San Juan National Forest
- December 29, 2023
- 0 comment
San Juan National Forest is a breathtaking wilderness area located in southwestern Colorado, covering over 1.8 million acres. It is a place of great natural beauty, with towering mountains, pristine streams, and dense forests. The region is rich in history and cultural heritage, with evidence of ancient civilizations, mining communities, and early explorers.
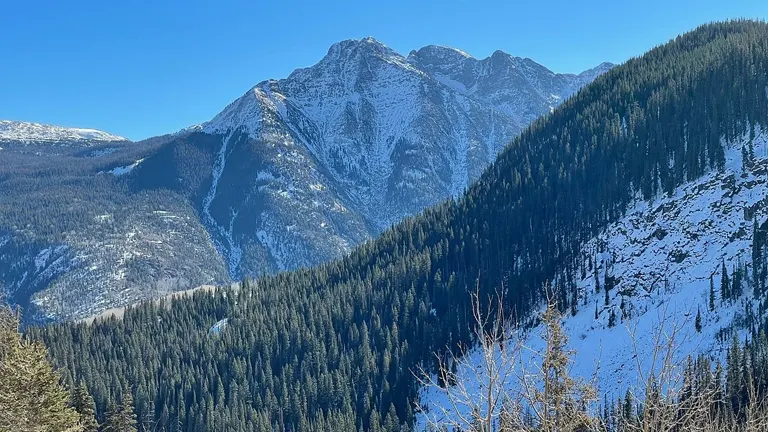

With its abundance of recreational opportunities, San Juan National Forest attracts visitors from all over the world who come to hike its trails, fish its rivers, camp under the stars, and marvel at its stunning scenery. Whether you are a seasoned adventurer or a nature lover seeking a peaceful escape, San Juan National Forest has something for everyone.
Characterizing Features of the San Juan National Forest
- Diverse Wilderness Areas: The San Juan National Forest boasts a mosaic of wilderness areas, each with its unique character. The Weminuche Wilderness, a centerpiece, sprawls over 499,771 acres and includes the iconic Chicago Basin, renowned for its four fourteeners. South San Juan Wilderness, with its rolling high plateaus and deep canyons, offers a distinct contrast. The Lizard Head Wilderness showcases the stunning Lizard Head Peak, a spire of volcanic rock, while Hermosa Creek Wilderness provides a more accessible yet equally enchanting backcountry experience.
- Colorado’s Largest Wilderness: At the heart of the San Juan National Forest lies the Weminuche Wilderness, claiming the title of Colorado’s largest wilderness area. Encompassing rugged terrains, alpine meadows, and over 500 miles of trails, it stands as a testament to the state’s commitment to preserving vast and untouched natural landscapes. Backpackers and outdoor enthusiasts flock to Weminuche to explore its vast expanses, offering a true wilderness experience.
- Historical Rail Journey: A distinctive feature of the San Juan National Forest is the Durango and Silverton Narrow Gauge Railroad, an operational steam train that winds its way through the forest. This historical relic, dating back to the mining era of the late 1800s, provides a nostalgic and scenic journey, immersing passengers in the forest’s beauty and transporting them back in time to an era of mining and exploration.
- Ancestral Puebloan Heritage: Chimney Rock National Monument, nestled within the San Juan National Forest, adds a layer of cultural significance. This archaeological site was once home to the ancestral Puebloans, and its twin rock spires align with celestial events. Preserving this historical treasure within the forest underscores the layered history of the region, connecting visitors to the ancient civilizations that once thrived in this landscape.
- Presidential Conservation Legacy: The San Juan National Forest stands as a living legacy of President Theodore Roosevelt’s commitment to conservation. Established in 1905, Roosevelt’s vision was to protect and manage these lands sustainably. Today, the forest reflects his foresight, offering a sanctuary for wildlife, recreational opportunities, and a testament to the enduring importance of preserving natural landscapes.
- Extensive Public Lands and Dispersed Camping: A notable feature of the San Juan National Forest is its vast public lands, enabling dispersed camping outside designated areas. This unique aspect allows visitors to immerse themselves in the wilderness, though it requires responsible camping practices. The freedom to camp in pristine landscapes, away from designated campgrounds, enhances the sense of connection to the natural surroundings.
- Rich Biodiversity and Wildlife Habitat: The San Juan National Forest’s diverse ecosystems provide a habitat for a rich array of flora and fauna. From elk and mule deer to rare species like lynx and pine martens, the forest supports a thriving biodiversity. This abundance of wildlife adds to the allure of the forest, offering opportunities for wildlife enthusiasts and photographers to witness these creatures in their natural habitat.
- Strategic Fire Mitigation Efforts: As part of its unique features, the San Juan National Forest actively engages in strategic fire mitigation efforts. Given the region’s susceptibility to wildfires, the forest management employs prescribed burns and other techniques to reduce the risk of catastrophic fires. This proactive approach underscores the commitment to maintaining a healthy and resilient ecosystem while minimizing the impact of natural disasters.
- Recreational Diversity: Beyond hiking and camping, the San Juan National Forest caters to a spectrum of outdoor interests. Mountain biking and gravel biking enthusiasts can explore designated trails, while anglers can cast their lines in the forest’s diverse water sources. The forest’s recreational diversity ensures that visitors with varying interests find avenues to connect with nature.
- Climbing Opportunities: The San Juan National Forest presents a unique playground for climbers of all skill levels. With diverse terrains, from boulders to technical ice walls, climbers can hone their skills against the backdrop of the forest’s stunning landscapes. This feature adds an adventurous dimension to the forest, inviting climbing enthusiasts to explore its natural vertical wonders.
History
The history of the San Juan National Forest is a tapestry woven with the threads of natural beauty, cultural significance, and a commitment to conservation. Established by President Theodore Roosevelt on June 3, 1905, the forest emerged in an era when environmental stewardship gained national attention. Theodore Roosevelt’s vision aimed to preserve the rugged landscapes of southwestern Colorado, creating a haven for both recreation and the protection of natural resources. Over the decades, the forest has played a crucial role in mitigating natural disasters like forest fires, reflecting the foresight embedded in its creation.
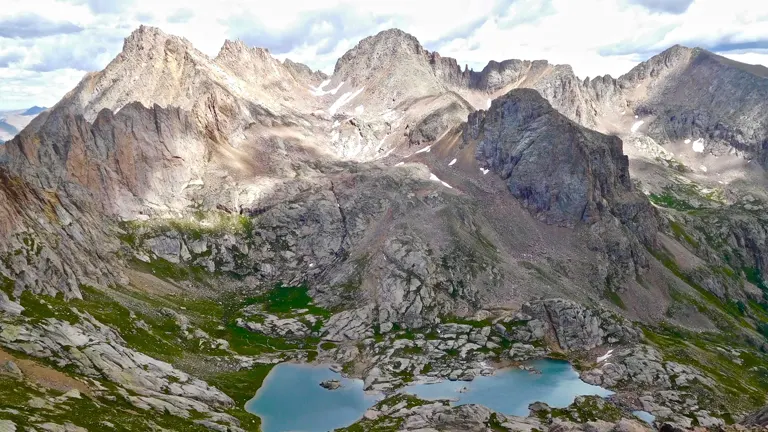

The Durango and Silverton Narrow Gauge Railroad, an enduring relic from the late 19th century, traverses the heart of the forest, providing a historical lens into the region’s mining past. In 2012, President Barack Obama added another layer to the forest’s legacy by designating part of it as Chimney Rock National Monument, recognizing its archaeological and cultural significance. Today, the San Juan National Forest stands as a living testament to a century of conservation efforts, offering a diverse tapestry of alpine wilderness, historic railways, and a commitment to preserving the natural wonders that define this corner of Colorado.
Importance in Conservation and Recreation of San Juan National Forest
The San Juan National Forest holds paramount importance in the realms of both conservation and recreation, embodying a delicate balance between preserving natural ecosystems and providing a sanctuary for outdoor enthusiasts. Established in 1905 by President Theodore Roosevelt, the forest has been a steadfast guardian of southwestern Colorado’s diverse flora and fauna. Its strategic location in the San Juan Mountains positions it as a critical component in the preservation of biodiversity, serving as a habitat for various species and contributing to regional ecological health. The forest’s commitment to conservation extends to proactive fire mitigation efforts, demonstrating a dedication to maintaining the delicate balance of its ecosystems.
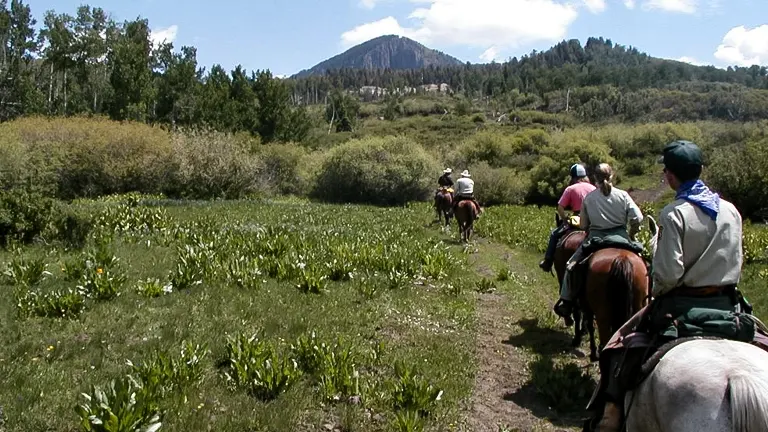

Simultaneously, the San Juan National Forest is a playground for recreational pursuits, offering a vast network of trails for hikers, backpackers, and mountain bikers. The historic Durango and Silverton Narrow Gauge Railroad provide a unique journey through time, while dispersed camping allows for an immersive connection with nature. By seamlessly intertwining conservation initiatives with recreational opportunities, the San Juan National Forest stands as a model for sustainable land management, inviting visitors to both appreciate its natural wonders and actively participate in the ongoing legacy of preservation.
Unique Location of San Juan National Forest
Located in the rugged embrace of southwestern Colorado, the San Juan National Forest occupies a truly unique and captivating location. Stretching across 1,878,846 acres, the forest spans a diverse array of landscapes in Archuleta, Conejos, Dolores, Hinsdale, La Plata, Mineral, Montezuma, Rio Grande, San Miguel, and San Juan Counties. Bordered by the Uncompahgre National Forest to the north and the Rio Grande National Forest to the east, it encompasses most of the southern expanse of the San Juan Mountains, showcasing alpine vistas, dense pine forests, and cascading waterfalls.
The forest’s strategic position west of the Continental Divide not only grants it access to some of Colorado’s highest peaks but also contributes to its unique microclimates and biodiversity. This geographical tapestry not only renders the San Juan National Forest a haven for outdoor enthusiasts but also underscores its significance in regional conservation efforts, as it serves as a vital link in the interconnected web of mountain ecosystems within the American West.
Diverse Vegetation and Unique Plant Species
- Engelmann Spruce (Picea engelmannii): Dominating the high-altitude landscapes of the San Juan National Forest, the Engelmann spruce thrives in subalpine and alpine ecosystems. Its gracefully drooping branches and cones contribute to the forest’s picturesque scenery, playing a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of these high-altitude environments.
- Quaking Aspen (Populus tremuloides): Blanketing vast areas with shimmering golden leaves in the fall, the quaking aspen is a deciduous marvel in the San Juan National Forest. Forming extensive groves, these trees are not only aesthetically pleasing but also essential for wildlife, providing habitat and sustenance for various species.
- Colorado Blue Spruce (Picea pungens): Adding a touch of vibrant blue-green to the forest’s palette, the Colorado blue spruce is well-adapted to the San Juan National Forest’s montane and subalpine zones. Its ornamental value, coupled with its resilience to diverse climates, makes it a hallmark of the region’s diverse vegetation.
- Engelmann Oak (Quercus engelmannii): Found in lower elevations, the Engelmann oak contributes to the forest’s biodiversity. Its dark green foliage provides shelter for numerous bird species, while the acorns sustain various mammals. This deciduous oak is a testament to the varied microclimates within the forest.
- Columbian Monkshood (Aconitum columbianum): Flourishing in moist meadows and near water sources, the Columbian monkshood is a distinctive wildflower in the San Juan National Forest. Characterized by its hooded, deep blue-purple flowers, this plant adds a splash of color to the understory and is crucial for pollinators.
- Alpine Forget-Me-Not (Eritrichium nanum): Thriving in the alpine tundra of the San Juan Mountains, the alpine forget-me-not graces the landscape with its small, sky-blue flowers. This hardy perennial symbolizes the resilience of plant life in the challenging high-altitude environments of the national forest.
- Mountain Mahogany (Cercocarpus montanus): Adapting to the drier slopes and higher elevations, the mountain mahogany is a sturdy shrub with distinctive feathery seeds. Its presence in the San Juan National Forest adds to the diversity of woody vegetation, playing a role in soil stabilization and erosion control.
- Fendler’s Barberry (Berberis fendleri): Flourishing in the lower elevations and rocky slopes, Fendler’s barberry displays yellow flowers and red berries. This deciduous shrub is part of the unique plant community in the forest, attracting birds and insects with its vibrant blooms.
- Rocky Mountain Juniper (Juniperus scopulorum): Scattered across the landscape, the Rocky Mountain juniper is well-adapted to the varied terrains of the San Juan National Forest. Its aromatic, scale-like leaves and berry-like cones contribute to the biodiversity of the forest, providing food for wildlife.
- Mountain Gentian (Gentiana parryi): Flourishing in alpine meadows and rocky slopes, the mountain gentian is a striking wildflower with deep blue, trumpet-shaped blooms. Its presence underscores the delicate beauty of high-altitude ecosystems within the San Juan National Forest.
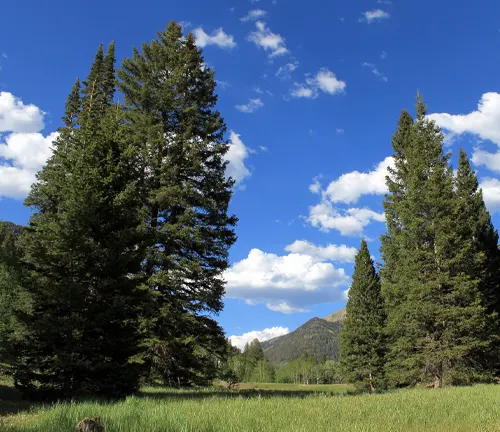


Different Species of Mushrooms in San Juan National Forest
- Chanterelle (Cantharellus cibarius): The San Juan National Forest hosts the golden treasures of chanterelle mushrooms, scientifically known as Cantharellus cibarius. Thriving in the forest’s moist and rich soils, these mushrooms are prized for their delicate, apricot-like flavor. Harvested by foragers, chanterelles add culinary delight to the diverse ecosystem of the forest.
- Morel Mushroom (Morchella): Various species of morel mushrooms, belonging to the Morchella genus, emerge in the forest’s springtime landscape. Recognizable by their distinctive honeycomb appearance, morels are highly sought after by foragers and chefs alike for their unique texture and rich, earthy flavor.
- Boletus Edulis (Boletus edulis): Commonly known as the king bolete or porcini, Boletus edulis graces the San Juan National Forest with its broad, chestnut-colored cap and thick stem. Widely appreciated in culinary circles, this mushroom forms symbiotic relationships with the forest’s trees, contributing to the intricate web of mycorrhizal connections.
- Amanita Muscaria (Amanita muscaria): Adding a touch of intrigue to the forest floor, the iconic Amanita muscaria, known as the fly agaric, displays vibrant red caps adorned with white speckles. While visually striking, this mushroom contains compounds that make it toxic, emphasizing the need for caution and proper identification when exploring the forest.
- Lobster Mushroom (Hypomyces lactifluorum): Transforming the appearance of other mushrooms it parasitizes, the lobster mushroom, scientifically identified as Hypomyces lactifluorum, exhibits vibrant orange hues. Often found in coniferous forests, its unique texture and seafood-like flavor make it a prized find for those scouring the forest floor.
- Russula Varieties (Russula): The San Juan National Forest is home to various Russula species, presenting a diverse array of cap colors and textures. These mycorrhizal mushrooms contribute to the forest’s ecological health by forming beneficial partnerships with trees, aiding in nutrient exchange.
- Turkey Tail Mushroom (Trametes versicolor): Adorning dead and fallen trees, the turkey tail mushroom, scientifically named Trametes versicolor, displays a spectrum of colors resembling a wild turkey’s tail feathers. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, this mushroom is studied for its potential medicinal properties, contributing to the forest’s ecological and pharmaceutical significance.
- Shaggy Mane Mushroom (Coprinus comatus): The shaggy mane mushroom, or Coprinus comatus, graces the San Juan National Forest with its distinctive appearance. Recognized for its tall, shaggy cap and deliquescing gills, this mushroom is a common sight in open woodlands and grassy areas, playing a role in the forest’s decomposition processes.
- Hedgehog Mushroom (Hydnum repandum): The hedgehog mushroom, scientifically known as Hydnum repandum, adds diversity to the forest floor with its toothed spines instead of traditional gills. This edible mushroom is cherished for its sweet, nutty flavor and often finds its way into culinary endeavors of those exploring the forest for wild edibles.
- Reishi Mushroom (Ganoderma): Certain species of the Ganoderma genus, commonly known as reishi mushrooms, find their habitat in the San Juan National Forest. Revered in traditional medicine, reishi mushrooms are recognized for potential health benefits, contributing to the forest’s role not only in biodiversity but also in the exploration of natural remedies.
Fauna
- Rocky Mountain Elk (Cervus canadensis nelsoni): The majestic Rocky Mountain elk, scientifically classified as Cervus canadensis nelsoni, roams the diverse landscapes of the San Juan National Forest. With its iconic antlers and impressive size, this herbivore plays a key role in shaping the forest’s ecosystems through its browsing habits and interactions with plant life.
- Mule Deer (Odocoileus hemionus): A common sight in the forest, the mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) gracefully navigates through its varied terrains. Adapted to the San Juan National Forest’s diverse vegetation, these herbivores contribute to the delicate balance of the ecosystem and are frequently encountered by visitors.
- American Black Bear (Ursus americanus): The American black bear, scientifically known as Ursus americanus, finds refuge in the wooded areas of the San Juan National Forest. These omnivores play a vital role in seed dispersal and nutrient cycling, contributing to the health and biodiversity of the forest ecosystem.
- Mountain Lion (Puma concolor): Stealthy and elusive, the mountain lion (Puma concolor) is a top predator in the San Juan National Forest. Also known as puma or cougar, these carnivores play a crucial role in regulating herbivore populations, ensuring the balance of the forest’s ecosystems.
- Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus): Soaring high above the forested canopies, the bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) is a symbol of the avian diversity in the San Juan National Forest. These majestic raptors contribute to the ecological health of the region by playing a role in the food web and indicating the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
- Cutthroat Trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii): The San Juan National Forest is home to the native cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii), inhabiting the clear mountain streams and lakes. These fish are crucial indicators of water quality and serve as a prized catch for anglers, contributing to the recreational value of the forest’s water bodies.
- Abert’s Squirrel (Sciurus aberti): Among the treetops of the ponderosa pine forests, Abert’s squirrel (Sciurus aberti) is a charismatic resident of the San Juan National Forest. With its distinctive tufted ears, this species plays a role in seed dispersal, contributing to the regeneration of the forest’s plant life.
- Peregrine Falcon (Falco peregrinus): The San Juan National Forest provides habitat for the peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus), a magnificent bird of prey. These falcons are known for their incredible speed and aerial hunting prowess, contributing to the forest’s avian diversity and acting as natural controllers of small bird and mammal populations.
- American Marten (Martes americana): The American marten (Martes americana) is a small carnivore that inhabits the dense forests of the San Juan National Forest. With its sleek fur and agile movements, the marten is an essential part of the forest’s ecosystem, contributing to the control of rodent populations.
- Yellow-bellied Marmot (Marmota flaviventris): Basking in t
- he sun on rocky outcrops, the yellow-bellied marmot (Marmota flaviventris) is a charismatic mammal found in the alpine and subalpine zones of the San Juan National Forest. These social animals contribute to the nutrient cycling of alpine ecosystems and are a delight for wildlife enthusiasts exploring the higher elevations of the forest.
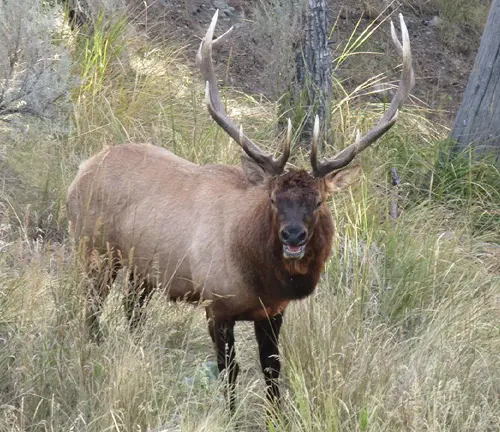
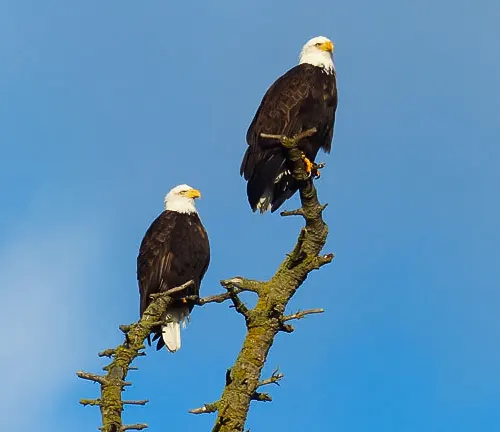


Importance as a Wildlife Corridor and Habitat for Threatened Species
The San Juan National Forest plays a pivotal role as a vital wildlife corridor and habitat, fostering biodiversity and offering a refuge for various species, including those facing threats to their survival. Serving as a crucial linkage between different ecosystems, the forest allows for the movement of wildlife, enabling genetic diversity and maintaining healthy populations. This connectivity is particularly significant for large mammals such as the Rocky Mountain elk and mule deer, which rely on expansive territories for their seasonal migrations.
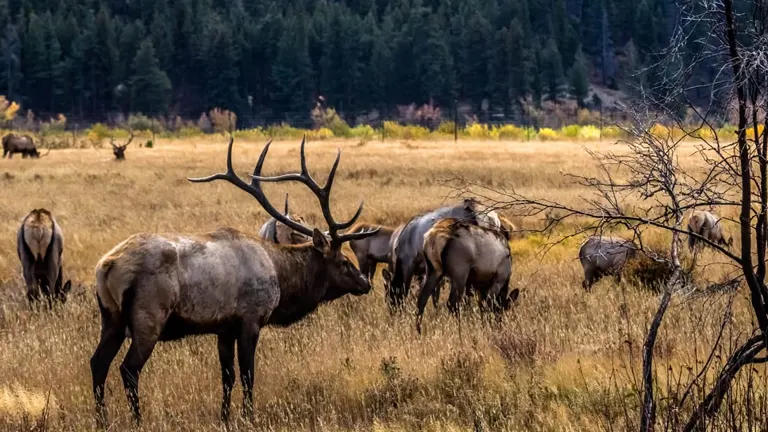

Additionally, the forest provides essential habitat for threatened and sensitive species, contributing to their conservation. The presence of the American black bear, mountain lion, and the elusive lynx underscores the forest’s importance as a haven for species facing challenges elsewhere. Avian diversity is also noteworthy, with species like the peregrine falcon finding suitable nesting sites in the forest’s cliffs and canyons. As a habitat for threatened cutthroat trout in its pristine streams, the San Juan National Forest not only supports aquatic life but also acts as a refuge for anglers and wildlife enthusiasts. This intricate interplay of ecosystems and the protection it affords to threatened and endangered species highlight the forest’s indispensable role in regional conservation efforts and the broader landscape of the American West.
Activities in San Juan National Forest for Visitors
1. Hiking
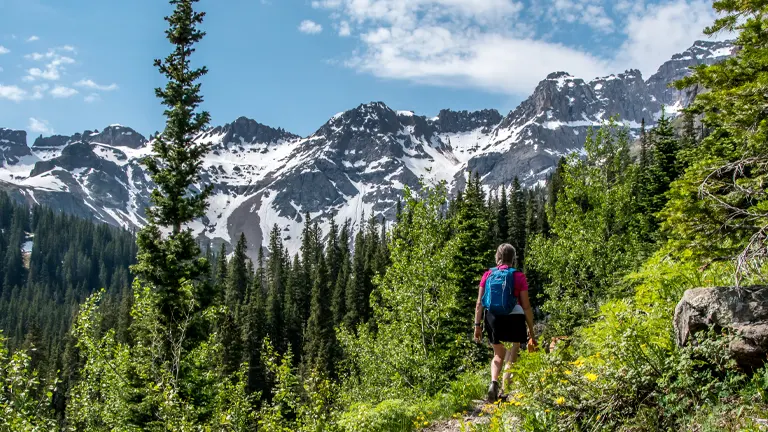

Hiking enthusiasts will find a paradise of trails crisscrossing the San Juan National Forest. From leisurely strolls through alpine meadows to challenging ascents up mountain peaks, the forest offers a diverse range of hiking experiences. Trails like the Colorado Trail provide stunning vistas of the surrounding mountains, while local paths offer glimpses into the unique flora and fauna that call this forest home.
2. Backpacking
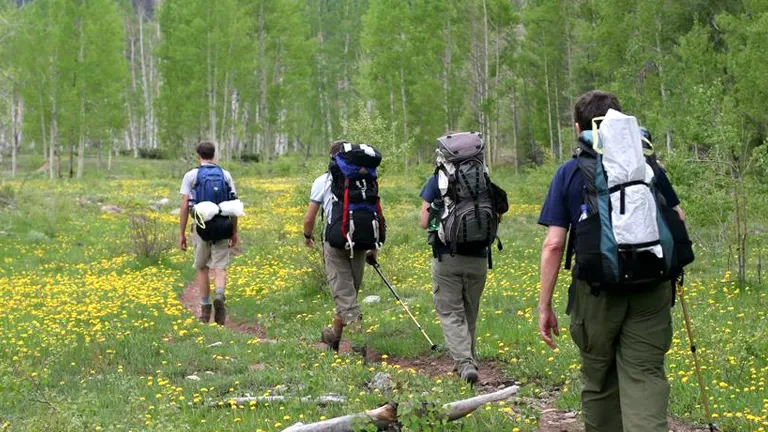

For those seeking a more immersive wilderness experience, backpacking in the San Juan National Forest unveils the true grandeur of its landscapes. With the expansive Weminuche Wilderness at its heart, backpackers can explore high alpine terrain, pristine lakes, and untouched backcountry, making every journey a memorable adventure into the heart of Colorado’s wilderness.
3. Mountain Biking and Gravel Biking
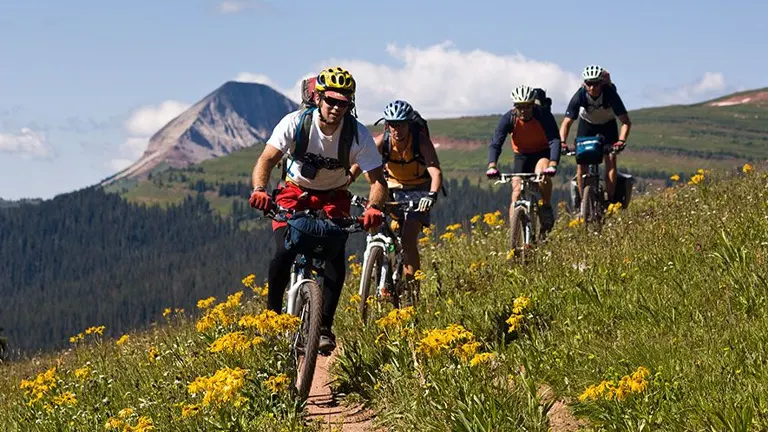

The San Juan National Forest caters to cycling enthusiasts with designated trails for both mountain biking and gravel biking. Whether navigating challenging mountain paths or cruising along forest service roads, bikers can enjoy the exhilarating experience of exploring the forest on two wheels. Proper safety equipment is essential, given the varied terrain and potential challenges encountered.
4. Dispersed Camping
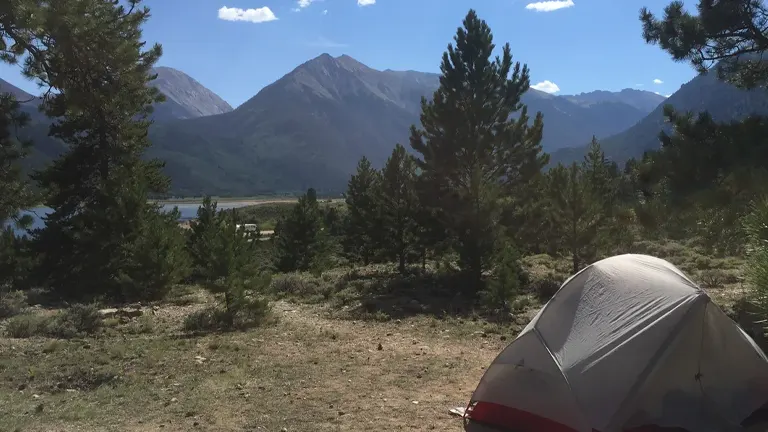

Embracing the spirit of exploration, dispersed camping in the San Juan National Forest allows visitors to set up camp beyond designated areas. This unique opportunity allows for a more intimate connection with nature, though it comes with the responsibility of leaving no trace and ensuring a minimal impact on the environment. The freedom to camp in pristine landscapes enhances the sense of solitude and adventure.
5. Hunting
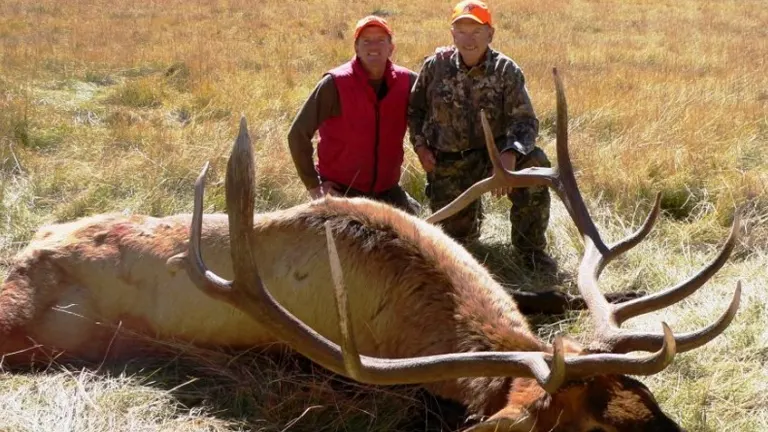

The San Juan National Forest offers a wide variety of game, making it a sought-after destination for hunters. From big game like elk and mule deer to game birds such as grouse, the forest provides a challenging and rewarding experience for those seeking both sustenance and trophies. All hunters must adhere to regulations, ensuring responsible and sustainable practices.
6. Fishing
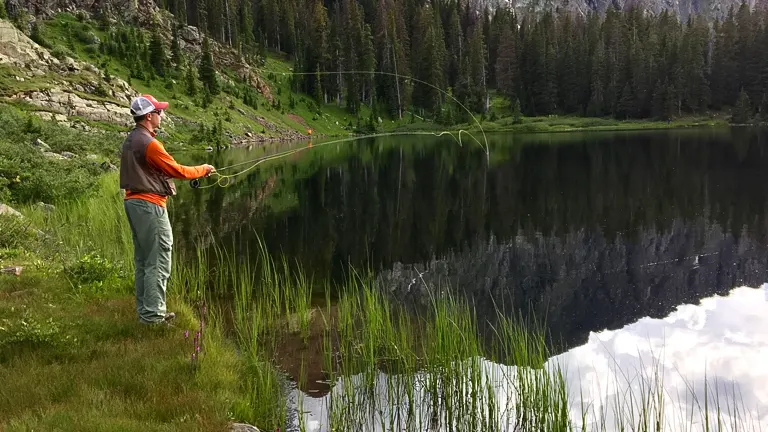

With numerous lakes, rivers, and ponds scattered across its expanse, the San Juan National Forest is a haven for fishing enthusiasts. Whether casting a line in crystal-clear streams for native cutthroat trout or trying to reel in a variety of fish from lakes, a valid Colorado fishing license is required, contributing to the conservation and management of these aquatic ecosystems.
7. Off-Highway Vehicle (OHV) Riding
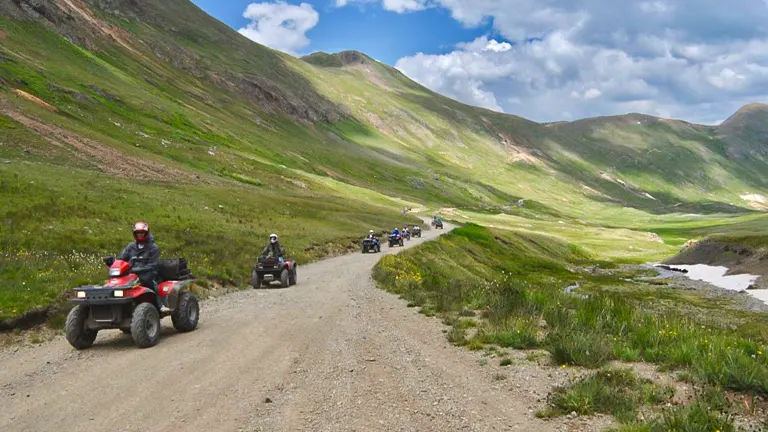

Adventure-seekers can explore the rugged beauty of the San Juan National Forest on designated trails for Off-Highway Vehicles (OHVs). This provides an alternative means of experiencing the forest, allowing visitors to venture further and faster, uncovering hidden gems and enjoying the thrill of off-roading. Proper permits and registrations are essential for both in-state and out-of-state OHVs.
8. Mushroom Foraging
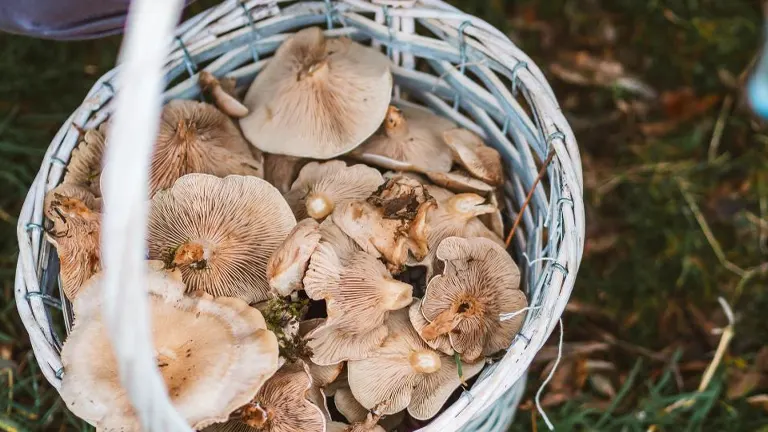

The forest’s diverse ecosystems offer a unique experience for mushroom foragers. From edible varieties like chanterelles to visually stunning, albeit toxic, species such as Amanita muscaria, mushroom foraging in the San Juan National Forest is a captivating pursuit. Caution and proper identification, preferably guided by an experienced forager, are crucial to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience.
9. Climbing
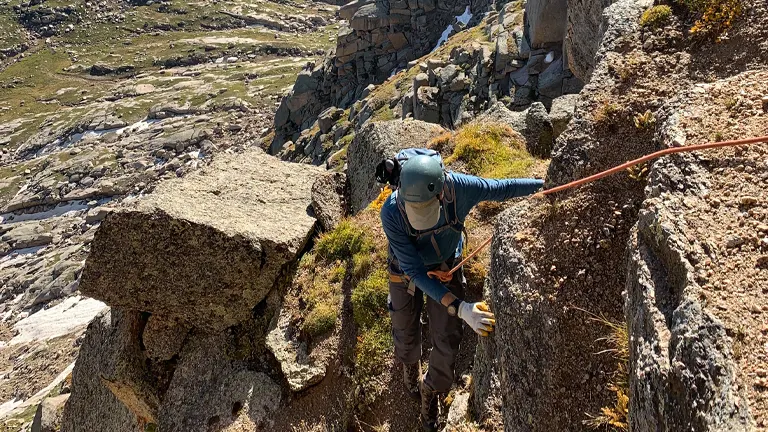

The San Juan National Forest provides climbing enthusiasts with a playground of diverse terrains. From simple boulders with ample handholds to technically challenging ice walls, climbers can test their skills against the backdrop of the forest’s stunning landscapes. The forest offers opportunities for climbers of all expertise levels, making it an attractive destination for those seeking vertical adventures.
10. Wildlife Viewing
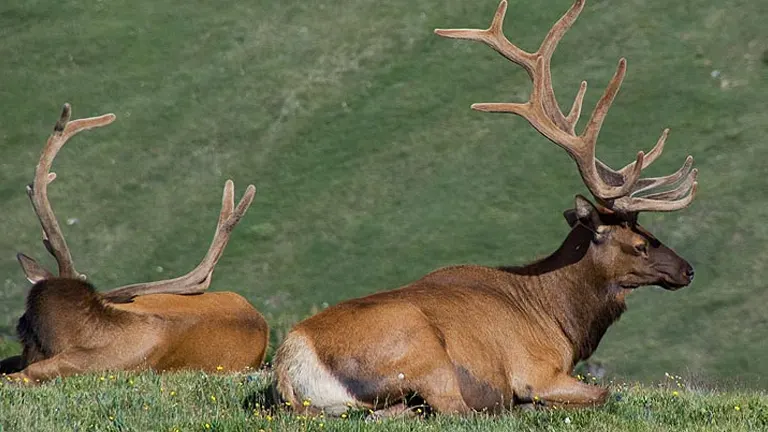

The rich biodiversity of the San Juan National Forest makes it a prime location for wildlife viewing. Whether observing elk in their natural habitat, spotting birds of prey soaring overhead, or catching glimpses of elusive species like the American marten, the forest provides opportunities for nature enthusiasts and photographers to connect with the region’s remarkable fauna. Wildlife viewing is an activity that emphasizes respect for animals and their habitats, promoting responsible and ethical interactions.
Conservation and Management
- Prescribed Burns and Fire Management: The San Juan National Forest engages in proactive fire management through prescribed burns. Recognizing the region’s susceptibility to wildfires, the forest implements controlled burns to reduce accumulated fuels and mitigate the risk of catastrophic wildfires. This strategic approach helps maintain a healthy ecosystem, regenerate certain plant species, and protect against uncontrolled infernos.
- Wildlife Habitat Protection: Conservation efforts in the San Juan National Forest prioritize the protection of wildlife habitats. By preserving diverse ecosystems, from alpine meadows to dense forests, the forest management ensures the availability of suitable habitats for a wide array of species. This approach contributes to biodiversity and supports the intricate web of relationships within the forest.
- Invasive Species Management: To safeguard the integrity of native ecosystems, the San Juan National Forest actively manages invasive species. Whether it’s non-native plants or pests that pose a threat to local flora and fauna, the forest employs measures to control and eradicate invasive species. This helps maintain the balance of the ecosystem and ensures the survival of native plant and animal species.
- Trail Maintenance and Erosion Control: The extensive trail system in the San Juan National Forest receives meticulous attention to ensure sustainable recreational access. Trail maintenance activities include erosion control measures to prevent soil degradation and protect water quality. By striking a balance between human enjoyment and environmental preservation, the forest management enhances the longevity and health of the trail system.
- Water Quality Management: Recognizing the importance of clean water sources, the San Juan National Forest prioritizes water quality management. Measures are implemented to prevent contamination and ensure that streams, rivers, and lakes within the forest maintain high water quality standards. This commitment is essential not only for the health of aquatic ecosystems but also for the enjoyment and safety of visitors.
- Timber Harvesting and Sustainable Forestry: Timber harvesting in the San Juan National Forest follows principles of sustainable forestry. By carefully managing timber resources, the forest ensures that logging activities are conducted in a manner that maintains the long-term health of the forest. Sustainable forestry practices contribute to both economic and ecological goals, supporting local industries while preserving the integrity of the ecosystem.
- Educational Outreach and Visitor Awareness: Conservation efforts extend beyond forest management practices to include educational outreach and visitor awareness programs. By informing the public about the delicate balance of the ecosystem, the importance of Leave No Trace principles, and the significance of responsible recreation, the forest management fosters a sense of stewardship among visitors. This proactive approach encourages sustainable interactions with the environment.
- Cultural Resource Preservation: Beyond natural resources, the San Juan National Forest is rich in cultural heritage. Efforts are directed towards preserving archaeological sites, historic structures, and artifacts. This commitment ensures that the forest not only serves as a natural sanctuary but also protects and showcases the historical and cultural significance embedded in its landscapes.
- Conservation of Threatened and Endangered Species: The San Juan National Forest plays a crucial role in the conservation of threatened and endangered species. Through habitat preservation, monitoring programs, and collaborative efforts with conservation organizations, the forest management strives to ensure the survival and recovery of species facing challenges to their existence. This commitment aligns with broader regional and national conservation initiatives.
- Collaborative Partnerships and Stakeholder Engagement: Recognizing the interconnected nature of conservation, the San Juan National Forest actively engages in collaborative partnerships and stakeholder involvement. Working with local communities, tribes, environmental organizations, and governmental agencies, the forest management fosters a collective approach to conservation. This collaborative ethos ensures that diverse perspectives contribute to the sustainable management of the forest for current and future generations.
Recommendation
I strongly encourage you to venture into the San Juan National Forest for a mesmerizing fusion of natural splendor and cultural importance. This forest, celebrated for its varied ecosystems, iconic landmarks, and recreational possibilities, provides a distinctive and engaging journey. Engage in contemplative outdoor pursuits like hiking and observing wildlife, actively playing a role in the continuous conservation initiatives. The picturesque trails, historical points of interest, and cooperative conservation initiatives position the San Juan National Forest as an essential destination for individuals in search of a seamless blend of nature and recreational discovery.
Conclusion
The San Juan National Forest stands as a testament to the remarkable beauty and ecological diversity found in the heart of southwestern Colorado. From its towering peaks and lush alpine meadows to the intricacies of its dense forests, the forest offers an immersive experience that goes beyond the ordinary. Its commitment to conservation, evident through proactive management practices and collaborative efforts, ensures the preservation of delicate ecosystems and the protection of threatened species. As visitors explore the vast network of trails, engage in outdoor activities, and witness the historical and cultural richness woven into the landscape, the San Juan National Forest becomes more than a destination—it becomes a sanctuary for nature enthusiasts, a haven for wildlife, and a living tapestry of both natural and cultural heritage. This is a place where the echoes of the past resonate with the vibrant life of the present, inviting all who enter to embrace the enduring spirit of exploration and conservation. In every rustling leaf, bubbling stream, and panoramic vista, the San Juan National Forest unfolds a story of resilience, interconnectedness, and the enduring allure of the great outdoors.
FAQs
- What rare flora and fauna can be found exclusively in San Juan National Forest?
The forest boasts unique plant species like the elusive San Juan snakeweed and the vibrant flame azalea. Rare sightings of the Mexican spotted owl and the San Juan subspecies of the cutthroat trout add to the forest’s distinct ecological tapestry. - How does San Juan National Forest celebrate its diverse cultural history?
Beyond traditional interpretive centers, the forest hosts cultural events like the annual Indigenous Peoples’ Day, highlighting the deep connection between the land and indigenous communities. Visitors can engage in interactive experiences, including storytelling sessions and cultural workshops. - Are there any hidden gems or secret spots that locals frequent in San Juan National Forest?:
Locals often cherish secluded spots like the ethereal Emerald Lake, known for its emerald-green waters. Off-the-beaten-path trails, such as the Whispering Pines Loop, offer a quieter escape, revealing the forest’s lesser-known wonders. - How does San Juan National Forest balance timber harvesting with preserving its ancient trees?
The forest employs innovative selective harvesting techniques that prioritize the preservation of ancient trees, ensuring the longevity of old-growth habitats. Sustainable forestry practices guarantee that logging activities are in harmony with the forest’s ecological resilience. - Can visitors participate in citizen science projects to contribute to San Juan National Forest’s research efforts?
Absolutely! The forest encourages citizen participation in projects like the annual BioBlitz, where visitors become temporary researchers, documenting flora and fauna. This collaborative approach fosters a deeper connection between visitors and the ongoing scientific exploration of the forest. - Are there any mysterious legends or folklore associated with San Juan National Forest?
Local lore tells of the mystical “Ghost Trees” deep within the forest, said to shimmer in the moonlight. While folklore adds an enchanting layer to the forest’s mystique, ecologists explain the phenomenon as a unique bioluminescent fungi found in certain areas. - How does San Juan National Forest cater to extreme adventure seekers beyond standard recreational activities?
For the adrenaline junkies, the forest offers extreme activities like heli-skiing in the pristine backcountry of the San Juan Mountains. This unparalleled experience provides access to untouched powder and challenging terrain for the ultimate thrill. - Can visitors participate in nighttime activities in San Juan National Forest?
Absolutely! The forest hosts moonlit interpretive strolls and stargazing events. The Cosmic Campout allows adventurous souls to experience the forest’s nocturnal magic, accompanied by expert guides pointing out constellations and sharing tales of celestial wonders.
San Juan National Forest is a true gem of the American wilderness, offering visitors a chance to experience the beauty and majesty of nature at its finest. As you explore its rugged terrain, you will be transported to a world of pristine beauty and solitude, where the only sounds you will hear are the rustling of leaves, the rush of a mountain stream, and the call of wild animals. Whether you come to hike, fish, camp, or simply relax and enjoy the scenery, San Juan National Forest is a place that will capture your heart and leave you with memories that will last a lifetime. So come and discover the wonders of this magnificent wilderness area and experience the magic of San Juan National Forest for yourself.














Leave your comment