Rhino Rat Snake
- December 17, 2023
- 0 comment
The Rhino Rat Snake, scientifically known as Rhynchophis boulengeri, is a strikingly beautiful snake indigenous to Southeast Asia. Its distinctive appearance is marked by vibrant colours and a unique horn-like scale on its snout, which gives it its intriguing name. The snake’s body is long and slender, adorned with a combination of green, yellow, and black scales arranged in a mesmerising pattern.
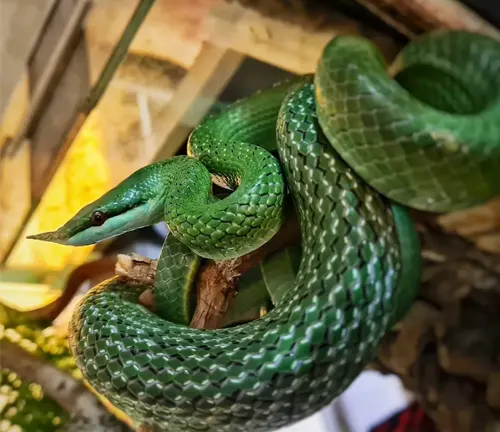

The Rhino Rat Snake is arboreal by nature, preferring to dwell in the lush, tropical rain forests and wooded areas of regions like Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia. Its prehensile tail aids in climbing trees with ease. These serpents are non-venomous and primarily feed on small mammals, birds, and eggs. Due to their captivating appearance, Rhino Rat Snakes are occasionally sought after in the exotic pet trade, although conservation efforts strive to protect their natural habitats and discourage their capture for private ownership. As an essential part of their ecosystems, these snakes play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, showcasing the delicate interdependence of various species within their habitat.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Rhynchophis boulengeri |
| Common Name | Rhino Rat Snake |
| Geographic Range | Southeast Asia, including Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia |
| Habitat | Tropical rainforests, wooded areas |
| Size | Approximately 3 to 4 feet in length |
| Coloration | Vibrant combination of green, yellow, and black |
| Unique Feature | Horn-like scale on the snout |
| Lifestyle | Arboreal, often found in trees |
| Tail | Prehensile tail for climbing |
| Diet | Feeds on small mammals, birds, and eggs |
| Venomous | Non-venomous |
| Conservation Status | Faces threats from habitat loss and pet trade; conservation efforts in place |
| Ecological Role | Plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance |
| Note | Captivating appearance makes it sought after in the exotic pet trade, but conservation is prioritized for their well-being and habitat protection |
Venomous or Not Venomous?
One of the intriguing aspects of the Rhino Rat Snake is its non-venomous nature. Unlike some of its serpent counterparts, this species relies on its mesmerising appearance and stealthy behaviour rather than venom to navigate its environment. As a result, it poses no direct threat to humans, making it an object of fascination rather than fear.
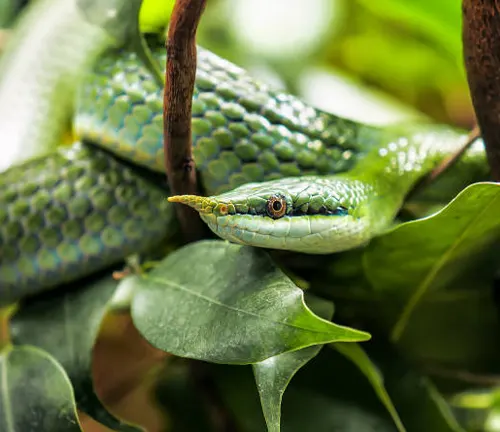

Ecological Importance
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the Rhino Rat Snake plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance within its habitat. As an arboreal species, it contributes to the regulation of small mammal and bird populations, helping to control prey numbers and prevent imbalances that could affect the broader ecosystem.
Habitat
The lush, tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia serve as the primary habitat for the Rhino Rat Snake. These wooded areas provide the perfect environment for the snake’s arboreal lifestyle, with ample trees for climbing and dense vegetation for concealment. As human activities encroach upon these habitats, there is a growing need to protect and preserve the ecosystems that sustain this captivating species.
Behaviour
The Rhino Rat Snake exhibits fascinating behavioral traits that contribute to its survival in the wild. Its prehensile tail allows for adept climbing, making it a skilled navigator in the tree canopies. This snake is predominantly active during the night, showcasing a nocturnal behavior that aligns with its hunting and survival strategies.
Art And Culture
In some cultures, the Rhino Rat Snake holds symbolic significance. Its unique appearance and graceful movements have inspired folklore and artistic representations, highlighting the intersection of nature and human creativity. The snake’s presence in cultural narratives underscores the deep connection between communities and the biodiversity of their surroundings.
Survival
Survival for the Rhino Rat Snake involves adapting to the challenges of its changing environment. While its captivating appearance may make it sought after in the exotic pet trade, the species faces threats from habitat loss and human activities. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of this species and maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystems it inhabits.
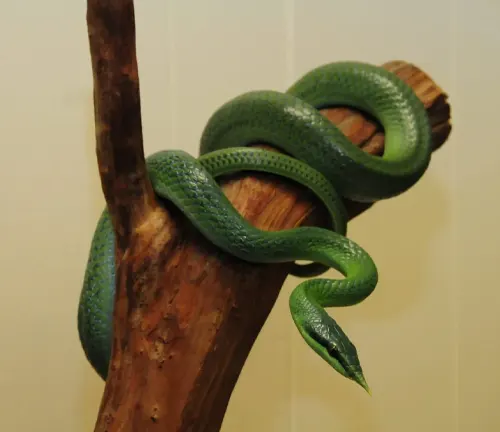

Conservation
Conservation initiatives are pivotal for safeguarding the Rhino Rat Snake and its habitat. Efforts focus on habitat protection, education about the importance of preserving biodiversity, and discouraging the capture of these snakes for the pet trade. Balancing human activities with the needs of this species is paramount for its long-term survival.
Common Food
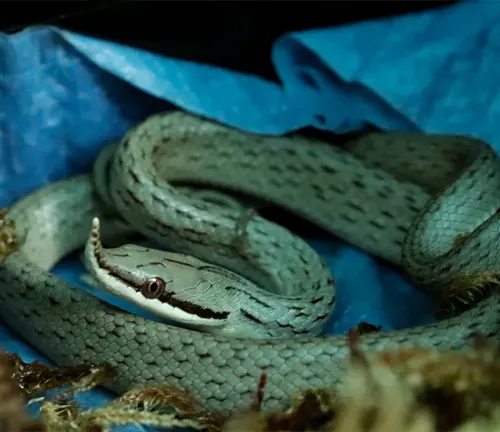

The Rhino Rat Snake sustains itself through a diet consisting of small mammals, birds, and eggs. Its role as a predator helps control the populations of these prey species, contributing to the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
Benefits
Beyond its ecological contributions, the Rhino Rat Snake offers valuable insights into the intricate web of life in Southeast Asian rain forests. Studying its behaviour, habitat preferences, and interactions with other species provides scientists and conservationists with crucial information for broader biodiversity conservation efforts.
Different Species
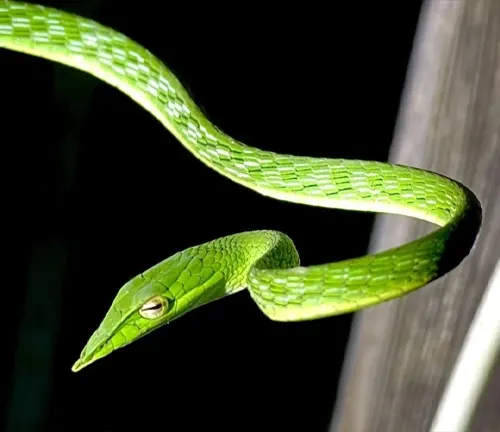
Long-nosed Whip Snake
(Ahaetulla nasuta)
This snake, also known as the Asian Vine Snake or Green Vine Snake, shares a slender and elongated body with the Rhino Rat Snake. It is non-venomous and arboreal, commonly found in Southeast Asia.
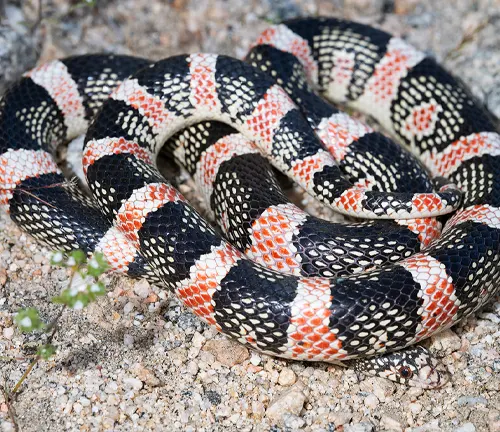


Rhinocheilus lecontei
(Long-nosed Snake)
While not a rat snake, the Long-nosed Snake, found in North America, is notable for its elongated rostral scale, resembling a horn. It is, however, a colubrid snake rather than a rat snake.
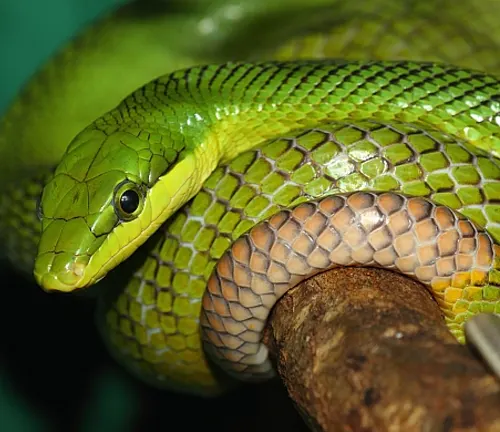
Gonyosoma oxycephalum
(Red-tailed Green Rat Snake)
Also known as the arboreal rat snake, this species is found in Southeast Asia and is renowned for its vibrant green coloration. It is not to be confused with the Rhino Rat Snake but shares a habitat and some behavioural traits.
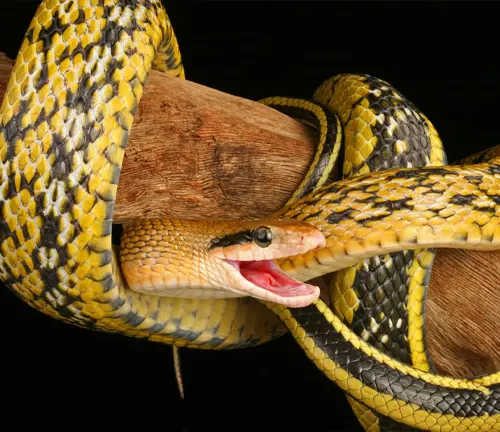


Orthriophis taeniurus
(Beauty Snake)
This species, also known as the Cave Racer or Cave Dwelling Rat Snake, is native to Southeast Asia. It exhibits various colour morphs and is appreciated for its striking appearance, much like the Rhino Rat Snake.
Conclusion
In the heart of Southeast Asian rain forests, the Rhino Rat Snake emerges as a symbol of both botanical beauty and ecological significance. Its enchanting presence, coupled with its non-venomous nature, invites admiration and underscores the importance of conservation in preserving the delicate ecosystems it calls home. As we strive to coexist with the natural world, the Rhino Rat Snake serves as a captivating ambassador for the wonders of biodiversity and the need for concerted efforts to ensure its continued existence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Rhino Rat Snake?
The Rhino Rat Snake (Rhynchophis boulengeri) is a species of non-venomous snake native to Southeast Asia, known for its vibrant colours and a distinctive horn-like scale on its snout. - Where is the Rhino Rat Snake found?
The snake is primarily found in the tropical rain forests and wooded areas of Southeast Asia, including countries like Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia. - Is the Rhino Rat Snake venomous?
No, the Rhino Rat Snake is non-venomous. It relies on its striking appearance and stealthy behaviour for survival rather than venom. - What does the Rhino Rat Snake eat?
The species primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, and eggs. It plays a role in controlling the populations of these prey species within its ecosystem. - What is the unique feature of the Rhino Rat Snake?
The snake is characterised by a horn-like scale on its snout, which contributes to its distinctive appearance and gives it its name. - How big does the Rhino Rat Snake get?
Adult Rhino Rat Snakes typically reach a length of about 3 to 4 feet. - What is the habitat preference of the Rhino Rat Snake?
The snake is arboreal and favours habitats with ample trees, such as tropical rain forests. Its prehensile tail assists in climbing. - Is the Rhino Rat Snake kept as a pet?
While its captivating appearance makes it desirable, conservation efforts discourage keeping Rhino Rat Snakes as pets due to the potential impact on their wild populations. - Why is the Rhino Rat Snake important ecologically?
The species plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling the populations of small mammals and birds within its habitat. - What are the conservation challenges for the Rhino Rat Snake?
The snake faces threats from habitat loss and the exotic pet trade. Conservation efforts focus on preserving its natural habitat and raising awareness about its ecological importance. - Can the Rhino Rat Snake be found in captivity?
Yes, Rhino Rat Snakes are occasionally found in captivity, but responsible breeding and ownership are crucial to prevent negative impacts on wild populations. - How can I contribute to the conservation of the Rhino Rat Snake?
Supporting conservation organisations, avoiding the illegal pet trade, and promoting awareness about the species and its habitat are effective ways to contribute to their conservation.














Leave your comment