European Bison
- December 29, 2023
- 0 comment
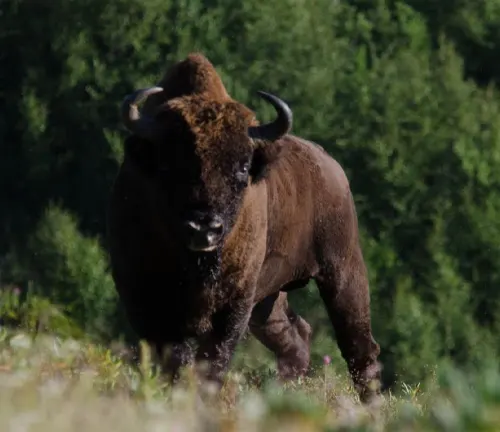
The European Bison, also known as Bison bonasus, is an iconic and majestic mammal that holds the title of being the continent’s heaviest land animal. Characterized by its robust build and distinctive hump at the shoulders, the European Bison is easily identified by its massive head, adorned with a formidable set of curved horns. These magnificent creatures exhibit a dark brown fur coat, which becomes lighter in the summer months, providing a striking contrast against the snow-draped landscapes they often inhabit.
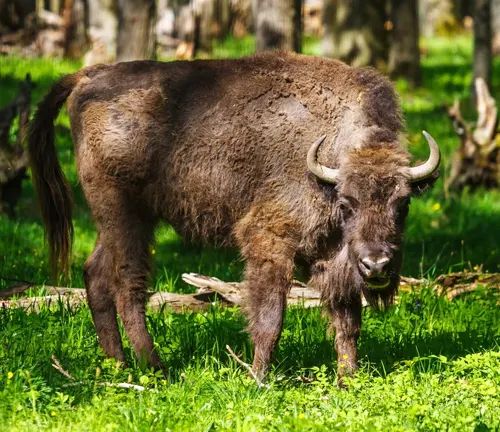

Physically, European Bison showcases a formidable stature, with males typically larger than females. Adult males can weigh up to a ton or more and stand around six feet tall at the shoulder. Their formidable horns can span up to three feet, adding to their imposing appearance. Despite their massive size, European Bison are surprisingly agile and are known for their ability to navigate dense forests and rough terrains.
Historically, the species faced near-extinction due to overhunting and habitat loss, but dedicated conservation efforts have successfully revived their populations. Today, European Bison inhabit protected areas and national parks in Eastern and Central Europe, with notable populations in countries such as Poland, Belarus, and Russia. These areas provide a range of habitats, from dense forests to open meadows, allowing these magnificent creatures to thrive. Efforts to reintroduce the European Bison into various regions continue to contribute to the conservation and preservation of this iconic species, ensuring that it remains an integral part of Europe’s natural heritage.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Bison bonasus |
| Common Names | European Bison, Wisent |
| Size (Adult Male) | Up to 10 feet (3 meters) in length |
| Height at Shoulder | Around 6 feet (1.8 meters) |
| Weight (Adult Male) | Up to 2,200 pounds (1,000 kilograms) |
| Horns | Distinctive, curved, can span up to 3 feet |
| Coat Color | Dark brown, lightening in summer |
| Habitat | Forests, meadows, open landscapes |
| Range | Eastern and Central Europe, including Poland, Belarus, Russia |
| Conservation Status | Near Threatened (IUCN Red List) |
| Distinctive Features | Massive head, hump at shoulders, formidable appearance |
| Lifespan | Up to 20 years in the wild |
| Behavior | Herbivorous, social animals with herding tendencies |
| Conservation Efforts | Successful reintroduction programs in various European countries |
| Historical Significance | Symbolic and cultural importance in European heritage |
A Closer Look at its General Biology
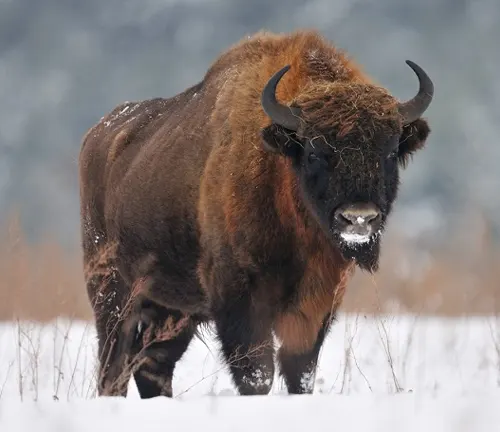

The European Bison, scientifically known as Bison bonasus, stands as a testament to the resilience of a species on the brink of extinction. This magnificent creature, with its robust build and distinctive appearance, is the largest terrestrial mammal in Europe. Exploring its general biology unveils the intricacies of its anatomy, including the imposing hump at the shoulders, formidable horns, and a dense coat that adapts to the changing seasons. As we delve into the biology of the European Bison, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable adaptations that have allowed it to endure and thrive in the wild.
The Circle of Life
In the intricate tapestry of the European Bison’s life, the chapter of reproduction plays a crucial role. Understanding the reproductive patterns and behaviors of these magnificent creatures sheds light on the species’ survival strategies. From courtship rituals to the nurturing of calves, the reproductive journey of the European Bison is a fascinating tale of resilience and adaptation. Join us as we explore the family dynamics and the efforts taken to ensure the continuity of this iconic species.
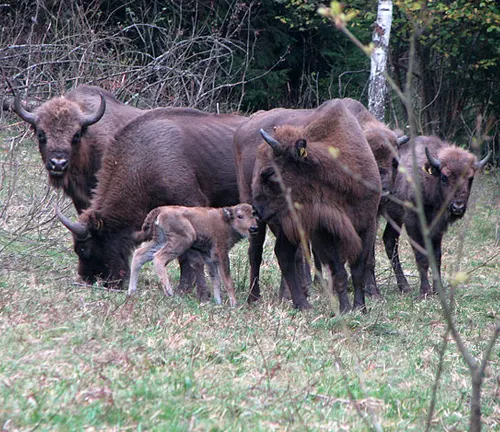

Social Symphony
The European Bison is not merely a solitary giant roaming the wilderness but a social being with complex behaviors. This article delves into the intricacies of their social structure, communication methods, and interactions within the herd. From hierarchical arrangements to communal defense mechanisms, the behavioral patterns of the European Bison paint a vivid picture of a species deeply connected to its environment and fellow herd members.
Beyond Borders
A journey through the habitats of the European Bison unveils a diverse range of landscapes that these creatures call home. From dense forests to open meadows, these giants navigate various terrains with surprising agility. Explore the regions of Eastern and Central Europe, including Poland, Belarus, and Russia, where conservation efforts have successfully reintroduced the European Bison. Discover how these habitats play a crucial role in the survival and well-being of this magnificent species.
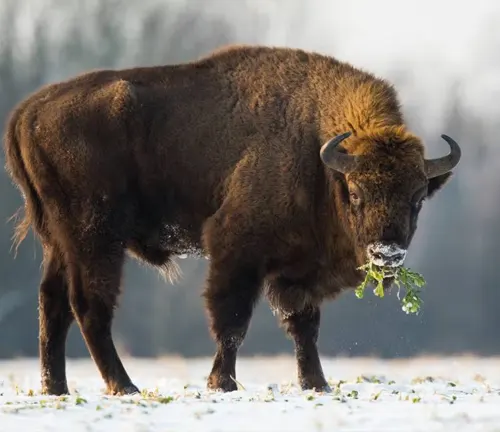

Culinary Choices
In the vast buffet of nature, the European Bison is a selective herbivore with specific dietary preferences. Understanding its food habits provides insights into the delicate balance of ecosystems where it roams. Join us as we explore the nutritional choices of the European Bison, from browsing on grasses and herbs to seasonal variations in diet. The intricate relationship between the bison and its food sources reveals the species’ role as a keystone herbivore in shaping the landscapes it inhabits.
Whispers in the Wild
The European Bison communicates not only through its massive physical presence but also through a nuanced language of sounds, tracks, and signs. From deep grunts to the subtle language of hoof prints in the snow, these creatures leave a trail of communication that echoes through their habitats. This article decodes the auditory and visual cues that contribute to the intricate web of interactions among European Bison, offering a glimpse into their silent yet expressive world.
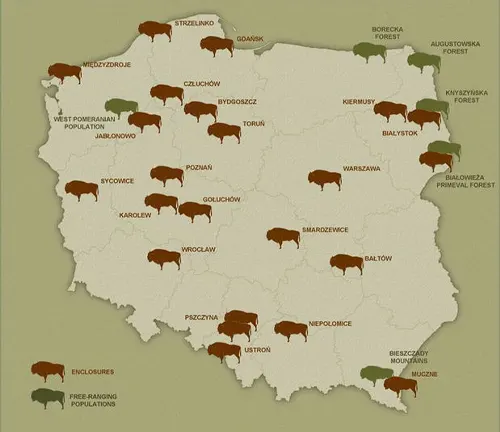
The Distribution of European Bison
The range of the European Bison extends far beyond national borders, creating a tapestry of distribution that reflects both historical significance and conservation triumphs. Tracing its distribution across Europe, we explore how concerted efforts have been made to reintroduce this species to areas where it once roamed freely. From the challenges of fragmented habitats to the success stories of protected reserves, the distribution of European Bison mirrors the ongoing efforts to preserve this symbol of natural heritage.
Different Species
Lowland European Bison
(Bison bonasus bonasus)
The Lowland European Bison is the more numerous of the two subspecies.
Historically, it inhabited the lowland forests of Eastern and Central Europe.

Caucasian European Bison
(Bison bonasus caucasicus)
The Caucasian European Bison is a subspecies that historically occupied the Caucasus region, including parts of Russia and the South Caucasus.
It is considered a distinct subspecies due to certain morphological differences and historical distribution.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the European Bison?
The European Bison, also known as Bison bonasus or Wisent, is the largest terrestrial mammal in Europe. It is a herbivorous species and holds cultural and ecological significance. - Where does the European Bison live?
European Bison historically inhabited large parts of Eastern and Central Europe. Conservation efforts have led to reintroductions in various countries, including Poland, Belarus, and Russia. - How big is a European Bison?
Adult European Bison can weigh up to 2,200 pounds (1,000 kilograms) and stand around 6 feet tall at the shoulder. Males are generally larger than females. - What is the conservation status of the European Bison?
The European Bison is classified as “Near Threatened” on the IUCN Red List. Conservation initiatives, including breeding programs and habitat protection, have helped increase their numbers. - What are the main threats to European Bison?
Historically, habitat loss and overhunting posed significant threats. Conservation efforts aim to address these challenges and mitigate potential conflicts with human activities. - How do European Bison contribute to ecosystems?
European Bison play a crucial role as keystone herbivores, shaping landscapes through their grazing and browsing activities. Their presence enhances biodiversity and supports the health of ecosystems. - Are European Bison dangerous to humans?
Generally, European Bison are not considered dangerous to humans. They are herbivores and prefer to avoid confrontations. However, like any wild animal, they can be unpredictable and should be observed from a safe distance. - What is the breeding behavior of European Bison?
European Bison engage in a mating season, and after a gestation period of around nine months, a single calf is born. The female cares for and protects the calf, and herds often exhibit social structures. - Can European Bison be domesticated?
European Bison are wild animals and not typically domesticated. Efforts focus on conserving them in their natural habitats and reintroducing them to suitable areas. - How can I support European Bison conservation?
Supporting conservation organizations, visiting wildlife reserves that house European Bison, and raising awareness about the importance of preserving their habitats are effective ways to contribute to their conservation.














Leave your comment