Sustainable Wood: Green Forestry Solutions
- July 29, 2024
- 0 comment
“Sustainable Wood: Green Forestry Solutions” encompasses a comprehensive approach to forestry that emphasizes environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility. This method prioritizes the careful management of forest resources to ensure their regeneration and long-term health. By adopting practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and the preservation of biodiversity, sustainable forestry aims to minimize ecological disruption and maintain the balance of forest ecosystems.

Additionally, it promotes the use of certified wood products, which are sourced from responsibly managed forests, thus supporting the conservation of natural habitats. Sustainable wood initiatives also involve community engagement and education, fostering a collective effort towards environmental sustainability. These strategies not only contribute to the mitigation of climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration but also support the livelihoods of communities that depend on forest resources. In essence, green forestry solutions offer a pathway to a more sustainable future, where the benefits of wood can be enjoyed without compromising the health of our planet.
Table of Content
- Principles of Sustainable Forestry
- Sustainable Forestry Practices
- Certification and Standards
- Environmental Benefits
- Economic and Social Impacts
- Challenges and Solutions
- Community Engagement and Education
- Future Directions
- FAQs
Sustainable Wood: Green Forestry Solutions
Principles of Sustainable Forestry

Definition and Goals of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry refers to the practice of managing forest resources in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The goals of sustainable forestry include maintaining the health and diversity of forest ecosystems, ensuring the ongoing availability of forest resources, and supporting the economic and social well-being of communities that rely on forests.
Key Principles: Environmental Stewardship, Economic Viability, Social Responsibility
Sustainable forestry is grounded in three key principles:
- Environmental Stewardship: This involves the careful management of forest ecosystems to preserve their health and biodiversity. Practices include protecting water resources, maintaining soil quality, and conserving wildlife habitats.
- Economic Viability: Sustainable forestry aims to provide economic benefits by ensuring that forest resources are used efficiently and responsibly. This includes generating income through sustainable harvesting practices and creating long-term economic opportunities for local communities.
- Social Responsibility: This principle emphasizes the importance of respecting the rights and needs of all stakeholders, including indigenous peoples, local communities, and future generations. Social responsibility also involves promoting fair labor practices and supporting community development.
Sustainable Forestry Practices

Selective Logging
Selective logging involves carefully choosing and removing specific trees from a forest, rather than clear-cutting large areas. This practice minimizes ecological disruption, helps maintain the forest structure, and supports the regeneration of the forest.
Reforestation and Afforestation
Reforestation involves planting trees in areas where forests have been depleted, while afforestation refers to establishing forests in areas where there were none previously. Both practices are essential for restoring degraded lands, increasing forest cover, and enhancing carbon sequestration.
Preservation of Biodiversity
Preserving biodiversity is a fundamental aspect of sustainable forestry. This includes protecting endangered species, maintaining a variety of plant and animal life, and ensuring that forest management practices do not harm the ecological balance.
Agroforestry and Mixed-Use Landscapes
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, promoting a harmonious coexistence between forestry and farming. Mixed-use landscapes combine different land uses, such as forestry, agriculture, and recreation, to maximize the benefits and sustainability of the land.
Certification and Standards

Importance of Certified Wood Products
Certified wood products come from forests that are managed according to strict environmental, social, and economic standards. These certifications assure consumers that the wood they purchase supports sustainable forestry practices.
Major Certification Bodies (e.g., FSC, PEFC)
Two major certification bodies are the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC). Both organizations set high standards for sustainable forest management and certify products that meet these criteria.
Criteria for Certification
Certification criteria typically include maintaining high conservation values, protecting biodiversity, ensuring sustainable harvest levels, and respecting the rights of indigenous peoples and local communities.
Environmental Benefits
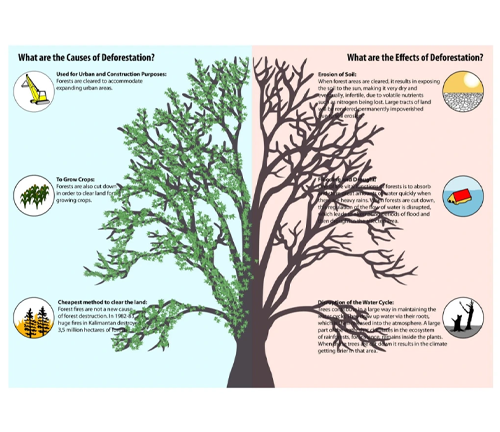
Reduced Ecological Disruption
Sustainable forestry practices minimize ecological disruption by maintaining the natural structure and function of forest ecosystems. This helps protect soil quality, water resources, and wildlife habitats.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Forests play a crucial role in sequestering carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas. Sustainable forestry enhances this process, helping mitigate climate change by absorbing more carbon and storing it in trees and soil.
Preservation of Natural Habitats and Biodiversity
Sustainable forestry practices protect natural habitats and preserve biodiversity. By maintaining healthy forest ecosystems, these practices ensure the survival of a wide range of plant and animal species.
Economic and Social Impacts
Supporting Local Economies and Communities
Sustainable forestry supports local economies by providing jobs and income through responsible harvesting and processing of forest products. It also helps sustain the livelihoods of communities that depend on forests.
Creating Sustainable Jobs in Forestry
Sustainable forestry creates long-term, stable jobs in forest management, conservation, and related industries. These jobs contribute to economic stability and growth in rural and forest-dependent areas.
Promoting Fair Trade and Ethical Practices
Sustainable forestry promotes fair trade and ethical practices by ensuring that workers are treated fairly, labor rights are respected, and communities benefit from forest resources. This includes fair wages, safe working conditions, and community involvement in decision-making processes.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Forestry
Challenges in sustainable forestry include illegal logging, land tenure issues, lack of enforcement of regulations, and economic pressures to overharvest. These challenges can undermine efforts to manage forests sustainably.
Solutions and Innovations in Green Forestry
Innovative solutions to these challenges include the development of advanced monitoring technologies, community-based forest management, and stronger enforcement of sustainable forestry regulations. Additionally, market incentives for certified wood products and international cooperation can help address these issues.
Community Engagement and Education

Role of Community Involvement in Sustainable Forestry
Community involvement is crucial for the success of sustainable forestry. Engaging local communities in forest management decisions ensures that their needs and knowledge are considered, leading to more effective and equitable outcomes.
Educational Initiatives and Awareness Programs
Educational initiatives and awareness programs help inform the public about the benefits of sustainable forestry. These programs can include school curricula, public workshops, and media campaigns that highlight the importance of responsible forest management.
Future Directions
Emerging Trends in Sustainable Forestry
Emerging trends in sustainable forestry include the integration of new technologies such as remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) for better forest monitoring and management. There is also a growing emphasis on the role of forests in climate change mitigation and adaptation.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological advancements are improving the efficiency and effectiveness of sustainable forestry practices. Innovations such as drones for forest monitoring, precision forestry techniques, and improved data analytics are helping foresters make better management decisions.
Policy Recommendations for Enhancing Sustainable Forestry
Policy recommendations for enhancing sustainable forestry include strengthening international agreements, improving forest governance, increasing funding for sustainable forestry projects, and promoting research and development. Additionally, policies should support market mechanisms that incentivize sustainable practices and ensure the rights and participation of local communities.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
1. What is sustainable wood?
Sustainable wood is sourced from forests that are managed in a way that ensures their long-term health and productivity. These practices aim to balance ecological, economic, and social benefits.
2. Why is sustainable forestry important?
Sustainable forestry is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, protecting ecosystems, and ensuring that forest resources are available for future generations. It also supports local economies and helps combat climate change through carbon sequestration.
3. What are the key principles of sustainable forestry?
The key principles include environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social responsibility. These principles guide the management of forest resources to achieve long-term sustainability.
4. What practices are involved in sustainable forestry?
Sustainable forestry practices include selective logging, reforestation, afforestation, preservation of biodiversity, and agroforestry. These practices help maintain the ecological balance and productivity of forests.
5. What is selective logging?
Selective logging involves removing specific trees based on criteria such as age, size, or species, rather than clear-cutting large areas. This method minimizes ecological disruption and promotes forest regeneration.
6. What is the role of certification in sustainable forestry?
Certification ensures that wood products come from responsibly managed forests. Major certification bodies like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) set standards for sustainable forest management.
7. How does sustainable forestry benefit the environment?
Sustainable forestry reduces ecological disruption, enhances carbon sequestration, and preserves natural habitats and biodiversity. These practices help mitigate climate change and protect vital ecosystems.
8. What are the economic and social impacts of sustainable forestry?
Sustainable forestry supports local economies by creating jobs and income through responsible harvesting. It also promotes fair trade, ethical practices, and the involvement of local communities in forest management.
9. What challenges does sustainable forestry face?
Challenges include illegal logging, land tenure issues, insufficient enforcement of regulations, and economic pressures to overharvest. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions and strong governance.
10. How can communities get involved in sustainable forestry?
Communities can participate in forest management decisions, engage in educational initiatives, and support sustainable practices through consumer choices and advocacy.
11. What are some successful examples of sustainable forestry projects?
Successful projects include sustainable logging and reforestation efforts in the Amazon, effective forest management practices in Scandinavian countries, and community-based forest management in various regions.
12. What is the future of sustainable forestry?
The future of sustainable forestry includes emerging trends like advanced monitoring technologies, increased focus on climate change mitigation, and stronger international cooperation. Continued innovation and policy support are essential for enhancing sustainable practices.
13. How can consumers support sustainable forestry?
Consumers can support sustainable forestry by purchasing certified wood products, advocating for responsible forest management, and participating in community initiatives that promote sustainable practices.

Gilbert Griffin
Forestry AuthorGilbert Griffin is a forest management expert specializing in sustainable practices, forest health, conservation, and land management. With extensive knowledge in pest control, disease management, and habitat restoration, Gilbert develops strategies to preserve forest ecosystems and biodiversity. Passionate about the natural world, Gilbert adapts to changes in forest management and stays updated through continuous learning. Gilbert also provides seasonal advice to optimize forest care throughout the year.








Leave your comment