How Nano Forestry is Transforming the Future of Timber Production
- August 16, 2024
- 0 comment
The application of nanotechnology in wood processing, is revolutionizing the timber industry by significantly enhancing the properties and sustainability of wood products. This innovative approach leverages nanomaterials to improve the strength, durability, and environmental performance of wood, making it a versatile and eco-friendly resource.

By integrating cutting-edge nanotechnology, nano forestry offers a transformative solution that enhances wood’s mechanical and physical properties while promoting sustainability. This discussion covers the fundamentals of nano forestry, its impact on wood properties, environmental benefits, practical applications, real-world examples, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Nano Forestry
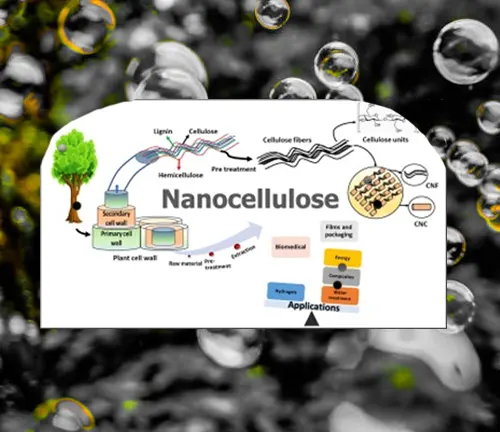
Nano Forestry involves the use of nanotechnology to manipulate materials at the molecular or atomic level to create wood products with enhanced properties. Key nanomaterials used in wood processing include nanocellulose and nanoparticles.
These materials are incorporated into wood to improve its mechanical and physical properties, offering advantages over traditional wood processing methods. Unlike conventional approaches, nano forestry allows for precise control over wood’s microstructure, leading to superior performance and sustainability.
Enhancements in Wood Properties
Mechanical Performance
Nanomaterials significantly enhance the mechanical properties of wood. By incorporating nanocellulose, wood’s tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear are dramatically improved.
For instance, research has shown that nanocellulose can increase the tensile strength of wood products by up to 3000% compared to traditional wood composites.
This makes nano-enhanced wood ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, such as construction materials and heavy-duty furniture.
Lightweight and Flexibility
Another advantage of nano forestry is the ability to reduce the weight of wood products without compromising their strength. Nanomaterials such as nanocellulose are lightweight yet incredibly strong, allowing for the production of flexible wood products that maintain structural integrity.
This flexibility is particularly beneficial in applications like curved or molded wood structures, where traditional wood might be too rigid or heavy.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Nano forestry significantly enhances sustainability by utilizing renewable and biodegradable nanomaterials like nanocellulose. These materials, derived from natural sources such as plant fibers and agricultural byproducts, help reduce reliance on fossil-based materials and promote eco-friendly practices.
Sustainability
Nano forestry promotes sustainability by utilizing renewable and biodegradable nanomaterials like nanocellulose. These materials are derived from natural sources, such as plant fibers and agricultural byproducts, reducing reliance on fossil-based materials.

Nanocellulose is not only renewable but also biodegradable, breaking down into non-toxic components at the end of its lifecycle. This eco-friendly characteristic aligns with the principles of green chemistry and sustainable development, minimizing the environmental impact of wood processing.
Energy Efficiency
The production and processing of nanomaterials in nano forestry are more energy-efficient compared to traditional methods. For example, the use of nanocellulose requires less energy-intensive processing techniques, resulting in lower overall energy consumption.

Case studies have demonstrated that incorporating nanotechnology into wood processing can reduce energy use by up to 50%, making it a more sustainable option for the timber industry.
Applications of Nano Forestry in Wood Products
Construction Materials
Nano forestry is transforming the construction industry by enhancing the properties of lumber, plywood, and engineered wood products. Nanomaterials improve fire resistance, longevity, and structural integrity, making these materials suitable for a wide range of construction applications.
For example, nanocellulose-treated wood exhibits superior fire retardancy, reducing the risk of fire-related damage in buildings.
Furniture and Interior Design
The aesthetic and functional properties of wood furniture are significantly enhanced through nano forestry. Nanotechnology allows for the creation of furniture that is not only stronger and more durable but also more visually appealing.
Innovative designs enabled by nano forestry include lightweight, flexible furniture pieces that retain the natural beauty of wood while offering improved performance.
Packaging and Bioplastics
Nanocellulose is also used in sustainable packaging solutions, offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics. Bioplastics derived from wood nanomaterials are lightweight, strong, and eco-friendly, reducing the environmental footprint of packaging materials.
These bioplastics can be used in a variety of applications, from food packaging to disposable containers, contributing to a circular economy.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
A notable example of nano forestry in action is the partnership between Domtar Corporation and FPInnovations. They have developed a demonstration plant to produce nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC), a type of nanocellulose with exceptional properties.

The plant, located at Domtar’s pulp and paper mill in Windsor, Quebec, explores the commercial viability of NCC and its applications in various industries. The project has demonstrated significant benefits, including enhanced product performance and reduced environmental impact.
Research in nano forestry shows that nanocellulose enhances wood products by increasing strength, reducing weight, and improving environmental resistance. Ongoing studies continue to explore new applications and benefits of nanotechnology in wood processing.
Technical Challenges and Considerations
Production Challenges
While nano forestry offers numerous benefits, it also presents technical challenges. Large-scale production and integration of nanomaterials into wood products can be complex and costly.

Overcoming these barriers requires advancements in processing techniques and the development of cost-effective methods for producing nanomaterials.
Health and Safety
The safety of nanomaterials is another critical consideration. There are concerns related to the potential health impacts of nanomaterials, particularly during production and handling. Ensuring the safety of workers and consumers involves adhering to strict regulations and best practices for the safe use and disposal of nanomaterials.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Emerging Technologies
The future of nano forestry is promising, with emerging technologies poised to further transform the timber industry. Innovations such as advanced nanocomposites, smart wood materials, and bio-based nanomaterials are expected to enhance the performance and sustainability of wood products.
These advancements will open up new possibilities for the application of nano forestry in various sectors.
Ongoing Research and Development
Continuous research and development are crucial for the progress of nano forestry. Collaborative efforts between industry and academia are driving innovation, leading to new discoveries and improved technologies.
Key areas of research include the development of more efficient production methods, the exploration of new nanomaterials, and the investigation of additional applications for nano-enhanced wood products.
Conclusion
Nano forestry is revolutionizing the future of timber production by enhancing the properties and sustainability of wood products. The incorporation of nanotechnology into wood processing offers significant benefits, including improved strength, durability, and environmental performance. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential of nano forestry to transform the timber industry is undeniable.
As research and development continue to advance, the future of nano forestry looks bright, promising a new era of sustainable and high-performance wood products. The ongoing innovation in this field is expected to lead to even more efficient and eco-friendly solutions, further solidifying the importance of nano forestry in modern wood processing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
- What is nano forestry?
Nano forestry involves the application of nanotechnology in wood processing to enhance the properties and sustainability of wood products. It utilizes nanomaterials like nanocellulose to improve strength, durability, and environmental performance. - How does nanotechnology improve the mechanical properties of wood?
Nanomaterials such as nanocellulose significantly enhance the tensile strength and resistance of wood to wear and tear. These improvements make wood products more durable and suitable for various demanding applications. - What are the environmental benefits of nano forestry?
Nano forestry promotes sustainability by using renewable and biodegradable nanomaterials, reducing reliance on fossil-based materials. It also lowers energy consumption in production, contributing to a greener industry. - What are some applications of nano forestry in wood products?
Applications include construction materials with improved fire resistance and longevity, enhanced furniture and interior design, and sustainable packaging solutions using nanocellulose-based bioplastics. These advancements offer significant benefits, including increased durability, eco-friendliness, and innovative design possibilities. Additionally, nanotechnology enhances the performance and aesthetic appeal of wood products. - How does nanocellulose contribute to the sustainability of wood products?
Nanocellulose is a renewable, biodegradable material derived from plant fibers, which breaks down into non-toxic components at the end of its lifecycle. Its use reduces the environmental footprint of wood products. - What are the challenges associated with nano forestry?
Challenges include the complexity and cost of large-scale production and integration of nanomaterials into wood products. Addressing health and safety concerns related to nanomaterials is also critical, along with ensuring regulatory compliance and public acceptance. - What role does research play in the development of nano forestry?
Continuous research and development are essential for advancing nano forestry, driving innovation, and discovering new applications and benefits. Collaborative efforts between industry and academia are key to progress. - Can nano forestry enhance the aesthetic properties of wood products?
Yes, nanotechnology can enhance the visual appeal and functional properties of wood furniture and interior design elements. This allows for innovative and attractive designs that retain the natural beauty of wood, while also improving durability and performance. Nano forestry thus offers a blend of aesthetics and functionality, perfect for modern design needs. - What future innovations can we expect in nano forestry?
Future innovations may include advanced nanocomposites, smart wood materials, and bio-based nanomaterials that offer superior performance and sustainability. These developments will further expand the applications of nano forestry. - How does nano forestry impact the construction industry?
Nano forestry provides construction materials with enhanced properties such as improved fire resistance, strength, and durability. These materials contribute to safer, longer-lasting buildings and structures.

Jordan Blake
Forestry AuthorJordan Blake is a forestry expert with over 15 years of experience in arboriculture and community education. Passionate about sustainable forest management, Jordan regularly writes for Forestry.com and Tree Care Magazine. Holding certifications in tree health assessments and urban forestry management, Jordan conducts workshops to educate the public on sustainable practices. Jordan has a degree in Environmental Science and enjoys hiking and photography in their free time.













Leave your comment