Eastern Redcedar Tree
- June 20, 2023
- 0 comment

Common Name: Eastern Redcedar
Botanical Name: Juniperus virginiana
Family: Cupressaceae
Plant Type: Evergreen tree
The Eastern Redcedar (Juniperus virginiana) is a remarkable tree that holds great significance in the natural world. Its common name refers to its rich reddish wood and distinct cedar-like aroma, which permeates the air when encountered. Let’s delve into the fascinating characteristics of this tree and explore its various attributes.
Lumber
It is native to North America and is commonly found in the eastern and central regions of the United States. This species is highly valued for its durability, distinct fragrance, and attractive reddish-brown heartwood. Eastern Redcedar lumber is known for its versatility and is used in a wide range of applications, including furniture, cabinetry, flooring, siding, and decorative items.
Mature Size and Growth Rate
The Eastern Redcedar is a slow-growing tree that can reach an average height of 40 to 50 feet, with some exceptional specimens reaching up to 90 feet. It typically has a conical shape, but it can become more irregular with age.
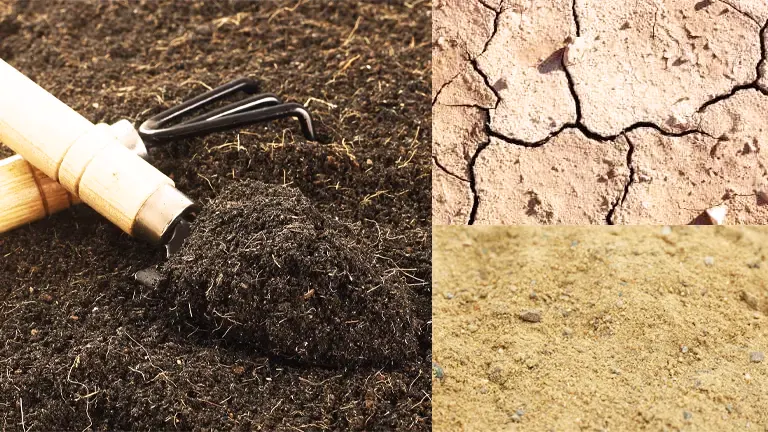

Soil Type and Preference
This tree is highly adaptable to a wide range of soil conditions, including sandy, loamy, and clay soils. It has excellent tolerance for drought and can thrive in both acidic and alkaline soils.
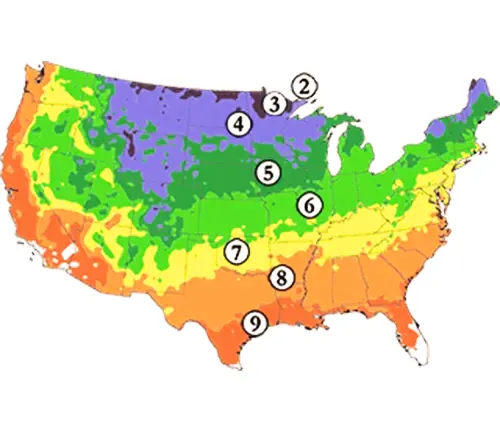
Hardiness Zones
The Eastern Redcedar is well-suited for a variety of climates, ranging from USDA hardiness zones 2 to 9.

Sun Preference
This tree exhibits a preference for full sun exposure, where it can receive at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. However, it can also tolerate partial shade.

Attributes and Characteristics
The Eastern Redcedar boasts several noteworthy features. Its dense evergreen foliage provides year-round interest, offering privacy and acting as a windbreak. The leaves are scale-like and arranged in pairs or whorls, giving the tree an attractive, feathery appearance. The reddish-brown bark further enhances its visual appeal.
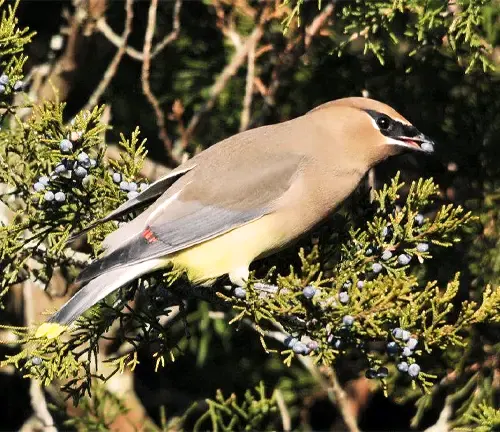

Wildlife Value
This tree plays a vital role in supporting wildlife. The Eastern Redcedar provides shelter and nesting sites for numerous bird species, such as the Eastern Bluebird and Cedar Waxwing. Its dense foliage offers protection from predators and harsh weather conditions. Additionally, the tree’s berry-like cones serve as a valuable food source for various birds and small mammals.
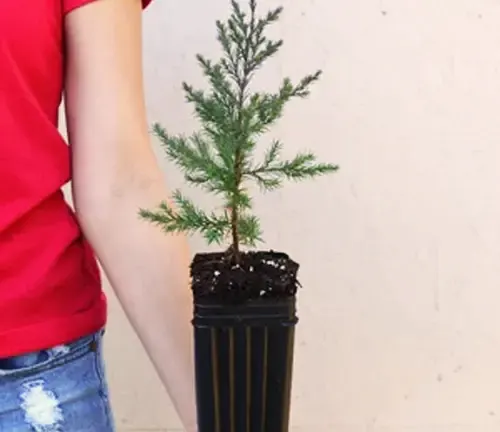

Care
The Eastern Redcedar requires minimal care once established. Regular watering is necessary during its initial growth period, but it becomes more drought-tolerant over time. Pruning can be done to shape the tree or remove dead branches, but it is generally not required. Mulching around the base helps retain moisture and control weeds.
Benefits
This versatile tree offers numerous benefits. Its wood is highly durable and resistant to rot, making it a popular choice for furniture, cabinetry, and fence posts. The aromatic qualities of the wood also make it desirable for cedar chests and closets, as it naturally repels moths and other pests. Furthermore, the Eastern Redcedar has been utilized for its medicinal properties by Native American tribes for centuries.
Invasive
Although the Eastern Redcedar is native to North America, it can become invasive in certain areas. It readily colonizes disturbed sites and open grasslands, out-competing native vegetation. However, when planted appropriately and managed responsibly, it poses no significant invasive threat.
Lifespan
The Eastern Redcedar is a long-lived tree, with an average lifespan of 100 to 150 years. Some specimens have been known to survive for over 300 years under optimal conditions.
Disadvantage
One potential drawback of the Eastern Redcedar is its allelopathic nature. It releases chemicals that inhibit the growth of nearby plants, which may limit the diversity of plant species in its vicinity.
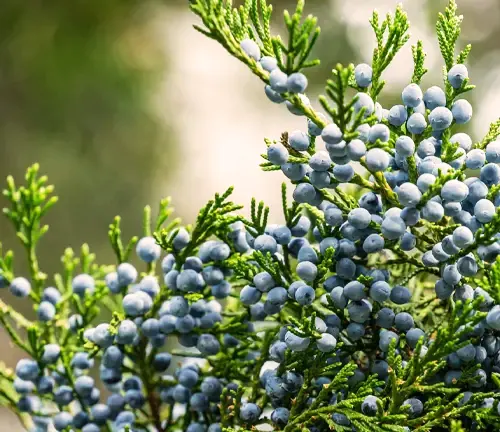

Edible or Not
While the Eastern Redcedar produces small, bluish-purple berries, they are not typically consumed by humans due to their bitter taste. However, some bird species rely on these berries as a food source.
Habitat Requirements
This tree is adaptable and can thrive in various habitats, including open woodlands, grasslands, and rocky slopes. It can tolerate dry, sandy soils and is often found growing near old fields or fence lines.
Name Origin
The name “redcedar” is somewhat misleading, as the Eastern Redcedar is not a true cedar. The term “cedar” was likely given to it due to its similar aromatic properties and reddish wood. The species name “virginiana” refers to the tree’s prevalence in the state of Virginia.

Varieties
Several cultivars of the Eastern Redcedar exist, offering variations in size, shape, and color. Some notable varieties include ‘Emerald Sentinel,’ ‘Hillspire,’ and ‘Taylor.’
Pruning
Pruning is generally not necessary for the Eastern Redcedar, as it naturally maintains a neat shape. However, if desired, pruning can be done in early spring to shape the tree or remove any dead or diseased branches.
Propagating
The Eastern Redcedar can be propagated through seeds, which require a period of cold stratification to break dormancy. Cuttings and transplanting of young seedlings are also viable methods of propagation.
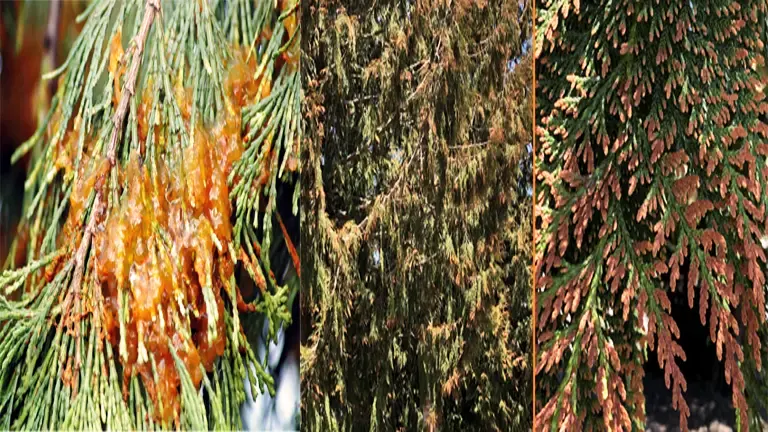

Common Pests & Diseases
This tree is relatively resistant to pests and diseases. However, it may occasionally be affected by cedar-apple rust, a fungal disease that can cause damage to both Eastern Redcedar and apple trees. Bagworms and cedar-apple rust are among the few pests that can pose a threat, but they can be managed through proper monitoring and appropriate insecticides.
Fun Facts:
- The Eastern Redcedar has been used by Native Americans for a variety of purposes, including making bows, ceremonial objects, and traditional herbal remedies.
- Despite being called a “cedar,” this tree is actually a juniper and is closely related to other juniper species found around the world.
- Eastern Redcedar forests provide critical habitat for numerous bird species, including the threatened Golden-winged Warbler.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Q: Is the Eastern Redcedar poisonous?
A: No, the Eastern Redcedar is not poisonous to humans or animals. However, the berries have a bitter taste and are generally not consumed by humans. - Q: Can I plant Eastern Redcedar in a small yard?
A: While the Eastern Redcedar can be planted in smaller yards, its size and potential spread should be considered. Regular pruning and maintenance may be necessary to control its growth. - Q: Does the Eastern Redcedar lose its needles in winter?
A: No, the Eastern Redcedar is an evergreen tree and retains its foliage throughout the year. - Q: Can I use Eastern Redcedar wood for outdoor projects?
A: Yes, Eastern Redcedar wood is naturally rot-resistant and can be used for outdoor projects such as fences, decking, and pergolas.
In conclusion, the Eastern Redcedar is a remarkable tree that offers both aesthetic appeal and ecological benefits. Its adaptability, longevity, and aromatic properties make it a valued addition to landscapes and natural habitats alike. By understanding its characteristics and implementing responsible planting practices, we can fully appreciate and harness the numerous qualities this tree has to offer.














Leave your comment