How Does Carbon Capture Help Fight Climate Change
- January 31, 2025
- 0 comment
Excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is a significant factor in trapping solar heat, leading to substantial changes in the Earth’s climate. As long as we depend on fossil fuels that emit carbon, CO2 levels will continue to climb. However, carbon capture technologies offer a promising solution to help decrease the concentration of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere.
What Is Carbon Capture?
Carbon capture refers to a range of methods designed to reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere. Some techniques focus on capturing carbon at its source, preventing it from entering the atmosphere, while others are aimed at removing carbon dioxide directly from the air. This technology is essential in the fight against climate change and global warming, as the accumulation of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) has led to a significant rise in Earth’s temperature since the Industrial Revolution. In the early 1800s, atmospheric CO2 levels were about 280 parts per million (PPM), but they have now surged to 415 PPM, increasing at a rate of 2.5 PPM annually.
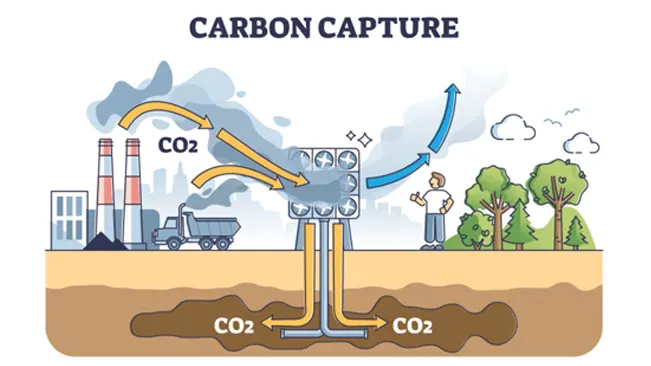
As carbon levels continue to rise, carbon capture offers a vital tool to help achieve the main objective of the Paris Agreement: limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit). By capturing emissions at power plants before they are released into the atmosphere, we can mitigate the ongoing increase in CO2 levels. Additionally, specialized carbon capture facilities that extract CO2 directly from the air present another effective method for sequestering carbon from our atmosphere.
What Are the Primary Types of Carbon Capture
Factory Carbon Capture
Carbon capture technology implemented in factories, refineries, and large-scale industrial facilities is designed to capture carbon before it is emitted into the atmosphere. Currently, there are 21 carbon emission capture sites operating worldwide, where these facilities separate CO2 from their emissions for either permanent storage or repurposing. Initially, the oil industry pioneered carbon capture by harvesting CO2 from their emissions and injecting it into oil fields to enhance oil recovery.

In the 1980s and 1990s, the focus shifted to capturing carbon from industrial emissions as a viable strategy for mitigating climate change. The process typically involves redirecting emissions into a chamber where a solvent absorbs the carbon dioxide. Afterward, the carbon-rich solvent is heated to separate the CO2, allowing the solvent to be reused while the carbon is stored or repurposed.
Direct Air Capture
Direct air capture (DAC) refers to the process of removing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere. Given the current abundance of CO2, simply preventing further emissions is insufficient to combat climate change. The most effective approach is to achieve net-zero emissions while simultaneously removing existing carbon from the air. Currently, there are 15 DAC facilities in operation across Europe, the United States, and Canada.

Although carbon removal is crucial for transitioning to a zero-emission future, it is not yet the most cost-effective solution due to the low concentration of CO2 (only 0.04%) in the atmosphere, making direct removal challenging. However, as technology advances and support for DAC increases, it will play an essential role in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels and preventing further global warming.
What Happens to Carbon Once It Is Captured
Carbon Capture and Storage
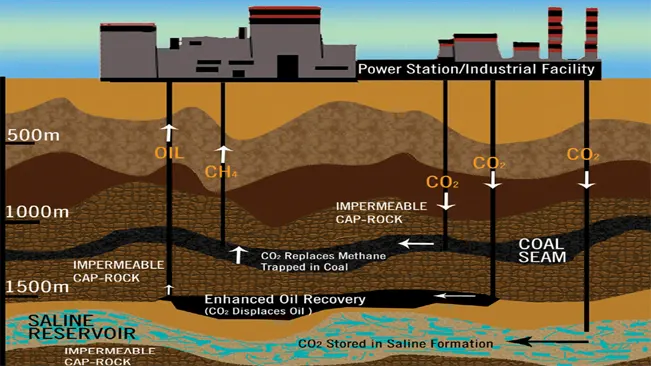
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process that involves capturing carbon dioxide and securely storing it to prevent its release into the atmosphere. Techniques for storing large quantities of carbon have been developed over the past 45 years. Once captured, the carbon is transported to a designated storage site, typically a geological formation.

This transportation is carried out using various methods, including trucks, railways, ocean vessels, and pipelines. The captured carbon is then injected deep underground into formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or deep saline aquifers, where it can remain safely without re-entering the atmosphere.
Carbon Capture and Utilization
Another approach is carbon capture and utilization (CCU), where captured carbon is repurposed for various applications. Some uses may eventually lead to CO2 re-entering the atmosphere, while others aim for longer-term storage. One common application is enhanced oil recovery, which, although it still relies on fossil fuels, improves the efficiency of extracting these resources and reduces carbon emissions during the process. Additionally, CO2 can be transformed into fuels, providing energy but also releasing carbon when burned.
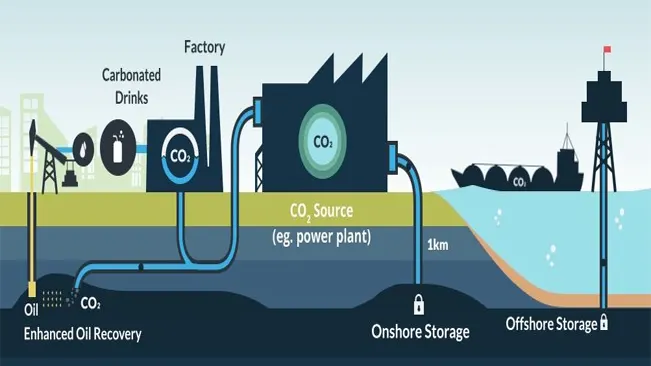
Carbon can also be converted into chemicals used in the production of polymers and pharmaceuticals. One promising and sustainable application is using carbon for water desalination, which addresses the challenges of water scarcity due to climate change while helping to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and supplying clean drinking water to communities in need.
Benefits of Carbon Capture
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Carbon capture technologies have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, which is a major contributor to global warming. Studies suggest that implementing carbon capture and storage (CCS) on a large scale could reduce CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial sources by up to 90%. This reduction is crucial for meeting international climate targets, such as those set by the Paris Agreement. The technology can effectively capture emissions at the source before they enter the atmosphere, providing a direct method to combat climate change.

Several successful case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of carbon capture in reducing emissions. For instance, the Petra Nova project in Texas captures over 1.6 million tons of CO2 annually from a coal-fired power plant, utilizing the captured carbon for enhanced oil recovery. Similarly, the Boundary Dam project in Canada has successfully captured and stored over 1 million tons of CO2 each year since its inception. These projects not only illustrate the practical application of carbon capture technology but also highlight its potential to contribute to emission reduction goals while promoting sustainable practices.
Supporting Renewable Energy Transition
Carbon capture can play a pivotal role in complementing renewable energy sources, facilitating a smoother transition to a low-carbon economy. While renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, are essential for reducing reliance on fossil fuels, they cannot yet fully meet global energy demands. Carbon capture technology allows existing fossil fuel plants to operate more sustainably by capturing their emissions, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint of energy production. This synergy can help bridge the gap between current energy needs and future sustainability goals.

Moreover, the integration of carbon capture with renewable energy systems enhances the overall resilience and flexibility of the energy grid. For instance, captured CO2 can be utilized in processes like producing synthetic fuels, which can help stabilize energy supplies when renewable generation is low. Additionally, CCS can contribute to the development of negative emission technologies, where captured carbon is permanently stored, effectively removing CO2 from the atmosphere. This combination of carbon capture and renewable energy solutions not only accelerates the transition to a sustainable energy future but also strengthens efforts to achieve climate goals.
How Efficient Is Carbon Capture
Carbon capture presents a promising solution for reducing emissions, but its efficiency is a crucial consideration. Typically, carbon capture systems implemented in industrial settings can capture over 90% of the carbon emitted from a facility. Some projects have even achieved capture rates exceeding 95%, and advancements in technology could push efficiency closer to 99%. However, higher efficiency often correlates with increased costs, posing a financial challenge for widespread implementation.
To address this investment issue, carbon finance mechanisms, such as carbon taxes, can incentivize businesses to adopt sustainable practices. These taxes apply to companies that exceed certain carbon emission thresholds, encouraging them to invest in advanced carbon capture technologies to avoid fines. By achieving net-zero or negative emissions, companies may also qualify for tax credits. As more industries embrace these innovations, we can expect significant improvements in the efficiency and effectiveness of carbon capture efforts in the near future.
Can Carbon Capture Reverse Climate Change
Carbon capture holds significant promise for addressing climate change, but it must be part of a multifaceted approach. Carbon dioxide is the leading factor contributing to the greenhouse effect that drives climate change. By removing more carbon from the atmosphere, we can mitigate the warming of the planet and the resulting shifts in climate patterns.

As carbon capture technologies advance, we can expect industries to decrease their carbon emissions. However, transitioning to clean and renewable energy sources is equally vital for reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions. Once we halt carbon emissions, methods like direct air capture and sustainable forestry practices can further help lower atmospheric CO2 levels. In the meantime, supporting sustainability initiatives is crucial. One effective way to get involved is through carbon offsetting, which not only reduces your carbon footprint but also supports environmentally friendly projects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon capture plays a vital role in the global effort to combat climate change by significantly reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. By employing technologies that capture emissions from industrial sources and even extract CO2 directly from the air, we can mitigate the greenhouse effect that is driving climate change. However, carbon capture alone is not a silver bullet; it must be part of a broader strategy that includes transitioning to renewable energy and implementing sustainable practices. As advancements in carbon capture technology continue, combined with supportive policies and public participation, we can make meaningful progress toward a more sustainable future and work towards limiting global warming. Engaging in carbon offsetting and supporting innovative projects are practical steps everyone can take to contribute to this critical mission.
FAQS
- What is carbon capture?
Carbon capture is a technology that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from sources such as power plants and industrial facilities before they enter the atmosphere. The captured CO2 can then be stored underground or repurposed for various applications. - How does carbon capture help combat climate change?
By capturing CO2 emissions, carbon capture technology reduces the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which helps mitigate global warming and its associated impacts. This reduction is crucial for achieving international climate goals. - What are the main types of carbon capture technology?
The primary types include point source capture, which captures emissions at the source; direct air capture (DAC), which removes CO2 directly from the atmosphere; and bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), which combines biomass energy production with carbon capture. - How effective is carbon capture in reducing emissions?
Carbon capture systems can typically capture over 90% of the CO2 emitted from industrial sources. Some advanced projects have achieved capture rates exceeding 95%, with ongoing technological advancements aimed at increasing efficiency further. - Can carbon capture be used alongside renewable energy?
Yes, carbon capture can complement renewable energy sources by allowing existing fossil fuel plants to operate more sustainably. It can also facilitate the development of synthetic fuels and contribute to a more resilient energy grid. - What are some successful examples of carbon capture projects?
Notable examples include the Petra Nova project in Texas, which captures over 1.6 million tons of CO2 annually, and the Boundary Dam project in Canada, which has captured more than 1 million tons of CO2 each year since its launch. - What challenges does carbon capture face?
Challenges include the high costs of implementation, the need for supportive policies, and potential public concerns about safety and environmental impacts. Additionally, carbon capture must be integrated with broader strategies to transition to renewable energy. - How can individuals contribute to carbon capture efforts?
Individuals can support carbon capture initiatives through participation in carbon offset programs, advocacy for sustainable practices, and supporting policies that promote investment in carbon capture technologies. - What is the future of carbon capture technology?
As technology advances and investment in carbon capture increases, we can expect significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness. Carbon capture will likely play a critical role in achieving net-zero emissions goals globally.

Charles Hayes
Forestry AuthorI'm Charles Hayes, I bring over 15 years of specialized expertise in landscaping and woodworking, blending artistic design with sustainable environmental stewardship. My career, fueled by a profound passion for the natural world, encompasses extensive education and hands-on experience in creating harmonious, eco-friendly outdoor spaces and responsibly managing forest resources. Recognized for my professional standing, I am committed to continuous learning and certification in cutting-edge practices. My expertise is not only reflected in my work but also in my contributions to community projects, educational workshops, and collaborations with industry leaders. As an authoritative voice in my field, I strive to share knowledge and promote environmentally conscious approaches, making me a trusted resource in landscaping and forestry.













Leave your comment