How to Plant Rose Apple Tree: Cultivation Secrets for Lush Growth
- March 26, 2024
- 1 comment
Learn how to plant Rose Apple Trees, scientifically known as Syzygium jambos, celebrated for their unique bell shape and appealing pink to yellow skin. Originating from Southeast Asia, rose apples are cherished not just for their mildly sweet flavor and rose-like aroma but also for their nutritional benefits, such as aiding digestion and enhancing immunity. This guide will assist you in adding these nutritious and aromatic trees to your garden, enriching your landscape’s beauty and providing a versatile tropical fruit for fresh consumption, juices, or culinary creations.

Rose Apple Tree Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Value | Rose Apples are low in calories and contain a good amount of Vitamin C, dietary fiber, Vitamin A, calcium, and thiamin. |
| Digestive Health | The dietary fiber in Rose Apples aids in digestion and helps prevent constipation. |
| Diabetes Management | Some studies suggest that Rose Apple can help in managing blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for people with diabetes. |
| Antioxidant Properties | Rich in antioxidants, Rose Apples can combat free radicals in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. |
| Hydration | Rose Apples have a high water content, which helps in keeping the body hydrated, especially in hot climates. |
| Skin Health | The Vitamin C and Vitamin A in Rose Apples contribute to healthy skin by aiding in collagen production and providing protection against skin damage. |
| Heart Health | The fiber, Vitamin C, and potassium in Rose Apples support heart health by helping to reduce cholesterol levels and regulate blood pressure. |
| Anti-inflammatory Effects | The fruit has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body, benefiting conditions like arthritis. |
| Immune System Support | The Vitamin C in Rose Apples is crucial for a healthy immune system, aiding in the prevention of infections and illnesses. |
| Weight Management | Being low in calories and high in fiber, Rose Apples can be a part of a weight loss diet, as they provide a feeling of fullness. |
List on How To Plant Rose Apple Tree
- Selecting the Right Location
- Preparing the Planting Site
- Planting the Tree
- Watering
- Mulching and Fertilizing
- Pest and Disease Control
- Harvesting
Selecting the Right Location
Rose Apple trees thrive in warm, tropical climates but are surprisingly adaptable to various soil types. However, they prefer well-draining soil. Choose a sunny location, as these trees need full sun exposure for optimal growth and fruit production.

- Soil Adaptability
- Rose Apple trees can grow in various soil types: sandy, loamy, or clayey.
- The crucial factor is good drainage.
- The soil must not retain standing water to prevent root diseases.
- Soil should balance moisture retention for nourishment and effective drainage of excess water.
- Enhancing soil with organic compost improves nutrient content and drainage.
- Sunlight Requirements
- Full sun exposure is essential, meaning at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day.
- Ample sunlight is vital for the tree’s energy production.
- Influences the strength of branches and leaves, and impacts the quality and quantity of fruit.
- A location with abundant sunlight ensures sufficient energy for a bountiful harvest.
- Space Considerations
- Rose Apple trees can grow large; adequate space is necessary for growth.
- Ensure enough room for expansion of both the canopy and roots.
- Avoid planting too close to buildings or other trees.
- Sufficient space supports healthy growth and air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Preparing the Planting Site
Prepare the site by clearing away any weeds or grass. Dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of your sapling. Amend the soil with organic compost to improve nutrient content and drainage.
- Hole Size
- Dig the hole approximately twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of the sapling. This size allows ample room for the roots to spread and establish.
- Soil Amendment
- Amend the soil with organic compost, particularly if your native soil lacks organic matter. This improves fertility, enhancing the soil’s ability to retain water and nutrients, and boosts drainage quality.
- Preventing Root Restriction
- Avoid digging a hole that’s too small as it can restrict root growth, affecting the tree’s health and stability.
- Enhancing Soil Structure
- The addition of compost not only feeds the tree but also improves the soil’s structure. This is vital for maintaining a good balance of moisture and aeration in the soil.
- Drainage Importance
- Good drainage is crucial. Enhanced drainage through amended soil helps prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root diseases.
- Pre-planting Watering
- Water the prepared hole before planting. This step ensures that the soil is adequately moist, creating a favorable environment for the sapling’s roots.
Planting the Tree
Carefully remove the Rose Apple sapling from its container. Loosen the roots gently if they are bound. Place the sapling in the center of the hole, ensuring it is standing straight. Backfill the hole with the amended soil, and gently tamp down to remove air pockets.

- Remove the Sapling Gently: Carefully take the Rose Apple sapling out of its container, being cautious not to damage the delicate roots.
- Loosen Bound Roots: If the roots are tightly bound in a circular pattern, slightly loosen them. This encourages the roots to spread into the soil and establish a strong foundation.
- Positioning the Sapling: Place the sapling in the center of the prepared hole, ensuring it is upright and centered. The base of the stem (where it meets the roots) should be level with the surrounding soil surface to avoid burying the stem too deep or exposing the roots.
- Backfill the Hole: Use the previously amended soil, preferably enriched with organic compost, to backfill the hole. Distribute the soil evenly around the roots, being careful not to compact it too firmly, which can hinder root growth and water penetration.
- Eliminate Air Pockets: Gently tamp down the soil as you fill the hole to remove any air pockets that could dry out the roots.
- Create a Soil Mound: Form a slight mound around the base of the tree, being careful not to cover the stem. This assists in water absorption.
- Water Thoroughly: After planting, water the tree thoroughly to settle the soil and provide essential moisture to the roots, supporting a healthy start for the tree’s growth.
Watering
Water the tree deeply right after planting. Rose Apple trees need regular watering, especially during dry periods. However, avoid waterlogging as it can lead to root rot.
- Initial Deep Watering Post-Planting:
- Immediately after planting, water the tree deeply to settle the soil around the roots and provide necessary hydration.
- This deep watering encourages roots to grow deeper, enhancing the tree’s resilience and nutrient uptake.
- Consistent Watering as Tree Matures:
- Regular watering is crucial, especially in areas with low rainfall or during dry periods.
- Aim to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Avoiding Over-Watering and Ensuring Good Drainage:
- Avoid excessive watering to prevent root rot, caused by waterlogged conditions that deprive roots of oxygen.
- Ensure the planting site has proper drainage.
- Adjusting Watering Based on Conditions:
- Modify watering frequency according to rainfall, season, and climate conditions.
- In general, weekly watering may suffice but increase frequency during heat waves or droughts.
- Optimal Times for Watering:
- Water early in the morning or late in the afternoon to minimize evaporation.
- Regularly check soil moisture to a depth of several inches to ensure adequacy.
- Use of Mulch:
- Apply mulch around the base of the tree to help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature.
- Mulching also aids in preventing soil erosion and weed growth.
Mulching and Fertilizing
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to help retain moisture and suppress weeds. Fertilize your Rose Apple tree with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer according to the product’s instructions, typically starting a few months after planting.
Mulching
Mulching involves covering the soil around the base of the tree with a layer of organic material. This can include materials like wood chips, straw, or compost. The layer of mulch serves several purposes:
- Moisture Retention: Mulch helps retain soil moisture by reducing evaporation. This is particularly beneficial during dry periods, ensuring that the tree has access to the water it needs.
- Weed Suppression: A layer of mulch suppresses weed growth around the tree. Weeds can compete with the tree for nutrients and water, so controlling them is crucial.
- Temperature Regulation: Mulch acts as an insulator for the soil, keeping it warmer in cold weather and cooler during hot spells. This can be especially helpful in climates with significant temperature fluctuations.
- Soil Health Improvement: As organic mulch decomposes, it adds nutrients back into the soil, thereby improving its fertility and structure.
Fertilizing
Fertilization is vital to provide additional nutrients to the Rose Apple tree, which might not be sufficiently available in the soil.

- Balanced Fertilizer: A balanced, slow-release fertilizer is recommended for Rose Apple trees. This type of fertilizer releases nutrients gradually, providing a steady supply over time.
- Timing: Start fertilizing a few months after planting to give the tree a chance to establish itself. Over-fertilizing a newly planted tree can be harmful.
- Application: Follow the specific instructions provided on the fertilizer product regarding the amount and frequency of application. Typically, fertilizing is done during the growing season.
- Nutrient Requirements: Rose Apple trees benefit from a fertilizer that contains a balanced mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with trace elements like magnesium and calcium.
Pruning
Pruning is essential for the Rose Apple tree to maintain its shape and promote healthier, more productive growth. Prune dead or diseased branches and thin out overcrowded areas to improve air circulation.
- Shaping the Tree: Pruning helps in shaping the tree, which is important for both aesthetics and maintaining structural integrity. It involves removing crossing or rubbing branches to reduce the risk of physical damage and disease.
- Improving Tree Health: By removing dead or diseased branches, pruning prevents the spread of decay and pests. It’s crucial to make clean cuts and ideally perform pruning during the dormant season to minimize stress on the tree.
- Enhancing Productivity: Thinning overcrowded branches allows more light and air to reach the inner parts of the tree, essential for the development of fruit buds. This increased sunlight and air circulation improve fruit production and quality.
- Technique: Use sharp, clean tools for precise cuts. Prune just above a bud facing the outside of the tree to encourage outward growth. Ensure cuts are clean to promote faster healing.
- Moderation in Pruning: Avoid over-pruning in a single session. As a general rule, do not remove more than a third of the tree’s overall canopy in one year to prevent undue stress on the tree.
- Respecting the Tree’s Natural Shape: Rose Apple trees naturally form a rounded canopy. It’s advisable to work with this growth pattern, carefully pruning to maintain the tree’s natural shape.
Pest and Disease Control
Keep an eye out for common pests like aphids and caterpillars. Use organic pesticides if necessary. Also, watch for signs of disease like leaf spot or root rot and treat promptly.
Managing Pests and Diseases in Rose Apple Trees
- Common Pests:
- Aphids: Small sap-sucking insects causing leaf curling and potentially spreading diseases.
- Caterpillars: Chew on leaves, leading to defoliation.
- Pest Control Methods:
- Introduce Beneficial Insects: Like ladybugs for controlling aphids.
- Manual Removal: Particularly effective for caterpillars.
- Organic Pesticides: Use as a last resort and choose environmentally friendly options.
- Common Diseases:
- Leaf Spot: Identified by brown or black spots on leaves.
- Root Rot: Caused by excessive moisture in the soil.
- Disease Control Strategies:
- Remove Affected Leaves: For leaf spot, also improve air circulation.
- Prevent Root Rot: Ensure good soil drainage and avoid overwatering.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Routine Checks: Especially during the growing season for early detection.
- Early Intervention: Manage pests and diseases before they become severe.
Harvesting
Rose Apple fruits typically ripen several months after flowering. Harvest the fruits when they are fully colored and emit a fragrant aroma. They should be soft to the touch.
Timing of Harvest

- Typically occurs several months after flowering.
- Varies based on climate and growing conditions.
Indicators of Ripeness

- Development of a full, uniform color (pale yellow to light pink).
- Emission of a strong, aromatic fragrance reminiscent of roses.
- Slight yielding to gentle pressure, indicating softness.
Handling and Picking

- Handle fruits gently to avoid bruising.
- Pluck directly by hand or use fruit-picking tools for hard-to-reach fruits.
Post-Harvest Use
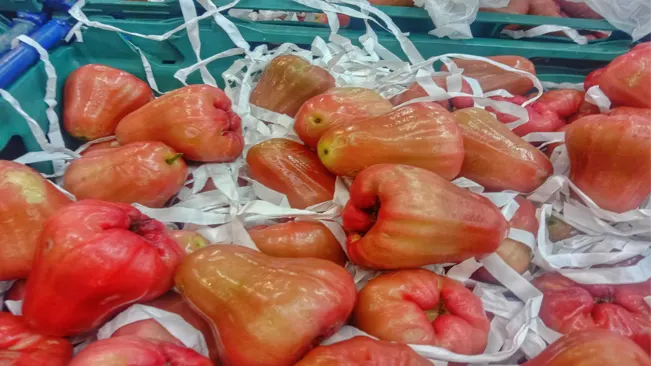
- Best enjoyed fresh due to their short shelf life.
- Ideal for culinary uses like salads, jams, and fruit drinks.
- The unique rose-like flavor offers a distinctive culinary experience.
Conclusion
Planting a rose apple tree can be a rewarding experience. By following these steps and providing the necessary care, you’ll be able to enjoy the sweet rewards of your labor in the form of delicious, home-grown rose apples. Remember, patience and consistent care are key to growing a healthy and fruitful rose apple tree.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is the best time to plant a Rose Apple tree?
- The best time to plant is during the spring or early summer when the weather is mild, allowing the tree to establish itself before the harsher seasons.
- The best time to plant is during the spring or early summer when the weather is mild, allowing the tree to establish itself before the harsher seasons.
- What kind of soil is ideal for Rose Apple trees?
- Rose Apple trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a slight acidity, although they can adapt to a range of soil types.
- Rose Apple trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a slight acidity, although they can adapt to a range of soil types.
- How much sunlight does a Rose Apple tree need?
- These trees require full sunlight for optimal growth and fruiting, so choose a location that receives direct sunlight for most of the day.
- These trees require full sunlight for optimal growth and fruiting, so choose a location that receives direct sunlight for most of the day.
- How often should I water my Rose Apple tree?
- Initially, water the tree deeply once a week. Once established, adjust the watering according to the climate and rainfall, ensuring the soil remains moist but not waterlogged.
- Initially, water the tree deeply once a week. Once established, adjust the watering according to the climate and rainfall, ensuring the soil remains moist but not waterlogged.
- Do Rose Apple trees need fertilizer?
- Yes, fertilize your Rose Apple tree with a balanced fertilizer starting a few months after planting, and then regularly as per the product’s instructions.
- Yes, fertilize your Rose Apple tree with a balanced fertilizer starting a few months after planting, and then regularly as per the product’s instructions.
- How far apart should Rose Apple trees be planted?
- Plant Rose Apple trees at least 15-20 feet apart from each other and other structures to allow enough room for growth.
- Plant Rose Apple trees at least 15-20 feet apart from each other and other structures to allow enough room for growth.
- How long does it take for a Rose Apple tree to bear fruit?
- Depending on the variety and growing conditions, Rose Apple trees can take 3-5 years to start bearing fruit after planting.
- Depending on the variety and growing conditions, Rose Apple trees can take 3-5 years to start bearing fruit after planting.
- Do I need to prune my Rose Apple tree?
- Yes, pruning is important for shaping the tree and promoting healthy growth. Prune dead or overgrown branches annually, ideally during late winter or early spring.
- Yes, pruning is important for shaping the tree and promoting healthy growth. Prune dead or overgrown branches annually, ideally during late winter or early spring.
- Can Rose Apple trees grow in pots?
- Yes, they can grow in large pots but their size and fruiting potential may be limited compared to trees planted in the ground.
- Yes, they can grow in large pots but their size and fruiting potential may be limited compared to trees planted in the ground.
- Are there any common pests or diseases to watch out for?
- Be on the lookout for pests like aphids and caterpillars, and diseases such as root rot and leaf spot. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatments can manage these issues effectively.
For more expert gardening advice, explore our guides, discover top recommendations in our best section, and delve into in-depth product reviews in our review section.

Kristine Moore
Forestry AuthorI'm Kristine Moore, a seasoned garden landscaping professional with over 30 years of experience. My extensive career has been dedicated to transforming outdoor spaces into stunning, sustainable landscapes. With a deep understanding of horticulture, design principles, and environmental stewardship, I have become a respected figure in the field, known for creating harmonious, visually appealing, and eco-friendly gardens. My commitment to excellence and continuous learning in landscaping trends and techniques has solidified my reputation as an expert in garden design and implementation.













This is the most comprehensive guide on the Rose Apple tree (Or any plants/tree) That I have ever come across . I’ve been gardening for 30 years. We had a rose apple tree on our property when I was growing up 60 years ago. I’ve not come across one in any nursery that I have visited. Very excited about planting and growing my new rose apple tree. Thank you so much for the detailed advice! I have 2 questions: 1. I live on a lagoon that has brackish water (1/2 salt water). The tree would be an about 200 feet from the river. Can it tolerate this location ? 2. The wind coming off the river can reach 31 mph a few times a year. Normally wind is still or slight breeze. Would this be a problem? Thank you in advance!
Rosie Bloehm
July 14, 2024 1:05 pm