Top 21 Lumber Industry Statistics To Know
- September 2, 2024
- 0 comment
The lumber industry drives much of the global economy, especially in construction and manufacturing. For industry stakeholders, policymakers, and anyone involved in the market, understanding essential statistics provides insights into industry trends and future growth. Here are the top 21 lumber industry statistics to know for a comprehensive view of lumber market trends, industry growth, and key forestry industry statistics shaping today’s market.

The lumber industry is a cornerstone of the global economy, supplying essential wood products for construction, paper production, and various other applications. Lumber, sourced from trees, stands out as one of the oldest and most sustainable building materials, with its use dating back thousands of years. This eco-friendly lumber industry continues to evolve, supporting sustainable practices and fueling economic growth.
The lumber industry supports a vast supply chain, contributing significantly to employment, economic growth, and environmental stewardship. From small-scale businesses to large multinational corporations, this industry spans the globe, with major production hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia. The global lumber industry plays a pivotal role in providing sustainable materials and promoting eco-friendly practices worldwide.
Latest Lumber Industry Statistics
Explore the dynamic lumber industry, where recent data highlights its impressive economic impact and resilience. This sector, deeply integrated into global economies, consistently shows growth through expanding markets and rising revenues. The latest lumber industry statistics reveal its powerful role in economic development, supporting industries from construction to manufacturing. These timber industry trends reflect a robust sector essential for ongoing market growth.
These lumber industry statistics emphasize not only the sector’s financial strength but also its role in shaping the broader economic landscape. With rising demand for sustainable building materials and eco-friendly practices, the lumber industry leads in market trends and contributes to global economic stability. By understanding these figures, stakeholders can gain insights into the industry’s future trajectory, helping them navigate the complexities of this essential sector.
Global Lumber Production
Recent data shows that global lumber production reaches around 500 million cubic meters annually. Leading countries, including the United States, Canada, Russia, and China, dominate production. North America alone contributes nearly 30% of the world’s lumber output, solidifying its role as a critical player in the global lumber industry.
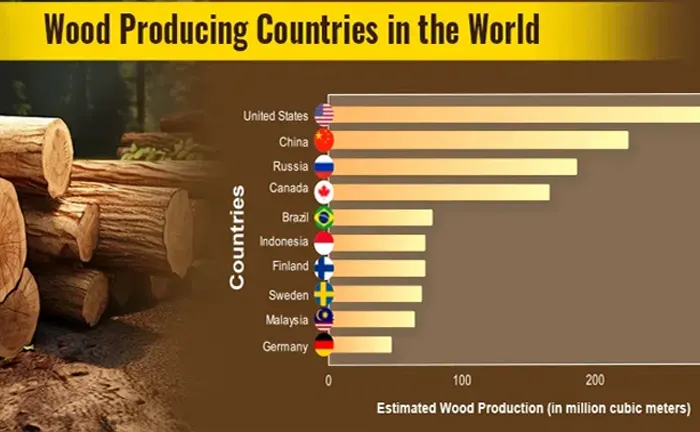
Countries like Canada and Russia are not only major producers but also key exporters in the lumber industry, supplying large volumes to markets in Europe, Asia, and the United States. Their robust production capabilities have positioned them as leaders in the global lumber industry, driving market growth and meeting rising global demand.
Market Size and Growth
In 2023, the global lumber market was valued at over $250 billion, with projections pointing to ongoing growth. Over the past decade, the market has steadily expanded, fueled by rising demand for wood products in construction, furniture manufacturing, and the paper industry. This consistent growth highlights the lumber industry’s vital role in supporting diverse sectors worldwide.

The lumber market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% between 2023 and 2030. This growth is driven by factors like rising urbanization, a growing middle class, and the increased use of wood in eco-friendly construction practices. These trends underscore the lumber industry’s growth potential as it adapts to sustainable and urban development demands.
Below is a detailed table for “Market Size and Growth” in the lumber industry, showcasing key statistics and projections:
| Year | Global Market Size (USD Billion) | Annual Growth Rate (%) | Key Markets | Major Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 186.5 | 3.2% | North America, Europe | Steady demand in construction and infrastructure development, rising housing starts in the U.S. |
| 2019 | 192.0 | 2.9% | North America, Asia | Continued growth in residential construction, increasing urbanization, and infrastructure projects in emerging economies |
| 2020 | 199.3 | 3.8% | Asia-Pacific, Europe | Boost in home renovation projects during COVID-19 lockdowns, increased demand for sustainable building materials |
| 2021 | 220.7 | 10.7% | North America, Europe | Significant price surge due to supply chain disruptions, record-high demand for lumber in residential construction |
| 2022 | 208.5 | -5.5% | Asia-Pacific, North America | Market correction post-2021 spike, stabilization of prices, but sustained demand from ongoing infrastructure investments |
| 2023 | 250.2 | 4.0% | North America, Asia-Pacific | Recovery from market correction, strong global demand for timber in sustainable construction and manufacturing sectors |
| 2024 (Proj.) | 260.2 | 4.0% | Asia-Pacific, Europe | Increasing adoption of engineered wood products, growth in urban development projects, and rising sustainability concerns |
| 2025 (Proj.) | 271.6 | 4.4% | North America, Europe | Expansion of green building initiatives, continued urbanization, and technological advancements in wood processing |
| 2026 (Proj.) | 283.5 | 4.4% | Asia-Pacific, North America | Continued growth in housing markets, global emphasis on carbon-neutral construction, increasing use of cross-laminated timber (CLT) |
| 2027 (Proj.) | 296.0 | 4.4% | Global | Increased demand for renewable materials, innovation in wood products, and global infrastructure development |
U.S. Lumber Industry Overview
In the United States, the lumber industry plays a crucial role in the economy, significantly contributing to GDP and employment. As one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of lumber, the U.S. meets much of its domestic demand through local production, underscoring its importance in US lumber industry trends and economic stability.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size (2023) | $120 billion |
| Contribution to GDP (2023) | Approximately 0.5% of U.S. GDP |
| Employment | Over 500,000 direct jobs in logging, sawmills, and manufacturing |
| Domestic Production (2023) | 75 million cubic meters of lumber produced |
| Domestic Consumption (2023) | 70 million cubic meters of lumber consumed |
| Top Lumber Products | Softwoods (pine, spruce) and hardwoods (oak, maple) |
| Exports | $10 billion worth of lumber exported, primarily to Canada, China, and the EU |
| Imports | $15 billion worth of lumber imported, mainly from Canada |
| Investment Areas | Sustainable forestry practices, advanced manufacturing, engineered wood products |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Significant adoption of certifications like FSC and PEFC |
| Technological Advancements | Increased use of automated sawmilling, precision forestry, and cross-laminated timber (CLT) |
The U.S. lumber market offers a diverse range of products, from softwoods like pine and spruce to hardwoods such as oak and maple. In recent years, the industry has attracted substantial investment, especially in sustainable forestry and advanced manufacturing techniques, reflecting a commitment to innovation and eco-friendly practices in lumber production.
Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the lumber industry. Initially, supply chain disruptions led to a sharp production decline and a spike in lumber prices. However, as the world adjusted, demand for lumber surged due to a boom in home renovations and construction projects, highlighting the industry’s resilience and adaptability in challenging times.
The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the global supply chain but also emphasized the essential role of the lumber industry. Despite these challenges, the industry has shown remarkable resilience, rebounding faster than many other sectors and continuing to support economic stability and growth.
Employment in the Lumber Sector
The lumber industry is a major employer, especially in rural and forest-rich areas. In the United States, it supports over 900,000 jobs across sectors like logging, sawmilling, transportation, and retail. Globally, millions depend on this industry for their livelihoods, highlighting its critical role in employment and economic stability worldwide.

Job growth in the lumber industry closely follows market demand and technological advancements. While automation has reduced some traditional roles, it has also opened up new opportunities in fields like precision forestry and sustainable management, reflecting the industry’s shift toward innovation and eco-friendly practices.
Lumber Pricing Trends
Lumber prices are known for their volatility, influenced by factors like supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, and shifts in demand. In recent years, prices have fluctuated dramatically, with a historic peak in 2021 followed by a sharp decline in 2022, reflecting the dynamic nature of the lumber market.
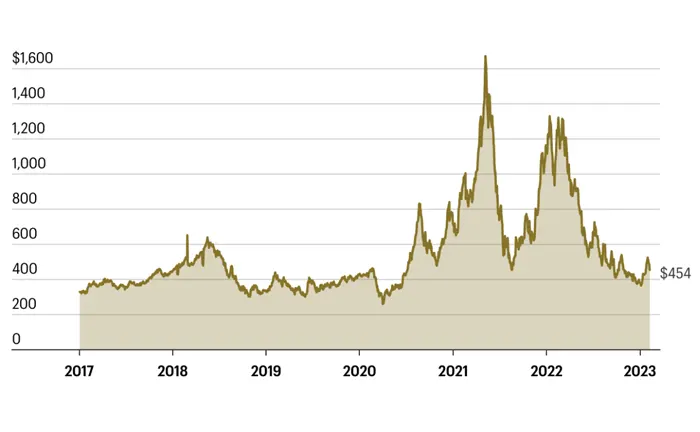
Several factors drive lumber price fluctuations, including tariffs, transportation costs, and the availability of raw materials. For industry stakeholders, understanding these pricing trends is essential, as they directly influence profitability and guide important investment decisions within the lumber industry.
Lumber Exports and Imports
The global lumber trade is a complex network, with major exporters like Canada, Russia, and Sweden supplying wood to markets worldwide. The United States, Japan, and China rank among the largest importers, driven by strong demand from their robust construction industries.

| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Top Exporting Countries (2023) | 1. Canada: $20 billion 2. Russia: $15 billion 3. Sweden: $10 billion |
| Top Importing Countries (2023) | 1. United States: $15 billion 2. China: $12 billion 3. Japan: $8 billion |
| Global Export Value (2023) | $80 billion |
| Global Import Value (2023) | $75 billion |
| Major Trade Routes | Canada to U.S., Russia to China, Sweden to EU |
| Key Trade Agreements | USMCA (U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement), EU-Sweden trade policies |
| Impact of Tariffs | U.S.-Canada softwood lumber dispute leading to 20% average tariffs on Canadian lumber |
| Primary Export Products | Softwood lumber (pine, spruce), Hardwood lumber (oak, beech) |
| Primary Import Products | Construction-grade lumber, plywood, engineered wood products |
| Recent Trends | Increasing exports from Russia to Asia, growing U.S. demand for high-quality European hardwood |
| Challenges | Trade disputes, tariff impacts, environmental regulations, and supply chain disruptions |
This table outlines the key elements of global lumber exports and imports, emphasizing the leading countries in the trade, the value of global trade, and the factors influencing the flow of lumber across borders. It also highlights the impact of trade policies and disputes, such as the ongoing U.S.-Canada softwood lumber issue, which significantly affects market dynamics.
Trade policies, tariffs, and international agreements heavily influence the dynamics of lumber exports and imports. For example, the longstanding softwood lumber dispute between the U.S. and Canada continues to impact trade flows and pricing, highlighting how such issues shape the global lumber market.
Demand in Construction
Lumber is essential in construction, especially for residential buildings. Demand in the construction sector closely aligns with housing starts, infrastructure projects, and renovation activities. In the United States, about 70% of lumber consumption is dedicated to construction, underscoring its importance in building and development.
Lumber is widely favored in construction for its strength, versatility, and sustainability. However, the industry faces challenges, including competition from materials like steel and concrete and the need to comply with stricter building codes and sustainability standards. These factors continue to shape the role of lumber in modern construction.
Technological Advancements
Technology is transforming the lumber industry, enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and product quality. Innovations like precision forestry, automated sawmilling, and digital supply chain management enable companies to optimize operations and reduce waste, positioning the industry for a more sustainable future.

A major advancement in the lumber industry is cross-laminated timber (CLT), an engineered wood known for its enhanced strength and durability. CLT is increasingly popular in construction, especially for high-rise buildings, due to its environmental benefits and reliable performance, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to traditional materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a key focus in the lumber industry, as it addresses the environmental impact of deforestation and forest degradation. The industry has made substantial progress in adopting sustainable forestry practices that balance the demand for wood products with the need to protect and preserve forest ecosystems.

Certification programs like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) are increasingly vital in the lumber industry. They ensure that wood products are sourced from responsibly managed forests, helping companies meet consumer demand for eco-friendly products and comply with regulatory standards.
Investment in the Lumber Industry
The lumber industry attracts substantial investment, especially in sustainable forestry, advanced manufacturing, and technological innovation. Investors are drawn to the industry’s long-term growth prospects, fueled by rising demand for wood products and the growing importance of sustainability in global markets.
Recent trends in investment include the growth of timberland as an asset class, with institutional investors and pension funds purchasing large tracts of forested land. These investments offer the potential for steady returns and diversification, particularly in the context of rising demand for carbon offsets and sustainable materials.
Future Outlook for the Lumber Industry
The future of the lumber industry is influenced by economic growth, technological advancements, and environmental priorities. The industry is projected to continue growing, fueled by urbanization, a shift toward sustainable construction practices, and the increasing use of wood as a renewable resource. These factors position the industry for a promising future in meeting both economic and environmental needs.

Despite its growth potential, the lumber industry faces challenges, including the need to address climate change, manage forest resources sustainably, and navigate complex trade dynamics. Companies that can adapt to these challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities will be well-positioned for success in the coming years.
Key Industry Players
The lumber industry is dominated by a few major players, including companies like Weyerhaeuser, West Fraser Timber, and Canfor. These companies have extensive operations across the entire value chain, from logging and sawmilling to distribution and retail.
Mergers and acquisitions are common in the industry, as companies seek to expand their market share, access new resources, and achieve economies of scale. Recent examples include the merger of B.C.-based West Fraser and Norbord, which created one of the largest wood products companies in the world.
Regional Differences in Lumber Markets
Lumber markets differ greatly by region, shaped by factors like forest resources, economic conditions, and cultural preferences. In North America, there’s high demand for softwoods, while the European market leans more toward hardwoods, reflecting distinct regional needs and preferences.
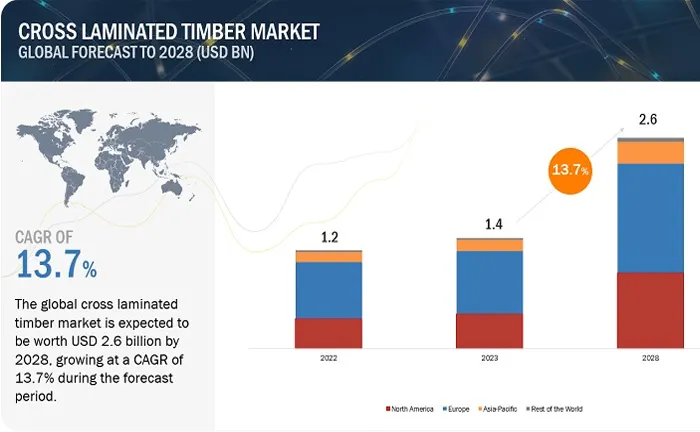
In emerging markets like Asia, the demand for lumber is rapidly increasing, fueled by urbanization and infrastructure development. However, these markets also face challenges, including supply chain constraints, regulatory barriers, and competition from alternative materials, all of which impact the lumber industry’s growth in the region.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations are crucial in shaping the lumber industry, impacting areas like production, trade, and sustainability practices. In the United States, for instance, the industry must comply with regulations concerning forest management, land use, and environmental protection, all of which guide responsible resource use and industry growth.
Trade policies also have a significant impact, as seen in the ongoing softwood lumber dispute between the U.S. and Canada. This dispute has led to tariffs and other trade barriers, affecting prices and market dynamics on both sides of the border.
Innovations in Lumber Products
The lumber industry is continually innovating, developing new products that meet the changing needs of consumers and businesses. Recent innovations include engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber (CLT), laminated veneer lumber (LVL), and oriented strand board (OSB).

| Product Innovation | Description | Market Growth (2023) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) | Engineered wood product made by layering panels of lumber in alternating directions for added strength | $2.5 billion (10% CAGR) | High-rise buildings, commercial construction |
| Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) | Manufactured by bonding thin wood veneers together, providing uniform strength and stability | $1.8 billion (8% CAGR) | Beams, rafters, headers, and trusses |
| Oriented Strand Board (OSB) | Engineered wood made from compressed wood strands, offering strength similar to plywood at lower cost | $4.5 billion (7% CAGR) | Flooring, wall sheathing, roofing |
| Bio-Based Wood Composites | Composites made from wood fibers and bio-based plastics, offering enhanced environmental performance | $1.2 billion (12% CAGR) | Furniture, decking, automotive interiors |
| Mass Timber | Large, solid wood panels used in place of steel or concrete, promoting sustainability in construction | $1.9 billion (11% CAGR) | Mid-rise and tall buildings, bridges |
| Wood-Based Plastics | Plastics derived from wood fibers, offering a renewable alternative to traditional plastics | $800 million (15% CAGR) | Packaging, automotive parts, consumer goods |
| Acetylated Wood | Wood treated with acetic anhydride to increase durability, stability, and resistance to rot | $600 million (13% CAGR) | Outdoor furniture, decking, cladding |
These engineered wood products provide enhanced strength, durability, and environmental benefits, making them increasingly popular in construction and various applications. Additionally, the development of bio-based products like wood-based plastics and composites is gaining momentum, creating new opportunities for the lumber industry to expand into sustainable materials.
Role of Lumber in Global Trade
Lumber plays a vital role in global trade, with billions of dollars in wood products exchanged annually. The industry’s contribution to global trade is substantial, especially for major exporters like Canada, Russia, and Sweden, which are key players in meeting worldwide demand for wood products.

Trade agreements, tariffs, and international standards are crucial in shaping lumber trade across borders. For instance, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its successor, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), have significantly impacted lumber trade among these countries, influencing pricing, supply, and market dynamics.
Lumber’s Role in Climate Change
Lumber contributes uniquely to climate change mitigation because trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their wood a process called carbon sequestration. This quality makes wood a valuable resource in combating climate change, supporting sustainable practices and environmental goals.

Using wood in construction can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially when compared to high-carbon materials like concrete and steel. However, for the lumber industry to make a positive impact on climate change mitigation, it must address the environmental effects of logging and adopt sustainable forest management practices.
Challenges Facing the Lumber Industry
The lumber industry faces various challenges, including environmental and sustainability concerns as well as economic pressures. Key environmental issues such as deforestation, habitat loss, and climate change require proactive solutions to ensure the industry’s long-term viability and positive impact on ecosystems.
The lumber industry also contends with economic challenges, including price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and competition from alternative materials. Labor issues add another layer of complexity, with a shortage of skilled workers and a need for adaptation to emerging technologies impacting the industry’s growth and efficiency.
Impact of Wildfires on Lumber Supply
Wildfires pose a significant threat to the lumber industry, especially in regions like North America and Australia, where large-scale fires are increasingly common. These wildfires can devastate vast forest areas, reducing the timber supply and driving up lumber prices, further straining the industry’s resources.

The economic impact of wildfires on the lumber industry is significant, influencing production, distribution, insurance costs, and regulatory compliance. To mitigate these risks, the industry is investing in improved forest management practices and fire-resistant infrastructure, aiming to protect resources and ensure stability.
Urbanization and Its Impact on Lumber Demand
Urbanization is a key driver of lumber demand as cities expand, increasing the need for housing and infrastructure. In emerging markets like China and India, rapid urbanization fuels a surge in construction activity, significantly boosting demand for wood products to support growth.
This trend is expected to persist, with urban populations projected to rise significantly in the coming years. The lumber industry will need to meet this growing demand while tackling challenges related to sustainability, resource management, and environmental impact.
Final Conclusion
The lumber industry is a complex, dynamic sector with a profound impact on the global economy, environment, and society. The statistics and trends discussed here underscore the industry’s significance and the critical challenges it must navigate to sustain growth and positive impact.
As the lumber industry evolves, stakeholders must stay informed about new developments and adapt to shifting conditions. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and strategic investment, the industry can continue to thrive and meet future demands effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the current trends in lumber prices?
Lumber prices have been volatile in recent years, influenced by factors such as supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, and changes in demand. Recent trends indicate a stabilization of prices, but they remain subject to fluctuations. - How does the lumber industry contribute to the economy?
The lumber industry is a major contributor to the global economy, providing jobs, supporting local economies, and supplying essential materials for construction and manufacturing. - What are the major challenges facing the lumber industry?
The lumber industry faces challenges such as environmental sustainability, price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and competition from alternative materials. - How does sustainability impact the lumber industry?
Sustainability is a critical concern in the lumber industry, with increasing emphasis on sustainable forestry practices, certifications, and reducing environmental impact. - What role does technology play in the lumber industry?
Technology plays a significant role in improving efficiency, sustainability, and product quality in the lumber industry, with innovations such as precision forestry, automated sawmilling, and cross-laminated timber. - What is the future outlook for the lumber industry?
The future outlook for the lumber industry is positive, with expected growth driven by urbanization, sustainable construction practices, and the increasing use of wood as a renewable resource.
We hope these top 21 lumber industry statistics give you clear insights into the industry’s trends and future. Have thoughts or experiences to share? Join the conversation below and help others stay informed. If you found this useful, share it with others in the industry!

James Wilson
Forestry AuthorJames Wilson has over 15 years of experience in forestry economics, specializing in sustainable practices, investment opportunities, and financial management. He has contributed to notable publications like "Forestry Today" and "EcoFinance Journal" and is known for providing practical and insightful advice. With a degree in Environmental Economics, James stays updated through continuous learning and active participation in industry discussions. Outside work, he enjoys hiking and nature photography, bringing a well-rounded perspective to his professional role.













Leave your comment