Yellow Rat Snake
- December 17, 2023
- 0 comment
The Yellow Rat Snake, scientifically known as Pantherophis alleghaniensis, is a striking and non-venomous snake species indigenous to the southeastern regions of the United States. Known for its vibrant yellow coloration with distinct black markings, this snake can grow to impressive lengths, often reaching around 4 to 6 feet. Its slender body and smooth scales contribute to its sleek appearance.
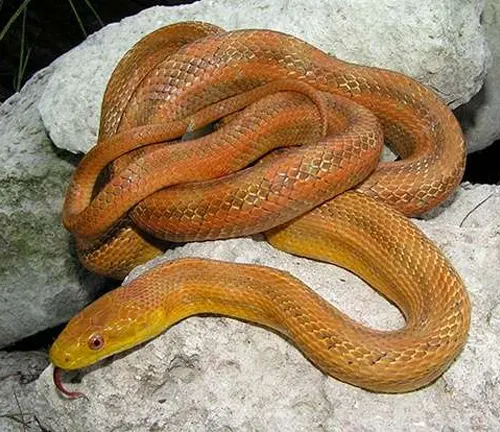
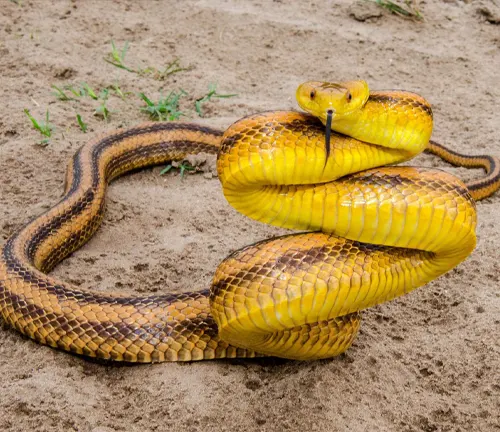


The Yellow Rat Snake is a proficient climber and is frequently spotted in trees, utilizing its agility to hunt birds and small mammals. With a primarily nocturnal nature, it actively hunts during the night, relying on its excellent sense of smell and keen eyesight. Despite its somewhat intimidating appearance, the Yellow Rat Snake is generally docile and seldom poses a threat to humans.
This species plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling rodent populations, making it a beneficial presence in its natural habitat. Enthusiasts appreciate the Yellow Rat Snake for its vibrant coloration, making it a popular choice among reptile enthusiasts who keep snakes as pets. However, it’s essential to adhere to legal and ethical guidelines when considering the ownership of any wildlife species.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pantherophis alleghaniensis |
| Common Name | Yellow Rat Snake |
| Length | 4 to 6 feet (approximately) |
| Coloration | Vibrant yellow with distinct black markings |
| Body Shape | Slender and elongated with smooth scales |
| Habitat | Southeastern regions of the United States |
| Activity | Primarily nocturnal, with increased activity at night |
| Diet | Feeds on birds and small mammals, a proficient climber |
| Behavior | Generally docile, not venomous, beneficial for rodent control |
| Conservation Status | Generally not a threatened species |
| Popularity as a Pet | Popular among reptile enthusiasts, but ownership should comply with regulations and ethical considerations |
A Diverse and Enduring Class of Vertebrates
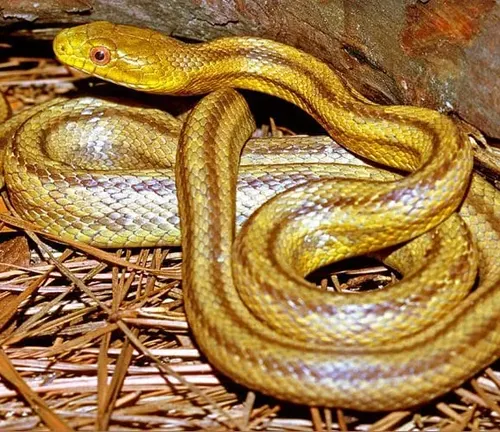

Unveiling the Reptile Form
Reptiles, a remarkable class of vertebrates, encompass a vast array of species with unique characteristics and adaptations. Among them, the Yellow Rat Snake (Pantherophis alleghaniensis) stands out as a captivating and adaptable member of the reptilian order.
Scaled Skin for Protection and Thermos regulation
One distinctive feature of the Yellow Rat Snake is its scaled skin, providing both protection and a crucial role in thermos regulation. These scales not only shield the snake from environmental hazards but also aid in maintaining optimal body temperature, essential for its physiological functions.
Exothermic Physiology and Adaptation to Temperature
Being ectothermic, the Yellow Rat Snake relies on external heat sources to regulate its body temperature. This adaptation allows the species to thrive in diverse environments with fluctuating temperatures, showcasing the reptile’s remarkable resilience.

Skull Structure and Diverse Dental Adaptations
The snake’s skull structure is intricately designed to accommodate its varied diet. The Yellow Rat Snake exhibits diverse dental adaptations, reflecting its ability to consume a range of prey items, from small mammals to birds.
Limb Variations and Locomotion Strategies
Unlike mammals, the Yellow Rat Snake has a lack of limbs. This limbless form is an adaptation for efficient movement, enabling the snake to navigate its surroundings with remarkable agility. The species employs diverse locomotion strategies, including slithering and climbing.
Exploring the Reptile Habitat and Distribution
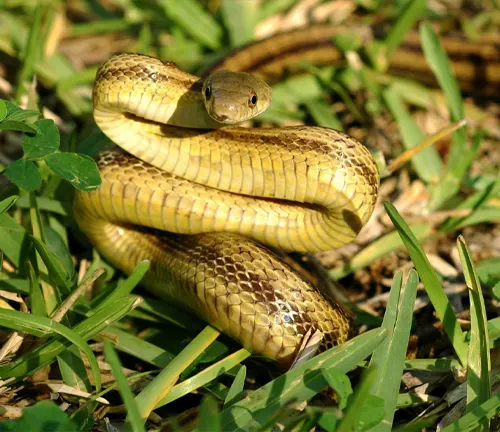

Thriving in Terrestrial, Aquatic, and Arboreal Environments
Yellow Rat Snakes showcase their adaptability by thriving in various habitats, including terrestrial landscapes, aquatic environments, and arboreal settings. This versatility contributes to their widespread distribution across the southeastern regions of the United States.
Adapting to Diverse Ecosystems Worldwide
From deserts to rainforests, mountains to swamps, Yellow Rat Snakes have demonstrated their ability to adapt to a multitude of ecosystems. This adaptability underscores their significance in maintaining ecological balance across diverse landscapes.
Geographic Distribution and Endemic
The geographic distribution of Yellow Rat Snakes reveals a concentration in tropical regions and biodiversity hotspots. Understanding their natural range aids conservation efforts and ensures the preservation of these fascinating reptiles.
Delving into the Reptile Diet and Hunting Strategies
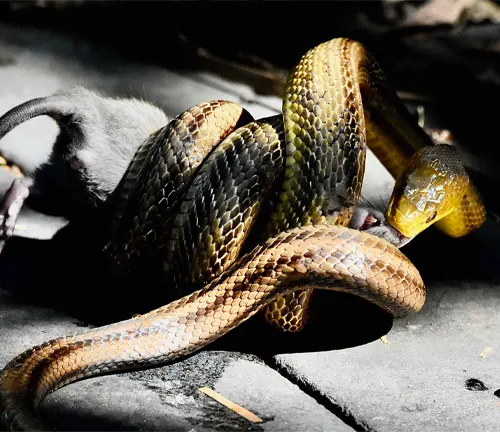

Carnivorous, Herbivorous, and Omnivorous Reptile Diets
Yellow Rat Snakes are carnivorous predators, showcasing a diet that includes birds and small mammals. This adaptability in their diet contributes to their success as a species.
Prey Selection and Hunting Techniques
The species employs various hunting techniques, including ambush and pursuit. Specialized adaptations, such as keen eyesight and an acute sense of smell, contribute to their effectiveness in capturing prey.
Symbiotic Relationships and Food Chains
Yellow Rat Snakes play essential roles in ecosystems by participating in symbiotic relationships and contributing to food chains. Their predation helps control rodent populations, influencing the delicate balance of their respective ecosystems.
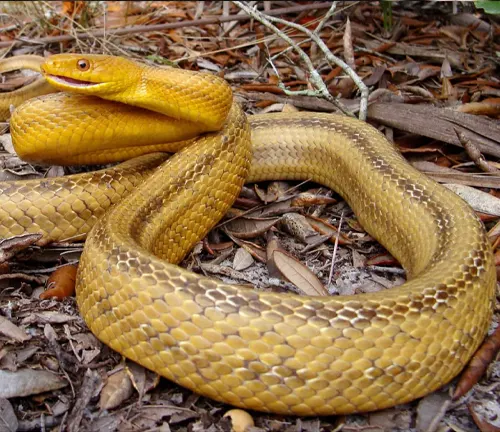

Reptile Roles in Ecosystem Balance and Nutrient Cycling
Beyond their role in food chains, Yellow Rat Snakes contribute to nutrient cycling through their interactions with prey and their environment. Understanding these ecological dynamics is crucial for comprehensive conservation strategies.
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Reptiles
Oviparous, and Viviparous Reproduction
Yellow Rat Snakes exhibit oviparous reproduction, laying eggs that require specific nesting conditions for successful incubation. Some related species, however, showcase viviparous reproduction, where the eggs develop inside the mother’s body.
Egg-Laying Strategies and Parental Care
Nesting sites, incubation periods, and hatchling survival are critical aspects of the Yellow Rat Snake’s reproductive strategy. While parental care is limited, these reptiles have evolved strategies to ensure the survival of their offspring.
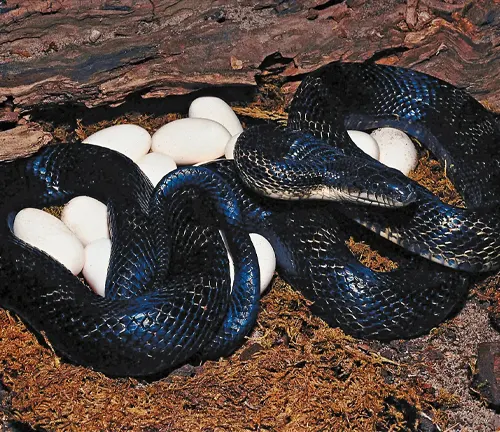

Nesting Sites, Incubation Periods, and Hatching Survival
Selecting suitable nesting sites and understanding the intricacies of incubation periods are vital for the survival of Yellow Rat Snake hatchlings. These aspects contribute to the continuation of the species’ life cycle.
Conservation Status and Threats to Reptiles
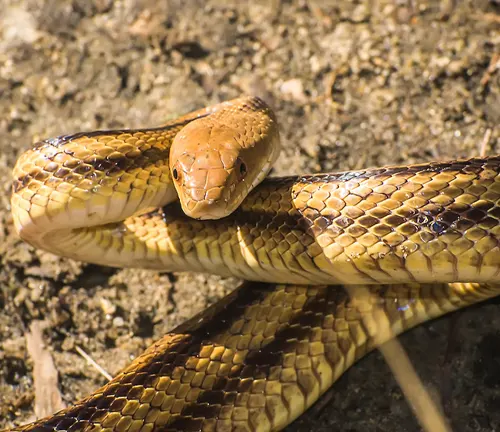

Facing Habitat Loss, Hunting, and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Yellow Rat Snakes, like many reptiles, face threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and involvement in the illegal wildlife trade. These factors contribute to the decline of reptile populations worldwide.
Human Encroachment and Climate Change Impacts
Human encroachment into natural habitats, coupled with the impacts of climate change, further exacerbates the challenges faced by Yellow Rat Snakes. Understanding and addressing these threats are crucial for their long-term survival.
Conservation Efforts Underway
Protected Species, International Agreements, and Habitat Preservation
Efforts to protect Yellow Rat Snakes involve designating them as protected species, adhering to international agreements, and implementing habitat preservation initiatives. Collaboration among scientists, conservationists, and policymakers is essential for the effective conservation of these reptiles.
Different Species
Eastern Yellow Rat Snake
(Pantherophis alleghaniensis alleghaniensis)
This subspecies is native to the southeastern United States and is known for its vibrant yellow colour with distinctive black markings. It is a non-venomous constrictor and is often found in a variety of habitats, including forests, fields, and near water sources.
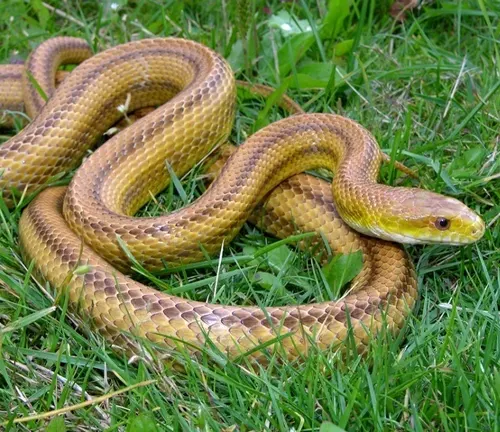
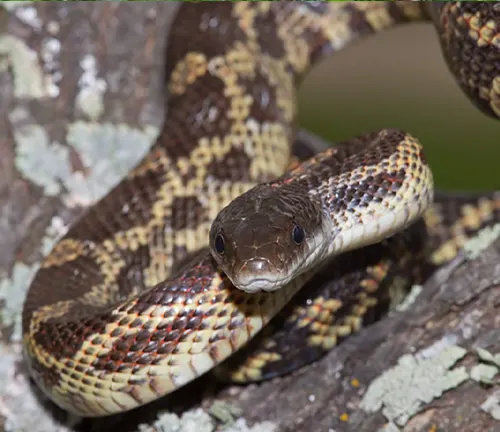


Texas Rat Snake
(Pantherophis obsoletus lindheimeri)
The Texas Rat Snake is found in the southern United States, particularly in Texas and parts of Louisiana. It exhibits a range of colour variations, including shades of yellow, orange, and brown. Like other rat snakes, it is an adept climber and can be found in trees.
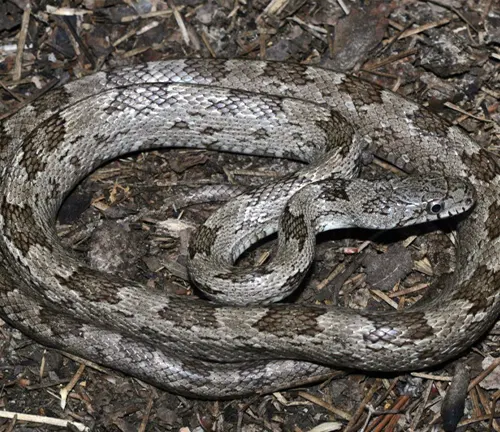
Gray Rat Snake
(Pantherophis spiloides)
Also known as the Central Rat snake, the Gray Rat Snake is found in the southeastern United States. While it can exhibit a greyish coloration, some individuals may display a yellow hue. It is a constrictor and plays a crucial role in controlling rodent populations.
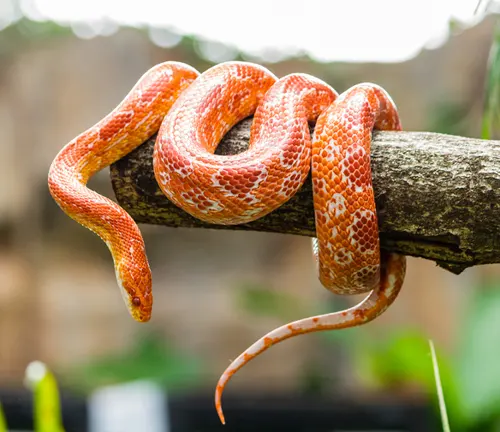


Corn Snake
(Pantherophis guttatus)
Although commonly known as the Corn Snake, it is another member of the Pantherophis genus and is closely related to the Yellow Rat Snakes. Corn Snakes are popular in the pet trade and come in a variety of colours and patterns, including those with yellowish hues.
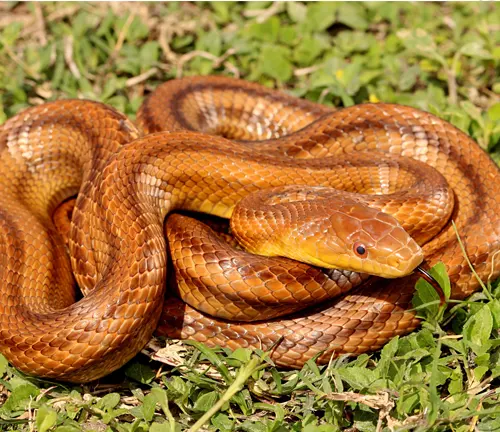
Everglades Rat Snake
(Pantherophis alleghaniensis rossalleni)
This subspecies is native to the Florida Everglades and has a coloration similar to other Yellow Rat Snakes. It is well-adapted to the unique ecosystem of the Everglades and is often found in wetlands.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the Yellow Rat Snake stands as a testament to the diversity and adaptability of reptiles. From its unique physical characteristics to its role in maintaining ecosystem balance, understanding and preserving this species is vital for the broader conservation of reptilian biodiversity. Through ongoing conservation efforts, we can ensure that future generations continue to marvel at the remarkable Yellow Rat Snake and appreciate the intricate web of life it contributes to in the vast world of reptiles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a Yellow Rat Snake?
The Yellow Rat Snake, scientifically known as Pantherophis alleghaniensis, is a non-venomous snake species found in the southeastern United States. It is characterized by its vibrant yellow color with distinct black markings. - How big do Yellow Rat Snakes get?
Yellow Rat Snakes can reach lengths of 4 to 6 feet on average, with some individuals growing slightly longer. Their slender bodies contribute to their sleek appearance. - Are Yellow Rat Snakes venomous?
No, Yellow Rat Snakes are not venomous. They are constrictors, relying on constriction to subdue their prey. While they may strike defensively if threatened, their bites are not harmful to humans. - What is the habitat of Yellow Rat Snakes?
Yellow Rat Snakes are versatile in their habitat preferences and can be found in a variety of environments, including forests, fields, and near water sources. They are adept climbers and may be seen in trees. - What do Yellow Rat Snakes eat?
Yellow Rat Snakes have a carnivorous diet, feeding on birds, small mammals, and occasionally amphibians. Their adaptability allows them to thrive on a variety of prey items. - Are Yellow Rat Snakes good as pets?
Some reptile enthusiasts keep Yellow Rat Snakes as pets due to their attractive coloration and generally docile nature. However, potential owners should be aware of the specific care requirements and legal considerations associated with keeping reptiles. - How do Yellow Rat Snakes reproduce?
Yellow Rat Snakes reproduce through oviparous means, laying eggs. After laying the eggs in a suitable nesting site, the female provides limited parental care, and the hatch lings emerge after an incubation period. - Are Yellow Rat Snakes endangered?
Yellow Rat Snakes are not considered endangered, but like many reptiles, they face threats such as habitat loss, human encroachment, and illegal wildlife trade. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these species and their ecosystems. - Can Yellow Rat Snakes be found in urban areas?
Yes, Yellow Rat Snakes can adapt to urban environments, and sightings in suburban or even urban areas are not uncommon. They are often encountered near homes, gardens, or wooded areas. - Do Yellow Rat Snakes make good pest controllers?
Yes, Yellow Rat Snakes play a valuable role in controlling rodent populations. Their diet includes small mammals, and their presence can help manage rodent numbers in their natural habitats.














Leave your comment