brown |
| Size | 10 to 15 centimeters (adults) |
| Habitat | Moist environments such as woodlands, gardens, and fields |
| Distribution | Europe, North America, parts of Asia |
| Behavior | Nocturnal; feeds and moves during the night to avoid predators |
| Diet | Herbivorous, consumes a variety of plant matter including leaves and fruits |
| Reproduction | Mates in spring and early summer; lays eggs in damp soil or under leaf litter |
| Role in Ecosystem | Decomposer; contributes to nutrient cycling and soil fertility |
| Pest Status | Can be a nuisance in gardens and agricultural settings |
| Conservation Status | Varies by region; generally not considered endangered |
| Predators | Birds, frogs, toads, snakes, certain insects |
Black slugs, scientifically known as Arion ater, are a common sight in many regions around the world. These gastropods belong to the mollusk family and are often found in moist environments such as forests, gardens, and fields.
Physical Characteristics
Coloration
Black slugs typically exhibit a dark coloration, ranging from deep black to dark brown. However, there can be variations within this spectrum, with some individuals displaying lighter shades along their bodies. The dark coloration serves as a form of camouflage, allowing them to blend into their natural environment, especially in shaded or damp areas like forests, gardens, and fields.
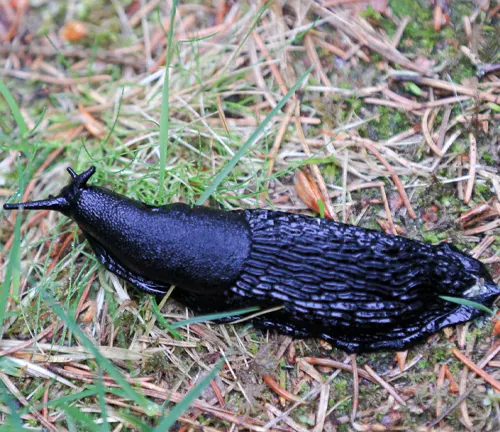

Size
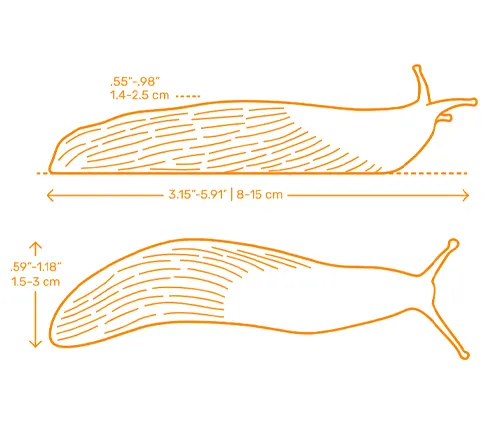
Adult black slugs generally measure between 10 to 15 centimeters in length, although there can be variations based on factors such as age, health, and environmental conditions. Some specimens may grow larger than others, but the typical size range provides a general indication of their dimensions. Despite their relatively small size compared to other species of slugs, black slugs can still have a significant impact on their surroundings, particularly in terms of their feeding habits and ecological interactions.
Habitat and Distribution
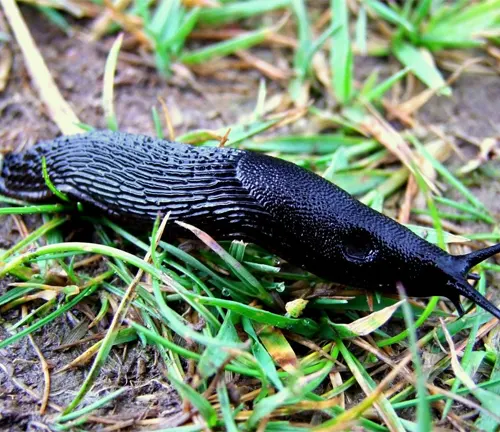
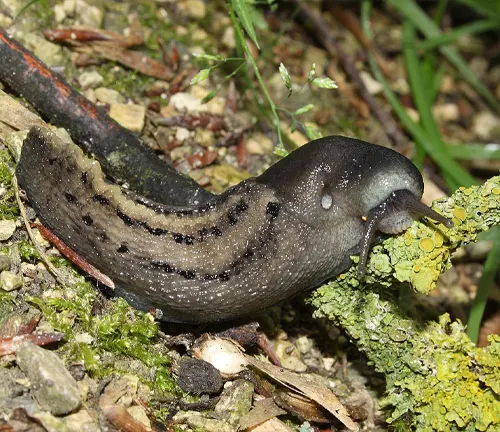


Black slugs are highly adaptable creatures, thriving in a variety of habitats across different continents. They are commonly found in moist environments such as woodlands, gardens, parks, and agricultural fields. These habitats provide the necessary moisture and shelter for black slugs to thrive, allowing them to feed on a diverse range of plant matter and fulfill their ecological roles as decomposers.
In terms of distribution, black slugs have a wide range that spans across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. They are not limited to specific geographical regions and can be encountered in various climates and ecosystems within their range. Their ability to inhabit diverse habitats and adapt to different environmental conditions contributes to their success as a species and ensures their presence in a multitude of ecosystems worldwide.
Behavior and Diet
Black slugs exhibit distinct behaviors and dietary preferences that contribute to their ecological role and interaction with their environment. Here’s an overview:


Behavior
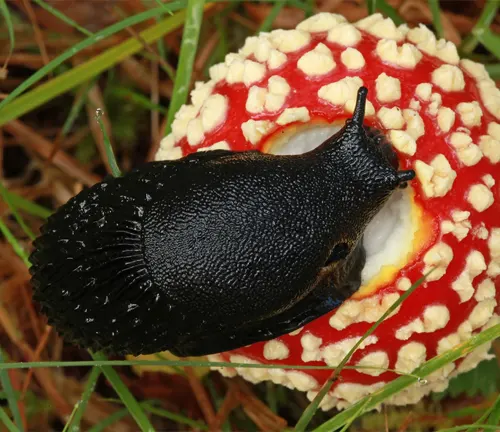
- Nocturnal Activity: Black slugs are primarily nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active during the night. This behavior helps them avoid predators and minimize moisture loss, as nighttime conditions are generally cooler and more humid.
- Moisture Dependency: Due to their soft bodies and lack of protective shells, black slugs rely heavily on moisture to survive. They are commonly found in damp or humid environments, where they can remain hydrated and mobile.
- Mucus Production: Black slugs produce a layer of mucus that covers their bodies, aiding in locomotion and moisture retention. This mucus also serves as a protective barrier against predators and helps them navigate across surfaces.
Diet
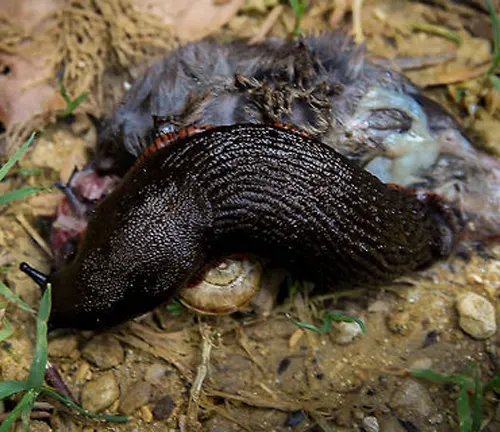
- Herbivorous Feeding: Black slugs are herbivores, meaning they primarily feed on plant matter. They consume a variety of vegetation, including leaves, fruits, vegetables, and seedlings.
- Feeding Patterns: Black slugs are opportunistic feeders and may consume a wide range of plant species depending on availability and preference. They are known to feed on both living plants and decaying organic matter.
- Feeding Habits: Black slugs use their rasping mouthparts to scrape and ingest plant material. They may leave behind characteristic feeding damage, including irregular holes and missing leaf sections, on the plants they consume.
Reproduction
Reproduction in black slugs follows a pattern common to many gastropod species, with distinct stages and behaviors involved in the process. Here’s an overview of how black slugs reproduce:
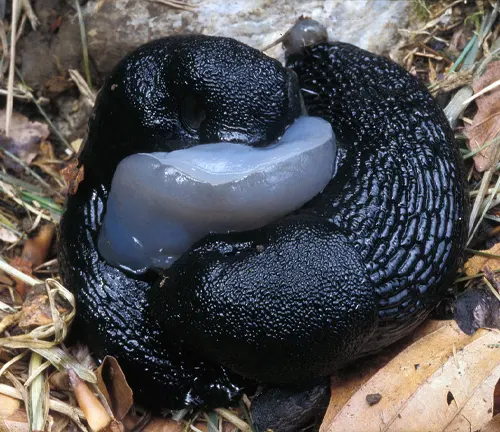
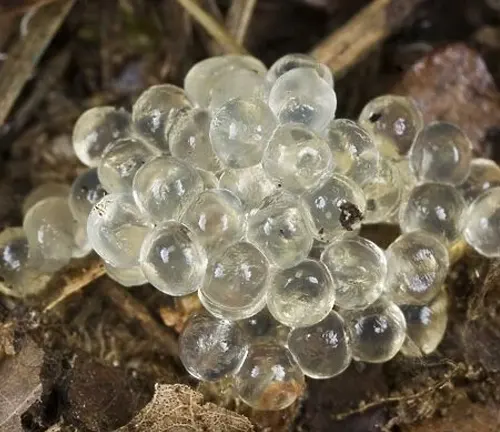


- Mating Season: Black slugs typically mate during the warmer months, with the mating season commonly occurring in spring and early summer. During this time, individuals become more active in seeking out mates and engaging in courtship rituals.
- Courtship Rituals: Before mating, black slugs engage in elaborate courtship behaviors to attract potential mates. These rituals may involve circling, nudging, and exchanging chemical signals to assess compatibility and readiness for mating.
- Copulation: Once compatible mates are identified, black slugs engage in copulation, where sperm is transferred from the male to the female. This process typically occurs through the exchange of spermatophores, specialized structures containing sperm cells.
- Egg-laying: After mating, the female black slug lays eggs in suitable locations within its habitat. These locations are often damp soil or concealed areas under leaf litter, providing protection and moisture for the developing eggs.
- Juvenile Development: The eggs hatch into juvenile slugs, which undergo a series of developmental stages before reaching maturity. During this time, they feed on organic matter and vegetation, gradually growing in size and maturity.
- Lifecycle Continuation: Once mature, adult black slugs are capable of reproducing and continuing the lifecycle. The reproductive cycle repeats, with individuals mating and laying eggs to ensure the survival and propagation of the species.
Importance in Ecosystem
Black slugs play significant roles in ecosystem dynamics, particularly as decomposers and nutrient recyclers. By feeding on decaying organic matter, such as fallen leaves and plant debris, they help break down organic material into simpler compounds, facilitating the recycling of nutrients back into the soil. This process enriches soil fertility and promotes the growth of plants, contributing to overall ecosystem health and functioning.
Black Slug as a Pest
Impact on Gardens
While black slugs serve beneficial roles in natural ecosystems, they can become pests in gardens and agricultural settings. Their voracious appetite for plants, particularly seedlings and tender shoots, can cause significant damage to crops.
Control Measures
Gardeners often employ various methods to control black slug populations, including handpicking, traps, barriers, and the use of natural predators such as birds and predatory insects. Additionally, certain deterrents and repellents may be applied to discourage slug activity.
Interesting Facts about Black Slugs
- Black slugs are capable of regenerating lost body parts, including their tails.
- They produce a layer of mucus to aid in locomotion and moisture retention.
- Despite their name, black slugs can exhibit variations in color, including shades of brown and gray.
Similarities and Differences with Other Slugs
Black slugs share similarities and differences with other species of slugs, both morphologically and behaviorally. While they may exhibit similar physical characteristics, such as dark coloration and slimy mucus secretion, differences in size, habitat preferences, and dietary habits may distinguish them from other slug species. Understanding these similarities and differences is essential for accurately identifying and studying different slug species and their ecological roles within ecosystems.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of black slugs varies depending on factors such as habitat degradation, pollution, and human activities. While they are not typically considered endangered species, localized populations may face threats from habitat loss, fragmentation, and the use of pesticides. Conservation efforts aimed at preserving natural habitats and mitigating human impacts on ecosystems can help ensure the continued survival of black slugs and maintain their ecological contributions.
Human Interaction and Perception
Humans have varied perceptions of black slugs, ranging from appreciation for their ecological roles to frustration over their potential as garden pests. While they are valued for their contributions to nutrient cycling and soil fertility, they may also be viewed negatively when they cause damage to crops and ornamental plants. Understanding human interactions with black slugs and promoting awareness of their ecological importance can foster coexistence and informed management practices.
Benefits of Black Slugs
Despite their reputation as garden pests, black slugs offer several benefits to ecosystems and human environments. As decomposers, they play vital roles in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients, which contributes to soil health and plant growth. Additionally, black slugs serve as food sources for various predators, helping to support biodiversity and maintain ecological balance within ecosystems.
Research and Studies
Scientists continue to conduct research and studies on black slugs to gain insights into their biology, behavior, and ecological significance. Research efforts may focus on topics such as population dynamics, habitat requirements, reproductive strategies, and interactions with other organisms. By advancing our understanding of black slugs, researchers can inform conservation efforts, develop sustainable management practices, and promote appreciation for these often overlooked creatures in the natural world.
Different Species
Arion rufus
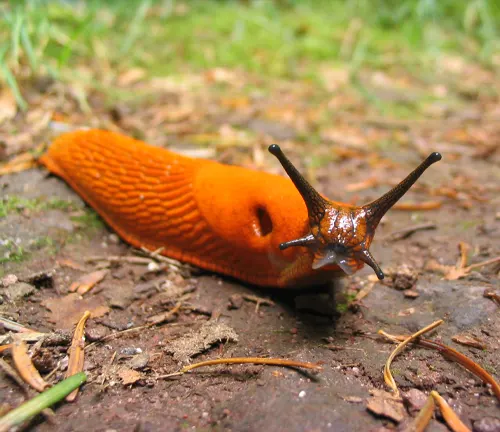
Also known as the Red Slug or Chocolate Arion, this species is similar in appearance to Arion ater but may exhibit reddish-brown coloration.
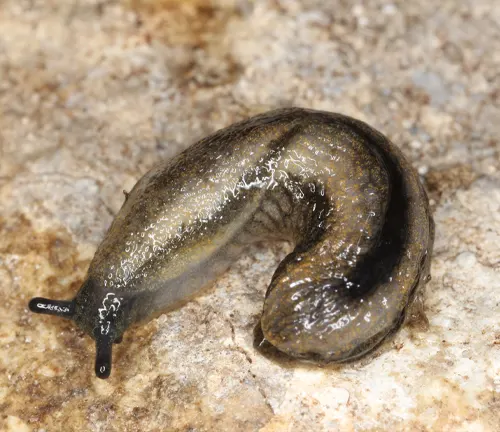


Arion distinctus
The Black Arion is another species closely related to Arion ater, characterized by its dark coloration and similar habitat preferences.
Arion vulgaris
Commonly known as the Spanish Slug or Spanish Stealth Slug, this species is native to southern Europe but has spread to other regions. It shares similarities with Arion ater in terms of coloration and habitat.
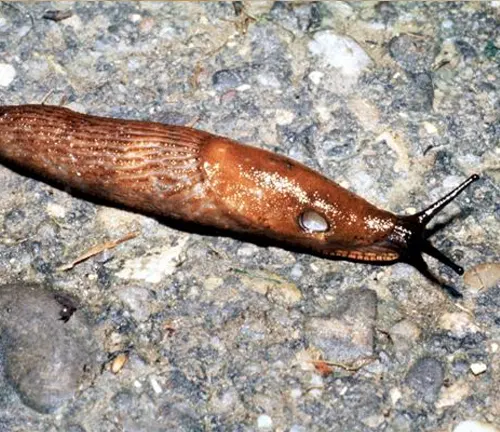
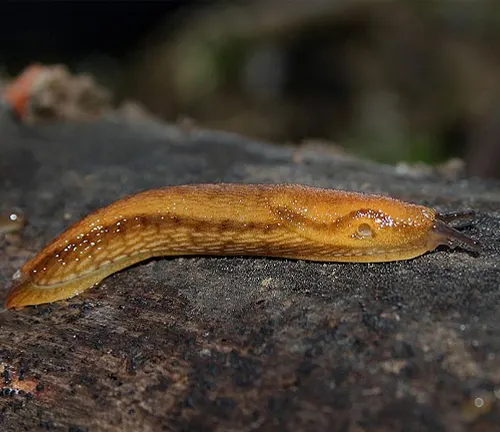


Arion fuscus
The Dusky Arion is a species native to Europe and North America, known for its dark coloration and preference for damp environments
Arion intermedius
This species, also called the Intermediate Arion, is found in Europe and Asia. It resembles Arion ater in appearance but may have slight variations in coloration.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a black slug?
A black slug, scientifically known as Arion ater, is a type of gastropod mollusk characterized by its dark coloration and moist habitat preferences. - Where are black slugs found?
Black slugs are found in various habitats around the world, including woodlands, gardens, parks, and agricultural areas. They are most commonly distributed across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. - How big do black slugs get?
Adult black slugs typically measure between 10 to 15 centimeters in length, although some specimens may grow larger. - What do black slugs eat?
Black slugs are herbivorous, consuming a variety of plant matter including leaves, fruits, and vegetables. - Do black slugs pose a threat to plants?
Yes, black slugs can be pests in gardens and agricultural settings, as they feed on a wide range of plants, including seedlings and tender shoots. - Are black slugs active during the day or night?
Black slugs are primarily nocturnal, preferring to feed and move during the night to avoid predators and conserve moisture. - How do black slugs reproduce?
Black slugs mate during the mating season, which typically occurs in spring and early summer. They lay eggs in damp soil or under leaf litter, which hatch into juvenile slugs. - What predators do black slugs have?
Black slugs have various predators in their natural habitats, including birds, frogs, toads, snakes, and certain insects. - Are black slugs beneficial to the environment?
Yes, black slugs play important roles as decomposers, contributing to nutrient cycling and soil fertility in ecosystems. - How can I control black slug populations in my garden?
Gardeners often employ various methods to control black slug populations, including handpicking, traps, barriers, and the use of natural predators or repellents. - Do black slugs hibernate during winter?
Black slugs may become less active during colder months but do not necessarily hibernate. They may seek shelter in protected areas to survive harsh conditions. - Can black slugs transmit diseases to humans or pets?
There is no evidence to suggest that black slugs transmit diseases to humans or pets. However, it’s always advisable to wash hands after handling slugs or their habitats to prevent potential risks.









Leave your comment