European Badger
- January 15, 2024
- 0 comment
The European badger, Meles meles, is a captivating mammal indigenous to the diverse landscapes of Europe. Instantly recognizable by its robust build, the European badger is adorned with striking black and white facial markings, adding a touch of charm to its appearance. These creatures exhibit a wide range of behaviors, from their nocturnal habits to their intricate social structures within family units. Preferring varied habitats, including woodlands and open fields, European badgers showcase adaptability that has allowed them to thrive across the continent. Their omnivorous nature is reflected in a diverse diet, encompassing earthworms, insects, fruits, and small mammals.
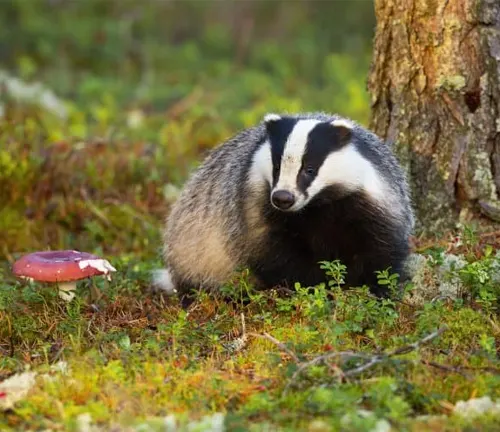

Beyond their physical characteristics and behaviors, European badgers play crucial roles in ecosystems and human culture. Despite being occasionally misunderstood and historically persecuted, these creatures are integral to biodiversity, contributing to soil health through their burrowing activities. The European badger also holds significance in various cultural myths and folklore, weaving stories that reflect its enigmatic nature.
While facing challenges such as habitat loss and disease concerns, concerted conservation efforts are underway to ensure the preservation of European badger populations. Their role in controlling pest populations, economic contributions, and the rise of badger-watching tourism highlight the multifaceted importance of these captivating creatures in both natural and human landscapes.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Meles meles |
| Common Name | European Badger |
| Physical Characteristics | Robust build, distinctive black and white facial markings |
| Size and Weight | Varies, with males larger than females; Weight ranges from 7 to 13 kg |
| Habitat | Adaptable, found in woodlands, open fields, and varied environments |
| Diet | Omnivorous, feeding on earthworms, insects, fruits, and small mammals |
| Behavior | Nocturnal, social animals with family units; Territory-marking behavior |
| Reproduction | Mating occurs in late winter or early spring; Gestation period around 7 weeks |
| Lifespan | Typically 6 to 8 years in the wild |
| Conservation Status | Listed as a species of least concern; Faces threats like habitat loss and disease |
| Economic Importance | Contributes to soil health, controls pest populations; Economic value in tourism |
| Cultural Significance | Features prominently in various myths and folklore, symbolizing different qualities |
| Threats and Challenges | Habitat loss, road accidents, persecution by humans, and diseases like bovine tuberculosis |
| Unique Features | Capable burrowers, unintentional seed dispersers, adaptable to urban environments |
| Conservation Initiatives | Ongoing efforts to protect habitats, mitigate human-wildlife conflicts, and manage diseases |
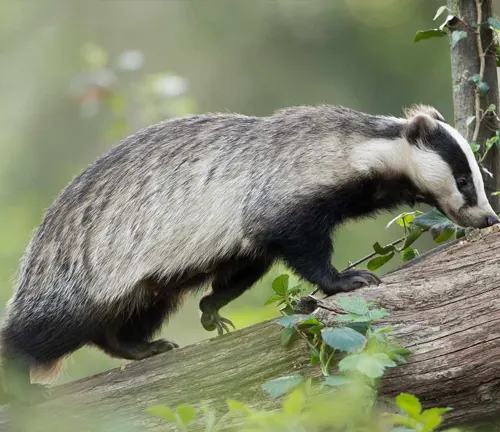

The European badger, a fascinating creature that graces the diverse landscapes of Europe, holds a unique position in the continent’s ecosystems. From its distinctive black and white facial markings to its nocturnal habits, this mammal intrigues both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Physical Characteristics
European badgers boast a robust build, with males typically larger than females. Their size and weight vary, but what sets them apart are the iconic black and white stripes on their faces, adding an element of charm to their appearance.

Habitat and Distribution
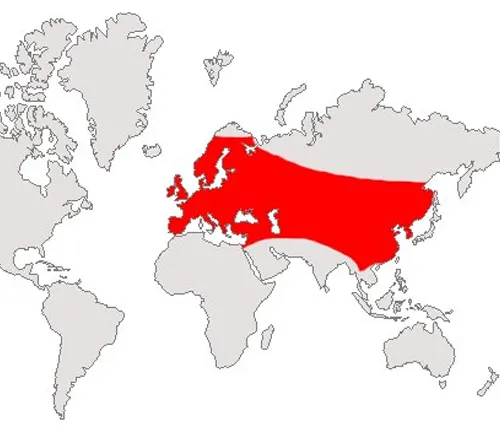
Map highlighting the distribution range of the European Badger in redThese badgers are adaptable, thriving in a range of environments from woodlands to open fields. Their geographic distribution spans across Europe, and understanding their preferred habitats is crucial for conservation efforts.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Omnivorous by nature, European badgers have a diverse diet that includes earthworms, insects, fruits, and small mammals. Exploring their feeding habits provides insight into their role within the ecosystem.
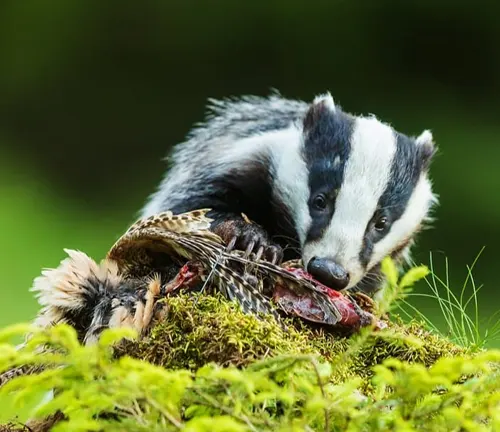

Behavioral Patterns
Nocturnal creatures, European badgers display intriguing social behaviors. Their tendency to form family units and the dynamics within these groups shed light on their complex yet fascinating social structures.
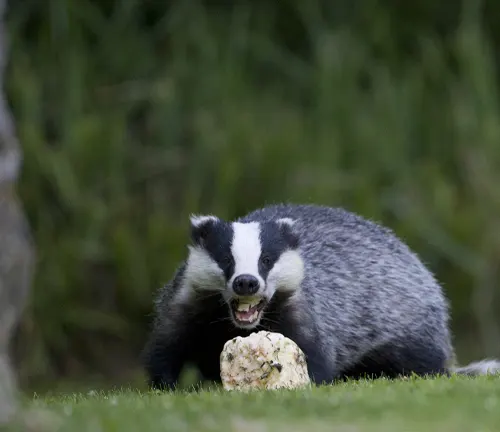

Reproduction and Life Cycle
The mating habits of European badgers, coupled with their gestation periods and birthing processes, offer a glimpse into the life cycle of these creatures.
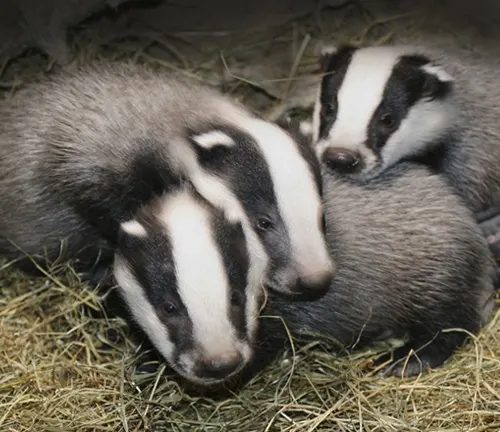

Interaction with Humans
Throughout history, European badgers have been both revered and persecuted by humans. Examining their historical significance and current conservation challenges emphasizes the need for coexistence.
Comparisons with Other Badger Species
Contrasting European badgers with their counterparts reveals unique adaptations and features that enable them to thrive in specific environments.
Role in Agriculture
The impact of badgers on agriculture, both positive and negative, raises questions about coexistence. Exploring the delicate balance between wildlife conservation and agricultural practices is crucial.
European Badger and Bovine Tuberculosis
Controversies surrounding the potential link between badgers and bovine tuberculosis have fueled debates. Delving into research findings and controversies provides a nuanced perspective on this complex issue.
European Badger Watching Tourism
The allure of observing these creatures in their natural habitats has given rise to badger watching tourism. Highlighting responsible tourism practices ensures that this activity benefits both the badgers and the communities involved.
Different Species
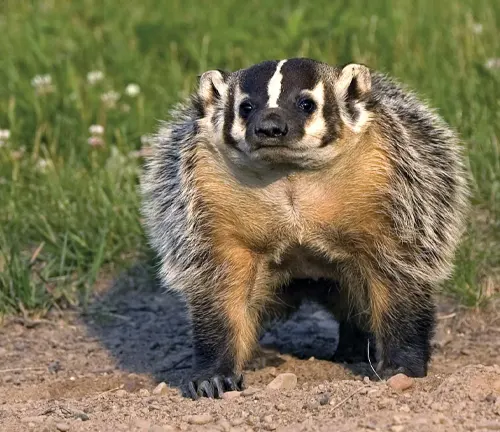
American Badger
(Taxidea taxus)
Found in North America, the American badger has a distinctive white stripe on its face and a stocky build. It prefers open grasslands.

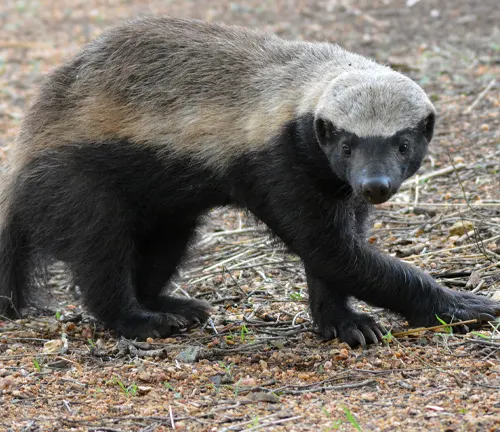
Honey Badger
(Mellivora capensis)
Native to Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent, the honey badger is known for its fearless nature and strong defensive capabilities.

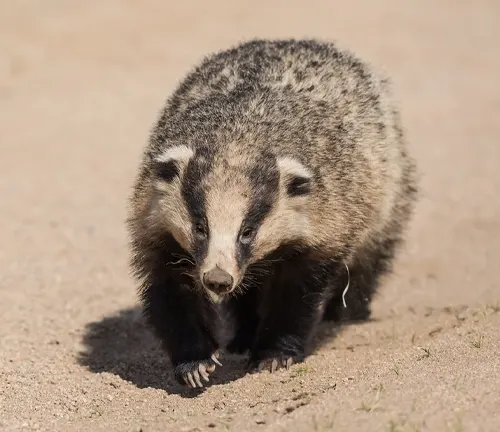
Japanese Badger
(Meles anakuma)
Endemic to Japan, this species is similar in appearance to the European badger but has a slightly different range and ecological niche.

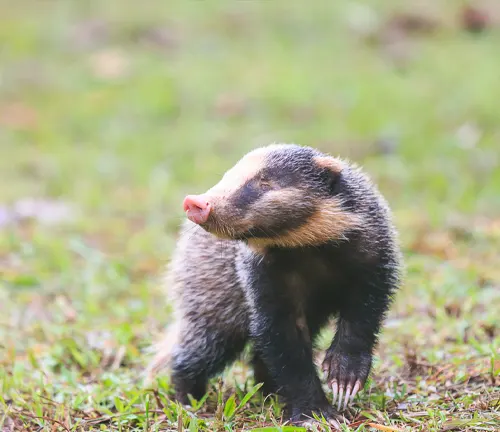
Hog Badger
(Arctonyx collaris)
Found in Southeast Asia, the hog badger has a more elongated snout and is adapted to forested habitats.

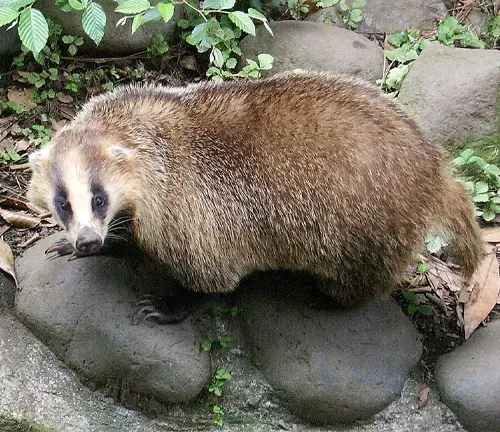
Asian Badger
(Meles leucurus)
Inhabiting parts of Central Asia and the Middle East, the Asian badger is closely related to the European badger and shares similar physical characteristics.

Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
- What is the average lifespan of a European badger in the wild?
European badgers typically live around 6 to 8 years in the wild, although some individuals may exceed this lifespan. - Do European badgers have any natural predators?
While adult European badgers don’t have many natural predators, young badgers may be vulnerable to larger carnivores such as wolves and large birds of prey. - How do European badgers communicate with each other?
European badgers communicate through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. They use a variety of sounds, including growls, squeals, and purrs. - Are European badgers territorial?
Yes, European badgers are territorial animals, and they mark their territories with scent markings. Territories are defended against other badgers. - What is the primary threat to European badger populations?
One of the main threats to European badgers is habitat loss due to human activities. Road accidents and persecution by humans also pose significant challenges. - Do European badgers migrate or have a fixed range?
European badgers are not migratory, and they usually have a defined home range. However, the size of their range can vary based on factors such as food availability. - How much territory does a European badger family unit cover?
A European badger family unit, also known as a clan, typically covers a territory of several square kilometers. The size depends on factors like food availability and population density. - Can European badgers climb trees?
No, European badgers are not skilled climbers. They are primarily ground-dwelling animals and are adapted to digging burrows rather than climbing. - Do European badgers have a distinct mating season?
European badgers generally mate in late winter or early spring. During this time, males may engage in ritualistic behaviors to compete for mates. - How do European badgers contribute to soil health?
European badgers are burrowers, and their digging activities help aerate the soil. This can enhance soil health and benefit smaller organisms in the ecosystem. - Are European badgers susceptible to diseases?
Yes, European badgers can be susceptible to various diseases, including bovine tuberculosis. Research is ongoing to understand and manage these health concerns. - Can European badgers swim?
Yes, European badgers are capable swimmers. They may swim across bodies of water if necessary, although they generally prefer to stay on land. - Do European badgers undergo a seasonal change in behavior?
Yes, European badgers may exhibit seasonal variations in behavior, such as increased activity during warmer months and reduced activity in winter. - What role do European badgers play in seed dispersal?
European badgers unintentionally contribute to seed dispersal by transporting seeds on their fur or in their feces, aiding in the regeneration of plant species. - How do European badgers adapt to urban environments?
Some European badger populations have adapted to urbanization by utilizing green spaces, parks, and even abandoned structures for shelter. This adaptation poses both challenges and opportunities for coexistence with humans.














Leave your comment