American Black Bear
- January 10, 2024
- 0 comment
The American Black Bear, Ursus americanus, stands as a captivating symbol of North America’s diverse wilderness. Renowned for its adaptability and resilience, this species thrives in a range of habitats, from dense forests to mountainous regions. Recognizable by its sleek black fur, though color variations can occur, the American Black Bear boasts an impressive size, with males weighing between 200 to 600 pounds and females ranging from 100 to 400 pounds.
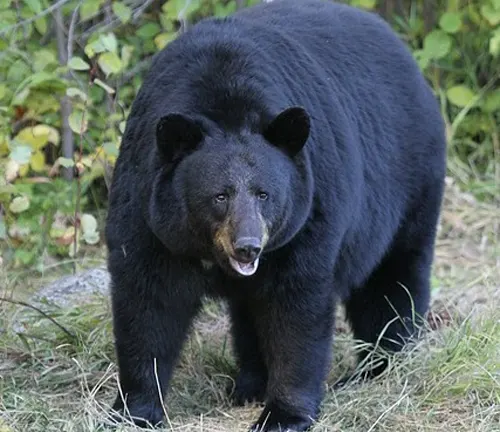

Despite its formidable appearance, this bear is typically solitary, except for mothers caring for their cubs. Known for its omnivorous diet, the American Black Bear forages for berries, plants, small mammals, and fish, contributing to its vital role in ecosystem health. Beyond the biological realm, these bears hold cultural significance in Native American folklore, symbolizing strength and a harmonious connection to nature. Conservation efforts strive to protect their habitats and mitigate human-bear conflicts, ensuring the continued existence of this remarkable species.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ursus americanus |
| Average Adult Weight | Males: 200-600 pounds, Females: 100-400 pounds |
| Coat Color | Typically black, but variations include brown and cinnamon |
| Habitat | Diverse – forests, swamps, mountains |
| Diet | Omnivorous, including berries, plants, small mammals, and fish |
| Social Behavior | Generally solitary, except for mothers with cubs |
| Reproductive Cycle | Mating in late spring or early summer, with cubs born every two to three years |
| Lifespan in the Wild | Around 20-25 years |
| Geographic Range | Throughout North America, from coast to coast |
| Cultural Significance | Symbolic in Native American folklore, representing strength and nature connection |
| Conservation Status | Various subspecies with different conservation statuses, overall concern for habitat preservation and human-bear coexistence |
Understanding the American Black Bear: A Deep Dive into Nature’s Enigmatic Omnivore
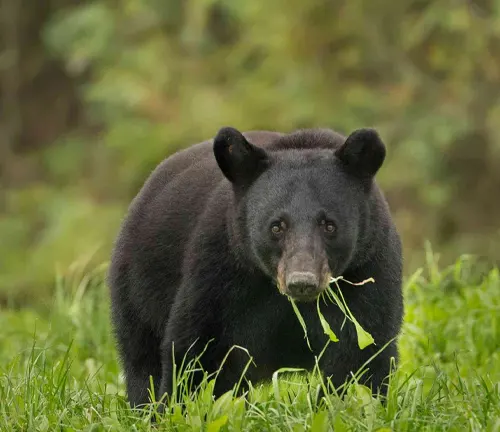

The American black bear, Ursus americanus, stands as a symbol of wild beauty in North America. From the dense forests of the Pacific Northwest to the Appalachian Mountains, these remarkable creatures roam a vast range, capturing the hearts of those fortunate enough to encounter them. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries surrounding these enigmatic omnivores and explore the intricate facets of their existence.
Physical Characteristics
The American black bear exhibits a fascinating array of physical characteristics. Ranging in size from petite to robust, these bears boast fur that varies not only in color but also in texture. From the sleek black coats prevalent in many individuals to the occasional cinnamon or brown hues, the diversity in their appearance reflects the adaptability of this species.
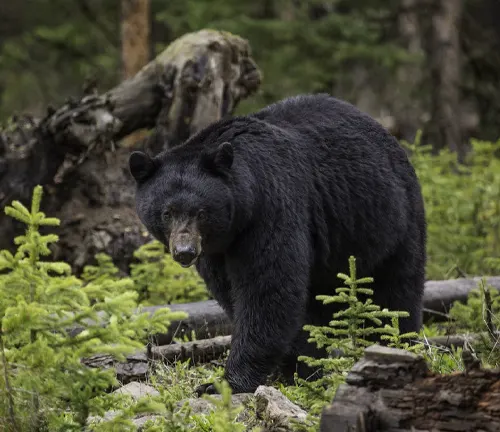

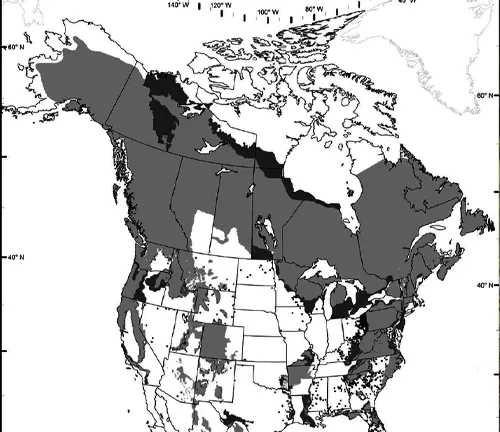
Geographic Distribution
To truly appreciate the American black bear, one must delve into its habitat preferences and expansive geographic range. From the dense coniferous forests of the Rockies to the swampy expanses of the Southeast, these bears have adapted to diverse environments, showcasing their resilience and ability to thrive in different ecosystems.
Behavior and Lifestyle
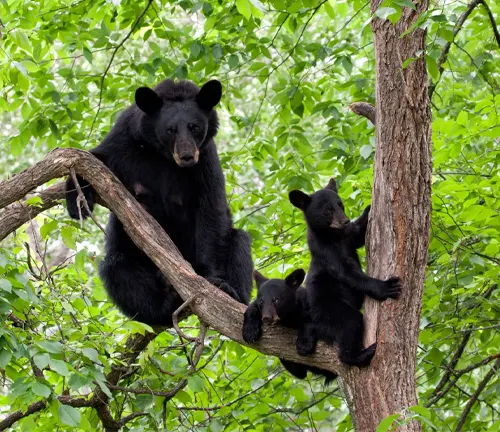
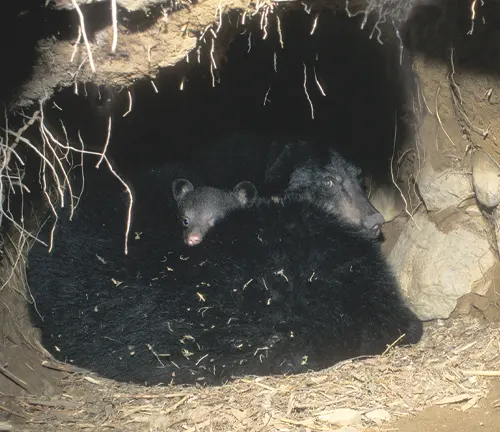
As primarily nocturnal creatures, black bears navigate their territories under the moonlit sky. Hibernation patterns add another layer to their intriguing lifestyle, with these bears entering a state of dormancy during the harsh winter months. Understanding these behaviors provides valuable insights into their daily lives and survival strategies.


Diet and Feeding Habits
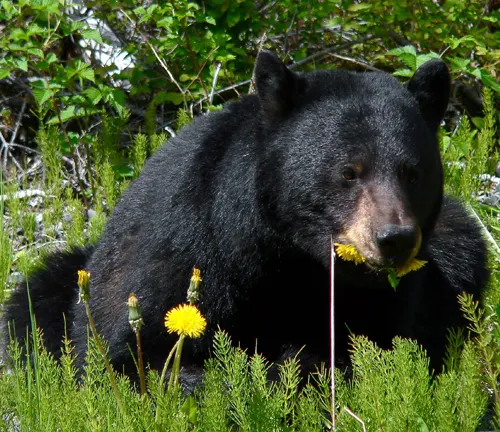
Omnivorous by nature, American black bears exhibit a broad spectrum of dietary habits. Their menu changes with the seasons, from foraging on berries and plants in the summer to scavenging for small mammals and fish. This adaptability plays a crucial role in their survival and ecological impact.
Reproduction
Mating habits and parenting behaviors shed light on the familial side of black bears. With a unique approach to reproduction, these creatures engage in intricate mating rituals, leading to the birth of cubs. Parental care is a fascinating aspect, showcasing the nurturing side of these formidable creatures.


Interaction with Humans
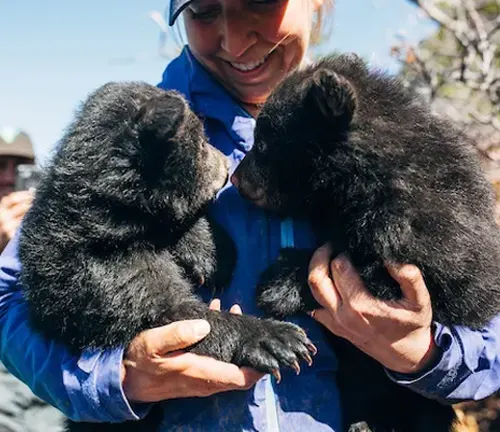
The historical significance of black bears in Native American cultures adds depth to their interaction with humans. While conflicts arise due to habitat encroachment, coexistence efforts and education contribute to fostering understanding between humans and bears.
Conservation Status
Exploring the current conservation status of American black bears reveals both success stories and ongoing challenges. Population trends and conservation initiatives provide hope for the future, emphasizing the importance of continued efforts to protect this species.
Threats and Challenges
Human-induced threats and the impact of climate change pose challenges to the survival of black bears. Awareness of these threats is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the long-term well-being of the species.
Importance in Ecosystem
The role of black bears in maintaining ecological balance cannot be overstated. Their interconnectedness with other species creates a delicate web of life, showcasing the ripple effect of conservation efforts on entire ecosystems.

Different Species
Ursus americanus americanus
(Eastern Black Bear)
Found in the eastern part of North America, including the Appalachian region.
Typically has a black coat, but brown variations are not uncommon.

Ursus americanus floridanus
(Florida Black Bear)
Inhabits the forests of Florida.
Often smaller in size compared to other subspecies, with a glossy black coat.

Ursus americanus luteolus
(Louisiana Black Bear)
Primarily found in Louisiana and surrounding areas.
Features a lighter, cinnamon-colored coat.

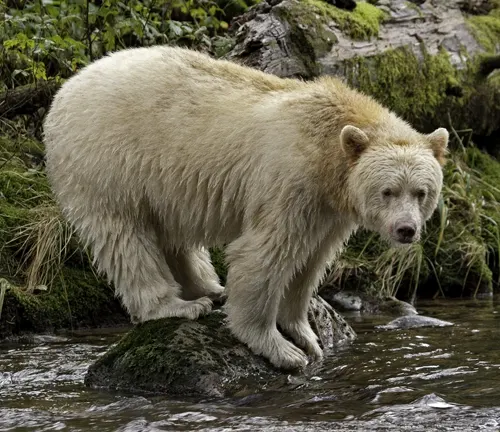
Ursus americanus kermodei
(Kermode Bear or Spirit Bear)
Occurs in certain areas of British Columbia, Canada.
Known for its unique white or cream-colored fur, although not all individuals display this trait.

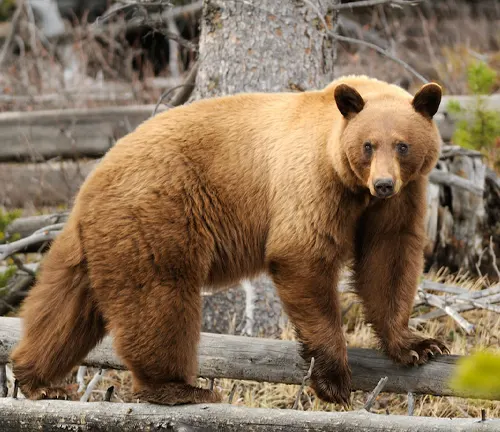
Ursus americanus cinnamomum
(Cinnamon Bear)
Distributed in the western part of North America.
Characterized by its cinnamon or reddish-brown fur.

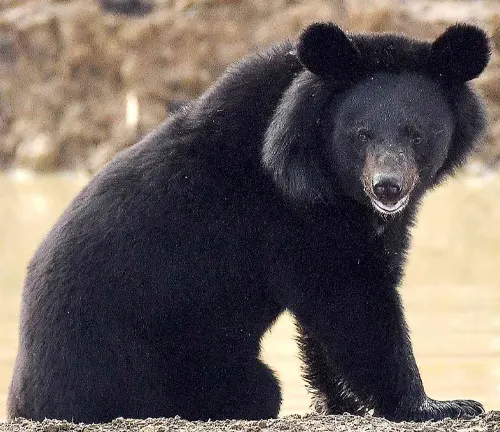
Ursus americanus altifrontalis
(Olympic Black Bear)
Inhabits the Olympic Peninsula in Washington state.
Often has a dark black coat, and some individuals may exhibit a lighter coloration.

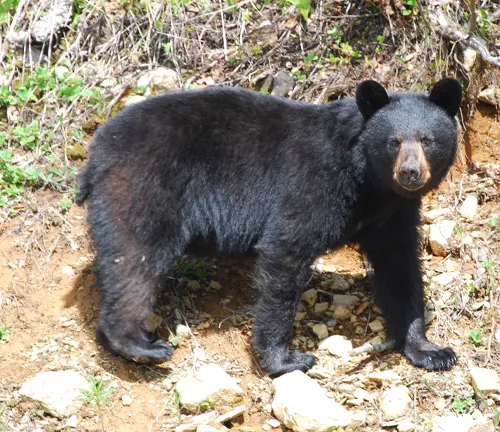
Ursus americanus emmonsii
(Newfoundland Black Bear)
Native to the island of Newfoundland.
Tends to have a smaller body size compared to mainland black bears.

Ursus americanus vancouveri
(Vancouver Island Black Bear)
Found on Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada.
Known for a higher percentage of individuals with a white “blaze” or chest mark.

Ursus americanus californiensis
(California Black Bear)
Inhabits the forests of California.
Exhibits a range of coat colors, including black, brown, and cinnamon.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Where can American black bears be found in North America?
American black bears can be found in various habitats throughout North America, including forests, swamps, and mountainous regions. - How many subspecies of American black bears exist, and what distinguishes them?
There are several subspecies of American black bears, including the Eastern Black Bear, Florida Black Bear, and Louisiana Black Bear. They differ in size, coat color, and geographic distribution. - What is the average weight range of adult male and female black bears?
Adult male black bears typically weigh between 200 to 600 pounds, while females generally range from 100 to 400 pounds. - Do American black bears have any natural predators in the wild?
Adult American black bears typically do not have natural predators, but cubs may be vulnerable to predators like wolves or cougars. - What is the reproductive behavior of black bears, and how often do they give birth?
Black bears reproduce through mating, and females usually give birth to cubs every two to three years. Mating occurs in late spring or early summer. - Are black bears social animals, or do they prefer a solitary lifestyle?
Black bears are generally solitary animals, except for mothers with cubs. They may share overlapping territories but are not highly social. - How do black bears contribute to ecosystem health and biodiversity?
Black bears play a crucial role in seed dispersal, helping maintain plant diversity. Their activities contribute to a healthy and balanced ecosystem. - What kind of vocalizations do American black bears make, and what do they signify?
Black bears produce vocalizations such as huffs, woofs, and jaw-popping sounds. These serve as communication signals, expressing various emotions or warnings. - How can humans safely coexist with black bears in areas where they are present?
Coexistence involves securing food, avoiding direct contact, and understanding bear behavior. Following guidelines for bear encounters helps minimize conflicts. - What is the significance of the American black bear in Native American cultures?
The American black bear holds cultural significance in Native American folklore, often symbolizing strength, wisdom, and a connection to nature. - How far can black bears travel in search of food or suitable habitats?
Black bears can cover large distances, ranging from several miles to over a hundred miles, in search of food, mates, or suitable habitats. - Do black bears have a specific range of activity during different seasons?
Their activity varies with the seasons. Black bears may hibernate in winter, forage during spring and summer, and prepare for hibernation in the fall. - Are there any known cases of American black bears living in urban environments?
Yes, there are instances of black bears adapting to urban areas, attracted by food sources. Proper waste management is crucial in such situations. - What measures are in place for the conservation of American black bears?
Conservation efforts include habitat protection, managing human-bear conflicts, and implementing laws against illegal hunting. - How can individuals contribute to black bear conservation efforts?
Individuals can support conservation by promoting responsible behavior in bear habitats, participating in community initiatives, and supporting conservation organizations. - Do black bears have a keen sense of smell, and how does it aid them in survival?
Yes, black bears have an excellent sense of smell, crucial for finding food, detecting predators, and navigating their environment. - Can black bears swim, and do they have a preference for aquatic habitats?
Black bears are proficient swimmers and may swim across bodies of water. However, they don’t have a specific preference for aquatic habitats. - What is the role of black bears in seed dispersal and forest regeneration?
Black bears aid in seed dispersal by consuming fruits and berries. They deposit seeds in different locations, contributing to forest regeneration. - How do black bears defend themselves against potential threats?
Black bears may use defensive behaviors like bluff charges, vocalizations, or climbing trees to escape threats. Their size and strength are also deterrents. - Are there any specific guidelines for camping or hiking in bear country?
Guidelines include storing food securely, using bear-resistant containers, making noise to alert bears of your presence, and avoiding surprise encounters.














Leave your comment