Nettle Plant
- December 22, 2023
- 0 comment
The nettle plant, scientifically known as Urtica dioica, is a versatile and often misunderstood herbaceous perennial that belongs to the Urticaceae family. Widely distributed across Europe, Asia, North America, and Africa, nettles are renowned for their stinging hairs that release irritating chemicals upon contact with the skin. Despite their prickly reputation, nettles have been valued for centuries for their myriad of uses.
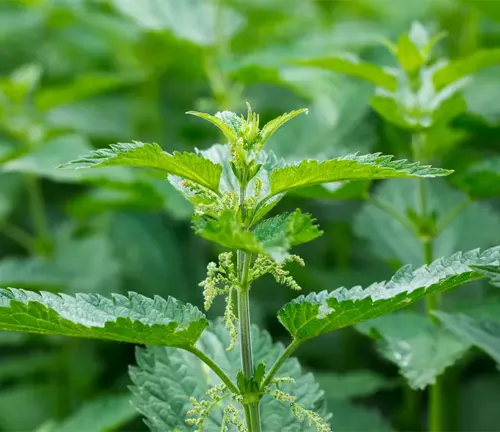

Rich in vitamins A and C, iron, and other essential minerals, nettles have been embraced for their nutritional benefits. Culinary enthusiasts incorporate young nettle leaves into soups, teas, and salads, offering a unique, earthy flavor. Medicinally, nettles are recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties and are traditionally used to alleviate conditions like arthritis and allergies. Moreover, nettle fibers have historically been woven into textiles, and the plant has been cultivated for its potential as a sustainable source of biofuel.

Beyond their utilitarian purposes, nettles also play a crucial role in ecosystems, serving as habitat and food for various insects and butterflies. Despite their occasional sting, nettles stand as a testament to nature’s multifaceted offerings, intertwining practicality, nutrition, and ecological significance.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Urtica dioica |
| Family | Urticaceae |
| Type | Herbaceous perennial |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, Africa |
| Stinging Hairs | Present, release irritating chemicals |
| Nutritional Content | Rich in vitamins A and C, iron, minerals |
| Culinary Use | Young leaves used in soups, teas, salads |
| Medicinal Properties | Anti-inflammatory, used for arthritis, allergies |
| Traditional Uses | Textile production, potential biofuel source |
| Ecological Role | Habitat and food for insects, butterflies |
Unveiling the Nettle Plant’s Intriguing Features
The nettle plant, scientifically known as Urtica dioica, stands as a botanical marvel with unique characteristics. A herbaceous perennial belonging to the Urticaceae family, this resilient plant boasts stinging hairs that release irritating chemicals upon contact. Beyond its prickly reputation, delve into the botanical intricacies that make the nettle plant a fascinating subject of study.
Nettle Plant’s Graceful Presence in Nature’s Tapestry
Amidst the woodlands of Europe, Asia, North America, and Africa, the nettle plant emerges with woodland elegance. Despite its stinging nature, the plant contributes to the lush tapestry of nature, providing habitat and sustenance for various insects and butterflies. Explore the graceful presence of the nettle plant in diverse ecosystems, weaving itself into the intricate fabric of the natural world.
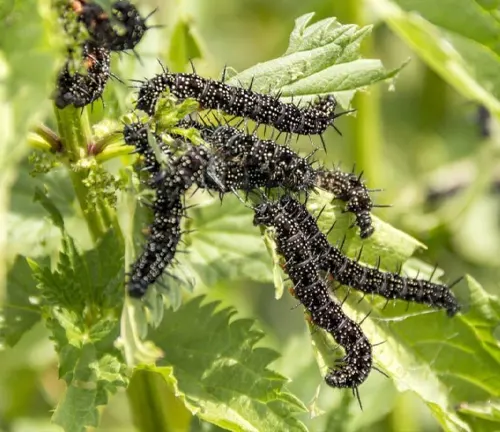


Nettle Plant’s Role in Sustaining Biodiversity
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the nettle plant plays a crucial role in sustaining biodiversity. Serving as a vital habitat and food source for insects and butterflies, it forms an integral part of the ecological web. Uncover the ecological importance of the nettle plant and its interconnected relationship with the diverse life forms that depend on it.
Nurturing the Nettle for Future Generations
As interest in the nettle plant grows, cultivation practices become essential for its conservation. Delve into the methods of cultivating nettles and the importance of conservation efforts to ensure the plant’s survival. Explore how cultivation practices can strike a balance between meeting human needs and preserving the delicate ecosystems where nettles thrive.

Nettle Plant’s Role in Maintaining Environmental Balance
One of the remarkable qualities of the nettle plant is its contribution to soil stabilization. Discover how the plant’s extensive root system helps prevent soil erosion, making it a valuable ally in maintaining environmental balance. Unearth the nettle plant’s role in stabilizing soil and preventing degradation, showcasing its significance in sustainable land management.

Textiles to Culinary Delights
The nettle plant transcends its prickly exterior to offer a spectrum of practical uses. Explore how its fibers have been historically woven into textiles, creating durable and sustainable materials. Delight in the culinary possibilities as young nettle leaves find their way into soups, teas, and salads, adding a distinctive and earthy flavor to gastronomic creations.
Medicinal and Nutritional Marvels of Nettles

Look beyond the sting, and you’ll find a treasure trove of benefits in the nettle plant. Dive into its medicinal properties, known for anti-inflammatory effects and applications in alleviating conditions such as arthritis and allergies. Uncover the nutritional richness of nettles, abundant in vitamins A and C, iron, and essential minerals, making them a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle.
Unveiling the Intricate Tapestry of the Nettle Plant
At the intersection of biology and botanical fascination lies the nettle plant, scientifically known as Urtica dioica. This article embarks on a journey into the biological wonders that define this herbaceous perennial, exploring its unique features and the fascinating intricacies that make it a subject of both curiosity and admiration.
Tracing the Nettle’s Global Footprint
Distributed across continents, the nettle plant paints a diverse and expansive habitat map. From the woodlands of Europe to the landscapes of Asia, North America, and Africa, this article delves into the regions where nettles thrive. Uncover the factors that shape the nettle’s preferred habitats and understand the nuances of its global distribution, creating a vivid picture of its ecological presence.
Decoding the Chemistry of the Nettle Plant
At the heart of the nettle plant’s identity lies a complex composition of components that contribute to its unique characteristics. Explore the chemical makeup of nettles, from the stinging hairs that release irritating chemicals to the medicinal compounds that endow it with anti-inflammatory properties. This section unravels the component chronicles of the nettle, shedding light on the chemical intricacies that define its nature.
Navigating the Sting and Beyond
While the nettle plant is celebrated for its myriad uses, it carries a notorious reputation for its stinging side effects. This article navigates the side effects of nettles, shedding light on the mechanisms behind their stinging hairs and the resulting skin irritation. Beyond the sting, explore other aspects of the nettle’s influence, both positive and challenging, as we delve into the nuanced world of side effects associated with this remarkable plant.
Different Species
Urtica dioica
Commonly known as the stinging nettle, Urtica dioica is the most widespread species. It is found in Europe, Asia, North America, and Africa. This species is well-known for its stinging hairs that release irritating chemicals upon contact.
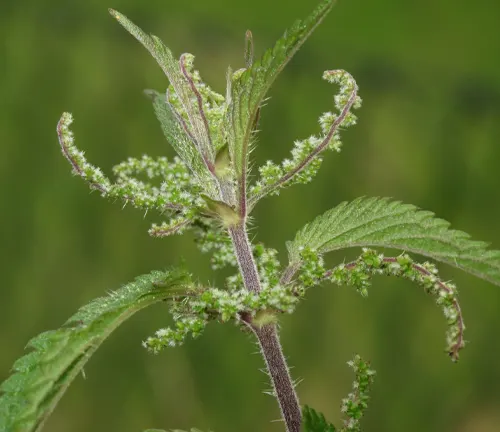
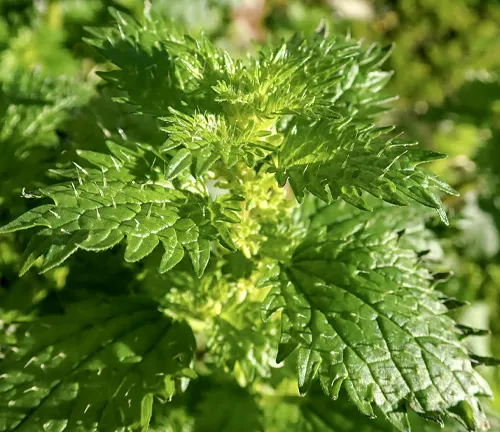


Urtica urens
Also called the small nettle or dwarf nettle, Urtica urens is a smaller species compared to Urtica dioica. It is found in similar regions and shares the characteristic stinging hairs.
Urtica pilulifera
Known as the Roman nettle or blister nettle, this species is found in Europe and Asia. It is named for its reputed ability to cause blistering on the skin upon contact.
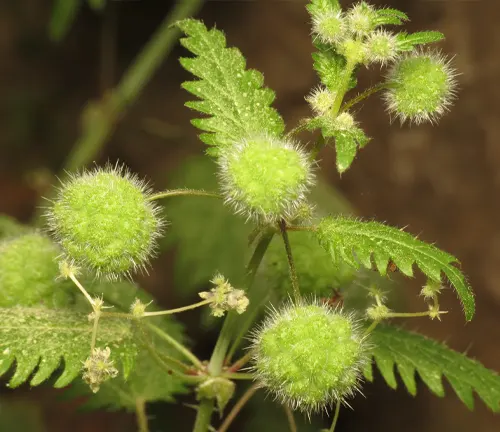
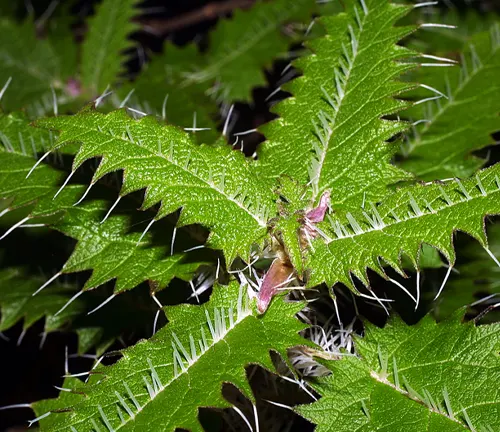


Urtica ferox
Native to New Zealand, Urtica ferox is commonly known as the Ongaonga or tree nettle. It is a particularly potent species, and its stings can cause severe pain and reactions.
Urtica membranacea
This species, also known as the membranous nettle, is found in the Mediterranean region. It is characterized by its membranous, translucent leaves.
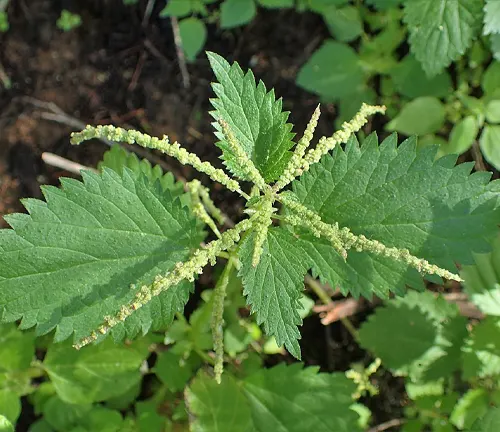


Urtica gracilenta
Native to North America, Urtica gracilenta is commonly known as the annual nettle. It is an annual species, meaning it completes its life cycle within one year.
Urtica incisa
Known as the scrub nettle or scrub itching bush, Urtica incisa is found in Australia and New Zealand. It typically grows in scrubland and has stinging hairs.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the nettle plant?
The nettle plant, scientifically known as Urtica dioica, is a herbaceous perennial with stinging hairs that release irritating chemicals upon contact. It is known for its widespread distribution across Europe, Asia, North America, and Africa. - Why do nettles sting?
Nettles sting due to tiny hairs on the leaves and stems that contain irritating chemicals. When these hairs come into contact with the skin, they cause a stinging sensation. - What are the common uses of nettle plants?
Nettle plants have various uses, including culinary applications where young leaves are used in soups, teas, and salads. The fibers from nettles have been historically woven into textiles, and the plant has medicinal properties, with applications in anti-inflammatory treatments. - Are all nettles the same?
No, there are several species of nettles. The most common is Urtica dioica, but other species like Urtica urens, Urtica pilulifera, and Urtica ferox exist, each with unique characteristics. - How can I cultivate nettles?
Nettles can be cultivated by planting seeds or transplanting young plants. They typically prefer nutrient-rich soil and can thrive in various environments. However, caution is needed due to their stinging hairs. - What is the ecological importance of nettles?
Nettles play a crucial role in ecosystems by providing habitat and food for various insects and butterflies. They contribute to biodiversity and environmental balance. - Are there any medicinal benefits to using nettles?
Yes, nettles have medicinal properties and are traditionally used for conditions such as arthritis and allergies. They contain vitamins A and C, iron, and other essential minerals. - Do all nettles sting equally?
The intensity of the stinging sensation can vary among nettle species. For example, Urtica ferox, also known as the tree nettle, is known for particularly potent stings. - Can nettles be harmful?
While nettles are generally safe, their stinging hairs can cause skin irritation. Some people may have allergic reactions, so caution is advised. Always use gloves when handling nettles. - Can nettles be grown for soil stabilization?
Yes, nettles are known for their extensive root system, making them effective in preventing soil erosion and contributing to soil stabilization.














Leave your comment