European Pear Tree
- September 21, 2023
- 0 comment

- Common Name: European Pear Tree
- Botanical Name: Pyrus communis
- Family: Rosaceae
- Plant Type: Deciduous fruit tree
Lumber
European Pear trees produce high-quality wood that is prized for its pale, creamy color and fine grain. This wood is often used for making furniture, musical instruments, and woodcrafts.

Mature Size and Growth Rate
European Pear trees typically reach a mature height of 15 to 30 feet (4.5 to 9 meters) with a spread of 10 to 20 feet (3 to 6 meters). They have a moderate growth rate, gaining approximately 12 to 24 inches (30 to 60 cm) in height per year.
Soil Type
European Pear trees, scientifically known as Pyrus communis, are known for their adaptability to various soil types, but they truly thrive in well-drained, loamy soils. Loamy soils offer a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, which allows for proper drainage while retaining essential moisture and nutrients. These trees can tolerate different pH levels but ideally prefer soils that are slightly acidic to neutral, typically in the range of 6.0 to 7.0. This pH preference ensures that the tree can effectively take up essential nutrients from the soil. Proper soil conditions are crucial for European Pear trees to establish healthy root systems and yield abundant fruit.

Soil Preferences
European Pear trees have distinct soil preferences when it comes to their fertility and organic matter content. They thrive in soils that are rich in organic matter, as it provides a steady supply of nutrients and helps with moisture retention. To enhance their growth and fruit production, gardeners often amend the soil with well-rotted compost or organic matter. This enrichment of the soil not only boosts nutrient availability but also promotes beneficial microbial activity in the root zone. In return, the trees develop stronger roots and produce more fruit, resulting in healthier and more productive European Pear trees.
Hardiness Zone
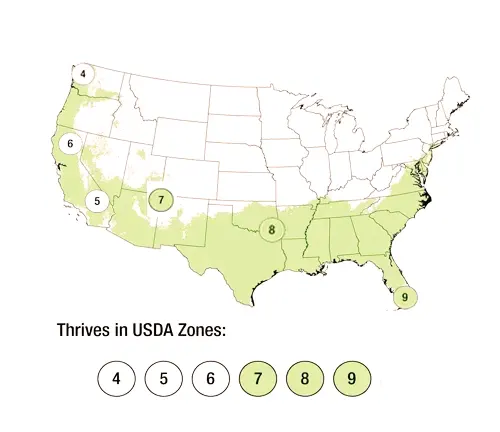
European Pear trees are hardy in USDA Hardiness Zones 4 to 9, making them suitable for a wide range of climates.
Sun Preference
They thrive in full sun, requiring at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight per day to produce abundant fruit.
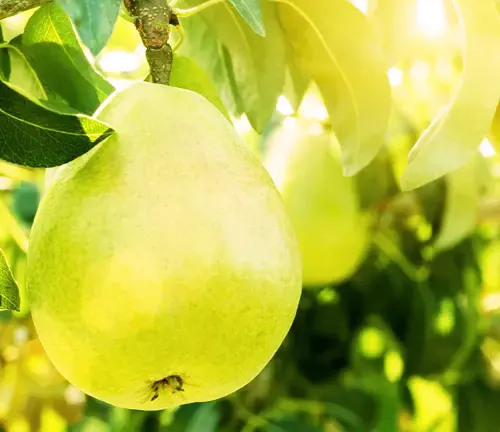

Attributes and Characteristics
The European Pear Tree (Pyrus communis) is prized for its delightful attributes and characteristics. It bears delicious, sweet, and juicy pears in a variety of colors, including green, yellow, and red, typically ready for harvest in late summer or early autumn. During spring, it adorns itself with clusters of white or cream-colored flowers, not only adding beauty to the landscape but also providing nectar for pollinators.
Wildlife Value
European pear trees provide food and habitat for various wildlife species, including birds, insects, and small mammals. Birds are particularly attracted to the fruit.
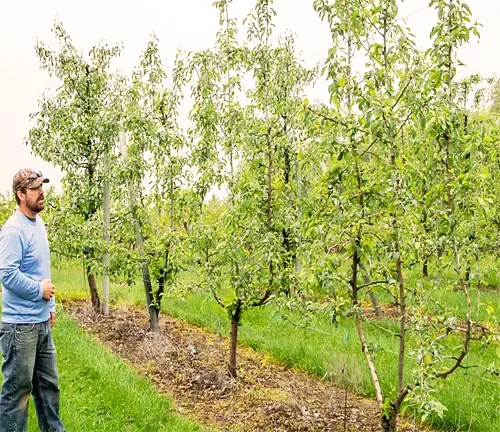

Care
Proper care of the European Pear Tree includes regular watering, especially in dry periods, to ensure robust fruit production. Applying a balanced fertilizer in the spring promotes healthy growth and fruit development. Pruning is crucial to uphold the tree’s shape, eliminate dead or diseased branches, and enhance air circulation, with the best time for pruning being during the dormant season.
Benefits
European Pear Trees offer a range of benefits. Their edible fruit is not only delicious but also nutritious, commonly enjoyed fresh, in cooking, or as jams and preserves. Additionally, these trees add aesthetic value to gardens and landscapes with their beautiful spring blossoms and colorful late-summer fruit. Furthermore, they play a role in enhancing local biodiversity by providing food and shelter for wildlife, making them a valuable asset to the ecosystem.
Invasive
European pear trees are not considered invasive, but they can naturalize in certain regions under favorable conditions.
Lifespan
With proper care, European pear trees can live for several decades, often reaching 20 to 50 years or more.
Disadvantages
European Pear Trees come with a few disadvantages to consider. They are susceptible to various diseases like fire blight, pear scab, and pear rust, often necessitating regular maintenance and treatments to keep them healthy. Additionally, pest issues can arise, with aphids, codling moths, and pear psylla being common culprits that can harm both the fruit and leaves. Vigilance and pest management practices may be required to address these challenges effectively.
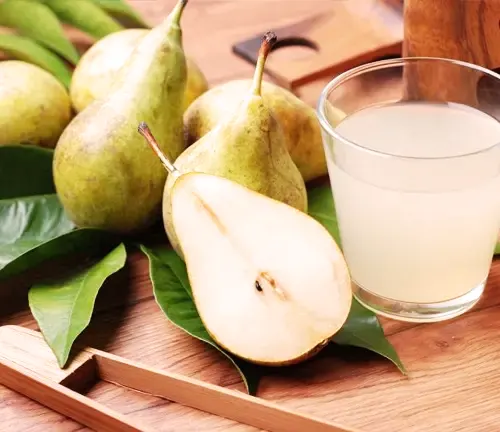

Edible or Not
European pears are edible and are widely enjoyed for their sweet and juicy flesh.
Habitat Requirements
European pear trees thrive in temperate climates with distinct seasons. They require sufficient sunlight, well-draining soil, and regular moisture to grow successfully.
Name of Origin
The European pear, Pyrus communis, is native to Europe and has been cultivated for thousands of years.
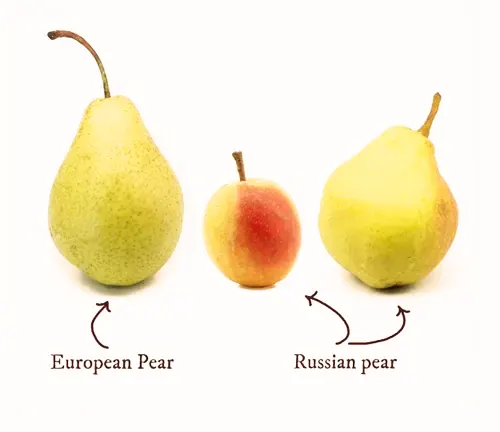

Varieties
There are numerous varieties of European pears, including popular cultivars like Bartlett, Anjou, Bosc, and Comice, each with its unique flavor and appearance.
Pruning
Pruning is essential for shaping the tree, promoting air circulation, and reducing disease risk. It’s best done during the dormant season in late winter or early spring.
Propagating
European pear trees can be propagated through methods such as grafting, budding, or rooting hardwood cuttings.

Common Pests & Diseases
Common pests include aphids, codling moths, and pear psylla. Diseases to watch for include fire blight, pear scab, and pear rust.
Experience the distinction now by exploring our array of Forestry Services. Don’t pass up the chance to enhance your experience!
Fun Facts
- European pears have a long history of cultivation, dating back to ancient Greece and Rome.
- The famous pear variety, Bartlett, is known as Williams pear in Europe.
- European pears are often used in making beverages like perry (pear cider) and pear brandy.
FAQs
- Can I grow European pear trees in containers?
Yes, dwarf varieties of European pear trees can be grown in large containers, but they require proper care and regular maintenance. - How do I prevent diseases in my European pear tree?
To prevent diseases, ensure good air circulation, avoid overhead watering, and apply appropriate fungicides as needed. Pruning to remove infected branches can also help. - When is the best time to harvest European pears?
European pears are typically harvested when they reach maturity, which varies depending on the variety but often occurs in late summer to early autumn. Pears should be picked when they are still firm and allowed to ripen off the tree.
In conclusion, the European Pear Tree (Pyrus communis) is a versatile and rewarding addition to gardens and orchards. Its delectable fruit, ornamental beauty, and contributions to local biodiversity make it a cherished choice for both home gardeners and nature enthusiasts. While it may require some care and attention to address potential diseases and pests, the joys of harvesting and savoring its sweet, juicy pears are well worth the effort. This remarkable tree continues to be a symbol of timeless orchard heritage and natural splendor.





Leave your comment