Future of Sustainable Forestry Practices
- August 8, 2024
- 0 comment
The future of sustainable forestry practices holds immense promise, marked by innovative techniques and heightened environmental consciousness. As the world grapples with the impacts of climate change, sustainable forestry emerges as a pivotal solution for maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity. The integration of advanced technologies, such as remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS), is revolutionizing how we monitor and manage forests, allowing for precise tracking of forest health and growth patterns.

Additionally, the adoption of agroforestry, which combines agriculture and forestry to create symbiotic ecosystems, is gaining traction, promoting both economic and environmental benefits. Communities and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable forestry, leading to more robust policies and incentives that encourage responsible forest management. Education and awareness campaigns are empowering a new generation of foresters committed to sustainability, ensuring that forests remain resilient and productive for future generations.
With these advancements, sustainable forestry practices are poised to play a crucial role in mitigating climate change, conserving wildlife habitats, and ensuring the well-being of our planet.
List of Future of Sustainable Forestry Practices
- Use of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Agroforestry and Integrated Practices
- Policy and Community Engagement
- Educational Initiatives and Awareness
- Climate Change Mitigation
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Economic Impacts
- Future Prospects and Innovations
Use of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
The integration of remote sensing and GIS technologies is revolutionizing sustainable forestry. These tools provide accurate and comprehensive data on forest health, composition, and changes over time. By using satellite imagery and aerial data, foresters can monitor vast forest areas efficiently, identifying issues such as deforestation, disease outbreaks, and illegal logging activities. This technological leap allows for proactive management, ensuring that forests are maintained and restored with precision and care.
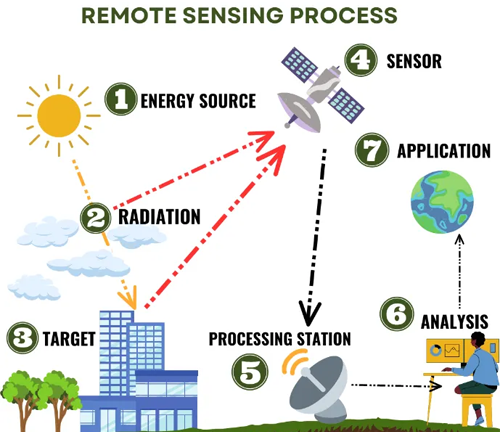
Advances in Data Analytics and Forest Management Software
Data analytics and sophisticated forest management software are becoming indispensable in the forestry sector. These advancements enable foresters to analyze complex data sets, predict trends, and make informed decisions. For instance, predictive modeling can forecast the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems, allowing for strategic planning and mitigation efforts. By harnessing the power of big data, sustainable forestry practices are becoming more effective, optimizing resource use and enhancing forest resilience.
Role of Drones and Satellite Imagery in Monitoring Forest Health
Drones and satellite imagery offer unparalleled capabilities in monitoring forest health. Drones can capture high-resolution images and videos, providing detailed insights into canopy structure, tree density, and signs of stress or disease. Satellite imagery, on the other hand, offers a broader perspective, enabling the tracking of large-scale forest changes and trends over time. Together, these technologies empower foresters to conduct thorough assessments and implement timely interventions, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of forests.
Agroforestry and Integrated Practices

Definition and Benefits of Agroforestry
Agroforestry, the practice of integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, offers numerous benefits for sustainable forestry. This approach enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, and increases carbon sequestration. Agroforestry systems also provide diversified income sources for farmers, contributing to economic stability and resilience. By blending agriculture and forestry, agroforestry creates multifunctional landscapes that support both ecological and economic goals.
Economic and Environmental Advantages
Agroforestry offers significant economic and environmental advantages. Economically, it diversifies income sources and reduces risks associated with single-crop farming. Environmentally, it enhances biodiversity, improves water retention, and reduces soil erosion. By creating resilient and productive landscapes, agroforestry contributes to sustainable development and climate change mitigation. The symbiotic relationship between trees and crops in agroforestry systems exemplifies the potential for harmony between human activities and natural ecosystems.
Policy and Community Engagement

Recent Policy Developments Supporting Sustainable Forestry
Recent policy developments are increasingly supporting sustainable forestry practices. Governments and international organizations are recognizing the critical role of forests in combating climate change and preserving biodiversity. Policies promoting sustainable forest management, conservation incentives, and reforestation initiatives are being implemented worldwide. These policy frameworks create an enabling environment for sustainable forestry, encouraging responsible practices and long-term stewardship of forest resources.
Role of Government and Non-Governmental Organizations
Governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play pivotal roles in advancing sustainable forestry. Governments provide regulatory frameworks, funding, and technical support for sustainable practices. NGOs, on the other hand, often spearhead conservation projects, advocate for policy changes, and engage communities in forest management. Collaborative efforts between these entities are crucial for the success of sustainable forestry initiatives, ensuring that diverse perspectives and expertise are integrated into forest conservation strategies.
Community-Led Initiatives and Participatory Forest Management
Community-led initiatives and participatory forest management are essential components of sustainable forestry. Engaging local communities in forest management fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more effective conservation outcomes. Participatory approaches ensure that local knowledge and needs are considered in decision-making processes. Examples of successful community-led initiatives include forest user groups in Nepal and community forestry projects in Mexico, where local involvement has resulted in improved forest health and livelihoods.
Educational Initiatives and Awareness

Importance of Education in Promoting Sustainable Practices
Education is vital for promoting sustainable forestry practices. By raising awareness about the importance of forests and sustainable management techniques, educational programs can inspire individuals and communities to take action. Schools, universities, and training centers play crucial roles in imparting knowledge and skills necessary for sustainable forestry. Educational initiatives also help to cultivate a new generation of environmentally conscious foresters committed to preserving our natural heritage.
Training Programs for New Generation Foresters
Training programs for aspiring foresters are essential for building capacity in sustainable forestry. These programs provide practical skills and theoretical knowledge on forest management, conservation techniques, and the use of modern technologies. By equipping future foresters with the tools and expertise needed for sustainable practices, training programs ensure the continued advancement and implementation of innovative forestry solutions.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Their Impact
Public awareness campaigns are instrumental in garnering support for sustainable forestry. Through various media channels, these campaigns educate the public about the benefits of forests, the threats they face, and the importance of sustainable management. Effective campaigns can mobilize communities, influence policy decisions, and drive positive changes in behavior. The impact of public awareness efforts is evident in increased community participation in conservation activities and greater support for sustainable forestry policies.
Climate Change Mitigation In Exciting Future

Role of Sustainable Forestry in Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable forestry plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in biomass and soil. By implementing sustainable practices such as reforestation, afforestation, and reduced-impact logging, foresters can enhance the carbon sequestration capacity of forests. These efforts contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and stabilizing the global climate.
Strategies for Enhancing Forest Resilience to Climate Change
Enhancing forest resilience to climate change is a key objective of sustainable forestry. Strategies include promoting species diversity, restoring degraded areas, and implementing adaptive management practices. By increasing the diversity and health of forest ecosystems, foresters can improve their ability to withstand and recover from climate-related disturbances. These resilience-building measures ensure that forests continue to provide essential ecosystem services in a changing climate.
Collaboration with Other Environmental Conservation Efforts
Collaboration with other environmental conservation efforts is essential for maximizing the impact of sustainable forestry. Integrating forestry initiatives with broader conservation programs, such as watershed management and wildlife protection, creates synergies that enhance overall ecosystem health. Collaborative approaches ensure that sustainable forestry practices are aligned with broader environmental goals, contributing to holistic and effective conservation outcomes.
Conservation of Biodiversity

Sustainable Practices for Protecting Wildlife Habitats
Sustainable forestry practices are vital for protecting wildlife habitats. By maintaining and restoring natural habitats, foresters support the survival and diversity of species. Practices such as selective logging, habitat corridors, and protected areas help to preserve critical habitats and minimize the impact of forestry activities on wildlife. Ensuring the coexistence of forestry operations and biodiversity conservation is a fundamental principle of sustainable forestry.
Integrating Conservation Goals with Forestry Management
Integrating conservation goals with forestry management is essential for achieving sustainable outcomes. This approach involves aligning forestry practices with biodiversity objectives, such as protecting endangered species, preserving genetic diversity, and maintaining ecosystem functions. By incorporating conservation priorities into forest management plans, foresters can balance the demands of resource use with the need to protect and enhance biodiversity.
Success Stories of Biodiversity Conservation Through Sustainable Forestry
Success stories of biodiversity conservation through sustainable forestry highlight the potential of this approach. In Costa Rica, sustainable forestry practices have led to the recovery of tropical forests and the resurgence of wildlife populations. Similarly, in the United States, the adoption of sustainable management techniques in national forests has improved habitat quality and supported diverse species. These examples demonstrate that sustainable forestry can be a powerful tool for biodiversity conservation.
Economic Impacts

Sustainable Forestry as a Driver of Green Economies
Sustainable forestry is a driver of green economies, providing economic benefits while preserving natural resources. By promoting responsible forest management, sustainable practices create opportunities for eco-friendly businesses, such as certified timber products, non-timber forest products, and ecotourism. These economic activities contribute to local and national economies, supporting livelihoods and fostering sustainable development.
Job Creation and Livelihood Opportunities
Sustainable forestry generates job creation and livelihood opportunities for communities. From forest management and conservation to value-added processing and eco-tourism, sustainable practices create diverse employment opportunities. These jobs not only provide income but also promote skills development and community resilience. By investing in sustainable forestry, societies can create a more equitable and sustainable economic future.
Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Sustainability
Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability is a central challenge for sustainable forestry. This balance can be achieved through practices that optimize resource use, minimize environmental impact, and enhance ecosystem services. Sustainable forestry provides a model for how economic activities can coexist with conservation goals, ensuring that forests continue to support both human and ecological well-being.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Emerging Trends and Future Technologies in Forestry
Emerging trends and future technologies in forestry promise to transform the field. Innovations such as precision forestry, bio-based products, and artificial intelligence are poised to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of forest management. These technologies enable more precise monitoring, better decision-making, and the development of sustainable products that reduce reliance on non-renewable resources. The future of forestry is one of continuous innovation and adaptation.
Predictions for the Future of Sustainable Forestry
Predictions for the future of sustainable forestry are optimistic. With ongoing advancements in technology, policy support, and public awareness, sustainable practices are expected to become the norm in forest management. Foresters will continue to play a crucial role in mitigating climate change, conserving biodiversity, and supporting sustainable development. The future will likely see more integrated and collaborative approaches to forestry, ensuring that forests remain healthy and productive.
Vision for a Sustainable and Resilient Forest Landscape
The vision for a sustainable and resilient forest landscape is one where forests thrive, supporting diverse species and ecosystems while providing essential resources for human well-being. This vision encompasses healthy, vibrant forests that are managed responsibly and sustainably. It involves communities actively participating in forest stewardship, innovative technologies enhancing management practices, and policies that support long-term conservation goals. The exciting future of sustainable forestry is one of hope, innovation, and a deep commitment to preserving our planet’s invaluable forest resources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is sustainable forestry?
Sustainable forestry is the practice of managing forest resources to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This involves maintaining the health and diversity of forest ecosystems while balancing ecological, economic, and social values.
2. How do remote sensing and GIS technologies benefit sustainable forestry?
Remote sensing and GIS technologies provide accurate and comprehensive data on forest health, composition, and changes over time. These tools enable precise monitoring, early detection of issues, and effective management of forest resources, helping to maintain and restore forest ecosystems.
3. What role do drones and satellite imagery play in forestry?
Drones and satellite imagery offer advanced capabilities for monitoring forest health and detecting changes. Drones capture high-resolution images and videos of forest areas, while satellite imagery provides a broader perspective, allowing for efficient and detailed assessments of forest conditions.
4. What is agroforestry and how does it contribute to sustainability?
Agroforestry is the practice of integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes. This approach enhances biodiversity, improves soil health, increases carbon sequestration, and provides diversified income sources for farmers, promoting both economic and environmental sustainability.
5. What are some examples of successful agroforestry projects?
Successful agroforestry projects include initiatives in Kenya, where agroforestry practices have improved soil fertility and crop yields, and in Brazil, where agroforestry systems have restored degraded lands and supported sustainable livelihoods for farmers.
6. How are recent policy developments supporting sustainable forestry?
Recent policy developments are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable forestry. Governments and international organizations are implementing policies that promote sustainable forest management, conservation incentives, and reforestation initiatives to support responsible forestry practices.
7. How can communities participate in sustainable forestry?
Communities can participate in sustainable forestry through community-led initiatives and participatory forest management. Engaging local communities in forest management fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more effective conservation outcomes.
8. Why is education important for sustainable forestry?
Education raises awareness about the importance of forests and sustainable management techniques, inspiring individuals and communities to take action. Training programs equip future foresters with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement sustainable practices.
9. How does sustainable forestry contribute to climate change mitigation?
Sustainable forestry helps mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration, maintaining forest health, and implementing practices that increase forest resilience. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in biomass and soil.
10. What are the economic benefits of sustainable forestry?
Sustainable forestry drives green economies by promoting responsible forest management and creating opportunities for eco-friendly businesses, such as certified timber products, non-timber forest products, and ecotourism. These activities support local and national economies and provide diverse employment opportunities.

Gilbert Griffin
Forestry AuthorGilbert Griffin is a forest management expert specializing in sustainable practices, forest health, conservation, and land management. With extensive knowledge in pest control, disease management, and habitat restoration, Gilbert develops strategies to preserve forest ecosystems and biodiversity. Passionate about the natural world, Gilbert adapts to changes in forest management and stays updated through continuous learning. Gilbert also provides seasonal advice to optimize forest care throughout the year.













Leave your comment